Abstract
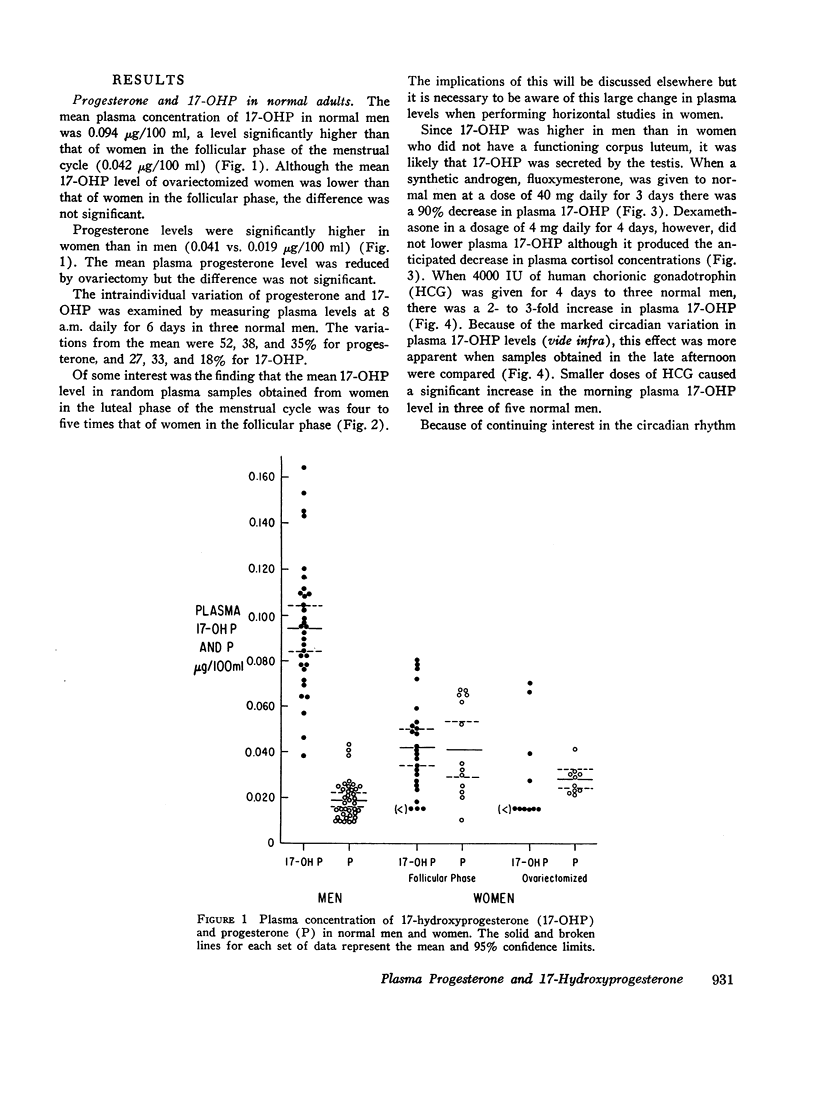
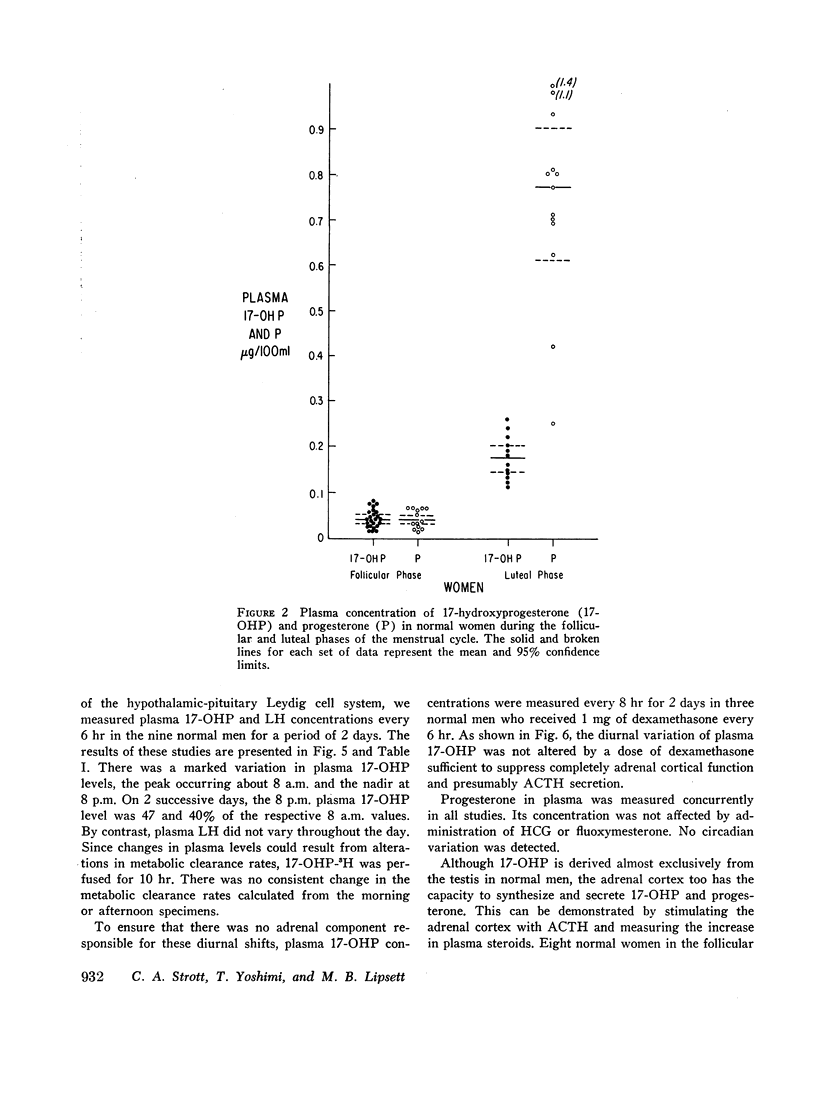
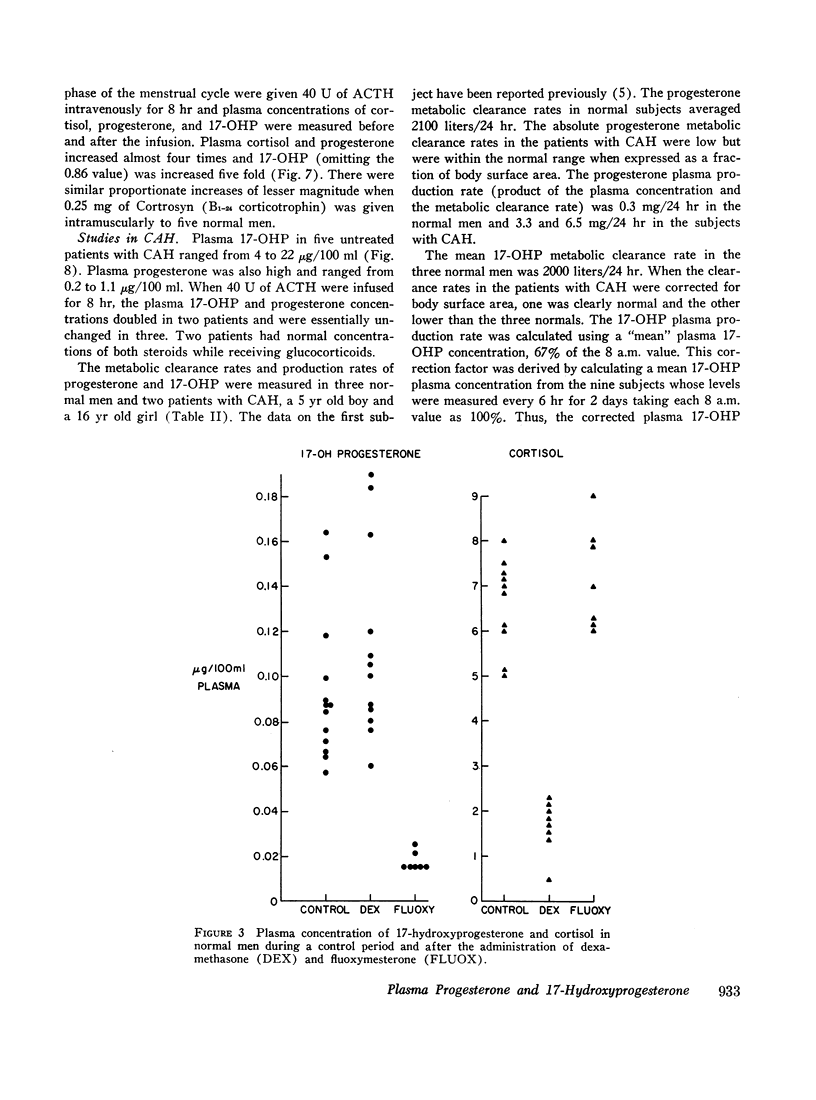
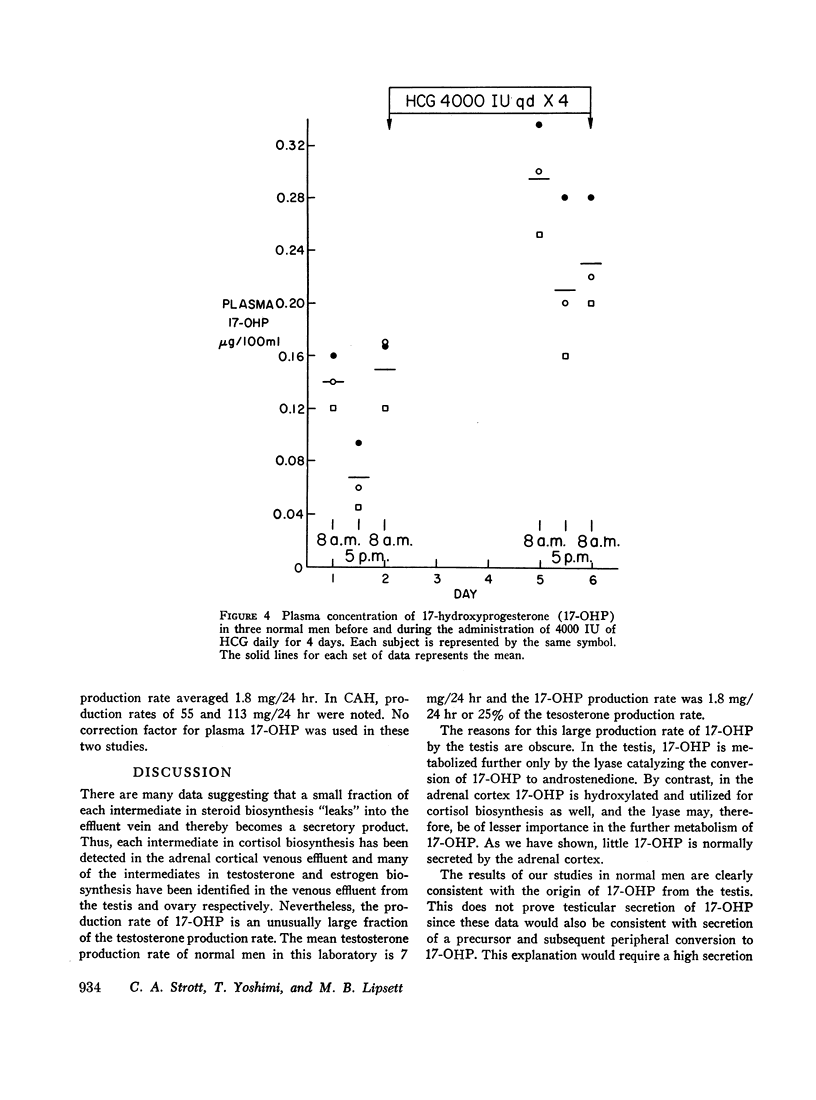
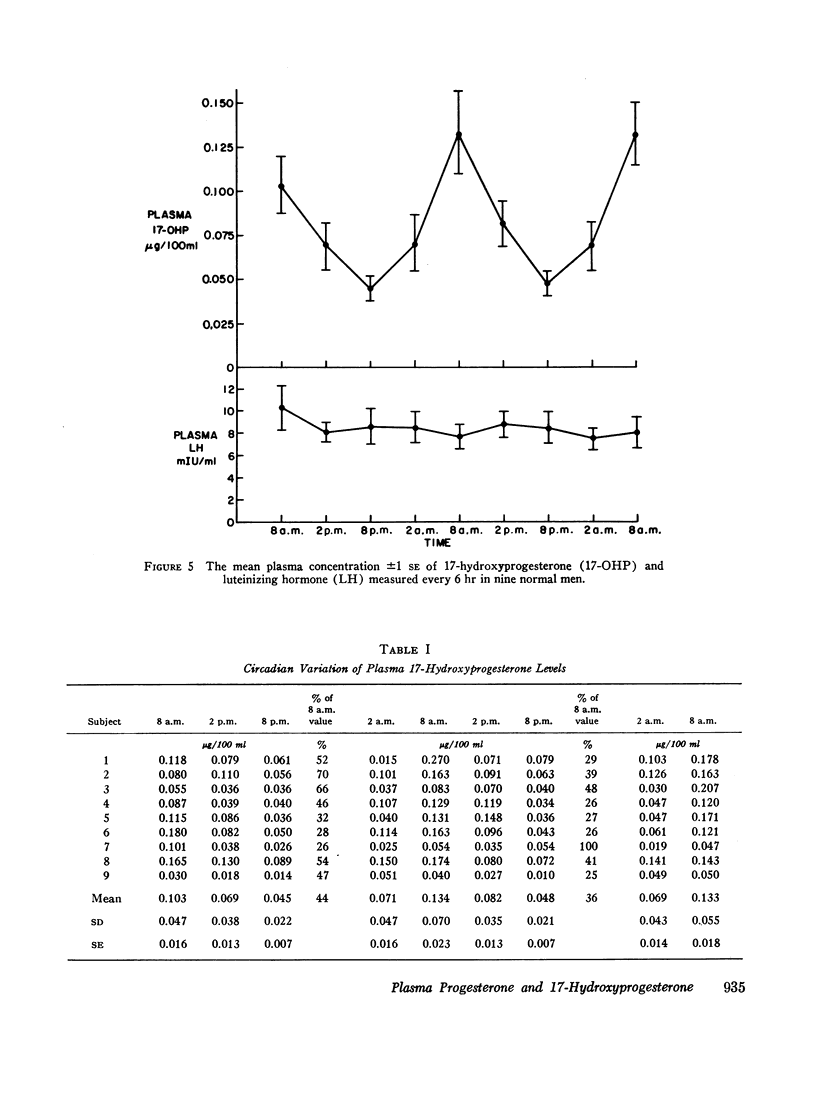
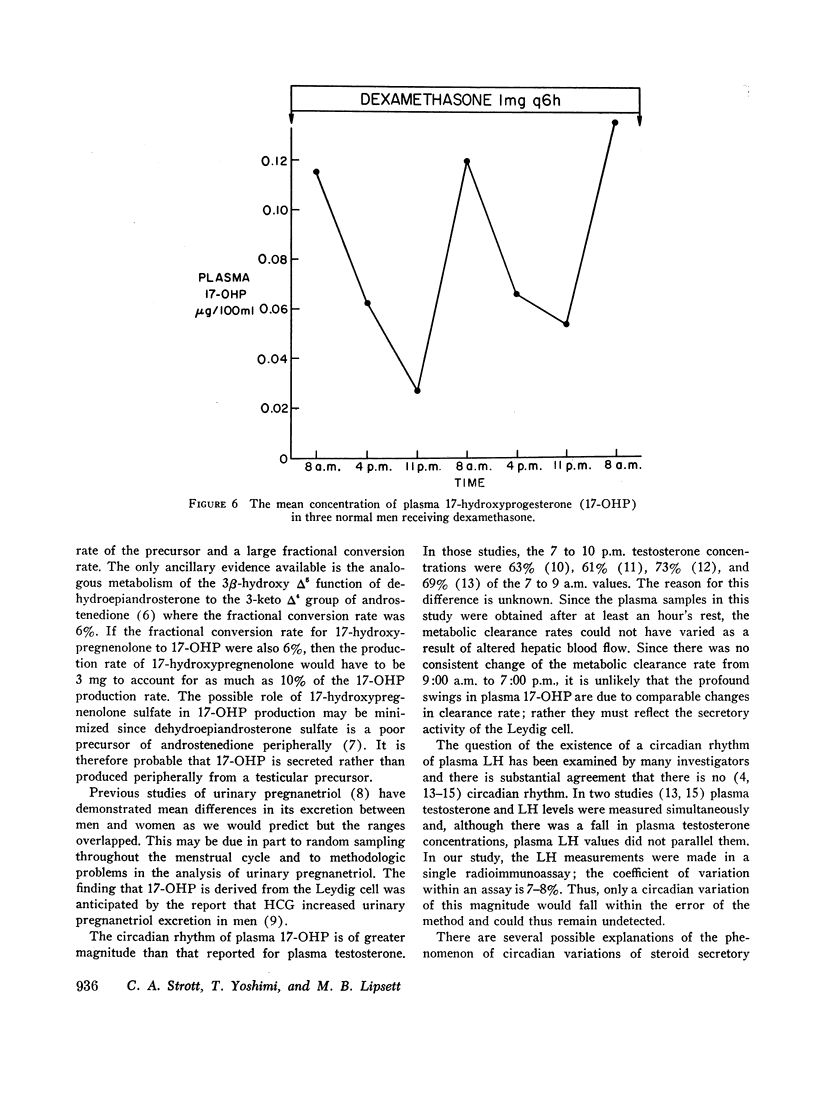
Plasma 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) concentrations in normal men averaged 0.094 μg/100 ml. Studies using suppressive doses of androgens and glucocorticoids showed that 90% of the 17-OHP originated from the Leydig cell. The 17-OHP production rate was 1.8 mg/24 hr. Plasma 17-OHP has a marked circadian variation, the 8 p.m. values being only 40% of the 8 a.m. values. Plasma luteinizing hormone measured in the same samples did not vary.
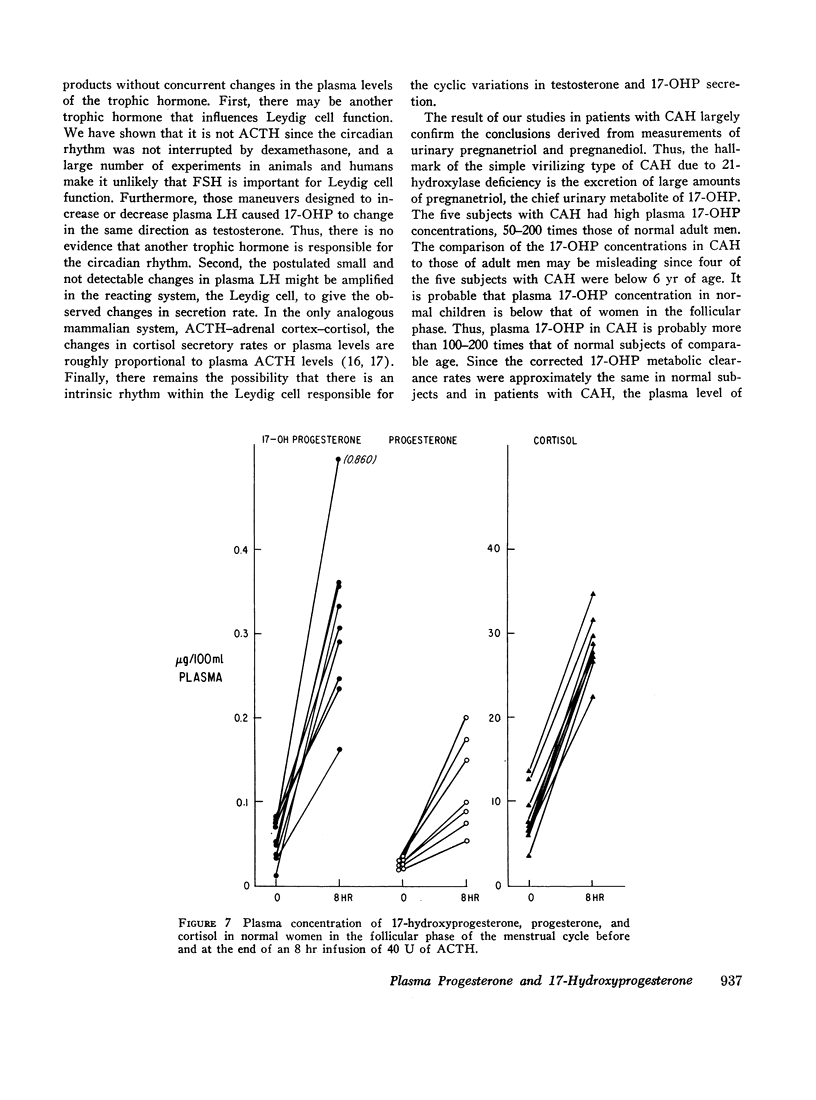
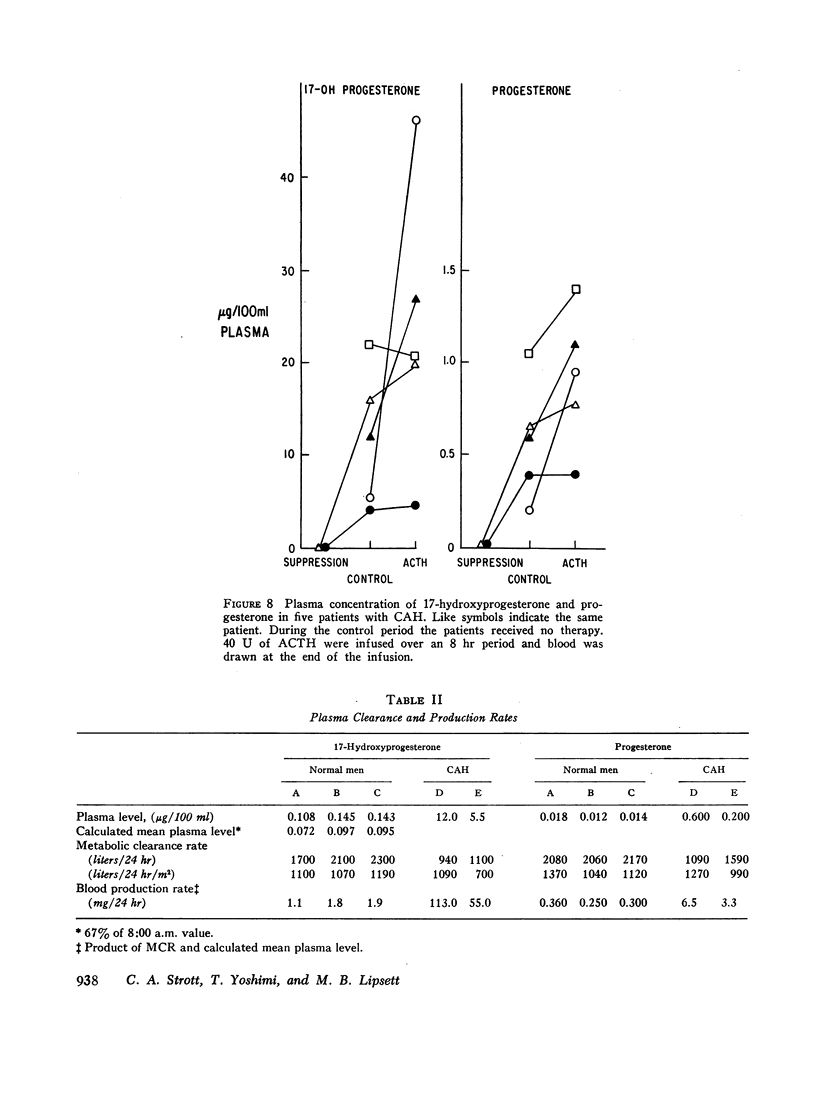
The adrenal cortex has the capacity to synthesize and secrete 17-OHP and progesterone since adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) caused a fourfold increase in these plasma steroids. In children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia, plasma 17-OHP levels were 50-200 times those of normal men and plasma progesterone was increased 6- to 10-fold over normal men.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGSTRAND C. G., GEMZELL C. A. Pregnanediol excretion in normal children and in children with various endocrine disorders, including congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Jul;17(7):870–877. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-7-870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crafts R., Llerena L. A., Guevara A., Lobotsky J., Lloyd C. W. Plasma androgens and 17-hydroxycorticosteroids throughout the day in submarine personnel. Steroids. 1968 Jul;12(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(68)80086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demura H., West C. D., Nugent C. A., Nakagawa K., Tyler F. H. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for plasma ACTH levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Dec;26(12):1297–1302. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-12-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F. Mesure de la testostérone du plasma veineux périphérique chez l'homme adulte par une technique de double dilution isotopique. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47(11):2145–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOTHERBY K., LOVE D. N. A modified method for the estimation of pregnanetriol in urine. J Endocrinol. 1960 Apr;20:157–162. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0200157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUSHIMA D. K., BRADLOW H. L., HELLMAN L., ZUMOFF B., GALLAGHER T. F. Study of 17-hydroxyprogsterone-4-C14 in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Jul;21:765–778. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-7-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faiman C., Ryan R. J. Diurnal cycle in serum concentrations of follicle-stimulating hormone in men. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):857–857. doi: 10.1038/215857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R., Tait J. F. In vivo conversion of dehydroisoandrosterone to plasma androstenedione and testosterone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jan;27(1):79–88. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LAVES M. L. Urinary pregnanetriol of testicular origin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Nov;19:1399–1404. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-11-1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Ross G. T., Rayford P. L. Radioimmunoassay for luteinizing hormone in human plasma or serum: physiological studies. J Clin Invest. 1967 Feb;46(2):248–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI105527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resko J. A., Eik-nes K. B. Diurnal testosterone levels in peripheral plasma of human male subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 May;26(5):573–576. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-5-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER PEET J., DALY J. R., SMITH V. A SIMPLE METHOD FOR IMPROVING THE SPECIFICITY OF THE FLUORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF ADRENAL CORTICOSTEROIDS IN HUMAN PLASMA. J Endocrinol. 1965 Feb;31:235–244. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0310235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena B. B., Demura H., Gandy H. M., Peterson R. E. Radioimmunoassay of human follicle stimulating and luteinizing hormones in plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Apr;28(4):519–534. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-4-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaunwhite W. R., Jr, Burgett M. J., Sandburg A. A. Disposition of dehydroepiandrosterone and its sulfate in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 May;27(5):663–670. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-5-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southren A. L., Tochimoto S., Carmody N. C., Isurugi K. Plasma production rates of testosterone in normal adult men and women and in patients with the syndrome of feminizing testes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Nov;25(11):1441–1450. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-11-1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strott C. A., Lipsett M. B. Measurement of 17-hydroxyprogesterone in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Oct;28(10):1426–1430. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-10-1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strott C. A., Nakagawa K., Nankin H., Nugent C. A. A phenylalanine-lysine-vasopressin test of ACTH release. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Mar;27(3):448–451. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-3-448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strott C. A., Yoshimi T., Bardin C. W., Lipsett M. B. Blood progesterone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels and production rates in a boy with virilizing congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jul;28(7):1085–1088. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-7-1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMEULEN A., SLAUNWHITE W. R., Jr, SANDBERG A. A. Biliary and urinary metabolites of 4-C14-17 Alpha-hydroxyprogesterone in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Dec;21:1534–1542. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-12-1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimi T., Lipsett M. B. The measurement of plasma progesterone. Steroids. 1968 Apr;11(4):527–540. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(68)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



