Abstract
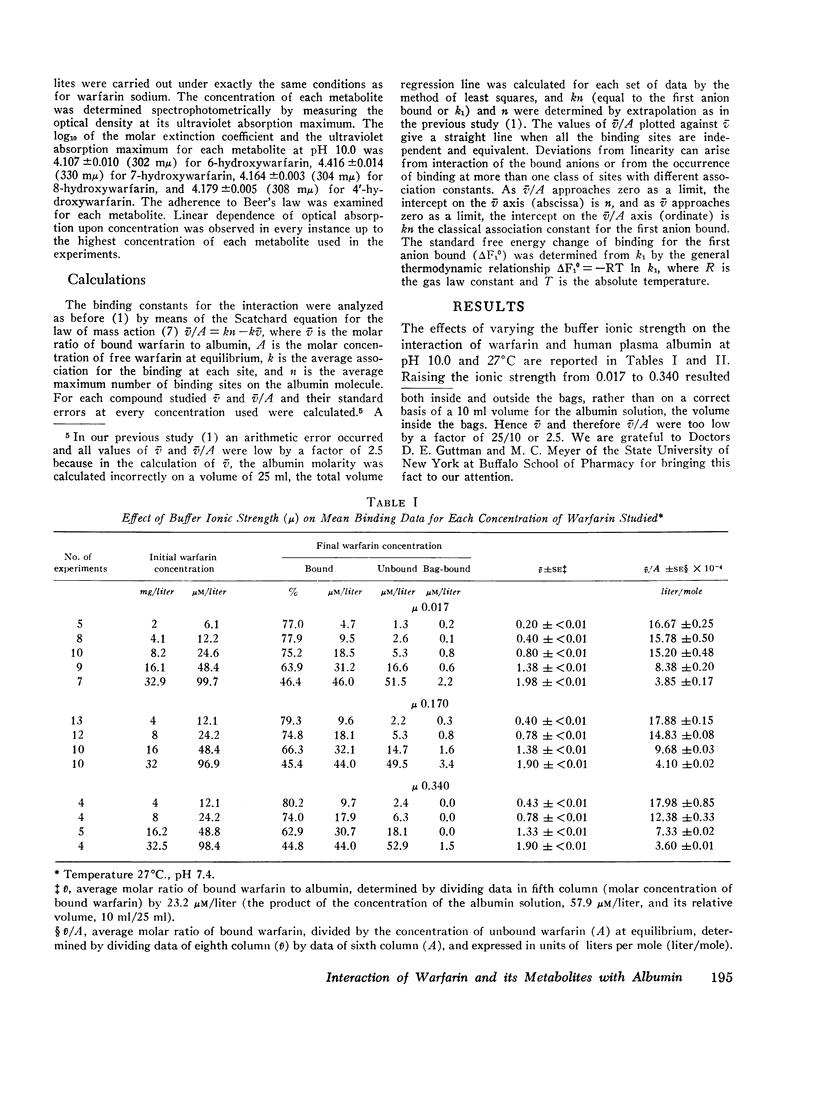
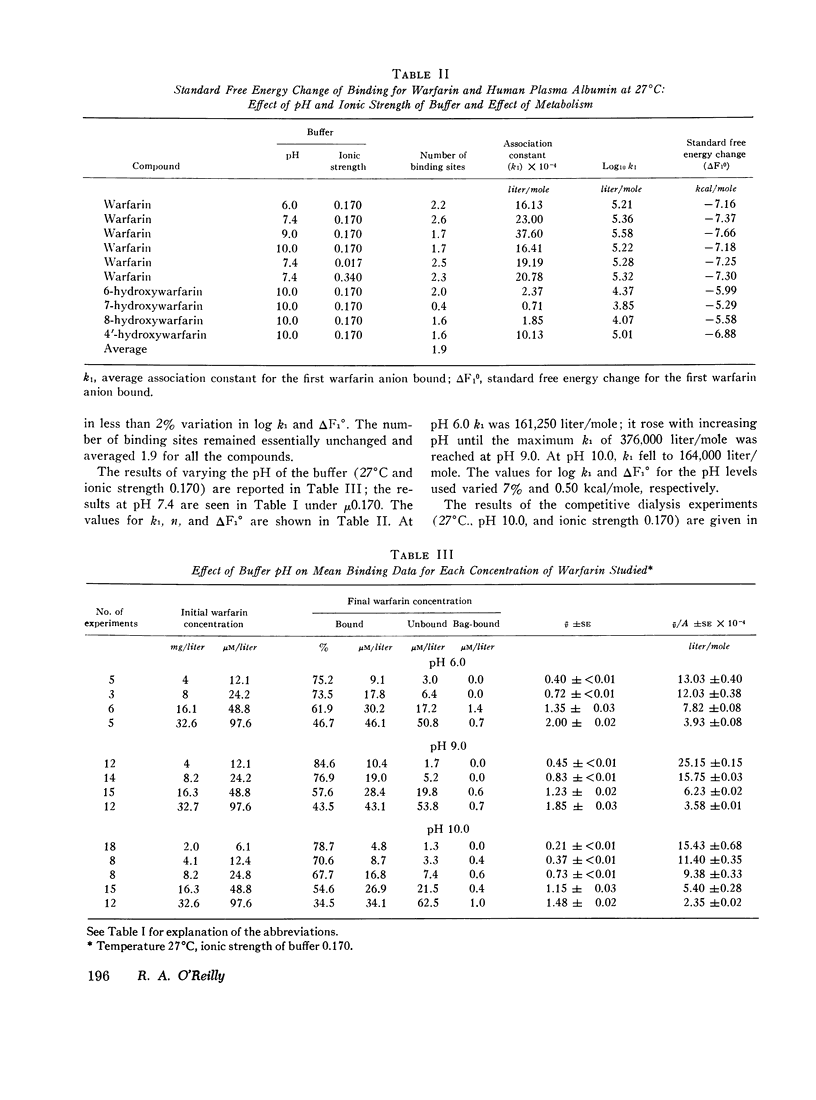
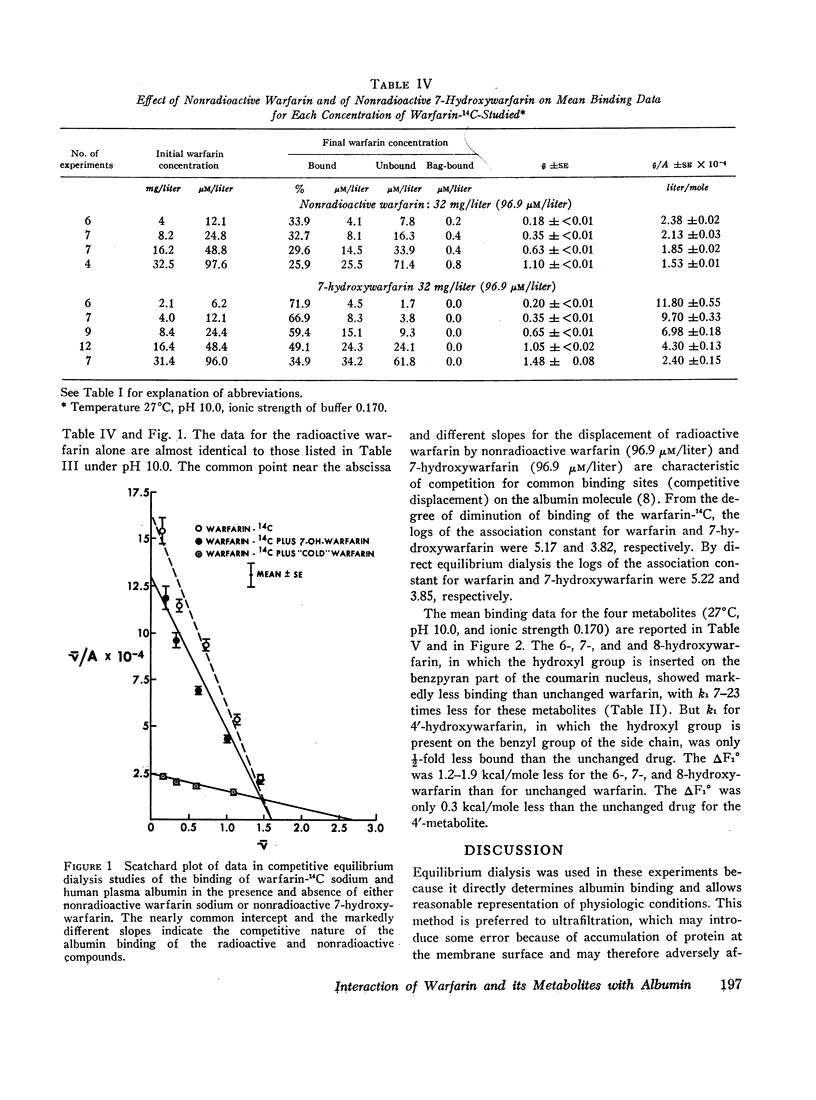
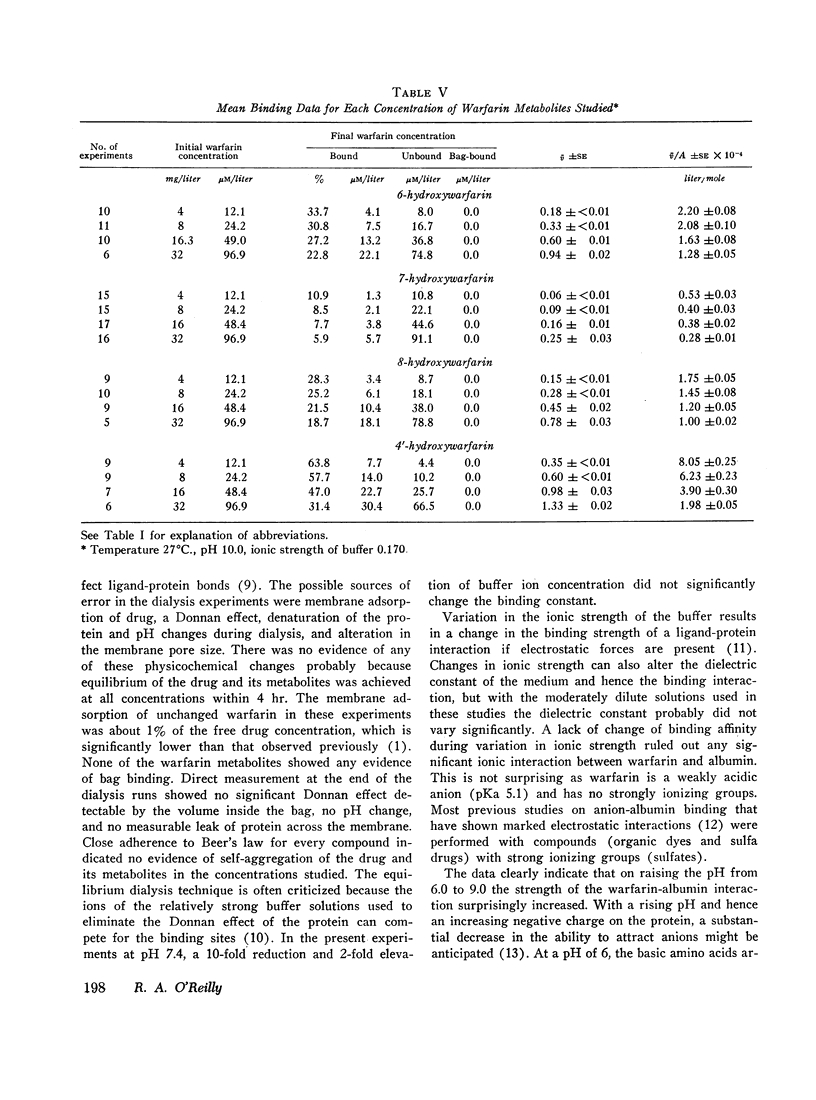
The interaction of the anticoagulant drug warfarin and its metabolites with human plasma albumin was studied by equilibrium dialysis. A 20-fold variation of buffer ionic strength (0.017-0.340) caused no significant change in the warfarin association constant. But the binding strength rose significantly as the pH was increased from 6.0 to 9.0 and then declined at pH 10.0. The 6-, 7-, and 8-hydroxywarfarin metabolites showed a 7- to 23-fold reduction in binding strength at pH 10.0. These data indicate that the molecular basis of the interaction is nonelectrostatic and that the introduction of polar hydroxyl groups on the coumarin nucleus by metabolism reduces its hydrophobic binding surface. The interaction was markedly exothermic and showed a positive entropy (increased molecular disorder), which suggests cooperative hydrogen and hydrophobic bonding as the molecular basis for the binding of warfarin to albumin.
The marked albumin binding and nonpolar character of warfarin explains the respective absence and presence of the unchanged drug in urine and plasma of warfarintreated patients, while the more polar character and lesser albumin binding of the metabolites probably determines their absence in plasma and presence in urine. The relatively marked binding to albumin of the 4′-hydroxywarfarin metabolite suggests that it may occur in the plasma of warfarin-treated patients. The data suggest that a direct correlation exists between the interaction of warfarin with plasma albumin and the interaction with the warfarin receptor site.
Full text
PDF

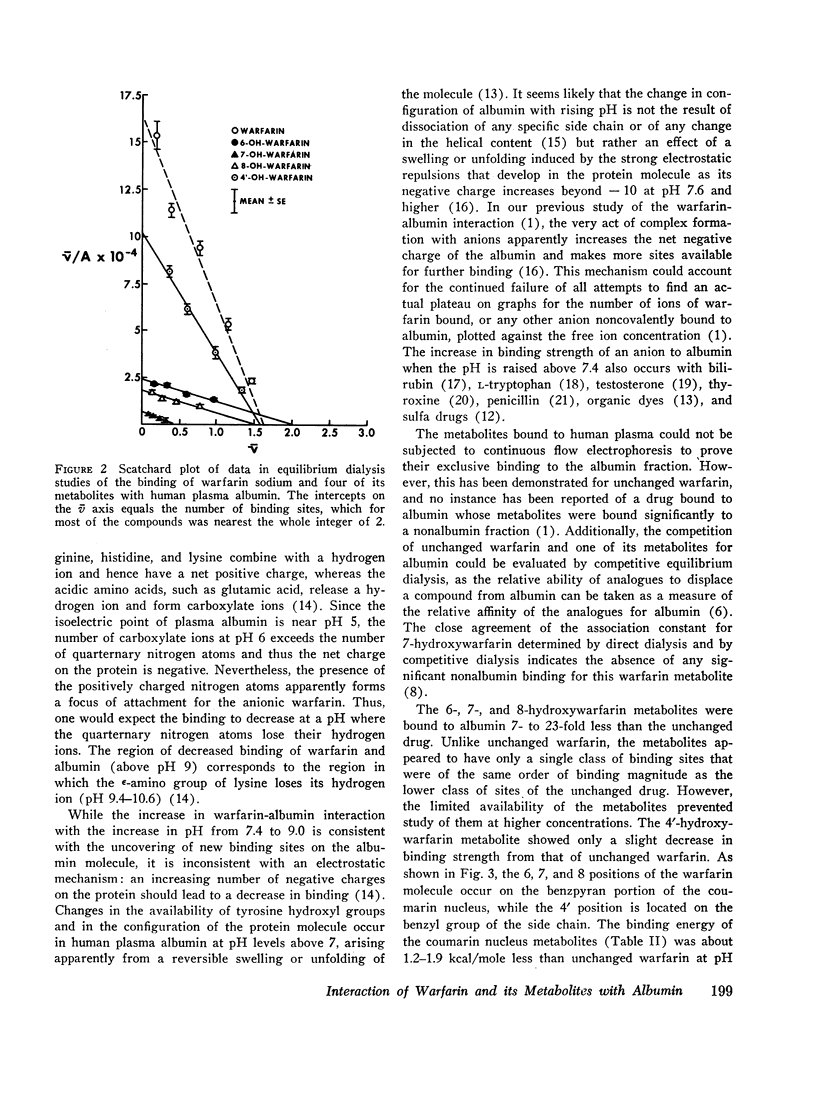



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggeler P. M., O'Reilly R. A., Leong L., Kowitz P. E. Potentiation of anticoagulant effect of warfarin by phenylbutazone. N Engl J Med. 1967 Mar 2;276(9):496–501. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196703022760904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggeler P. M., O'Reilly R. A. The pharmacological basis of oral anticoagulant therapy. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1966;21:227–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet L. Z., Goyan J. E. Thermodynamics of chelation by tetracyclines. J Pharm Sci. 1966 Nov;55(11):1184–1190. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600551103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corn M., Berberich R. Rapid fluorometric assay for plasma warfarin. Clin Chem. 1967 Feb;13(2):126–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON C., SMITH P. K. The binding of salicylic acid and related substances to purified proteins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Aug;133:161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen P. M. The binding of penicillins to bovine serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Apr;15(4):447–463. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARD W. J., Jr, VIJAI K. K., FOSTER J. F. A structural transformation in bovine and human plasma albumins in alkaline solution as revealed by rotatory dispersion studies. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1984–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCMENAMY R. H., SEDER R. H. THERMODYNAMIC VALUES RELATED TO THE ASSOCIATION OF L-TRYPTOPHAN ANALOGUES TO HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3241–3248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYER Y. P., SCHELLMAN J. A. The interaction of ribonuclease with purine and pyrimidine phosphates. I. Binding of adenosine 5'-monophosphate to ribonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:361–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90791-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'REILLY R. A., AGGELER P. M., LEONG L. S. STUDIES ON THE COUMARIN ANTICOAGULANT DRUGS: A COMPARISON OF THE PHARMACODYNAMICS OF DICUMAROL AND WARFARIN IN MAN. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Apr 15;11:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'REILLY R. A., AGGELER P. M., LEONG L. S. STUDIES ON THE COUMARIN ANTICOAGULANT DRUGS: THE PHARMACODYNAMICS OF WARFARIN IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1542–1551. doi: 10.1172/JCI104839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. A. Studies on the coumarin anticoagulant drugs: interaction of human plasma albumin and warfarin sodium. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):829–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI105582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL G. B. The dissociation of bilirubin from albumin and its clinical implications. J Pediatr. 1959 Sep;55:268–279. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(59)80223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OYAKAWA E. K., LEVEDAHL B. H. Testosterone binding to bovine and human serum albumin: the role of tyrosine groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Mar;74(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollay M., Stevens A., Davis C., Jr Determination of plasma-thiocyanate binding and the Donnan ratio under simulated physiological conditions. Anal Biochem. 1966 Nov;17(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG I. Z., SCHERAGA H. A. Entropy changes accompanying association reactions of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K. MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF THYROXINE IN RELATION TO ITS BINDING BY HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Sep;43:1721–1729. doi: 10.1172/JCI105047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRITSCH G. L., RATHKE C. E., TRITSCH N. E., WEISS C. M. Thyroxine binding by human serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3163–3167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. Y., Bulbrook R. D., Ellis F., Coombs M. M. Metabolic clearance rates of pregnenolone, 17-acetoxypregnenolone and their sulphate esters in man and in rabbit. J Endocrinol. 1967 Nov;39(3):395–403. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


