Abstract
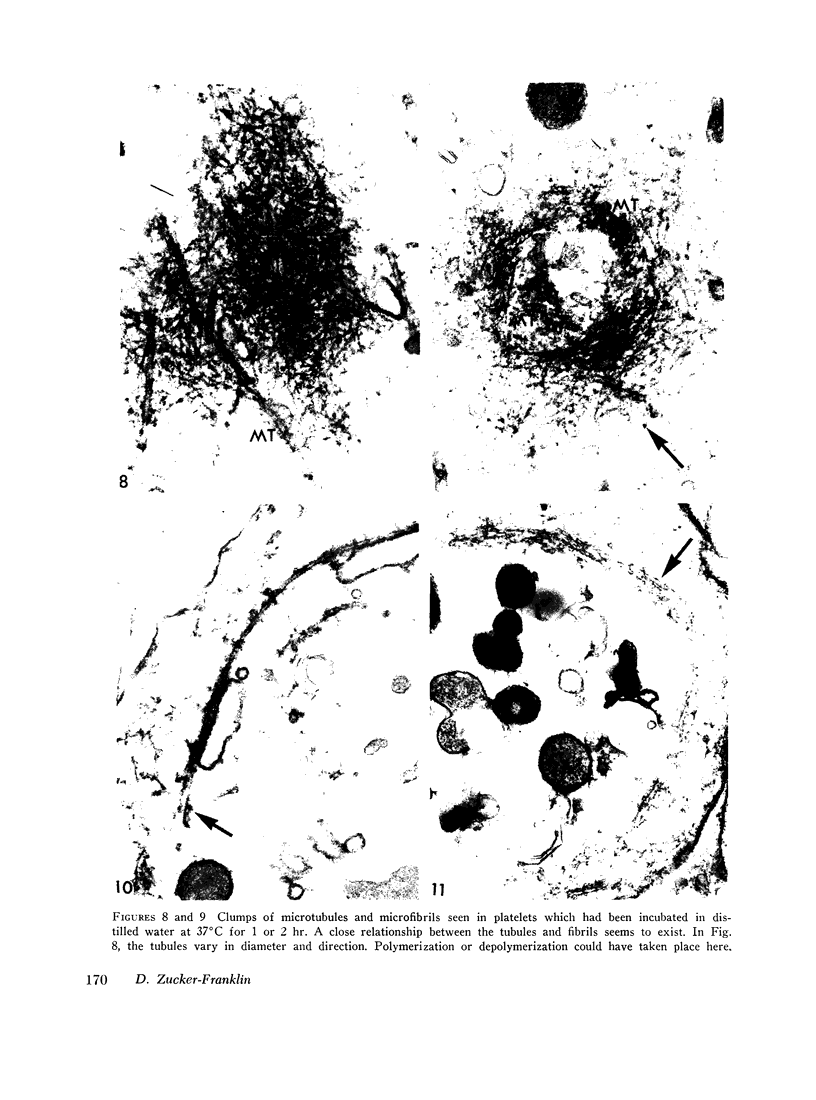
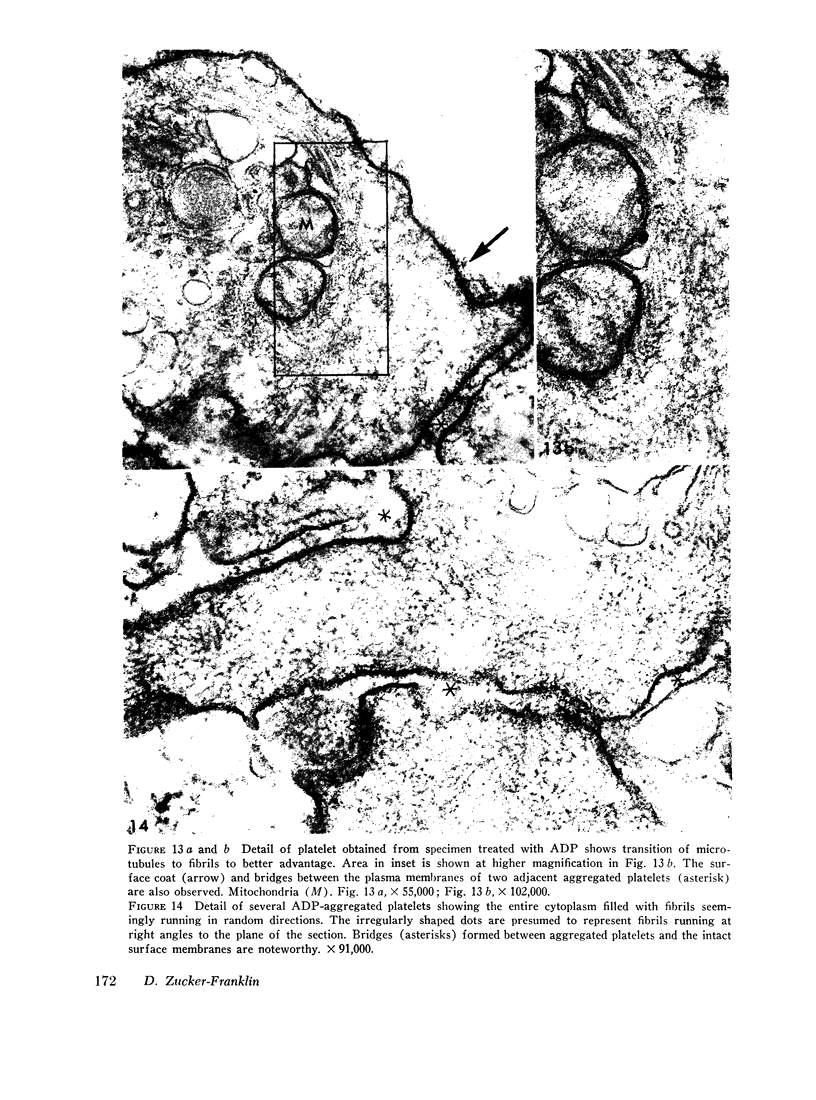
Human blood platelets were subjected to osmotic shock, brief sonication, pressure homogenization, or treatment with adenosine diphosphate (ADP). These procedures demonstrated an abundance of cytoplasmic microfibrils. The fibrils resembled those found on electron microscopy of partially purified thrombosthenin, the actomyosin-like protein isolated from platelets, and they also appeared to resemble the myofilaments of smooth muscle. Similar fibrils were not found in leukocytes studied under identical conditions. Treatment with colchicine (2 × 10-5 mole/liter) resulted in the disappearance of microtubules but did not affect the morphology of the microfibrils or interfere with platelet-dependent clot retraction. Thus, microfibrils rather than microtubules may represent the morphologic counterpart of the contractile protein. Brief osmotic shock at low temperature or treatment with 10-4 M ADP caused the marginal band of microtubules to be replaced by a bundle of intertwining microfibrils. The apparent inter-conversion of microtubules and microfibrils under a variety of conditions led to the hypothesis that fibrils and tubules consist of similar subunits whose degree of polymerization might be dependent on local cytoplasmic forces. Furthermore, on the basis of these observations, it is postulated that the contractile properties of the cells may be vested in the microfibrils, whereas the tubules may serve to maintain the highly asymmetric shape characteristic of circulating and irreversibly aggregated platelets.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V., CROSS M. J. THE AGGREGATION OF BLOOD PLATELETS. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:178–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Further studies on microtubules. A marginal bundle in human and rat thrombocytes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Dec;13(5):469–477. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Morphological changes in the hyalomere of rat blood platelets in experimental venous thrombi. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(2):136–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Zelander T. Substructure in negatively stained microtubules of mammalian blood platelets. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Aug;43(1):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Zucker M. B. Changes in platelet volume produced by temperature, metabolic inhibitors, and aggregating agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):296–301. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT W., WITEBSKY F. OBSERVATIONS ON THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF NUCLEATED ERYTHROCYTES AND THROMBOCYTES, WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE STRUCTURAL BASIS OF THEIR DISCOIDAL SHAPE. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 May 29;62:785–806. doi: 10.1007/BF00342184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAARDER A., JONSEN J., LALAND S., HELLEM A., OWREN P. A. Adenosine diphosphate in red cells as a factor in the adhesiveness of human blood platelets. Nature. 1961 Nov 11;192:531–532. doi: 10.1038/192531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Sato H. Cell motility by labile association of molecules. The nature of mitotic spindle fibers and their role in chromosome movement. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):259–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. P. Alterations in the cytologic detail of intestinal smooth muscle cells in various stages of contraction. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):199–213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macmillan D. C. Secondary clumping effect in human citrated platelet-rich plasma produced by adenosine diphosphate and adrenaline. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):140–144. doi: 10.1038/211140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Sharp A. A. Platelet volume and shape in relation to aggregation and adhesion. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):604–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Porter K. R. Microtubules in the spermatids of the domestic fowl. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):153–173. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Safier L. B. Platelet thrombosthenin: subcellular localization and function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1380–1389. doi: 10.1172/JCI105630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai R., Rebhun L. I. Cytoplasmic microfilaments in streaming Nitella cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):571–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. P., Thimann K. V. Intracellular fibers in oat coleoptile cells and their possible significance in cytoplasmic streaming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):888–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outka D. E., Kluss B. C. The ameba-to-flagellate transformation in Tetramitus rostratus. II. Microtubular morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):323–346. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., CIECIURA S. J., ROBINSON A. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells. III. Long-term cultivation of euploid cells from human and animal subjects. J Exp Med. 1958 Dec 1;108(6):945–956. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.6.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun L. I. Structural aspects of saltatory particle movement. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):223–239. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. D. Cytoplasmic microtubules in rabbit platelets. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Nov 15;68(4):474–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00347711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR E. W. THE MECHANISM OF COLCHICINE INHIBITION OF MITOSIS. I. KINETICS OF INHIBITION AND THE BINDING OF H3-COLCHICINE. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:SUPPL–SUPPL:160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Porter K. R. Studies on microtubules in Heliozoa. I. The fine structure of Actinosphaerium nucleofilum (Barrett), with particular reference to the axial rod structure. Protoplasma. 1965;60(4):317–344. doi: 10.1007/BF01247886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Porter K. R. Studies on the microtubules in heliozoa. II. The effect of low temperature on these structures in the formation and maintenance of the axopodia. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):327–343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Krivit W. An ultrastructural basis for the shape changes induced in platelets by chilling. Blood. 1967 Nov;30(5):625–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J. Ultrastructure of thrombosthenin, the contractile protein of human blood platelets. Science. 1967 Aug 25;157(3791):945–946. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3791.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
















