Abstract
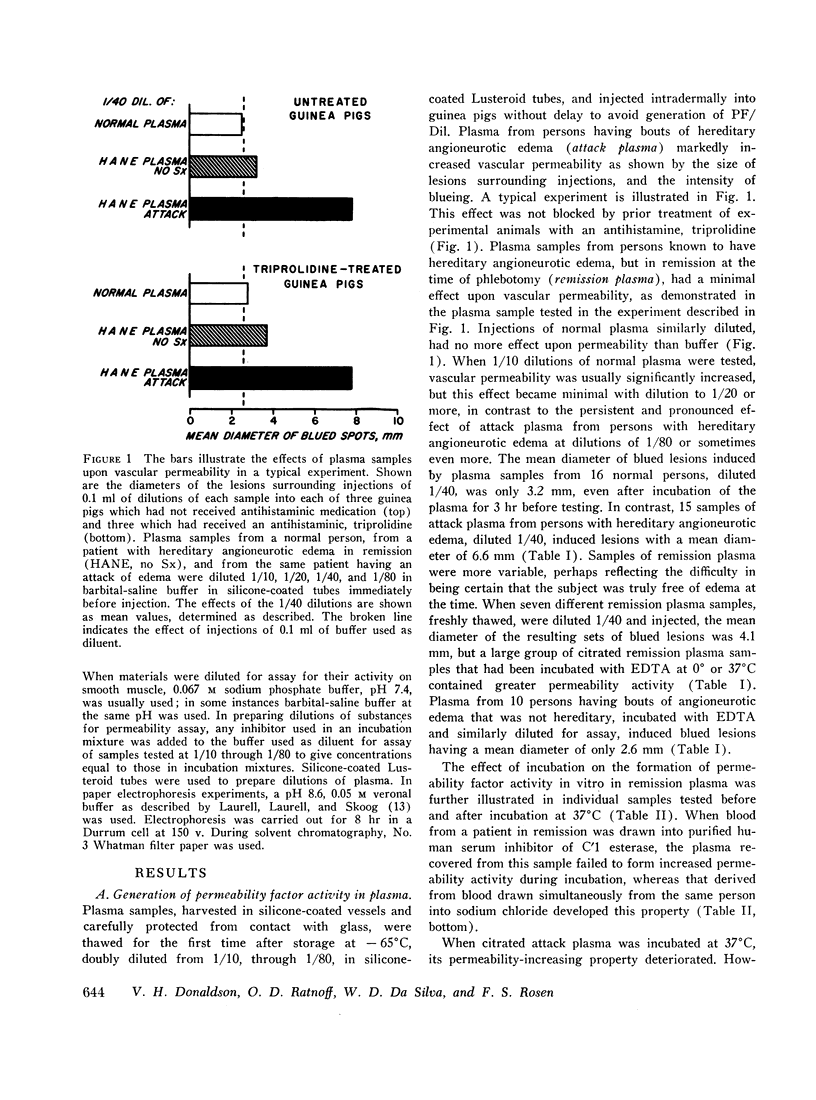
Plasma from persons with hereditary angioneurotic edema readily developed the capacity to increase vascular permeability and to induce the isolated rat uterus to contract. Both activities resided in a small, heat-stable molecule that was apparently a polypeptide. Crude preparations of the polypeptide were inactivated during incubation with trypsin. They also failed to produce pain and erythema, but caused markedly increased vascular permeability in human skin. These characteristics differ from those of bradykinin, from which crude preparations of the polypeptide could also be distinguished by electrophoretic mobility and paper chromatographic behavior. Proof that the polypeptide is truly different from bradykinin must await its further purification. Histamine played no role in the activities observed.
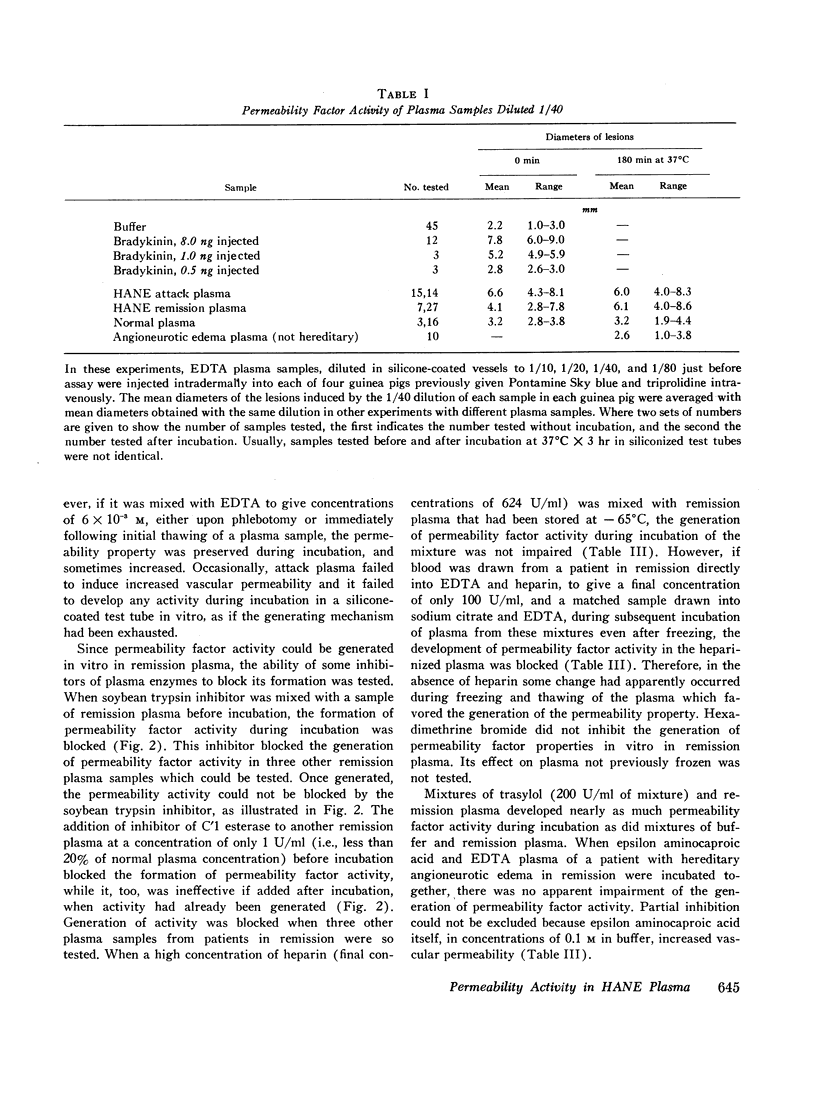
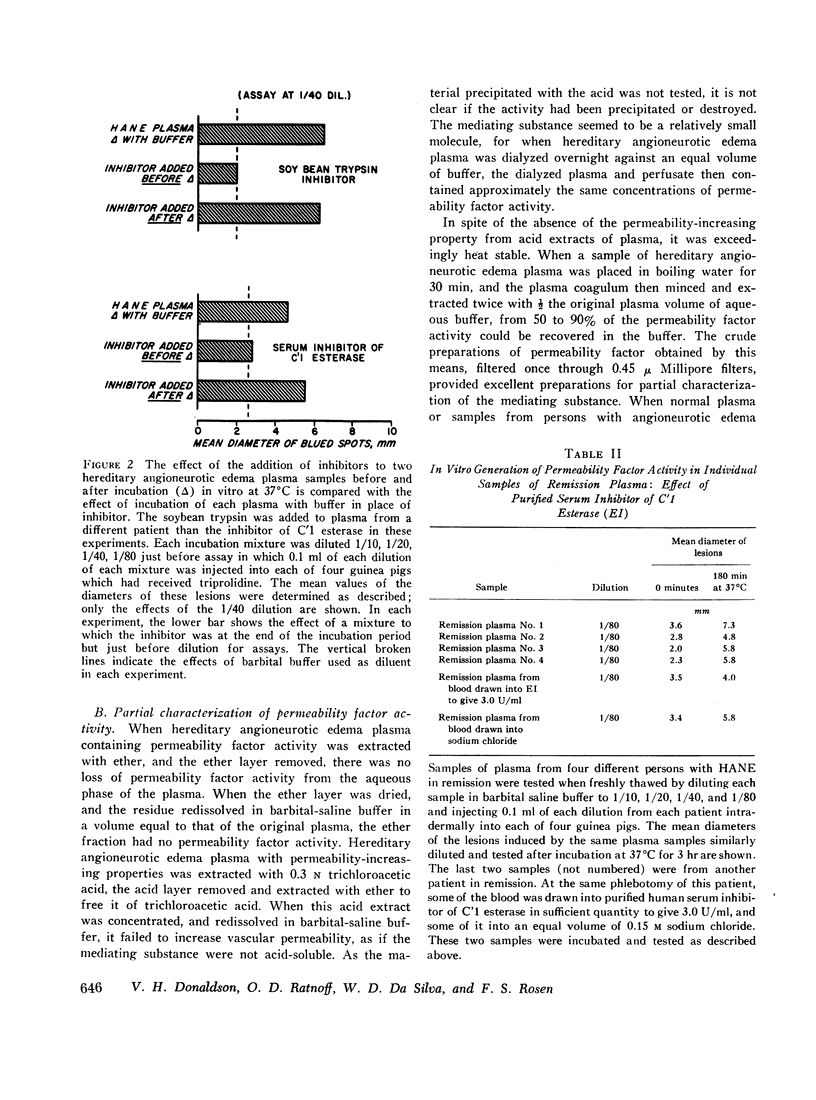
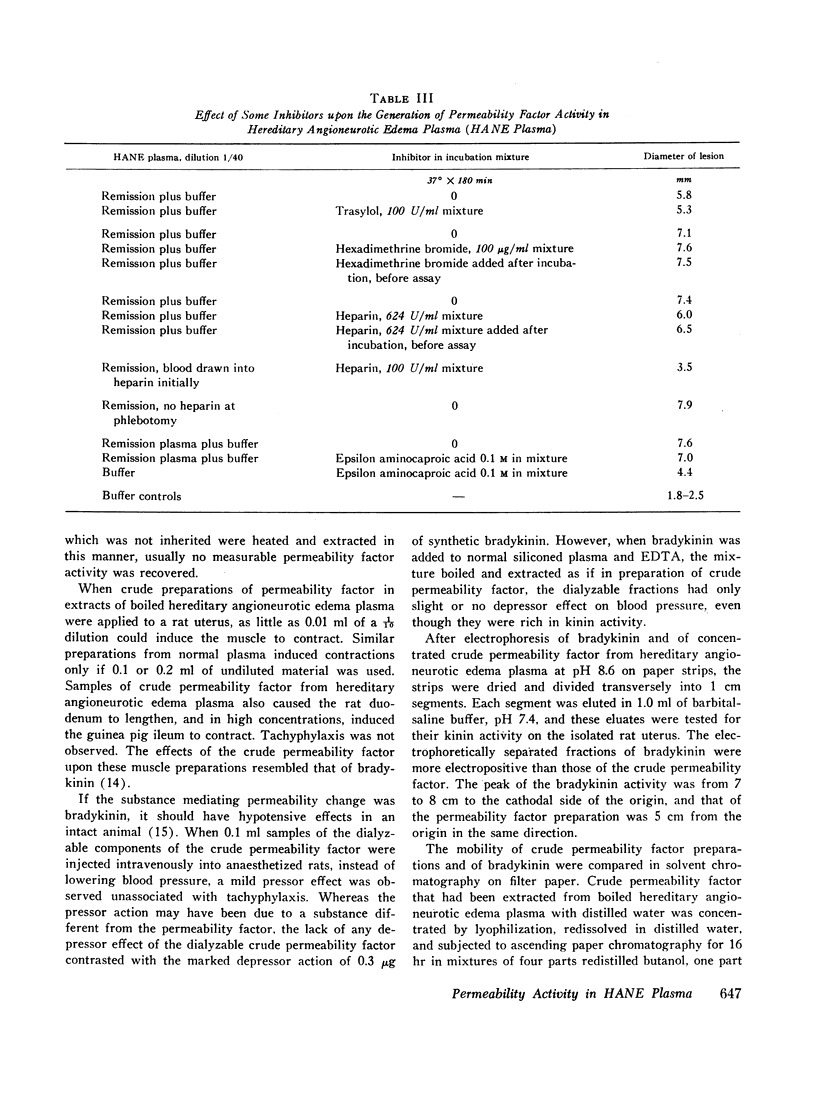
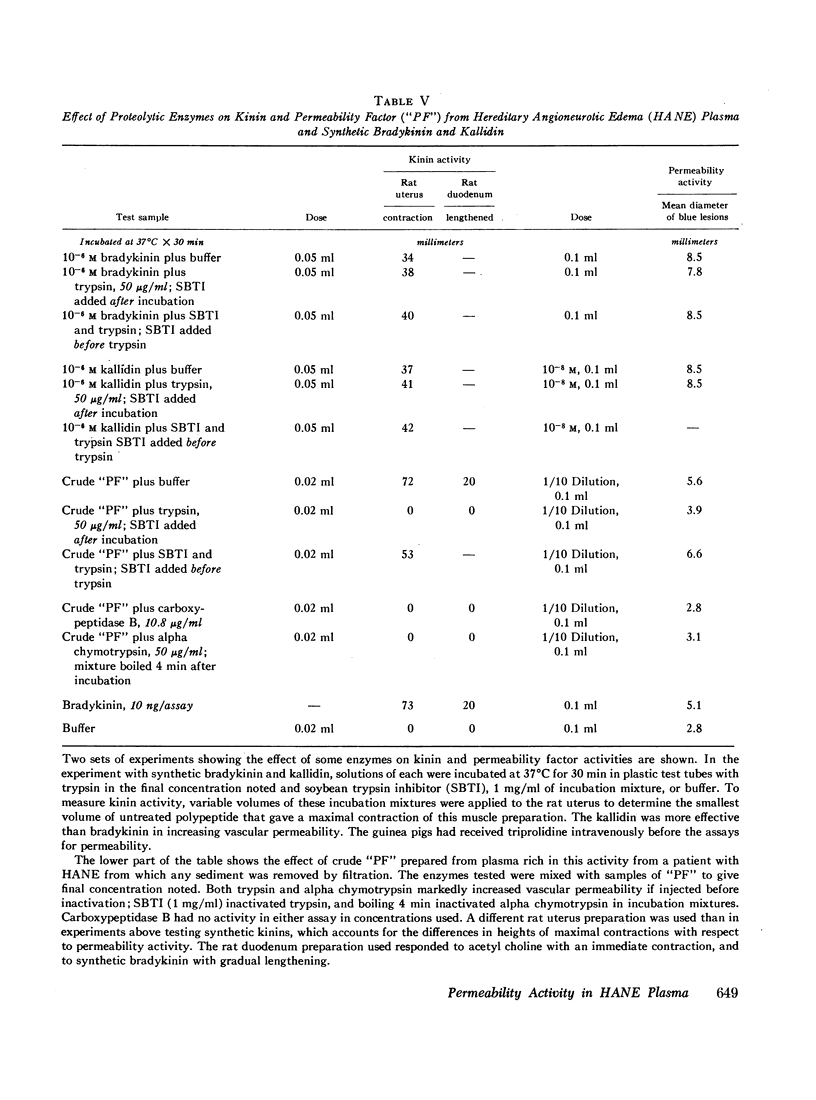
Although the enzymes functioning to release the permeability factor and kinin activities in hereditary angioneurotic edema plasma were not clearly defined, one or more plasma enzymes other than C′1 esterase presumably participated either in conjunction with C′1 esterase or in pari passu events to release the polypeptide mediating these activities.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABLONDI F. B., HAGAN J. J., PHILIPS M., DE RENZO E. C. Inhibition of plasmin, trypsin and the streptokinase-activated fibrinolytic system by 6-aminocaproic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERER F. A., HOERNLE S. STRUKTURUNTERSUCHUNGEN AM KALLIKREIN-INAKTIVATOR AUS RINDERLUNGE. I. MOLEKULARGEWICHT, ENDGRUPPENANALYSE UND AMINOSAEURE-ZUSAMMENSETZUNG. Z Naturforsch B. 1965 May;20:457–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG D. A., MILLS G. L. A HIGHLY PURIFIED KININ-FORMING ENZYME FROM HUMAN PLASMA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1964 Oct;13:1393–1402. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(64)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUSTEN K. F., SHEFFER A. L. DETECTION OF HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA BY DEMONSTRATION OF A REDUCTION IN THE SECOND COMPONENT OF HUMAN COMPLEMENT. N Engl J Med. 1965 Apr 1;272:649–656. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196504012721301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP E., MARGOLIS J. STUDIES ON PLASMA KININS. II. SOME PROPERTIES OF THE KININ-DESTROYING ENZYME. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1963 Aug;41:307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge R. T., Ratnoff O. D. The Role of Proaccelerin in Human Blood Coagulation. Evidence that Proaccelerin Is Converted to a Prothrombin-converting Principle by Activated Stuart Factor: With Notes on the Anticoagulant Action of Soybean Trypsin Inhibitor, Protamine Sulfate, and Hexadimethrine Bromide. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44(2):302–314. doi: 10.1172/JCI105144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon K. L., Queng J. T., Thomas O. C., McGovern J. P. Observations on biochemical abnormalities in hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Allergy. 1965 Nov-Dec;36(6):546–557. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(65)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The derivation of two distinct anaphylatoxin activities from the third and fifth components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):371–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., ROSEN F. S. ACTION OF COMPLEMENT IN HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: THE ROLE OF C'1-ESTERASE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2204–2213. doi: 10.1172/JCI105094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias Da Silva W., Lepow I. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation. II. Biological properties of anaphylatoxin prepared with purified components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 May 1;125(5):921–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias da Silva W., Lepow I. H. Anaphylatoxin formation by purified human C'1 esterase. J Immunol. 1965 Dec;95(6):1080–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H. Mechanisms of activation of C'1 esterase in hereditary angioneurotic edema plasma in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):411–429. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H. Serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase in health and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Sep;68(3):369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOES E. G., WOHLER J. R., LEVINE M. I. BLOCKING OF THE IN VIVO EFFECTS OF BRADYKININ AND KALLIDIN WITH CARBOXYPEPTIDASE B. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Dec;142:327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOS E. G., JACKMAN V., BARNES W. C. Instrument for recording isotonic contractions of smooth muscles. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Mar;17:367–368. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.2.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOS E. G., SLOANE E. M. An enzyme in human blood plasma that inactivates bradykinin and kallidins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Jul;11:585–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Observations on intrinsic kinin-forming factors in human plasma: the effect of acid, acetone, chloroform, heat and euglobulin separation on kinin formation. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(3):496–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. Anaphylatoxin in its relation to the complement system. Science. 1967 Mar 3;155(3766):1122–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3766.1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGEN L. J. SOME BIOCHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HUMAN PERMEABILITY GLOBULINS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Dec;45:604–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUT H., BHARGAVA N. VERSUCHE ZUR ISOLIERUNG DES KALLIKREIN-INAKTIVATORS. V. ISOLIERUNG EINES KALLIKREIN-INAKTIVATORS AUS RINDERLUNGE UND SEINE IDENTIFIZIERUNG MIT DEM INAKTIVATOR AUS RINDERPAROTIS. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1964;338:231–237. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1964.338.1-2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer M. R., Donaldson V. H., Rosen F. S. Effect of C'1 esterase on vascular permeability in man: studies in normal and complement-deficient individuals and in patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):604–611. doi: 10.1172/JCI105756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDERMAN N. S., WEBSTER M. E., BECKER E. L., RATCLIFFE H. E. Hereditary angioneurotic edema. II. Deficiency of inhibitor for serum globulin permeability factor and/or plasma kallikrein. J Allergy. 1962 Jul-Aug;33:330–341. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(62)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B., LAURELL S., SKOOG N. Buffer composition in paper electrophoresis; considerations on its influence, with special reference to the interaction between small ions and proteins. Clin Chem. 1956 Apr;2(2):99–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundh B., Laurell A. B., Wetterqvist H., White T., Granerus G. A case of hereditary angioneurotic oedema, successfully treated with epsilon-aminocaproic acid. Studies on C'1 esterase inhibitor, C'1 activation, plasminogen level and histamine metabolism. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Sep;3(7):733–745. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., WILHELM D. L. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. I. An activable permeability factor and its inhibitor in guinea-pig serum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Feb;36(1):71–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky I. A. INHIBITION OF beta HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI FIBRINOLYSIN BY TRYPSIN INHIBITOR (ANTIPROTEASE). Science. 1944 Sep 1;100(2592):198–200. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2592.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates J. A., Pettinger W. A., Doctor R. B. Evidence for the release of bradykinin in carcinoid syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):173–178. doi: 10.1172/JCI105329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENSKY J., LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Partial purification of a serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1674–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., LEPOW I. H. Some properties of an esterase derived from preparations of the first component of complement. J Exp Med. 1957 Aug 1;106(2):327–343. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MILES A. A. THE INDUCTION OF PERMEABILITY-INCREASING ACTIVITY IN HUMAN PLASMA BY ACTIVATED HAGEMAN FACTOR. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:328–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSCHILD A. M., ROCHA E SILVA M. Activation of a histamine-releasing agent (anaphylatoxin) in normal rat plasma. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Oct;35(5):507–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitomer G., Stroud R. M., Mayer M. M. Reversible adsorption of C'2 by EAC'4: role of Mg2+, enumeration of competent SAC'4, two-step nature of C'2a fixation and estimation of its efficiency. Immunochemistry. 1966 Jan;3(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR F. B., Jr, FUDENBERG H. INHIBITION OF THE C'-1 COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT BY AMINO ACIDS. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:319–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., PIERCE J. V. Action of the kallikreins on synthetic ester substrates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 May;107:186–191. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster M. E., Gilmore J. P. The estimation of the kallidins in blood and urine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;14(7):1161–1163. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva W. D., Eisele J. W., Lepow I. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation. 3. Purification of the activity with anaphylatoxin properties generated by interaction of the first four components of complement and its identification as a cleavage product of C'3. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1027–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



