Abstract
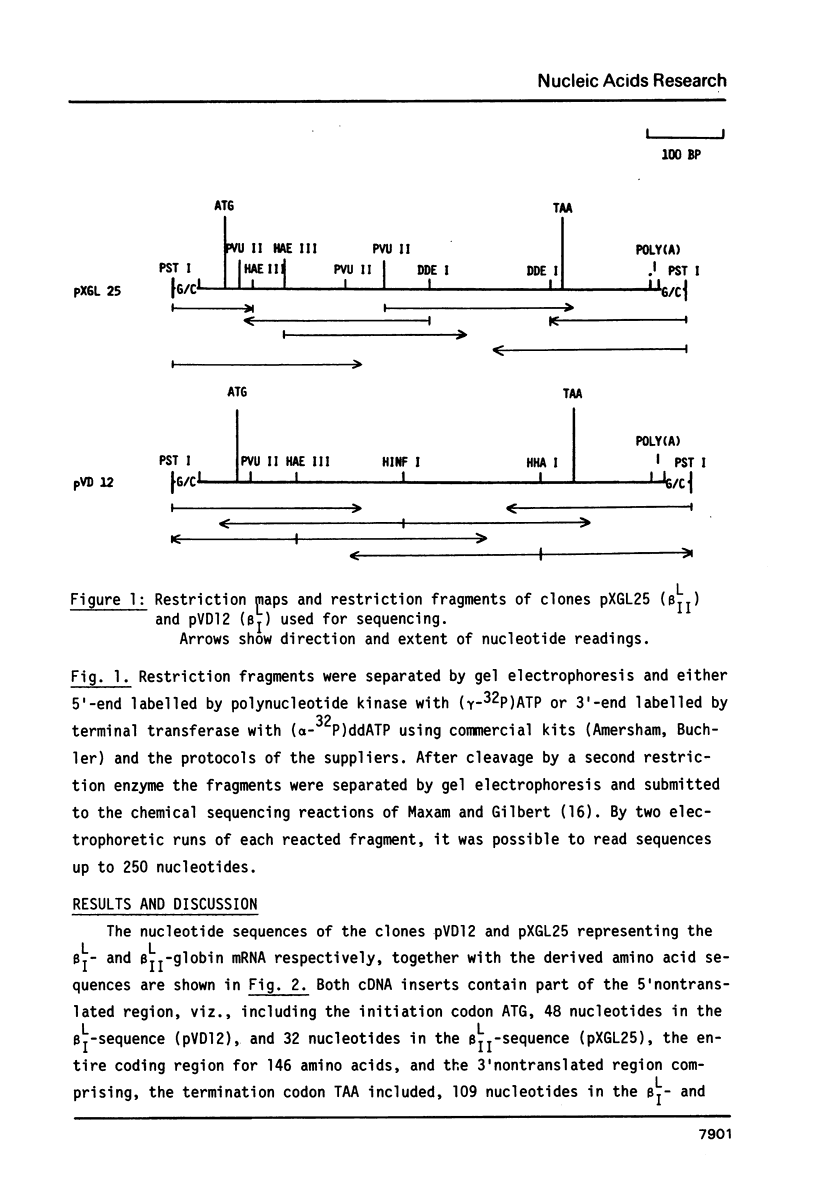
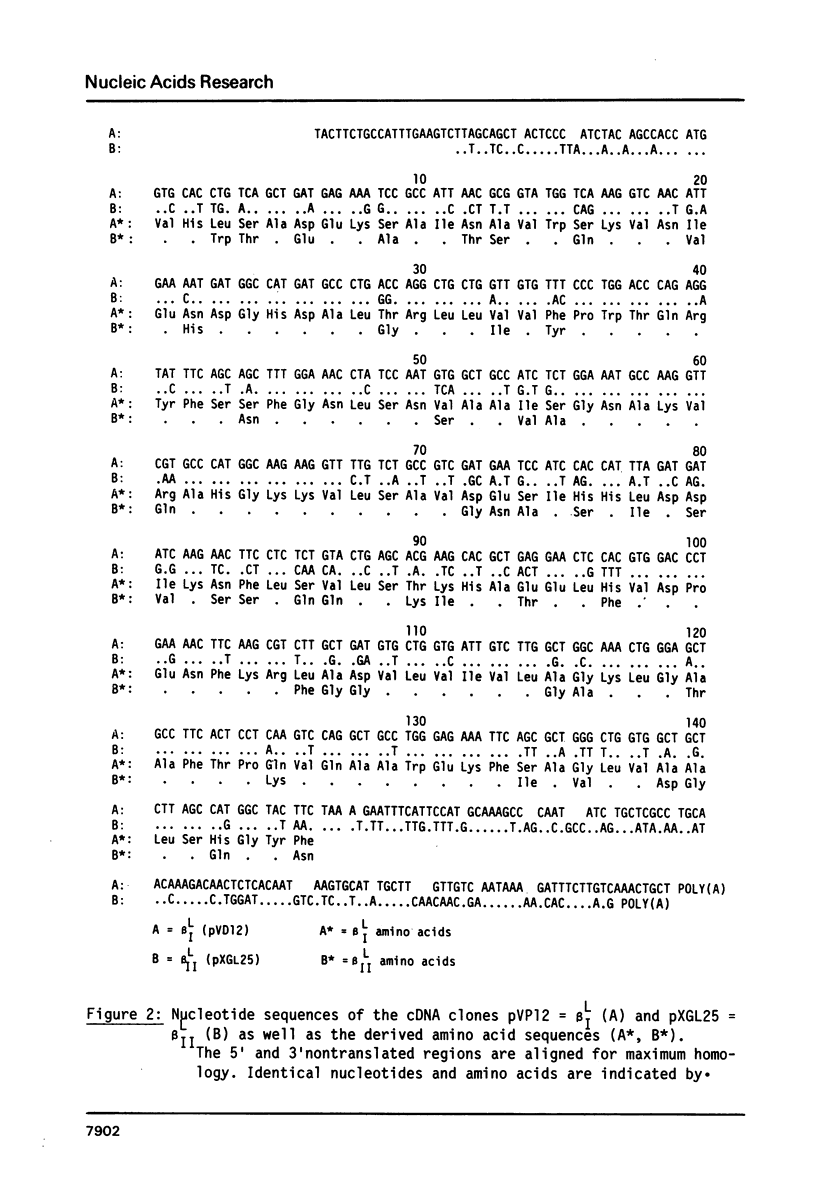
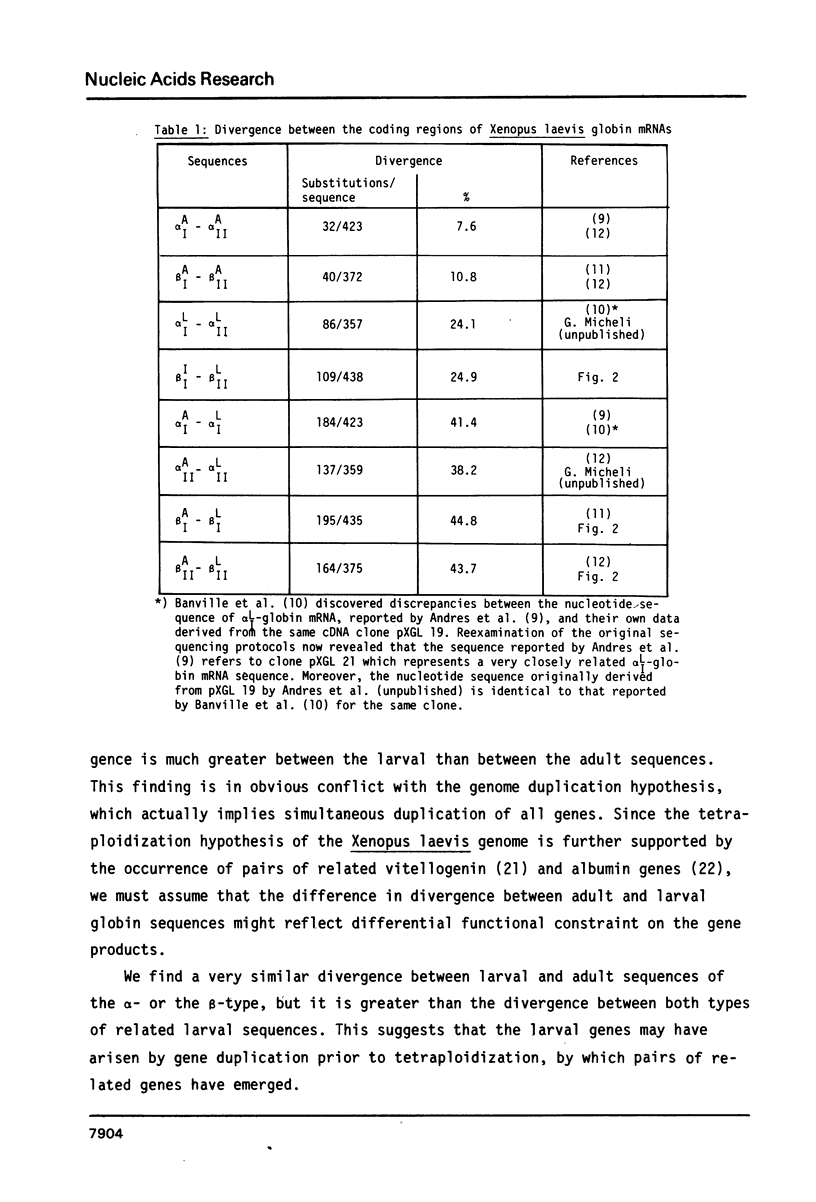
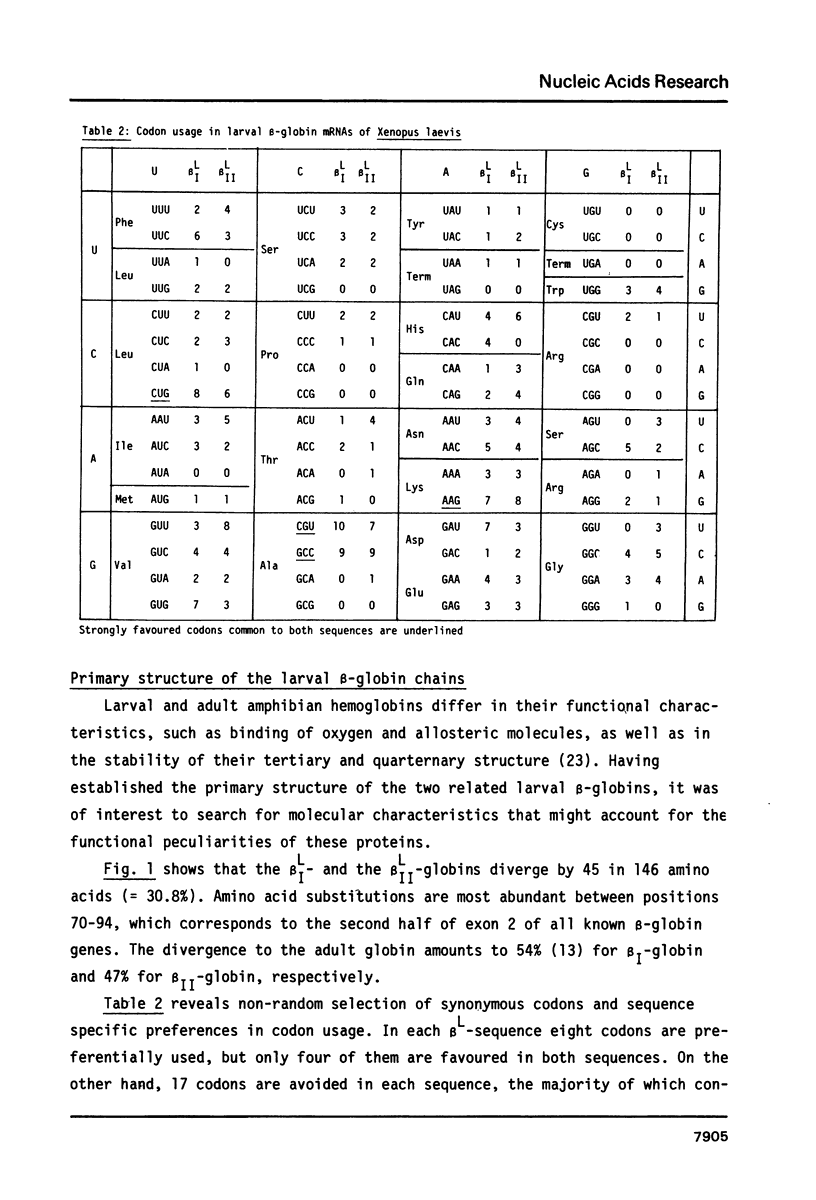
The complete nucleotide sequence of the cDNA insert of the clone pXGL25 derived from the larval beta II-globin mRNA of Xenopus laevis has been determined. The sequence of 593 nucleotides represents part of the 5'nontranslated region, the coding region for 146 amino acids and the entire 3'nontranslated region. It diverges from the related larval beta I-sequence by 24.9% in the coding region. Alignment of the 5' and 3'nontranslated regions of the two related larval beta-sequences to maximum matching resulted in 31.2% and 46.7% divergence, respectively. Divergence between the corresponding adult and larval sequences considerably exceeds that of related larval sequences, suggesting that larval genes may have arisen by gene duplication prior to genome duplication. In contrast to mammalian beta-globin mRNAs, replacement and silent base substitutions are equally abundant, thus indicating less functional constraint on the larval Xenopus laevis beta-globin chains. The larval beta I- and beta II-globins diverge by 30.8% and show most variation in the alpha 1/beta 2-chain interaction sites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. C., Hosbach H. A., Weber R. Comparative analysis of the cDNA sequences derived from the larval and the adult alpha 1-globin mRNAs of Xenopus laevis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 5;781(3):294–301. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banville D., Kay R. M., Harris R., Williams J. G. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding a tadpole beta-globin polypeptide of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7924–7927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banville D., Williams J. G. The pattern of expression of the Xenopus laevis tadpole alpha-globin genes and the amino acid sequence of the three major tadpole alpha-globin polypeptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5407–5421. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Proudfoot N. J. The primary structure of the human epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Stadt S. J., Choi O. R., Dolan M., Fischer H. D., Engel J. D. The nucleotide sequence of the embryonic chicken beta-type globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12685–12692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Analysis of the adult chicken beta-globin gene. Nucleotide sequence of the locus, microheterogeneity at the 5'-end of beta-globin mRNA, and aberrant nuclear RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3983–3990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermi G. Three-dimensional fourier synthesis of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 2-5 A resolution: refinement of the atomic model. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):237–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Mercier R., Pavé A. Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r49–r62. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosbach H. A., Wyler T., Weber R. The Xenopus laevis globin gene family: chromosomal arrangement and gene structure. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Wood D., Simons J. P., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Linkage of adult alpha- and beta-globin genes in X. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Efstratiadis A., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Molecular evolution of human and rabbit beta-globin mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5618–5622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. M., Harris R., Patient R. K., Williams J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cloned cDNA derived from the major adult alpha-globin mRNA of X. laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1537–1542. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöchel W., Meyerhof W., Hummel S., Grundmann U. Molecular cloning and sequencing of mRNAs coding for minor adult globin polypeptides of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1543–1553. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Tilghman S. M., Leder P. The sequence of the chromosomal mouse beta-globin major gene: homologies in capping, splicing and poly(A) sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Efstratiadis A., O'Connell C., Maniatis T. The nucleotide sequence of the human beta-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):647–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhof W., Klinger-Mitropoulos S., Stalder J., Weber R., Knöchel W. The primary structure of the larval beta 1-globin gene of Xenopus laevis and its flanking regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7705–7719. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Species adaptation in a protein molecule. Mol Biol Evol. 1983 Dec;1(1):1–28. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Cappello J., Cochran M. D., Armentrout R. W., Brown R. D. Partial sequence analysis of Xenopus alpha- and beta-globin mRNA as determined from recombinant DNA plasmids. Dev Biol. 1980 Jul;78(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Maruyama T., Riggs A. Hemoglobins of the tadpole of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. Amino acid sequence of the beta chain of a major component. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3294–3301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Wyler T., Ryffel G., Weber R. Xenopus laevis serum albumins are encoded in two closely related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3557–3574. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer H. J., Andres A. C., Niessing J., Hosbach H. A., Weber R. Comparative analysis of cloned larval and adult globin cDNA sequences of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1981 Dec;88(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer H. J., Hosbach H. A., Weber R. Globin gene expression in Xenopus laevis: anemia induces precocious globin transition and appearance of adult erythroblasts during metamorphosis. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kay R. M., Patient R. K. The nucleotide sequence of the major beta-globin mRNA from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4247–4258. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


