Abstract
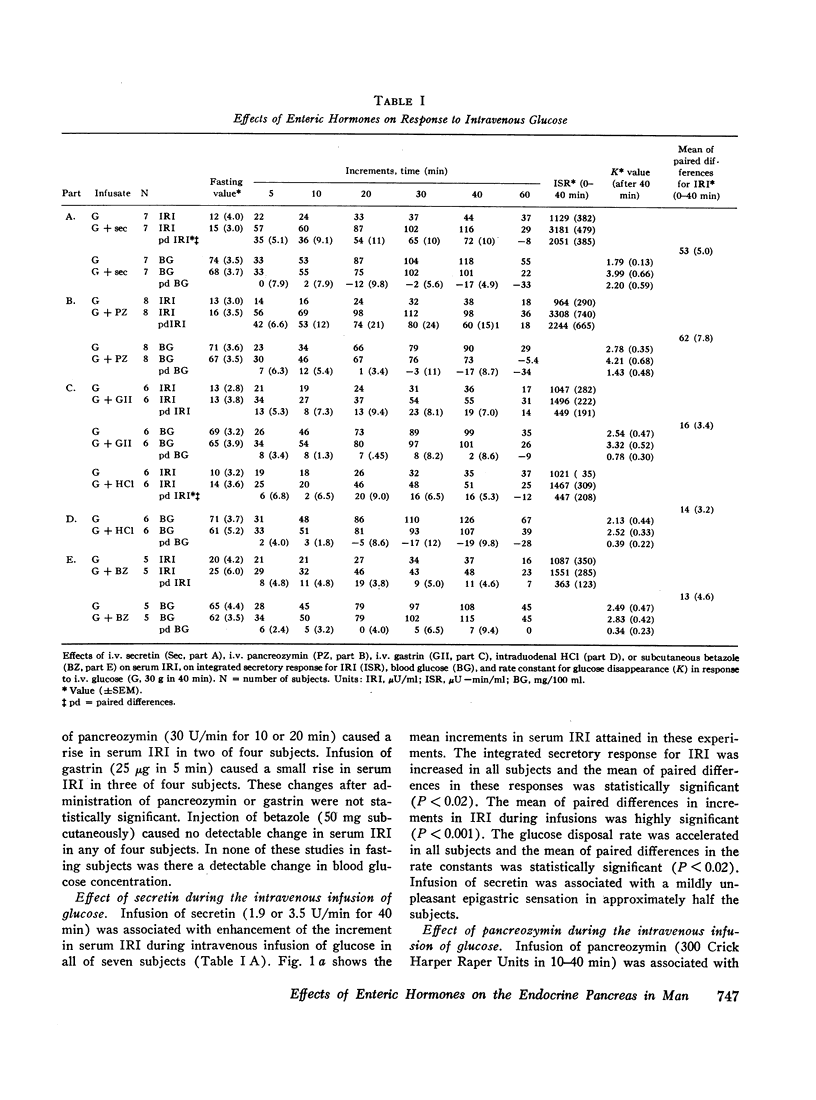
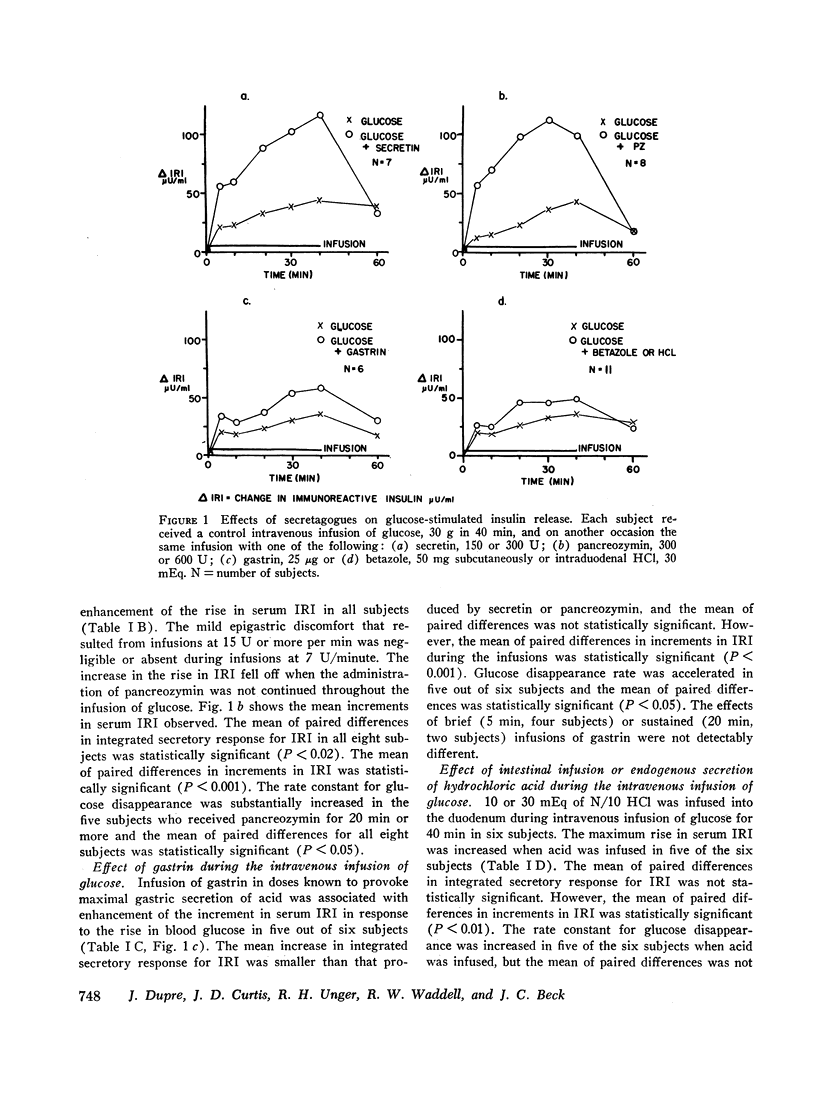
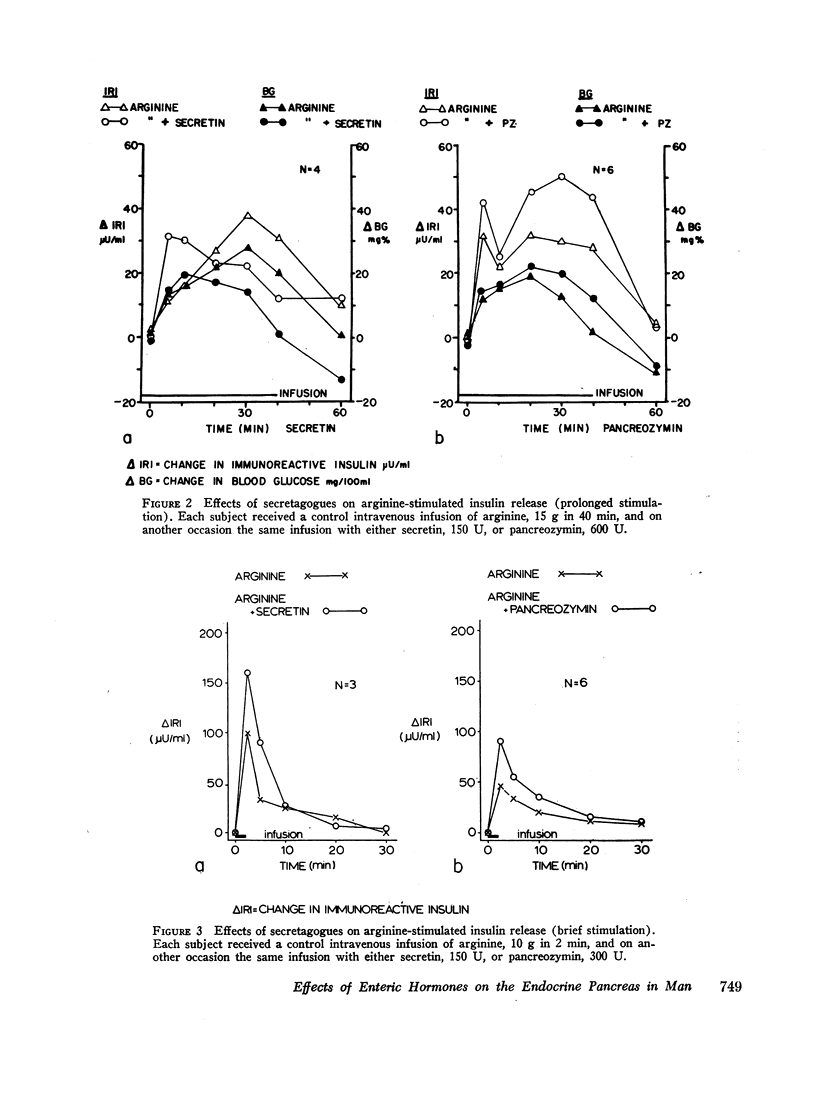
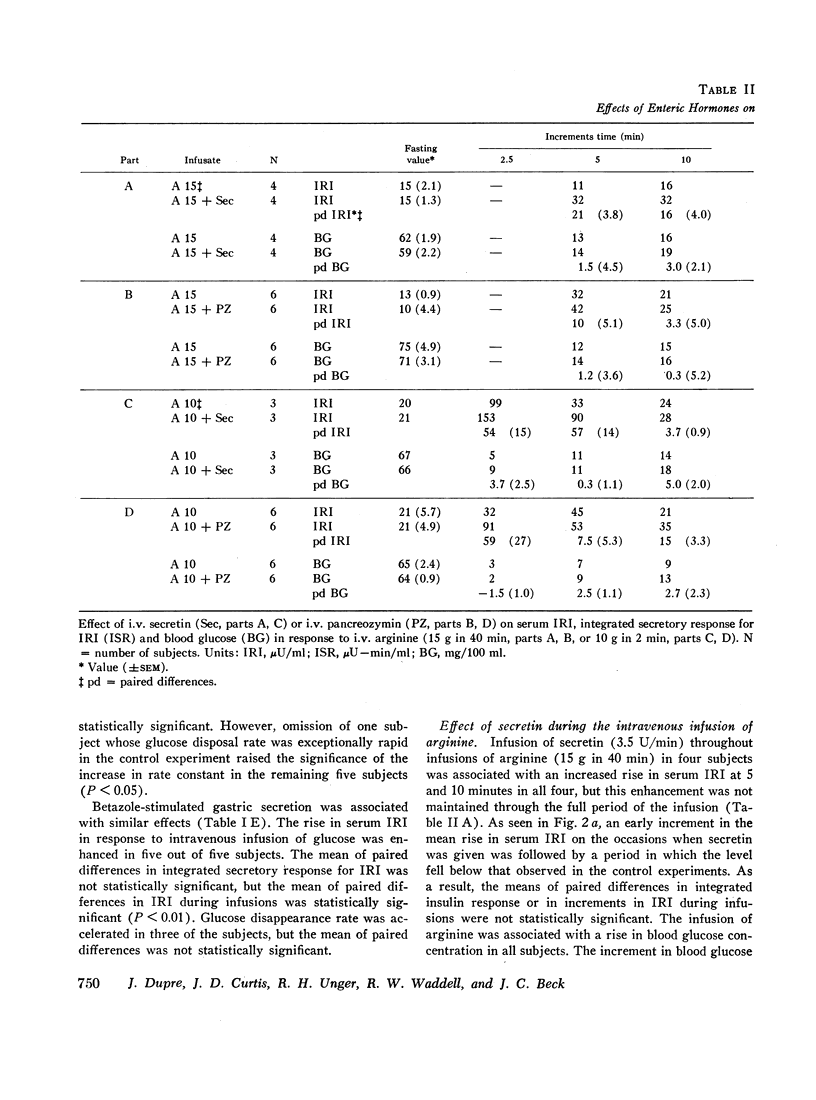
Intravenous administration of porcine secretin or pancreozymin or synthetic human gastrin II resulted in raised increments in serum immunoreactive insulin during intravenous infusion of glucose in normal man. Enhancement of serum immunoreactive insulin by each hormone was associated with accelerated disposal of glucose. In response to prolonged intravenous infusion of arginine with pancreozymin there was a maintained rise in immunoreactive insulin and glucagon-like immunoreactivity in the blood. These effects of pancreozymin and arginine were not reproduced with secretin and arginine, and may have been due to the stimulation of glucagon secretion together with insulin by pancreozymin.
Enteric infusion of hydrochloric acid, or stimulation of gastric acid secretion by betazole, presumed to cause release of endogenous secretin, led to enhancement of insulin secretion during intravenous infusion of glucose. Enteric infusion of arginine, presumed to cause release of endogenous pancreozymin, led to a rise in serum immunoreactive insulin not attributable to effects of circulating glucose and amino acids. It is concluded that secretin and pancreozymin released in response to physiological stimuli contribute to stimulation of the endocrine pancreas after ingestion of food.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyns D. R., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Intestinal hormones and plasma insulin: an insulinotropic action of secretin. Br Med J. 1967 Jun 10;2(5553):676–678. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5553.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyns D. R., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Intestinal hormones and plasma-insulin. Lancet. 1966 Feb 19;1(7434):409–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91400-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONARD V. Mesure de l'assimilation du glucose; bases théoriques et applications cliniques. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1955 Jul-Aug;18(7-8):655–contd. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUPRE J. AN INTESTINAL HORMONE AFFECTING GLUCOSE DISPOSAL IN MAN. Lancet. 1964 Sep 26;2(7361):672–673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupré J., Beck J. C. Stimulation of release of insulin by an extract of intestinal mucosa. Diabetes. 1966 Aug;15(8):555–559. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.8.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupré J., Rojas L., White J. J., Unger R. H., Beck J. C. Effects of secretin on insulin and glucagon in portal and peripheral blood in man. Lancet. 1966 Jul 2;2(7453):26–27. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91750-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., STIMMLER L., HLAD C. J., Jr, ARAI Y. PLASMA INSULIN RESPONSE TO ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS GLUCOSE ADMINISTRATION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1076–1082. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACY W. W., CROFFORD O. B. AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF FREE PLASMA ALPHA-AMINO ACIDS BY THE NINHYDRIN-CARBON DIOXIDE METHOD: NORMAL SEX DIFFERENCE IN HUMAN PLASMA. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Nov;64:828–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence A. M. Radioimmunoassayable glucagon levels in man: effects of starvation, hypoglycemia, and glucose administration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE N., HOLDSWORTH C. D., TURNER D. S. NEW INTERPRETATION OF ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE. Lancet. 1964 Jul 4;2(7349):20–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler R. J., Weisberg H. Failure of endogenous stimulation of secretin and pancreozymin release to influence serum-insulin. Lancet. 1968 Mar 2;1(7540):448–451. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92780-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H., Ashmore J. Effects of adrenergic and cholinergic agents upon insulin secretion in vitro. Endocrinology. 1967 May;80(5):975–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-5-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Holdsworth C. D., Turner D. S. Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1317–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade R. C., Kneubuhler H. A., Schulte W. J., Barboriak J. J. Stimulation of insulin secretion by pancreozymin. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):141–144. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohneda A., Parada E., Eisentraut A. M., Unger R. H. Characterization of response of circulating glucagon to intraduodenal and intravenous administration of amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2305–2322. doi: 10.1172/JCI105916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rune S. J. Individual variation in secretory capacity of gastric acid to stimulation with solid food and with histamine. Clin Sci. 1967 Jun;32(3):443–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Tyler J., Marri G., Marks V. Stimulation of glucagon secretion by oral glucose. Lancet. 1965 Dec 18;2(7425):1257–1259. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal J. E., Ezdinli E. Z. Basal plasma glucagon levels of man. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):778–785. doi: 10.1172/JCI105578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sum P. T., Preshaw R. M. Intraduodenal glucose infusion and pancreatic secretion in man. Lancet. 1967 Aug 12;2(7511):340–341. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J. E. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF PANCREATIC STIMULI STUDIED BY MEANS OF ATROPINELIKE DRUGS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jan;206:124–128. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ketterer H., Dupré J., Eisentraut A. M. The effects of secretin, pancreozymin, and gastrin on insulin and glucagon secretion in anesthetized dogs. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):630–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI105565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ohneda A., Valverde I., Eisentraut A. M., Exton J. Characterization of the responses of circulating glucagon-like immunoreactivity to intraduodenal and intravenous administration of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):48–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI105714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG C. C., GROSSMAN M. I. Physiological determination of release of secretin and pancreozymin from intestine of dogs with transplanted pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):527–545. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. J., Dupré J. Regulation of insulin secretion by the intestinal hormone, secretin: studies in man via transumbilical portal vein catheterization. Surgery. 1968 Jul;64(1):204–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



