Abstract
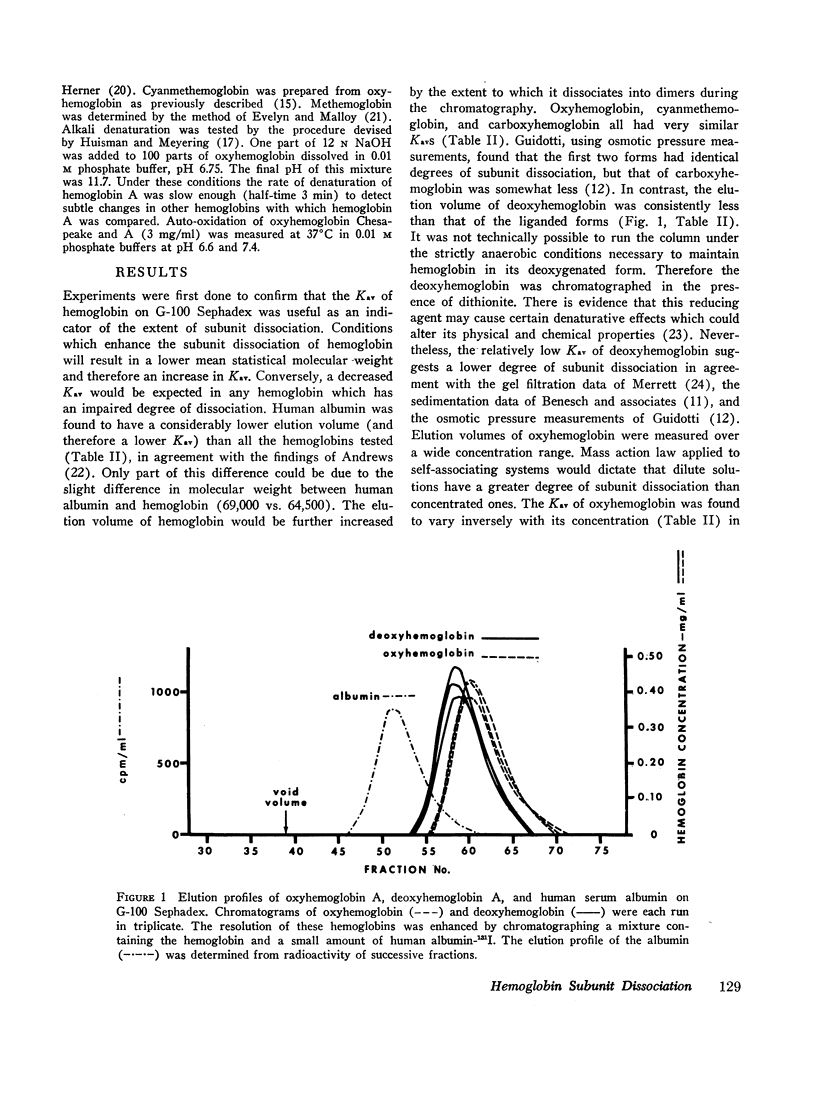
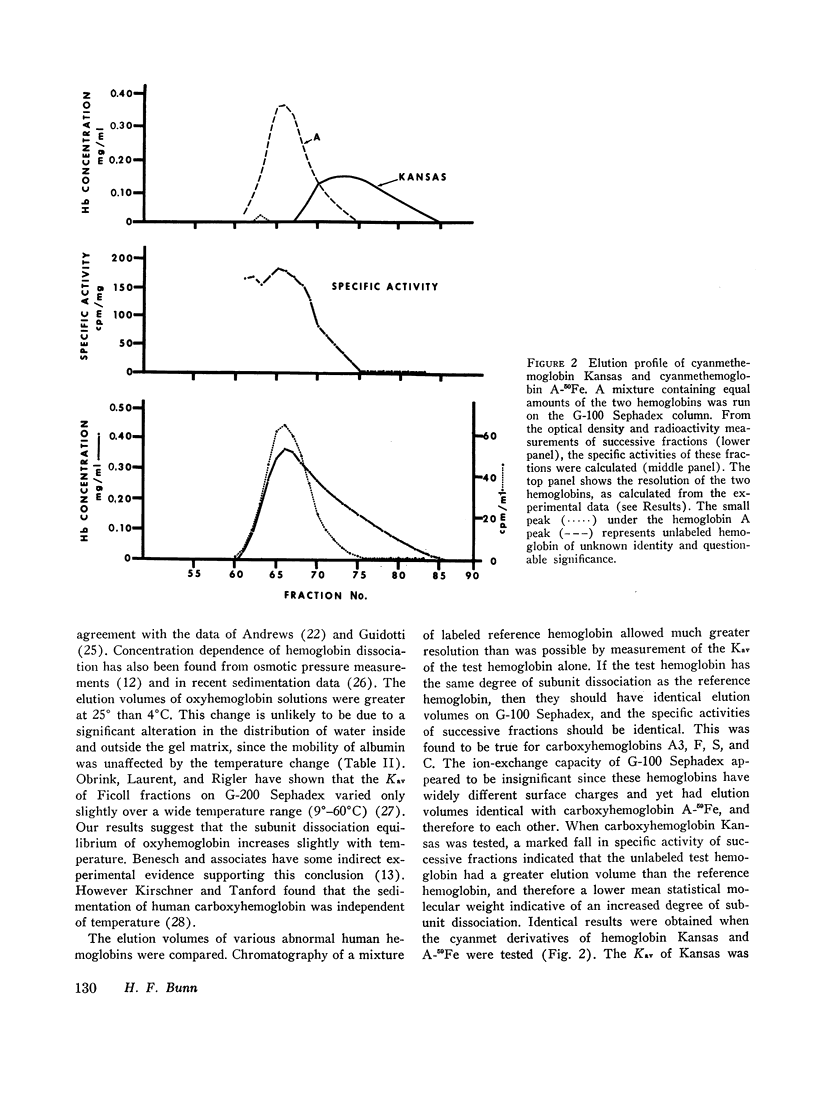
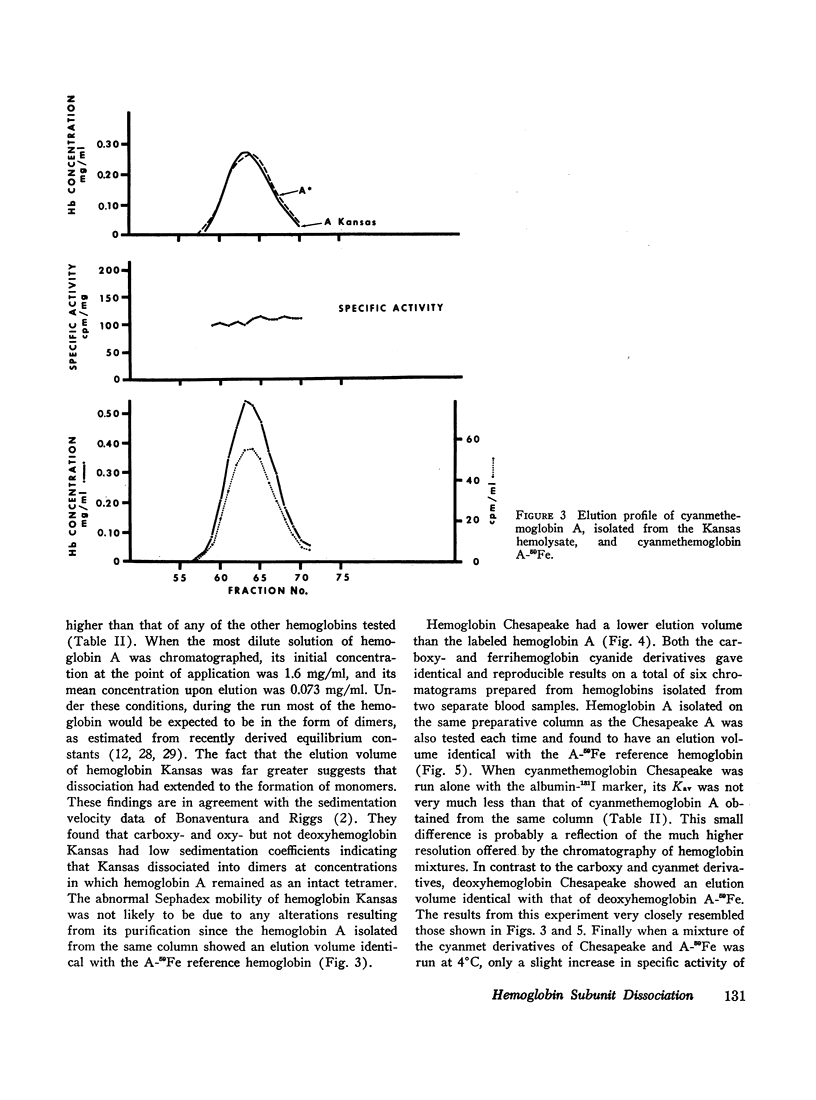
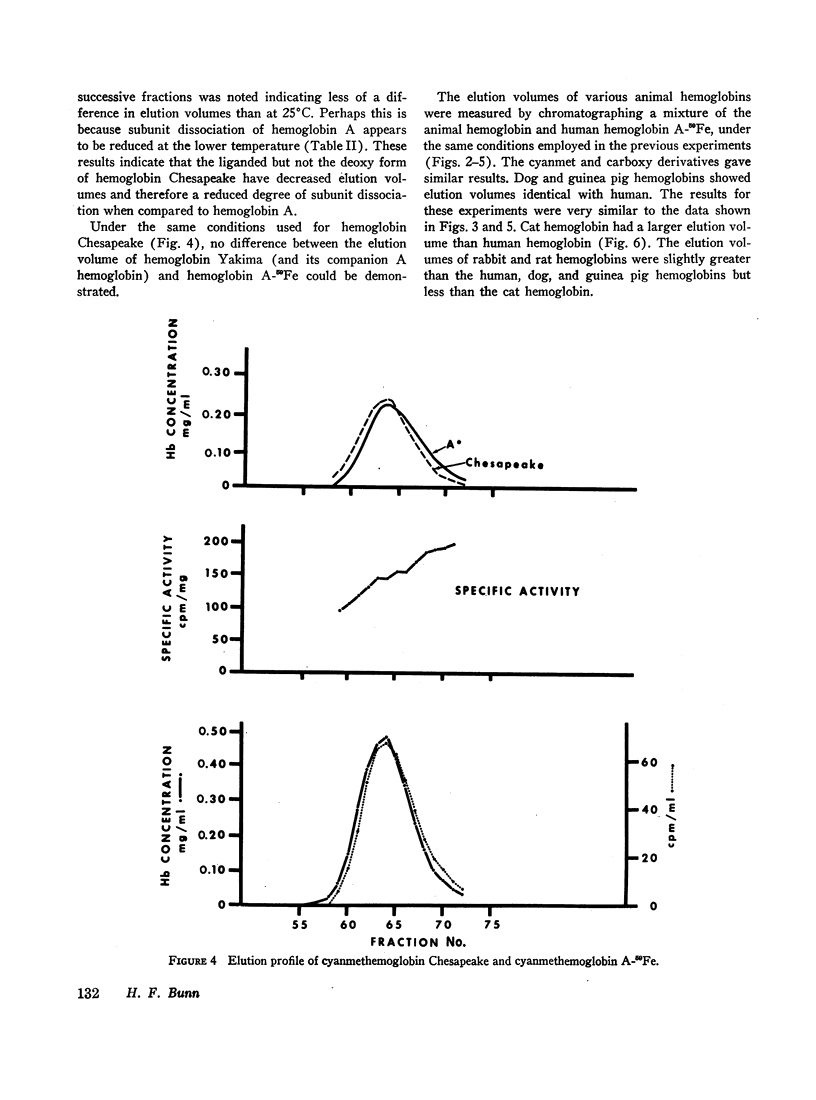
The extent of dissociation of various hemoglobins into subunits was estimated from their elution volumes (Ve) on G-100 Sephadex. Under the same controlled conditions carboxyhemoglobins A, A3 (A1), F, S, and C all had the same elution volumes. The carboxy and cyanmet derivatives of hemoglobin Kansas (a variant with very low oxygen affinity) had a relatively high Ve, indicating a decreased mean molecular weight and therefore an increased tendency to form dimers and even monomers. Conversely, the liganded derivatives of hemoglobin Chesapeake (a variant with high oxygen affinity) had a relatively low Ve, suggestive of an impaired degree of subunit dissociation. Deoxyhemoglobin Chesapeake had a Ve identical with that of deoxyhemoglobin A. Cat hemoglobin, known to have an unusually low oxygen affinity, was found to have a higher Ve than human, dog, rabbit, rat, or guinea pig hemoglobins.
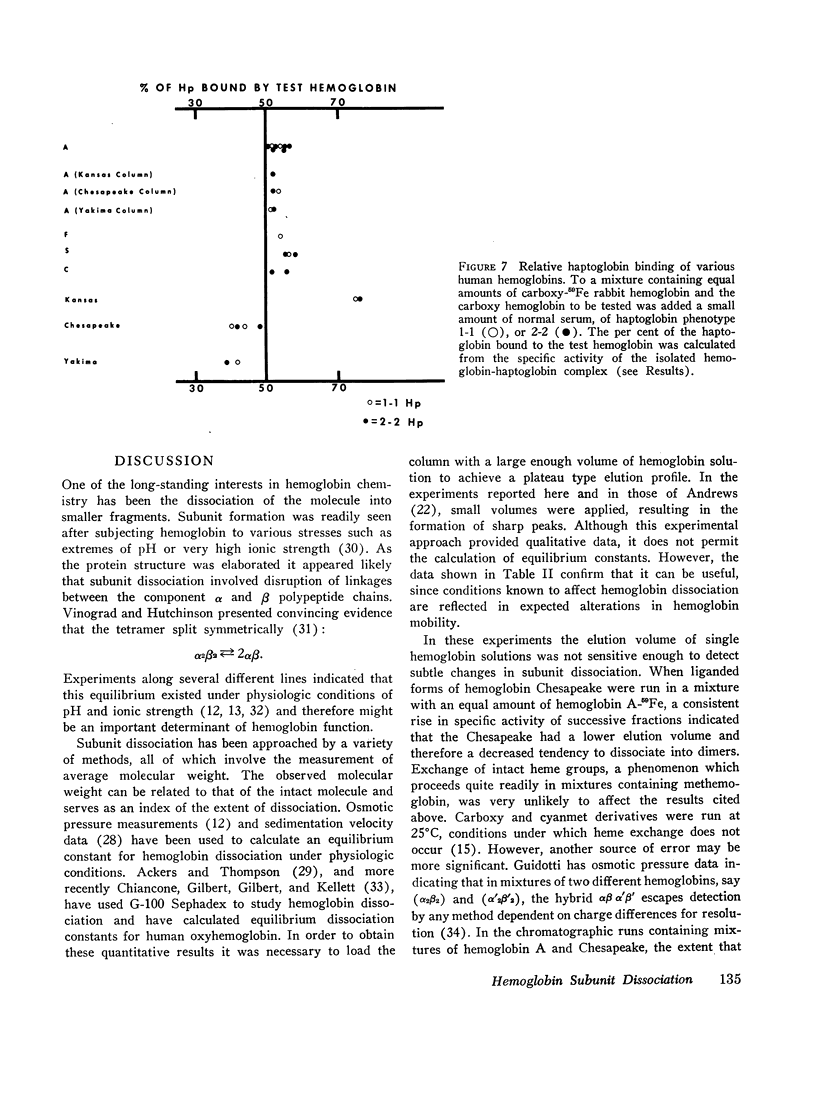
Haptoglobin is thought to bind αβ dimers in preference to the α2β2-tetramer. The comparative haptoglobin affinities of the human hemoglobins were measured by competition between the test hemoglobin and radioactive reference hemoglobin for haptoglobin binding sites. Hemoglobins A, F, S, and C all seemed to bind equally readily, but hemoglobin Kansas and cat hemoglobin showed a higher affinity, and hemoglobin Chesapeake a lower affinity.
These results are in accord with recently proposed models which predict that hemoglobins which have an increased degree of subunit dissociation will have a low oxygen affinity, and vice versa.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K., THOMPSON T. E. DETERMINATION OF STOICHIOMETRY AND EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANTS FOR REVERSIBLY ASSOCIATING SYSTEMS BY MOLECULAR SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:342–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESCH R. E., BENESCH R., WILLIAMSON M. E. The influence of reversible oxygen binding on the interaction between hemoglobin submits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R. E., Benesch R., Macduff G. Subunit exchange and ligand binding: a new hypothesis for the mechanism of oxygenation of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):535–542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaventura J., Riggs A. Hemoglobin Kansas, a human hemoglobin with a neutral amino acid substitution and an abnormal oxygen equilibrium. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):980–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F. Effect of sulfhydryl reagents on the binding of human hemoglobin to haptoglobin. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):606–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Jandl J. H. Exchange of heme among hemoglobins and between hemoglobin and albumin. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):465–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache S., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Polycythemia associated with a hemoglobinopathy. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):813–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI105397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E. Dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. II. Human oxyhemoglobin: gel filtration studies. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K., O'BRIEN J. R. Side reactions in the deoxygenation of dilute oxyhaemoglobin solutions by sodium dithionite. Biochem J. 1957 Sep;67(1):119–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUIDOTTI G., KONIGSBERG W., CRAIG L. C. ON THE DISSOCIATION OF NORMAL ADULT HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:774–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert G. A. Layer technique in gel filtration for estimating differences in the degree of dissociation of closely related proteins. Nature. 1966 Oct 15;212(5059):296–297. doi: 10.1038/212296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Studies on the chemistry of hemoglobin. 3. The interactions of the alpha-beta subunits of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3694–3703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Studies on the chemistry of hemoglobin. II. The effect of salts on the dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3685–3693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUISMAN T. H., MEYERING C. A. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. I. The heterogeneity of different human hemoglobin types in carboxymethylcellulose and in amberlite IRC-50 chromatography qualitative aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 1960 Jan;5:103–123. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(60)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huehns E. R., Beaven G. H., Stevens B. L. Recombination studies on haemoglobins at neutral pH. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):440–444. doi: 10.1042/bj0920440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Osgood E. E., Brimhall B., Koler R. D. Hemoglobin Yakina. I. Clinical and biochemical studies. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1840–1847. doi: 10.1172/JCI105674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSHNER A. G., TANFORD C. THE DISSOCIATION OF HEMOGLOBIN BY INORGANIC SALTS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:291–296. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Kirshner A. G., Tanford C. DISSOCIATION OF HUMAN CO-hemoglobin by urea, guanidine hydrochloride, and other reagents. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1203–1213. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. Purification and properties of different haptoglobins. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 Jan;4(1):79–81. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIONETTI F. J., VALERI C. R., BOND J. C., FORTIER N. L. MEASUREMENT OF HEMOGLOBIN BINDING CAPACITY OF HUMAN SERUM OF PLASMA BY MEANS OF DEXTRAN GELS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Sep;64:519–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD H., PERUTZ M. F. STRUCTURE OF HAEMOGLOBIN. A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FOURIER SYNTHESIS OF REDUCED HUMAN HAEMOGLOBIN AT 5-5 A RESOLUTION. Nature. 1963 Aug 17;199:633–638. doi: 10.1038/199633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrett T. Observations on the dissociation of oxy-, deoxy- and ferrihaemoglobin in relation to pH and ionic strength by the Sephadex method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 24;124(2):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel R. L., Gibson Q. H., Charache S. Relation between structure and function in Hemoglobin Chesapeake. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2395–2402. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novy M. J., Edwards M. J., Metcalfe J. Hemoglobin Yakina. II. High blood oxygen affinity associated with compensatory erythrocytosis and normal hemodynamics. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1848–1854. doi: 10.1172/JCI105675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSMANN K. R., RUTH W. E., NOMURA T. A human hemoglobin with lowered oxygen affinity and impaired heme-heme interactions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Oct;40:1826–1833. doi: 10.1172/JCI104406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS A., HERNER A. E. The hybridization of donkey and mouse hemoglobins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1664–1670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed C. S., Hampson R., Gordon S., Jones R. T., Novy M. J., Brimhall B., Edwards M. J., Koler R. D. Erythrocytosis secondary to increased oxygen affinity of a mutant hemoglobin, hemoglobin Kempsey. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):623–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemeyer M. A., Huehns E. R. On the mechanism of the dissociation of haemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):253–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIM B. S., BEARN A. G. IMMUNOLOGICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON SERUM HAPTOGLOBIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:611–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachman H. K., Edelstein S. J. Ultracentrifuge studies with absorption optics. IV. Molecular weight determinations at the microgram level. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2681–2705. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim B. S., Lee T. H., Kang Y. S. Immunological and biochemical investigations of human serum haptoglobin: composition of haptoglobin-haemoglobin intermediate, haemoglobin-binding sites and presence of additional alleles for beta-chain. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1264–1267. doi: 10.1038/2071264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. R., Konigsberg W. H. Chemical modification of hemoglobins: a study of conformation restraint by internal bridging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):749–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Yoshida A., Adamson J., Heinenberg S. Hemoglobin Rainier (beta145 Tyrosine rarr Histidine): Alkali-Resistant Hemoglobin with Increased Oxygen Affinity. Science. 1968 Feb 16;159(3816):741–743. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3816.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan B. The effect of dilution on the oxygenation properties of cat and human hemoglobins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 7;28(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketa F., Morell S. A. Oxygen affinity of cat hemoglobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 8;24(5):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90382-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. F., Antonini E., Brunori M., Wyman J. Studies on human hemoglobin treated with various sulfhydryl reagents. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINOGRAD J., HUTCHINSON W. D. Carbon-14 labelled hybrids of haemoglobin. Nature. 1960 Jul 16;187:216–218. doi: 10.1038/187216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vliet G., Huisman T. H. Changes in the haemoglobin types of sheep as a response to anaemia. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):401–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0930401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



