Abstract
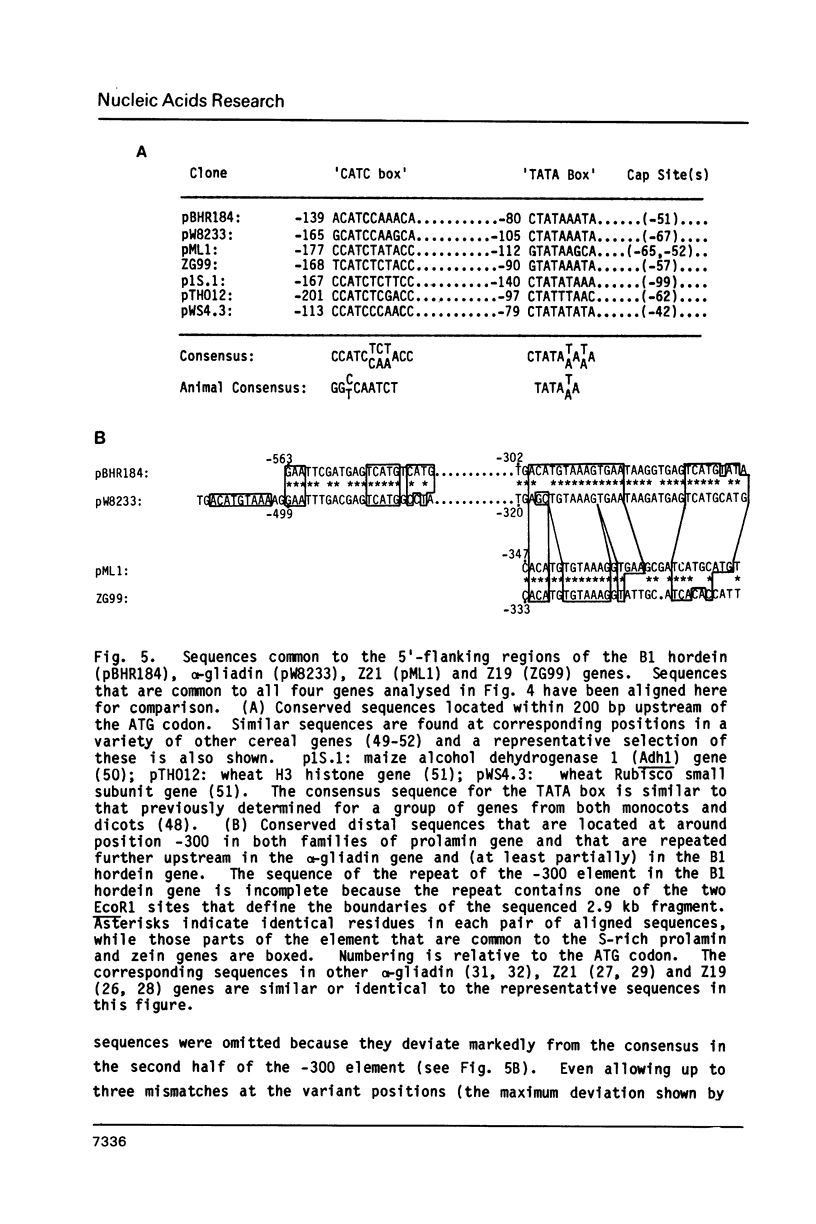
The B-hordeins are the major group of prolamin storage proteins in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and they are encoded by a small multigene family that is expressed specifically in the developing endosperm. We report the complete nucleotide sequence of a clone of one B-hordein gene (pBHR184). The cloned gene contains no introns and belongs to the B1 sub-family of B-hordein genes. Comparison of the 5'-flanking sequences of pBHR184 with those of related S-rich prolamin genes from wheat shows that several short sequences within 600 bp upstream of the translation initiation codon are strongly conserved. A sequence that is conserved at around -300 bp in the S-rich prolamins is also conserved at similar locations in genes encoding the two major classes of maize prolamin (the Z19 and Z21 zeins) and appears to be unique to prolamin genes. We discuss the possible role of this '-300 element' in the control of gene expression in the developing cereal endosperm.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson O. D., Litts J. C., Gautier M. F., Greene F. C. Nucleic acid sequence and chromosome assignment of a wheat storage protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8129–8144. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. S., Gerlach W. L., Pryor A. J., Bennetzen J. L., Inglis A., Llewellyn D., Sachs M. M., Ferl R. J., Peacock W. J. Molecular analysis of the alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh1) gene of maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3983–4000. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. S., Sachs M. M., Gerlach W. L., Finnegan E. J., Peacock W. J. Molecular analysis of the alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (Adh2) gene of maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):727–743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Daves R. S., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A short nucleotide sequence required for regulation of HIS4 by the general control system of yeast. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forde B. G., Kreis M., Bahramian M. B., Matthews J. A., Miflin B. J., Thompson R. D., Bartels D., Flavell R. B. Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences derived from poly A+ RNA from barley endosperm: identification of B hordein related clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6689–6707. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forde B. G., Kreis M., Williamson M. S., Fry R. P., Pywell J., Shewry P. R., Bunce N., Miflin B. J. Short tandem repeats shared by B- and C-hordein cDNAs suggest a common evolutionary origin for two groups of cereal storage protein genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene F. C. Expression of Storage Protein Genes in Developing Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seeds : Correlation of RNA Accumulation and Protein Synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):40–46. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Yang R. C., Wu R. An improved strategy for rapid direct sequencing of both strands of long DNA molecules cloned in a plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5521–5540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N. T., Peifer M. A., Heidecker G., Messing J., Rubenstein I. Primary structure of a genomic zein sequence of maize. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1337–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasarda D. D., Okita T. W., Bernardin J. E., Baecker P. A., Nimmo C. C., Lew E. J., Dietler M. D., Greene F. C. Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of alpha-type gliadins from wheat (Triticum aestivum). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4712–4716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis M., Shewry P. R., Forde B. G., Rahman S., Bahramian M. B., Miflin B. J. Molecular analysis of the effects of the lys 3a gene on the expression of Hor loci in developing endosperms of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Biochem Genet. 1984 Apr;22(3-4):231–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00484227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kridl J. C., Vieira J., Rubenstein I., Messing J. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a zein genomic clone with a short open reading frame. Gene. 1984 Apr;28(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge P., Feix G. A zein gene of maize is transcribed from two widely separated promoter regions. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90559-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauro V. P., Nguyen T., Katinakis P., Verma D. P. Primary structure of the soybean nodulin-23 gene and potential regulatory elements in the 5'-flanking regions of nodulin and leghemoglobin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):239–249. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., MacKay V. L., Nasmyth K. A. Identification and comparison of two sequence elements that confer cell-type specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):598–603. doi: 10.1038/314598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Devereux J., Wilson D. R., Sheldon E., Larkins B. A. Cloning and sequence analysis reveal structural variation among related zein genes in maize. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafalski J. A., Scheets K., Metzler M., Peterson D. M., Hedgcoth C., Söll D. G. Developmentally regulated plant genes: the nucleotide sequence of a wheat gliadin genomic clone. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1409–1415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. H., Carter G. H., Watson M. D., Shaw C. H. A functional map of the nopaline synthase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7831–7846. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spena A., Viotti A., Pirrotta V. Two adjacent genomic zein sequences: structure, organization and tissue-specific restriction pattern. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 5;169(4):799–811. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Computer methods to locate signals in nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):505–519. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Rafalski J. A., Sugiyama T., Stoll M., Söll D. Conservation and variability of wheat alpha/beta-gliadin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3905–3916. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]