Abstract
Background
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the commonest cause of primary hepatocellular (PHC) carcinoma worldwide. Co-infection with the HIV leads to more rapid progression of liver disease.
Objectives
We described prevalence of HBV and HIV among patients with PHC admitted to Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda.
Methods
We assessed all patients admitted to the gastrointestinal service of Mulago hospital with a diagnosis of PHC for HBV and HIV infection.
Results
From March to June 2008, we recruited 15 patients. Nine (60%) were male; the overall median age was 32 years (IQR 15 –67), with median ages for male and female 33 and 36 years respectively. Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and AFP were all elevated with median values of 57.5 IU/L, 222 IU/L, 392 IU/L and 362 ng/ml respectively (IQR 14–145, 49–393, 165–1294 and 7–480). Eight (53%) patients were from North and Northeastern Uganda. The HBsAg was reactive in 13(87%) patients and HIV in 3(20%), all of whom were also co-infected with HBV.
Conclusion
There is high prevalence of HBV and HBV/HIV co-infection among patients with PHC in Uganda with high mortality. Reduction in incidence and mortality due to PHC in Uganda will require urgent large scale HBV vaccination.
Keywords: Hepatitis B, HIV, Primary Hepatocelular Carcinoma
Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the commonest cause of primary hepatocarcinoma (PHC) all over the world and the distribution of PHC mirrors the prevalence of HBV, being very high in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia1.
So far reports of HBV and HIV co-infection and rapid liver disease progression have mainly come from the West2,3. In Uganda earlier studies on PHC before the HIV epidemic showed high prevalence rates of HBV (60–80%) among patients with PHC4–7.
Indeed analysis from Kampala cancer registry indicated an increase of PHC among women over the periods 1960– 1980 and 1991 to 2005. The reason for this increase needs further studies8.
In this study we describe the prevalence of HBV and HIV among patients with PHC admitted to Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda as well as the histological types and 1 month outcome from time of diagnosis.
Methods
During the study period we assessed consecutively all patients admitted to the gastrointestinal service of Mulago hospital with a diagnosis of PHC. Primary hepatocelluar carcinoma was defined as definite (histopathologic evidence of PHC) or highly probable (elevated alpha fetoprotein (AFP) >100 IU/ml + liver mass compatible with PHC on ultrasound scan). A questionnaire collecting demographic characteristics was administered to all participants. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) testing was performed using the rapid HBV testing (HBsAg dipstick, Cypress Diagnostics, Belgium) while HIV serology status was ascertained using rapid Abbott test kits (Abbott determine HIV-1/2, Abbott Park, IL). All patients had AFP levels determined; upper limit of normal was 8 IU/ml. Liver biopsies were performed under ultrasound guidance and the liver tissues processed at Pathology Department of Makerere University School of Medicine.
First the tissue is kept in 10% formal saline solution for 24 hours after which it is embedded in paraffin wax and sections cut for staining using Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E). Examination of the sections was done by a senior pathologist (HW).
Patient attendant telephone contacts were taken and telephone calls made one month after PHC diagnosis (for those who were discharged) to define patient status.
The study was approved by the Institutional review Board of the Faculty of Medicine, Makerere University and all patients consented to participate in the study.
Results
From March to June 2008, we recruited 15 patients diagnosed with PHC. Nine (60%) were male; the overall median age was 32 years (IQR 15 –67), with median ages for male and female 33 and 36 years respectively (Table 1). Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and AFP were all elevated with median values of 57.5 IU/L, 222 IU/L, 392 IU/L and 362 ng/ml respectively (IQR 14–145, 49–393, 165–1294 and 7–480). Eight (53%) patients originated from North and Northeastern Uganda.
Table 1.
Characteristics of 15 patients with Primary Hepatocellular carcinoma admitted to the Gastroenterology service of Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda
| Serial | Age | Sex | HBsAg | HIV | ALT(Normal | AST(Normal | ALP(Normal | GGT(Normal | AFP(Normal | Histopathology | Status at 1 month |
| No | serology | </=40 | </=32 | </=129 | </=65 | </=8 | type | ||||
| IU/ml) | IU/ml) | IU/ml) | IU/ml) | IU/ml) | |||||||
| 1 | 38 | F | P | N | 43 | 549 | 165 | 457 | 400 | Trabecular | A |
| 2 | 18 | F | P | N | 46 | 46 | 356 | 248 | 326 | Trabecular | D |
| 3 | 28 | M | P | N | 54 | 119 | 1294 | 365 | 400 | X | A |
| 4 | 19 | M | P | N | 87 | 321 | 346 | 535 | 400 | Trabecular | D |
| 5 | 15 | M | P | N | 130 | 100 | 392 | 250 | 362 | Trabecular | D |
| 6 | 26 | M | P | N | 105 | 307 | 601 | 315 | 400 | Trabecular | A |
| 7 | 43 | F | P | N | 74 | 332 | 449 | 633 | 326 | Trabecular | D |
| 8 | 33 | F | P | P | 79 | 222 | 1043 | 312 | 400 | X | A |
| 9 | 30 | F | N | N | 14 | 96 | 680 | 413 | 400 | Trabecular | D |
| 10 | 38 | M | P | N | 51 | 270 | 294 | 122 | 362 | Trabecular | D |
| 11 | 36 | M | P | P | 145 | 393 | 930 | 484 | 7 | Trabecular | D |
| 12 | 38 | M | N | N | 55 | 136 | * | 268 | 338 | Fibrolamellar | D |
| 13 | 45 | F | P | P | 60 | 40 | 120 | 60 | 480 | X | D |
| 14 | 33 | M | P | N | 60 | 275 | * | 192 | 400 | Adenoid | D |
| 15 | 67 | M | P | N | 18 | 88 | 349 | 226 | 350 | X | D |
M-Male, F- Female, P- positive, N- negative, X- Biopsy not done, D-Dead, A-Alive, ALT- Alanine aminotransferase, ALP- Alkaline phosphatase, AST Aspartate aminotransferase, GGT- Gamma glutamyltraspeptidase, AFP- Alpha-fetoprotein, HBsAg- Hepatitis B surface antigen, HIV- Human immune deficiency virus
Patients in whom ALP measurements were missing
A liver biopsy was performed in 11 (73 %) patients. In 4 (27 %), because of coagulopathy a biopsy was not performed and the PHC diagnosis was made on the basis of liver mass (es) on ultrasound scan and these patients had AFP of 350 IU/ml or more.
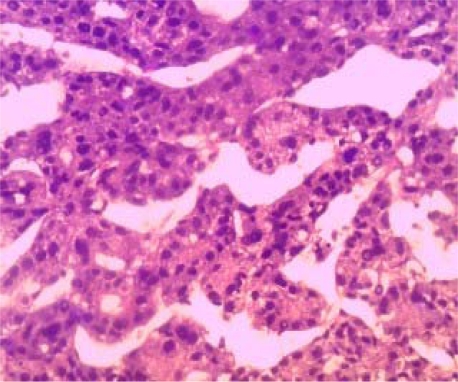
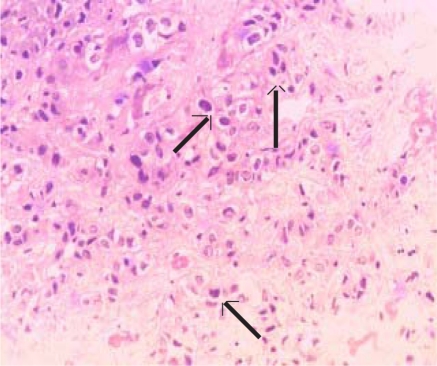
In 9 (82%) of the 11 patients in whom a liver biopsy was obtained, the liver cancer was of the trabecular type (Figure 1a) In the remaining 2 patients the PHC was either of fibrolamellar (1) (Figure 1b) or adenoid (1) types.
Figure 1a.
H and E stain of liver tissue showing hyperchromatic cells forming trabeculae. (Magnification X200)
Figure 1b.
H and E stain of liver tissue showing hyperchromatic pleomorphic cells of fibrolamellar type hepatocellular carcinoma (arrows). (Magnifications ×200
Hepatitis B surface antigen was positive in 13(87%) patients while HIV serology was reactive in 3(20%), all of whom were also co-infected with HBV.
Eleven (73%) patients died in the first month of the diagnosis of liver cancer two of whom died while still on admission.
Discussion
The results of this study underscore the critical role of HBV in the pathogenesis of PHC. The HBV surface antigen was positive in 86% of the PHC patients. Worldwide, the prevalence of HBV among patients with PHC varies considerably with lower rates seen in Western studies compared to Asia and some sub-Saharan African countries1, 9,10.
There are strong reasons to suspect that HIV might increase the prevalence of PHC, since it clearly accelerates HBV-related liver disease3. However, in our study the HIV/HBV co-infection prevalence mirrors the 14% to 18% co-infection reported in previous Ugandan studies11,12.
It may be that high HIV-related mortality has masked expression of the effects of HIV on liver disease progression. With the rapid roll out of antiretroviral therapy, as patients live longer, we may begin to see higher rates of chronic liver disease including cirrhosis and PHC in HIV infected persons.
Primary hepatocellular carcinoma in Uganda occurs in young patients5,6. In our study the youngest patient was 15 years old. This is probably a result of either perinatal or early childhood pattern of HBV transmission that progresses on to cirrhosis, and in some, to PHC during 20–30 years of life. Unfortunately in Uganda, there is no regular screening for HBV, and even in patients with cirrhosis, monitoring for PHC is not routinely done. Almost all patients therefore present late for treatment leading to the high one month mortality rate of up to 73% in our study. Indeed all patients had multiple liver masses that could not be ressected. However even in those cases where resection would be possible in Africa, this extensive surgery is performed in only a few hospitals. Moreover with that late presentation mortality in the very experienced centers is still very high10. The most important preventive measure is vaccination against HBV. It is important to note that there was only modest elevation of ALT in these patients, most likely due to the chronic nature of the liver disease, also evidenced by a higher elevation in the AST.
This study only assessed few patients with PHC who presented to the gastroenterology service during this period of observation. The role of other factors such as hepatitis C, aflatoxins, alcohol, schistosomiasis, obesity and HIV needs to be considered in a larger well designed study.
Conclusion
Our study confirms the high prevalence of HBV and HBV/HIV co-infection among patients with PHC in Uganda with high mortality. Since there is an effective vaccine against HBV, reduction in incidence and mortality due to PHC in Uganda will require urgent large scale HBV vaccination but the effects will take long to be seen since even infant vaccination against HBV only started recently in Uganda
Acknowledgments
We thank Lawrence Osuwat who performed histological processing of all the liver tissues and Godfrey Gemageine for providing the photomicrographs. The study was supported by the SIDA SAREC small grants project from the faculty of Medicine, Makerere University
References
- 1.Raza SA, Clifford GM, Franceschi S. World wide variation in the relative importance of hepatitis B and hepatitis C in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:1127–1134. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hoffmann CJ, Thio CL. Clinical implications of HIV and hepatitis B co-infection in Asia and Africa. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:402–409. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thio CL, Seaberg EC, Skolasky R, et al. HIV-1 hepatitis B virus and risk of liver related mortality in the multicenter cohort study (MACS) Lancet. 2002;360:1921–1926. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)11913-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wogan GN. Dietary factors and special epidemiological situations of liver cancer in Thailand and Africa. Cancer research. 1975;35:3499–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Olweny CLM, Toya T, Katongole-Mbidde E, et al. Treatment of Hepatocellular carcinoma with adriamycin- preliminary communication. Cancer research. 1975;36:1250–1257. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197510)36:4<1250::aid-cncr2820360410>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Olweny CLM, Katongole-Mbidde E, Bahendeka S, et al. Further experience in treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Uganda. Cancer. 1980;46:2717–2722. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19801215)46:12<2717::aid-cncr2820461230>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tabor E, Gerety RJ, Vogel CL, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977;58:1197–2000. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.5.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ocama P, Nambooze S, Opio CK, Shiels MS, Wabinga HR, Kirk GD. Trends in the incidence of primary liver cancer in Central Uganda, 1960–1980 and 1991–2005. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(5):799–802. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.But DYK, Lai CL, Yuen MF. Natural history of hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:1652–1656. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ocama P, Katwere M, Piloya T, et al. The spectrum of liver disease in HIV infected patients at an HIV treatment clinic in Kampala, Uganda. African Health Sciences. 2008;8:8–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nakwagala N, Kagimu M. Hepatitis B virus and HIV infections among patients in Mulago hospital. East Afr Med J. 2002;29:68–72. doi: 10.4314/eamj.v79i2.8903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]