Abstract
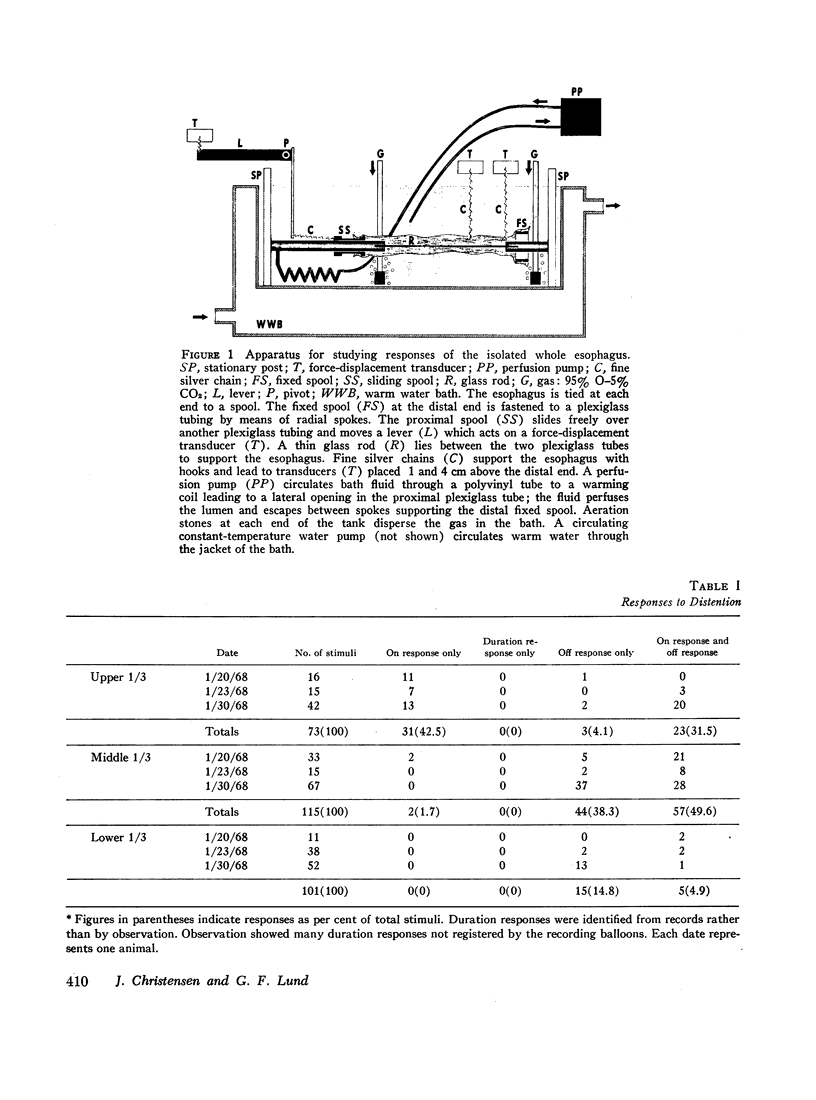
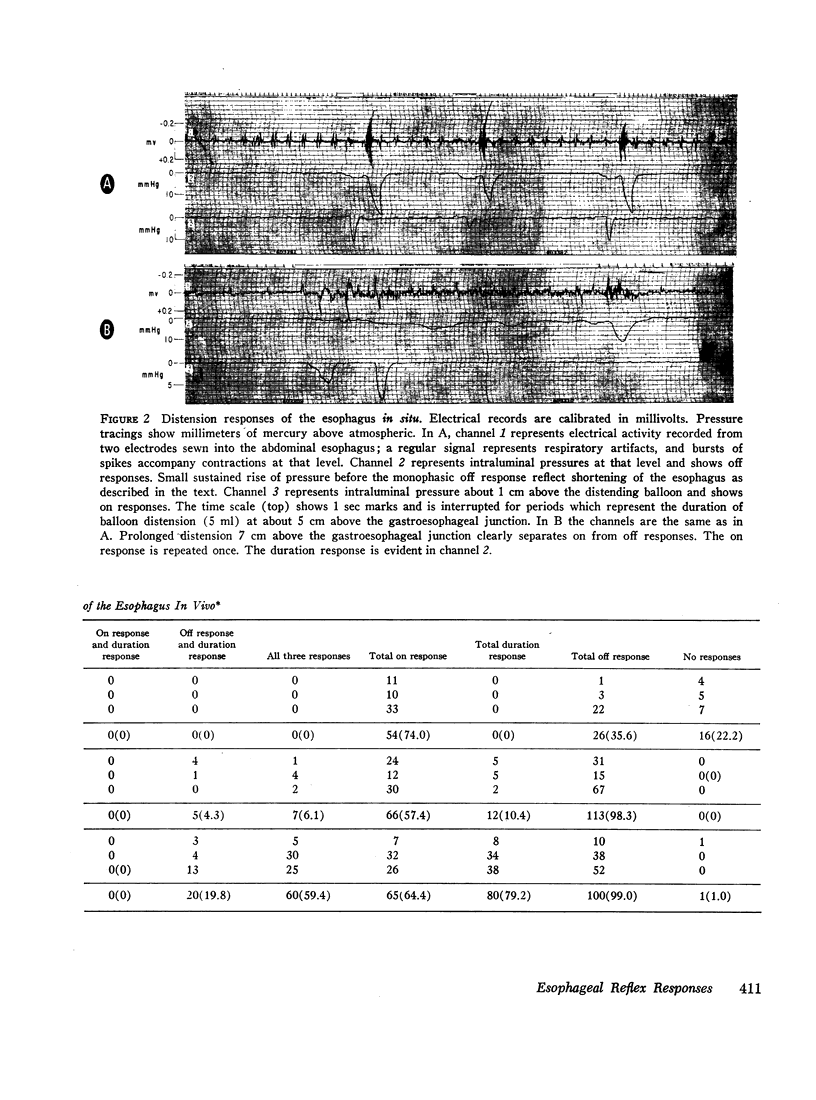
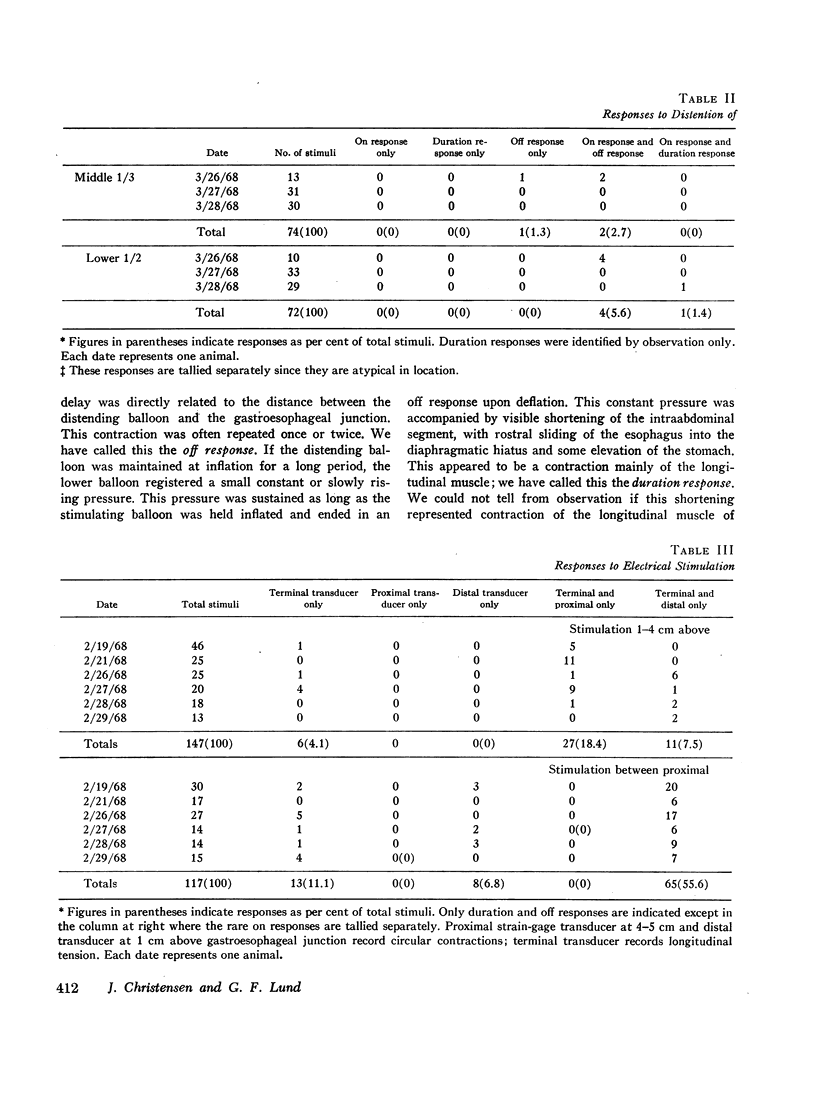
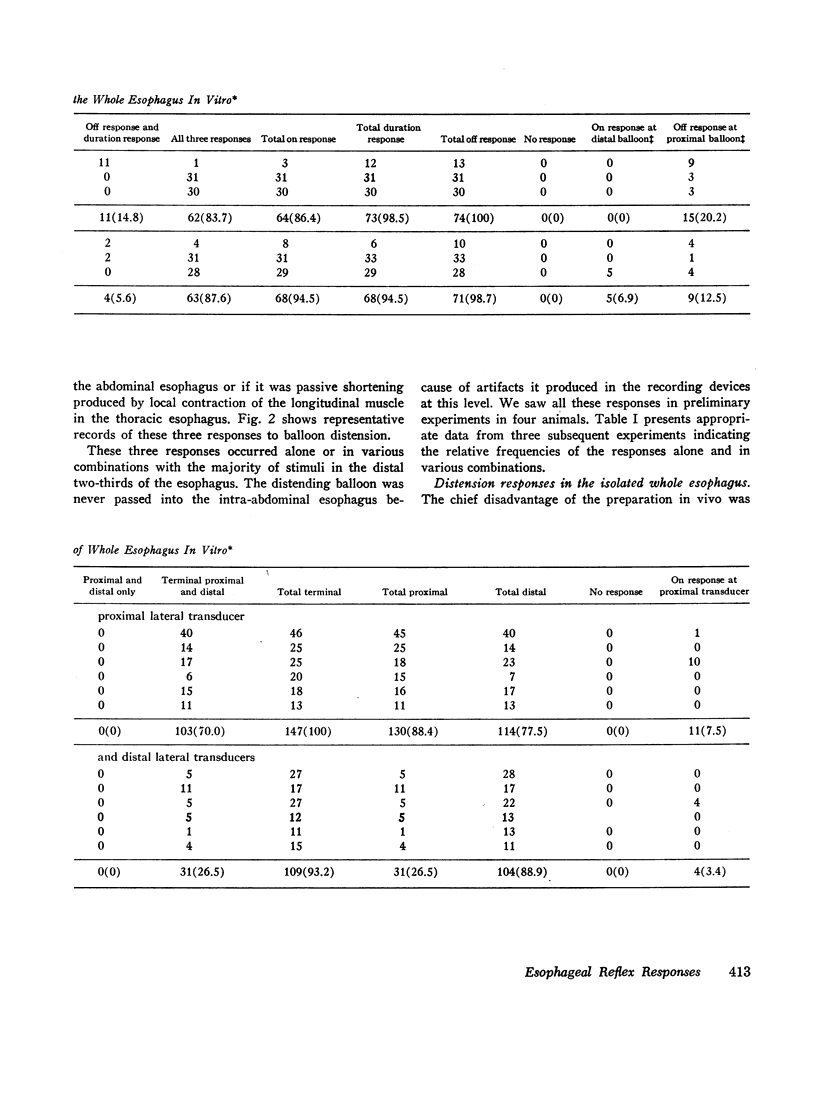
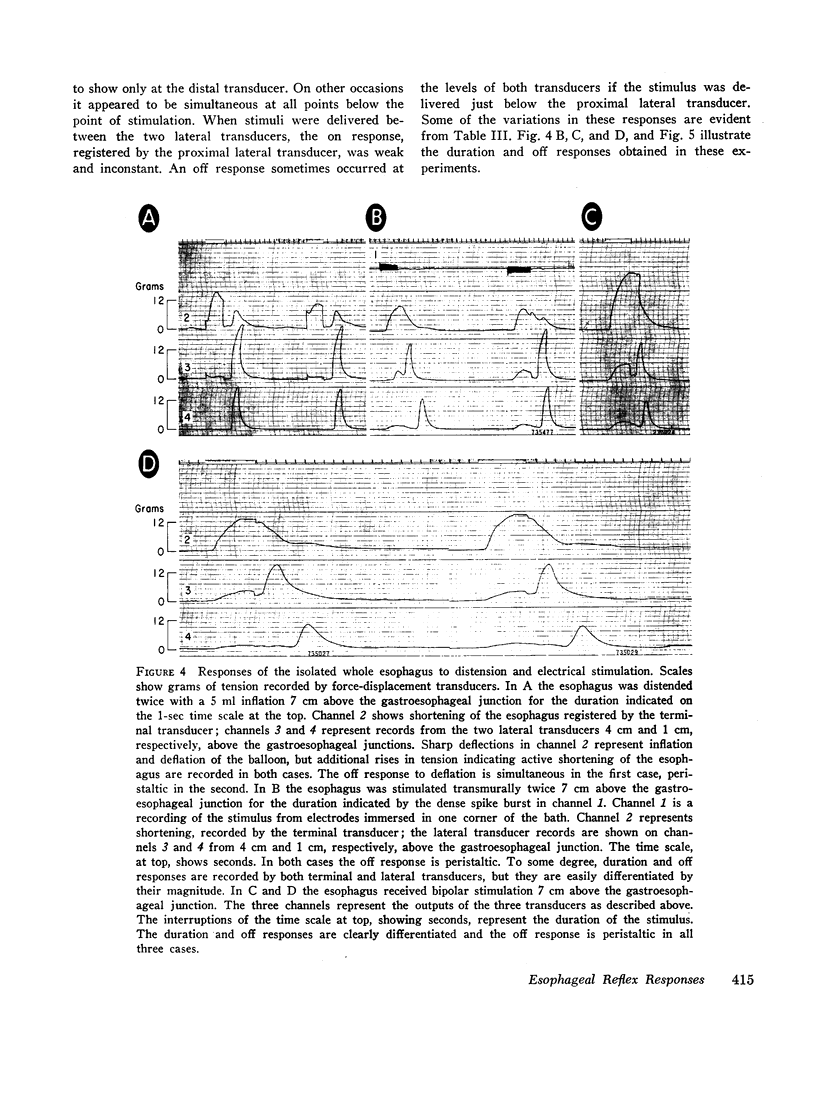
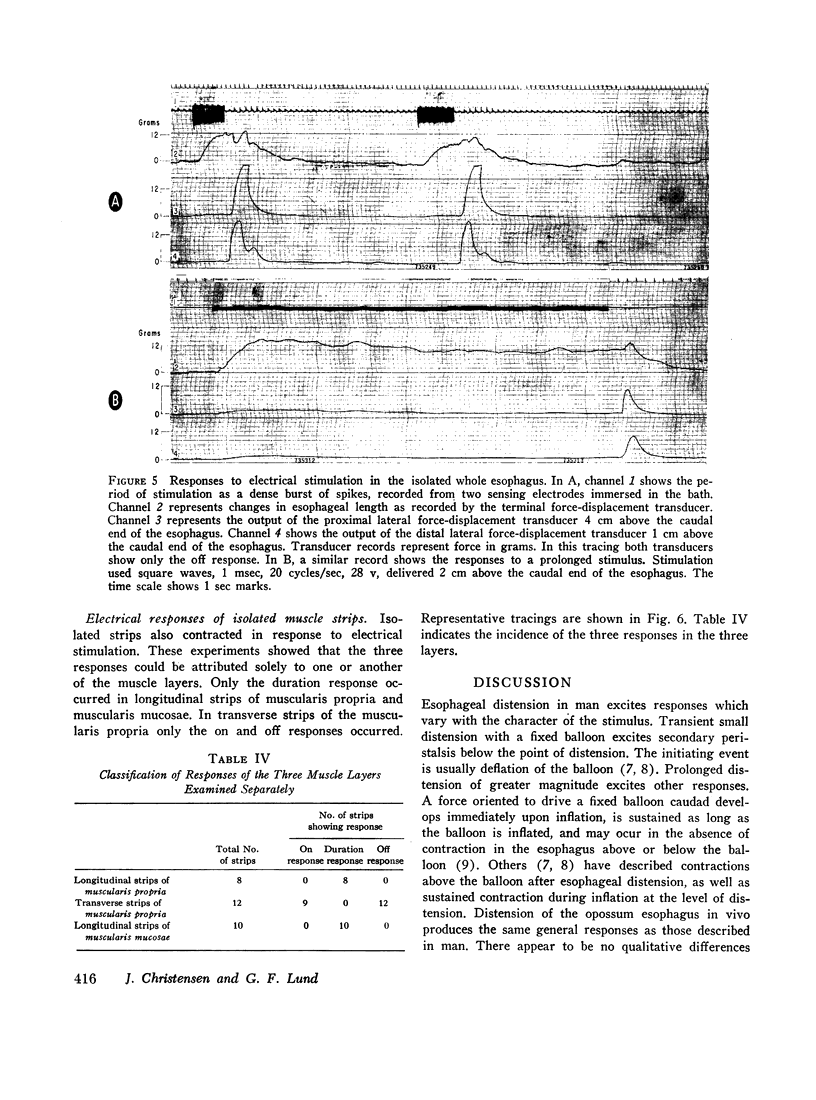
The opossum esophagus contains only smooth muscle in the distal two-thirds; it can be used to study autonomic control of esophageal smooth muscle. Three different preparations of opossum esophagus were used; the esophagus in vivo, the isolated whole esophagus, and isolated strips of the three layers of esophageal smooth muscle. Responses were examined to localized distension and to electrical stimulation. Distension of the esophagus in vivo produced three separate responses: inflation of a distending balloon caused a brief contraction rostral to the point of distension, the on response; maintenance of distension produced shortening of the esophagus, sustained for the duration of the distension, the duration response; and deflation of the balloon caused a single brief caudal circumferential contraction, apparently propagated caudad, the off response. In the isolated whole esophagus distension produced the same three responses. Electrical stimulation in this preparation produced apparently identical responses. Electrical stimulation of isolated strips of the three muscle layers showed that the muscularis mucosae and the longitudinal layer of the muscularis propria always respond with a duration response only. The circular layer of the muscularis propria responds with on and off responses only. These observations suggest that both types of stimuli excite the same afferent nerve fibers in local reflex pathways. Peristalsis can be maintained by these reflexes in the smooth muscle part of the esophagus independent of central nervous connections.
Full text
PDF


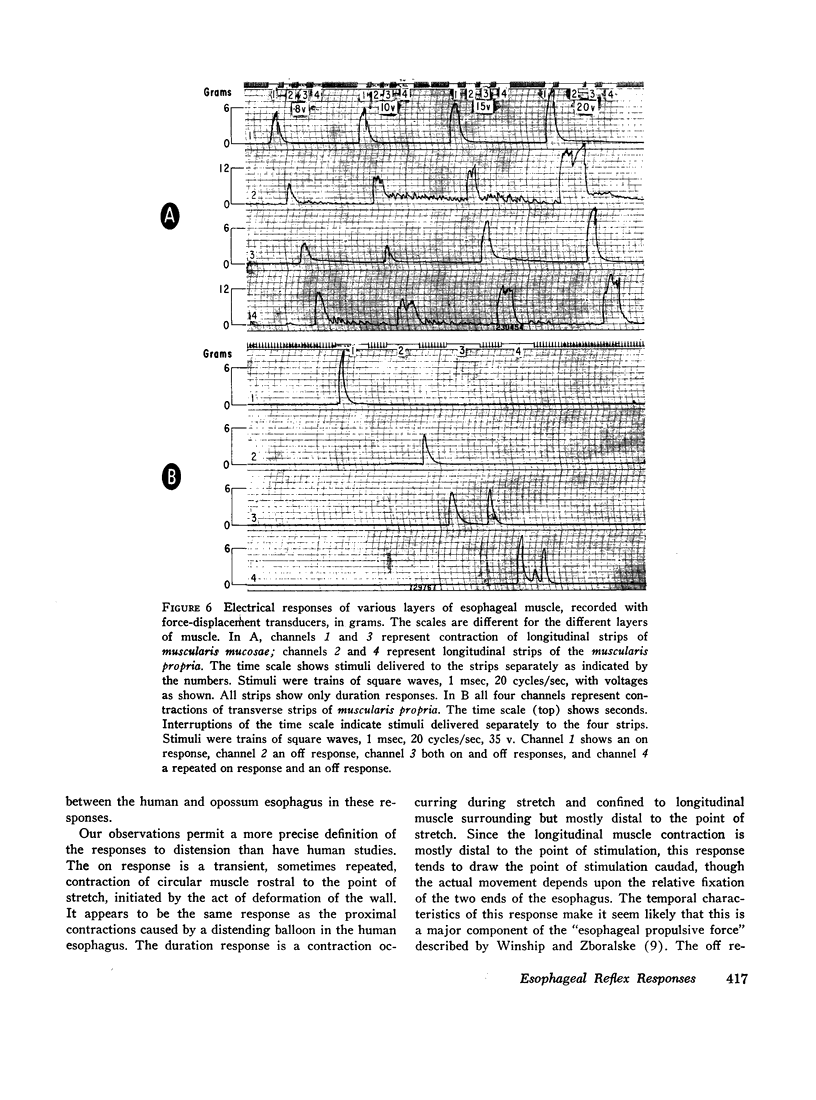


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen J., Daniel E. E. Electric and motor effects of autonomic drugs on longitudinal esophageal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1966 Aug;211(2):387–394. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER B., HENDRIX T. R., KRAMER P., INGELFINGER F. J. The characteristics and similarity of primary and secondary peristalis in the esophagus. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):110–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI103780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGELFINGER F. J. Esophageal motility. Physiol Rev. 1958 Oct;38(4):533–584. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEI N. ETUDE 'ELECTROPHYSIOLOGIQUE DES R'ECEPTEURS SENSIBLES DE L'OESOPHAGE THORACIQUE DU CHAT. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Jan 4;260:302–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]