Abstract
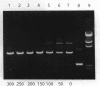
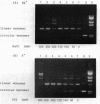
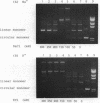
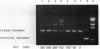
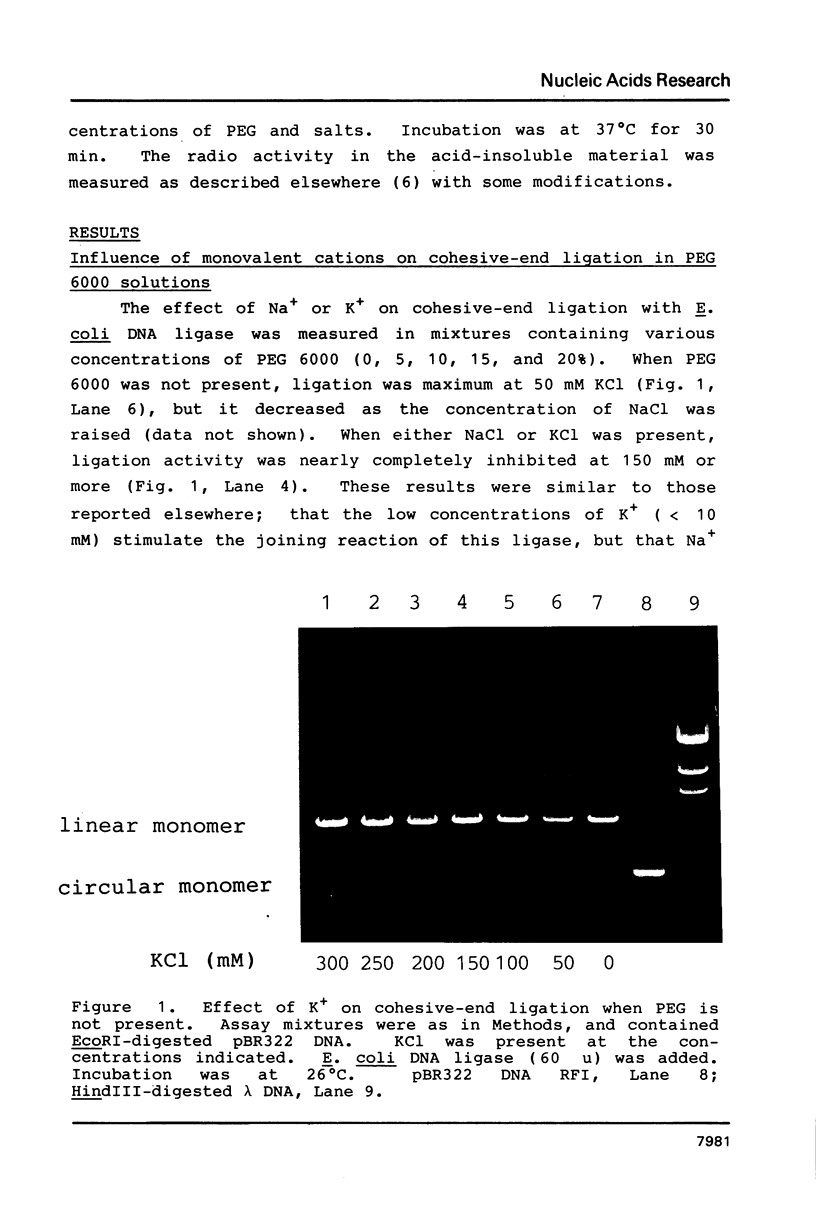
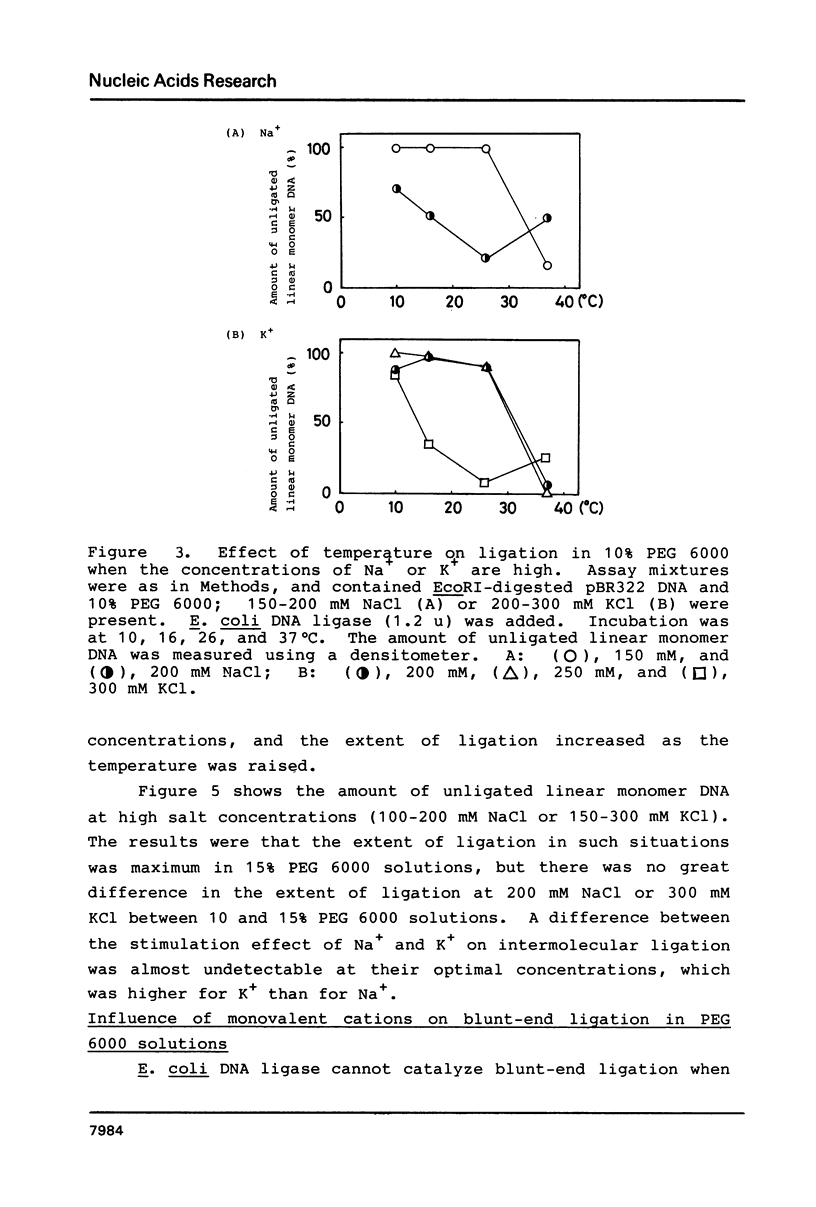
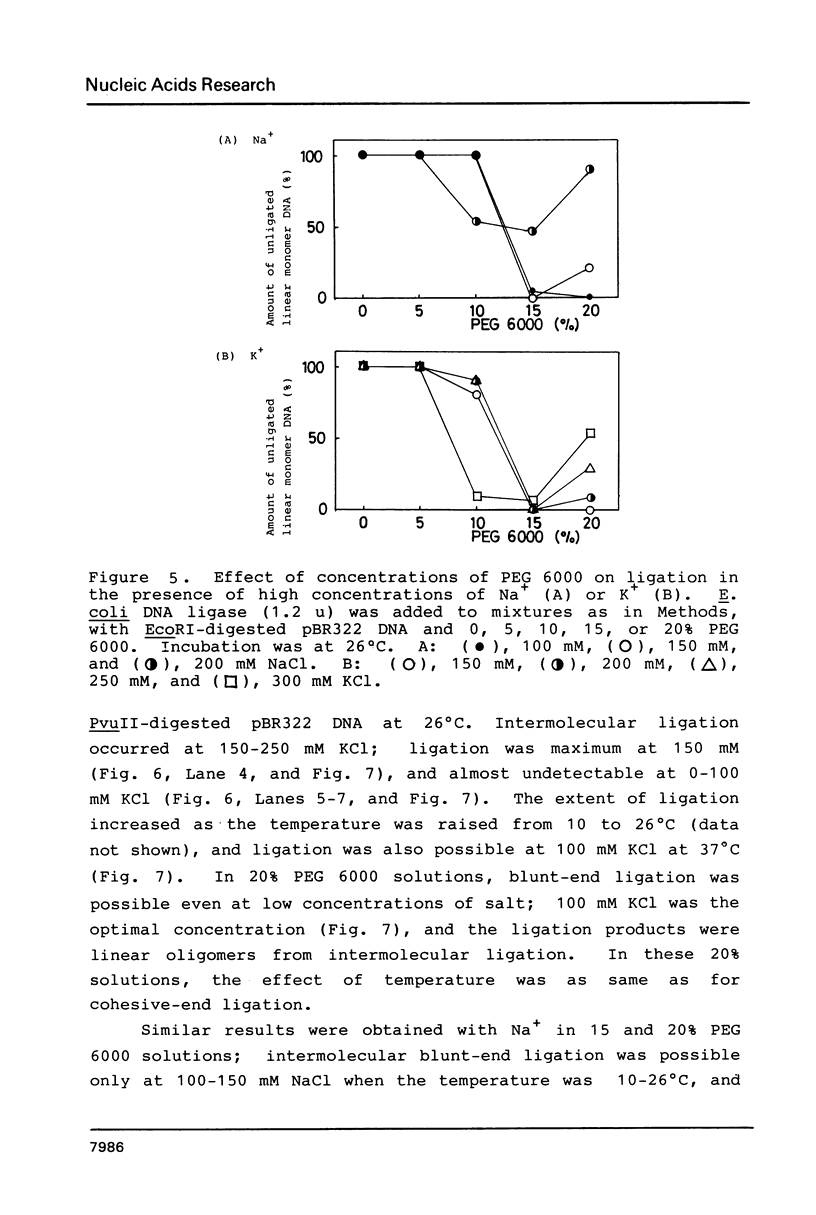
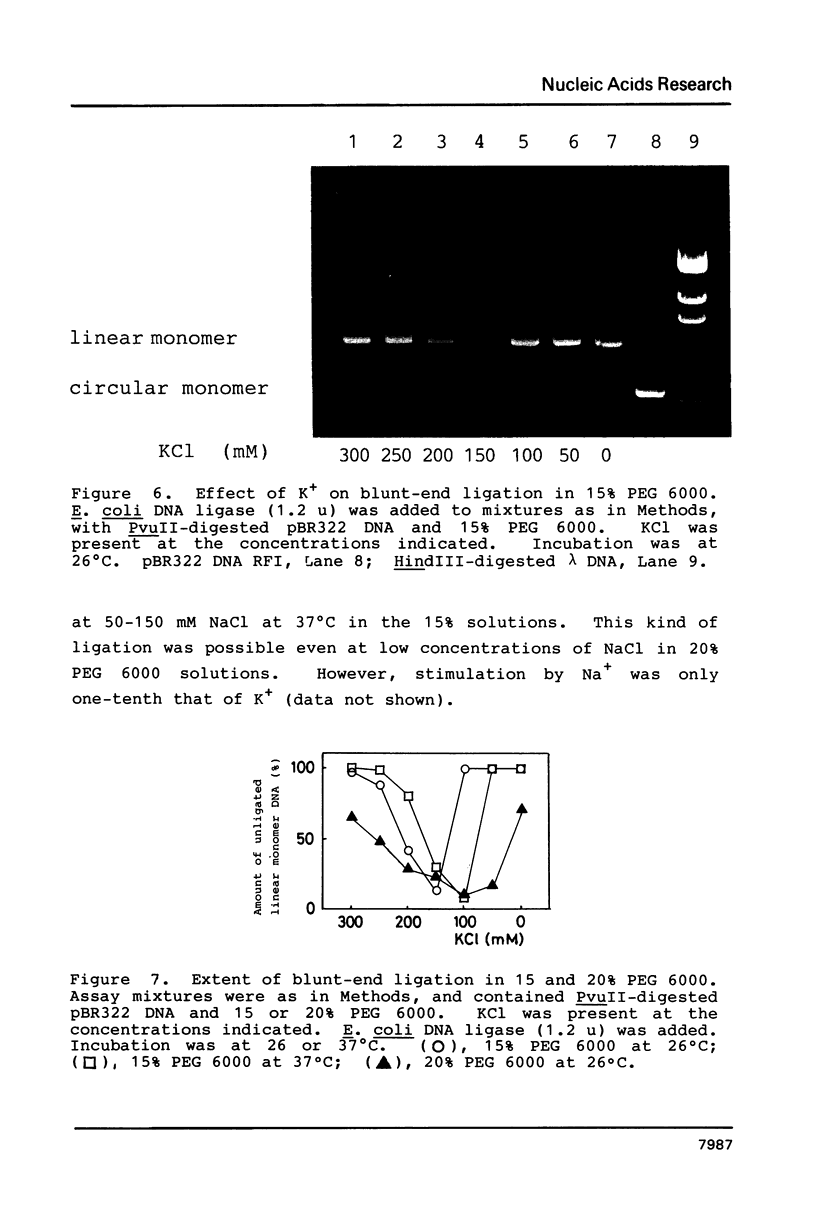
In the presence of high concentrations of the nonspecific polymer polyethylene glycol (PEG), intermolecular cohesive-end ligation with the DNA ligase from Escherichia coli was stimulated by high salt concentrations: 200 mM NaCl or 300 mM KCl in 10% (w/v) PEG 6000 solutions, and 100-200 mM NaCl or 150-300 mM KCl in 15% PEG 6000 solutions. Intermolecular blunt-end ligation with this ligase was also stimulated at 100-150 mM NaCl or 150-250 mM KCl in 15% PEG 6000 solutions. The extent of such intermolecular ligation increased and the salt concentrations at which ligation was stimulated extended to lower concentrations when we raised the temperature from 10 to 37 degrees C.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayashi K., Nakazawa M., Ishizaki Y., Obayashi A. Influence of monovalent cations on the activity of T4 DNA ligase in the presence of polyethylene glycol. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3261–3271. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Preston B. N., Carlsson B. Conformational transitions of polynucleotides in polymer media. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 1;43(2):231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modorich P., Lehman I. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid ligase. A steady state kinetic analysis of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7502–7511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P., Anraku Y., Lehman I. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid ligase. Isolation and physical characterization of the homogeneous enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7495–7501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panasenko S. M., Alazard R. J., Lehman I. R. A simple, three-step procedure for the large scale purification of DNA ligase from a hybrid lambda lysogen constructed in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4590–4592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaramella V. Enzymatic oligomerization of bacteriophage P22 DNA and of linear Simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3389–3393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Goodman H. M., Heyneker H. L., Shine J., Boyer H. W., Cozzarelli N. R. Interaction of bacteriophage T4 RNA and DNA ligases in joining of duplex DNA at base-paired ends. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3987–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Thompson A., Richardson C. C. Ezymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VII. Properties of the enzyme-adenylate intermediate in the polynucleotide ligase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4556–4563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Pheiffer B. H. Macromolecular crowding allows blunt-end ligation by DNA ligases from rat liver or Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5852–5856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]