Abstract
Background
Spodoptera litura is a noctuid moth that is considered an agricultural pest. The larvae feed on a wide range of plants and have been recorded on plants from 40 plant families (mostly dicotyledons). It is a major pest of many crops. To better understand Spodoptera litura granulovirus (SpliGV), the nucleotide sequence of the SpliGV DNA genome was determined and analyzed.
Methodology/Principal Findings
The genome of the SpliGV was completely sequenced. The nucleotide sequence of the SpliGV genome was 124,121 bp long with 61.2% A+T content and contained 133 putative open reading frames (ORFs) of 150 or more nucleotides. The 133 putative ORFs covered 86.3% of the genome. Among these, 31 ORFs were conserved in most completely sequenced baculovirus genomes, 38 were granulovirus (GV)-specific, and 64 were present in some nucleopolyhedroviruses (NPVs) and/or GVs. We proved that 9 of the ORFs were SpliGV specific.
Conclusions/Significance
The genome of SpliGV is 124,121 bp in size. One hundred thirty-three ORFs that putatively encode proteins of 50 or more amino acid residues with minimal overlap were determined. No chitinase or cathepsin genes, which are involved in the liquefaction of the infected host, were found in the SpliGV genome, explaining why SpliGV-infected insects do not degrade in a typical manner. The DNA photolyase gene was first found in the genus Granulovirus. When phylogenic relationships were analyzed, the SpliGV was most closely related to Trichoplusia ni granulovirus (TnGV) and Xestia c-nigrum granulovirus (XecnGV), which belong to the Type I-granuloviruses (Type I-GV).
Introduction
The family Baculoviridae includes invertebrate-specific viruses with circular, covalently closed, double-stranded DNA genomes ranging in size from 80–180 kb [1]. To date, more than 600 baculoviruses have been described to infect species from the insect orders Lepidoptera, Diptera, and Hymenoptera, and it is likely that baculoviruses represent the largest and most diverse family of DNA viruses [2], [3]. Previously, the family Baculoviridae was subdivided into two genera, Nucleopolyhedrovirus (NPV) and Granulovirus (GV), mainly based on the morphology of their occlusion bodies (OBs) [4]. Recently, a proposed reclassification has expanded the family to include four genera: the viruses of Lepidoptera are divided into the Alpha- and Beta-baculoviruses, encompassing the NPVs and GVs, respectively, and those infecting Hymenoptera and Diptera are named the Gamma- and Delta-baculoviruses, respectively [5]. While NPVs have OBs with many virions and have been isolated from lepidopteran and non-lepidopteran hosts, the OBs of GVs each contain a single virion and have only been isolated from lepidopteran insects [6]. The lepidopteran-specific NPVs are further classified into two groups, I and II, based on the phylogenetic analysis of their polyhedrin (polh) genes [7], [8]. GVs cause three distinct types of pathology in infected hosts [9]: Type I-GVs only infect the fat body, usually resulting in a relatively slow speed of killing; Type II-GVs infect most of the insect host's tissues, resulting in a faster speed of killing; and Type III-GVs infect only the midgut epithelium, resulting in the rapid death of the host. At present, Type III-GVs contain only one member, Harrisina brillians granulovirus (HabrGV). Phylogenetic analysis of GV sequences suggests that these different types of GV pathogenesis do not have monophyletic origins [10].
As a novel and steady pesticide, baculoviruses have been used as agents for the biological control of certain insect pest species. Baculoviruses possess several suitable properties, including high efficacy in controlling insect pests and a less negative impact on the environment and non-target species than chemical pesticides [11], [12]. However, their use has been limited due to their slow speed of killing and narrow host specificity. Recent studies have shown that baculoviruses expressing foreign genes, such as a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene and an insect-specific neurotoxin gene have accelerated killing speeds and promise to be effective biological insecticides [13]. To date, GVs have been isolated only from lepidopteran larvae. In particular, GVs infect both agricultural and forest insect pests, making them potentially important as biological insecticides [14].
The tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura, has totally polyphagous noctuid larvae as well as high reproductive potential and the ability to migrate long distances as adults. The host range of S. litura covers over 40 families [15]. Among the main crop species attacked by S. litura in the tropics are Colocasia esculenta, cotton, flax, groundnuts, jute, alfalfa, maize, rice, soybeans, tea, tobacco, and vegetables (including eggplants, brassica, capsicum, cucurbit vegetables, wild bean, potatoes, and sweet potatoes). Other hosts include ornamentals, wild plants, weeds, and shade trees (e.g., Leucaena leucocephala, the shade tree of cocoa plantations in Indonesia). These factors contribute to the role of S. litura as a major pest of many agricultural crops throughout its geographical range, and as a result, many insecticide treatments target this pest [16].
Several properties of baculoviruses, such as their relatively slow killing speed, narrow host spectrum, and high production costs, are disadvantageous. To overcome these disadvantages, it is necessary to develop a better understanding of the biology and pathology of baculoviruses. One approach is to conduct extensive research into diverse viruses that possess distinct biological and pathological characteristics. Detailed information about a wide range of isolates will provide a more comprehensive overview of baculoviruses and help to overcome their shortcomings as biological pest control agents. In this study, to add our knowledge of granulovirus molecular genetics, the complete genome of SpliGV was sequenced and analyzed.
Results and Discussion
Characteristics of the SpliGV genome sequence
So far, 49 baculovirus genomes have been sequenced (Table 1). Thirty-eight NPV genome sequences have been reported, but to date, complete genome sequences have only been reported for seven GVs [1], [17]–[22], with genome sequences for another four GVs (from Phthorimaea operculella, Agrotis segetum, Pseudaletia unipuncta and Pieris rapae) on file in GenBank. A 6× sequence of the SpliGV genome was compiled from all sequence data generated. The size of the final draft sequence was 124,121 nt. The SpliGV genome has an A+T content of 61.2%, which is closest to that of Pseudaletia unipuncta GV (60.2%) (PsunGV, GenBank accession no. EU678671). Among GV genomes, that of Cryptophlebia leucotreta GV (CrleGV) has the highest A+T content, 67.6%, and that of Cydia pomonella granulovirus (CpGV) has the lowest A+T content, 54.8%. Coding sequences represent 86.3% of the genome of SpliGV.
Table 1. Characteristics of baculovirus genomes (February 2010).
| Virus | No.ORFs | Genomesize (bp) | Accession No. | AT content(%) | Sequenced |
| Autographa californica MNPV | 155 | 133,894 | NC_001623 | 59.3 | 1994–07–16 |
| Bombyx mori NPV | 143 | 128,413 | NC_001962 | 59.6 | 1996–01–18 |
| Orgyia pseudotsugata MNPV | 152 | 131,995 | NC_001875 | 44.9 | 1997–03–27 |
| Mamestra configurata NPV–A | 169 | 155,060 | NC_003529 | 58.3 | 1997-03–29 |
| Lymantria dispar MNPV | 166 | 161,046 | NC_001973 | 42.5 | 1998–11–03 |
| Spodoptera exigua MNPV | 139 | 135,611 | NC_002169 | 56.2 | 1999-12–29 |
| Helicoverpa armigera NPV (G4) | 135 | 131,403 | NC_002654 | 61.0 | 2001–01-25 |
| Epiphyas postvittana NPV | 136 | 118,584 | NC_003083 | 59.3 | 2001–08–19 |
| Culex nigripalpus NPV | 109 | 108,252 | NC_003084 | 49.1 | 2001–08-22 |
| Helicoverpa armigera NPV | 134 | 130,759 | NC_003094 | 61.1 | 2001–08–31 |
| Spodoptera litura NPV | 141 | 139,342 | NC_003102 | 57.2 | 2001–09–11 |
| Helicoverpa zea SNPV | 139 | 130,869 | NC_003349 | 60.9 | 2002-01–01 |
| Mamestra configurata NPV–B | 168 | 158,482 | NC_004117 | 60.0 | 2002–08–25 |
| Rachiplusia ou MNPV | 146 | 131,526 | NC_004323 | 60.9 | 2002–10–02 |
| Adoxophyes honmai NPV | 125 | 113,220 | NC_004690 | 64.4 | 2003–04–05 |
| Choristoneura fumiferana MNPV | 145 | 129,593 | NC_004778 | 49.9 | 2003–05–06 |
| Choristoneura fumiferana DEF NPV | 149 | 131,160 | NC_005137 | 54.2 | 2003–10–11 |
| Neodiprion sertifer NPV | 90 | 86,462 | NC_005905 | 66.2 | 2004–06–17 |
| Neodiprion lecontei NPV | 90 | 81,755 | NC_005906 | 66.7 | 2004–06–17 |
| Chrysodeixis chalcites NPV | 151 | 149,622 | NC_007151 | 60.9 | 2005–06–29 |
| Trichoplusia ni SNPV | 144 | 134,394 | NC_007383 | 61.0 | 2005–09–07 |
| Hyphantria cunea NPV | 148 | 132,959 | NC_007767 | 54.5 | 2006–02–02 |
| Agrotis segetum MNPV | 153 | 147,544 | NC_007921 | 54.3 | 2006–03–27 |
| Antheraea pernyi NPV | 147 | 126,630 | NC_008035 | 46.5 | 2006–05–16 |
| Neodiprion abietis NPV | 93 | 84,264 | NC_008252 | 66.6 | 2006–07–24 |
| Clanis bilineata NPV | 129 | 135,454 | NC_008293 | 62.3 | 2006–08–24 |
| Plutella xylostella MNPV | 152 | 134,417 | NC_008349 | 59.3 | 2006–09–16 |
| Leucania separata NPV | 169 | 168,041 | NC_008348 | 51.4 | 2006–09–16 |
| Anticarsia gemmatalis NPV | 152 | 132,239 | NC_008520 | 55.5 | 2006–10–21 |
| Ecotropis obliqua NPV | 126 | 131,204 | NC_008586 | 62.4 | 2006–11–21 |
| Maruca vitrata MNPV | 126 | 111,953 | NC_008725 | 61.4 | 2006–12–27 |
| Spodoptera frugiperda MNPV | 142 | 131,330 | NC_009011 | 59.6 | 2007–02–16 |
| Orgyia leucostigma NPV | 135 | 156,179 | NC_010276 | 60.1 | 2008–01–18 |
| Agrotis ipsilon MNPV | 163 | 155,122 | NC_011345 | 51.4 | 2008–10–08 |
| Helicoverpa armigera SNPV NNg1 | 143 | 132,425 | NC_011354 | 60.9 | 2008–10–28 |
| Adoxophyes orana NPV | 121 | 111,724 | NC_011423 | 65.0 | 2008–10–28 |
| Helicoverpa armigera MNPV | 162 | 154,196 | NC_011615 | 59.9 | 2008–12–01 |
| Spodoptera litura NPV (II) | 147 | 148,634 | NC_011616 | 55.0 | 2008–12–01 |
| Xestia c-nigrum GV | 181 | 178,733 | NC_002593 | 59.3 | 2000–06–07 |
| Plutella xylostella GV | 120 | 100,999 | NC_002331 | 59.3 | 2000–10–29 |
| Cydia pomonella GV | 143 | 123,500 | NC_002816 | 54.8 | 2001–04–02 |
| Phthorimaea operculella GV | 130 | 119,217 | NC_004062 | 64.3 | 2002–07–01 |
| Adoxophyes orana GV | 119 | 99,657 | NC_005038 | 65.5 | 2003–07–15 |
| Cryptophlebia leucotreta GV | 129 | 110,907 | NC_005068 | 67.6 | 2003–08–13 |
| Agrotis segetum GV | 132 | 131,680 | NC_005839 | 62.7 | 2004–04–09 |
| Choristoneura occidentalis GV | 116 | 104,710 | NC_008168 | 67.3 | 2006–06–19 |
| Spodoptera litura GV | 133 | 124,121 | NC_009503 | 61.2 | 2007–05–30 |
| Helicoverpa armigera GV | 179 | 169,794 | NC_010240 | 59.2 | 2008–01–09 |
| Pseudaletia unipuncta GV | 183 | 176,677 | EU678671 | 60.2 | 2008–10–31 |
| Pieris rapae GV | 120 | 108,592 | NC_013797 | 67.0 | 2010–02–11 |
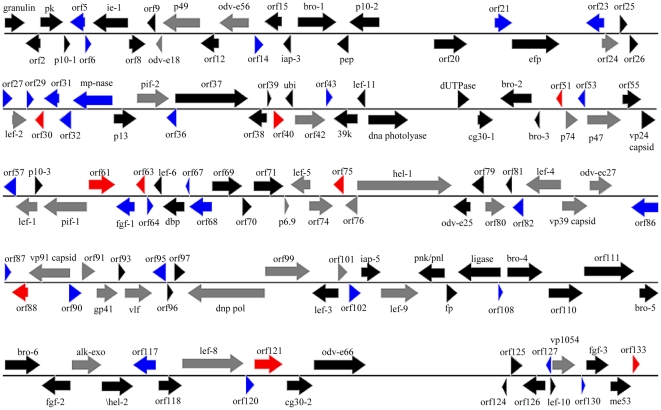
One hundred thirty-three ORFs of at least 50 codons in length that had minimal overlap with larger ORFs or shared significant sequence identity with previously characterized baculovirus ORFs were identified (Fig. 1). Among these, 31 ORFs were conserved in most completely sequenced baculovirus genomes, 38 were GV-specific, and 64 were present in some NPVs and/or GVs. By convention, the first nucleotide of the methionine start codon of the granulin gene was defined as nucleotide 1 of the genome, and the sequence was numbered in the direction of transcription of the granulin gene. As with other baculovirus genomes, the ORFs were randomly distributed with 77 ORFs in the granulin-sense orientation and 56 in the opposite orientation. Canonical baculovirus early and late gene promoter sequences were associated with 119 ORFs of the SpliGV (Table S1). As we have known, there is little overlap in baculovirus genomic DNAs. Minimal overlaps (less than 16 codons) were observed between 57 adjacent ORFs. More notably, greater levels of overlap were found between Spli22 and Spli23 (62 bp), Spli23 and Spli24 (110 bp), Spli35 and Spli36 (108 bp), Spli58 and Spli59 (110 bp), Spli74 and Spli75 (57 bp), Spli107 and Spli108 (113 bp), and Spli128 and Spli129 (152 bp) (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Representation of the SpliGV genome.
ORFs and transcriptional direction are indicated by arrows. The ORFs present in most completely sequenced baculovirus genomes are colored gray; GV-specific ORFs are in blue; SpliGV unique ORFs are in red; and ORFs present in some NPVs and/or some GVs are in black.
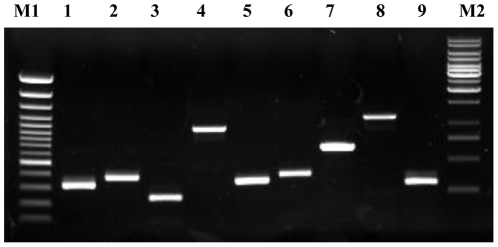
BLAST comparisons of the nucleotide sequences and the deduced amino acid sequences of 133 ORFs of SpliGV indicated that 9 ORFs have no similarity to any reported baculovirus genes. We proved that these 9 SpliGV-specific ORFs could be transcribed from the SpliGV genome by RT-PCR (Fig. 2). These 9 ORFs were named Spli30, Spli40, Spli51, Spli61, Spli63, Spli75, Spli88, Spli121, and Spli133. Except for Spli51, the other SpliGV-specific ORFs had some similarities to genes from other microbes.
Figure 2. RT-PCR of 9 SpliGV-specific ORFs using mRNAs from S. litura larvae infected with SpliGV as a template.
M1, 100-bp DNA ladder (Fermentas, USA); 1, Spli30; 2, Spli40; 3, Spli51; 4, Spli61; 5, Spli63; 6, Spli75; 7, Spli88; 8, Spli121; 9, Spli133; M2, 1-kb DNA ladder (Fermentas, USA).
Relationships with other baculoviruses
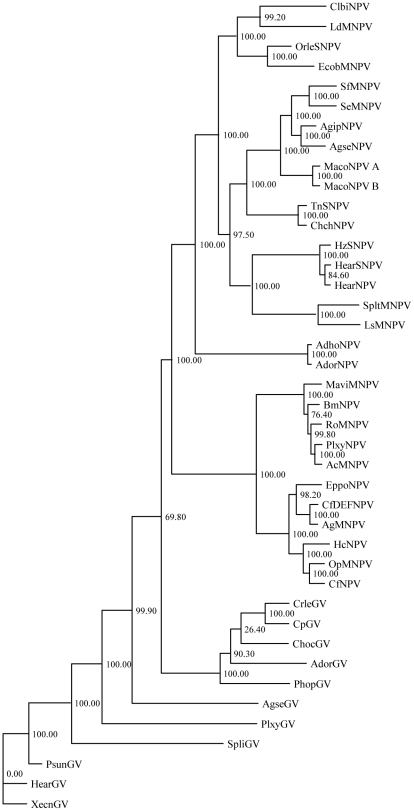
Previously, when the nucleotide and the deduced amino acid sequences of the SpliGV granulin gene were aligned with those of granulin and polyhedrin genes from other baculoviruses, SpliGV was most closely related to TnGV and XecnGV, which belong to the Type I-GVs [23]. To further investigate to the relationship between SpliGV and other baculoviruses, phylogenetic trees were inferred from a set of concatenated, aligned, partial amino acid sequences of 24 genes from SpliGV and 40 other completely sequenced lepidopteran baculoviruses (Fig. 3). This result did not confirm a clear relationship between SpliGV and XecnGV, as shown in Figure 3. However, we can place SpliGV and XecnGV in a clade of closely related GVs isolated from Lepidoptera of the family Noctuidae, including AgseGV, Plutella xylostella GV (PlxyGV), PsunGV and Helicoverpa armigera GV (HearGV). These viruses, along with XecnGV, are considered to be isolates of the same virus species [2].
Figure 3. Phylogenic relationship between 41 complete baculovirus genomes based on the nucleotide sequences of 24 genes.
The numbers on the branches represent bootstrap values for 1,000 replicates.
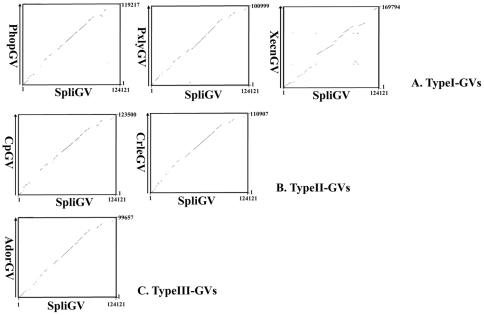
Dot plot sequence comparisons revealed a strong degree of co-linearity between the genome of SpliGV and those of other GVs (Fig. 4). SpliGV lacked many of the ORFs found in XecnGV, which is expected given the significantly smaller size of the genome of SpliGV. Comparison of the SpliGV genome with that of Spodoptera litura multicapsid NPV (SpltMNPV) revealed that the order of some ORFs was conserved between the two viruses, but the orientation of a large proportion of these ORFs was inverted relative to the polyhedron gene (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Nucleotide sequence comparison of the SpliGV genome and other GV genomes by matrix dot plot.
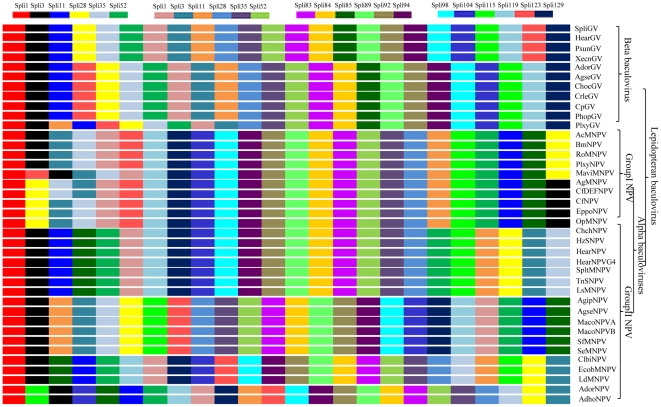
Comparative analysis of the gene organization of the SpliGV genome with those of 44 other baculoviruses was carried out using a gene order diagram (GOD) (Fig. 5). The GOD analysis was performed using the 24 genes of the SpliGV genome along with those of 44 other baculoviruses. Homologs of the 24 genes of the SpliGV genome are found in all 40 of the lepidopteran baculovirus genomes. However, some of these homologs have been lost from the three hymenopterous baculovirus genomes and the one dipteran baculovirus genome (Fig. 5). The homologs of Spli73, Spli77, Spli78, Spli83, Spli84, Spli89, Spli92, Spli94, and Spli98 occur in the same order in all 44 lepidopteran baculovirus genomes in either the forward direction or reverse direction relative to the SpliGV genome. In all of the lepidopteran GV genomes, a total of 13 homologs of genes of the SpliGV genome, including Spli55, Spli104, Spli115, and Spli119 as well as the homologs found in all of the lepidopteran baculovirus genomes, are organize in the same order and direction as in the SpliGV genome (Fig. 5). We also found that the order of the SpliGV gene homologs was generally more conserved in the group I NPVs than in the group II NPVs (Fig. 5). The GOD analysis technique may be able to supplement other baculovirus classification methods.
Figure 5. Gene order diagram of 24 genes from 45 complete baculovirus genomes.
SpliGV genes involved in DNA replication and transcription
There are 19 lef genes in Autographa californica multicapsid NPV (AcMNPV) that have been implicated in DNA replication and transcription [24]. Early baculovirus genes are transcribed by the host cell RNA polymerase II, but these genes are often transactivated by genes such as ie-0, ie-1, ie-2, and pe38 [25]. Among these genes, only ie-1 is present in the SpliGV genome (Table 2). Both ie-2 and pe38 are also absent from all group II NPVs and GVs with the exception of CpGV and PhopGV, which have a pe38 gene [22]. Six genes have been reported to be essential for baculovirus DNA replication: lef-1, lef-2, lef-3, dnapol, helicase, and ie-1 [26]. Homologs of all of these essential genes are present in SpliGV (Table 2). They are moderately well conserved, with the exception of lef-3 and ie-1 (Table 2). SpliGV does not have the lef-7 or lef-12 typically found in group I NPVs. SpliGV encodes a DNA ligase (Spli107) and a second helicase (Spli116) (Table 2), as do Lymantria dispar multicapsid NPV (LdMNPV) and other GVs. In LdMNPV, neither the helicase-2 nor the dna ligase gene stimulates DNA replication in transient assays. As their homologs are involved in DNA repair and recombination, these genes could also be involved in DNA repair [27].
Table 2. SpliGV genes grouped according to functional comparison with other baculoviruses.
| Genes present in SpliGV | Genes missing in SpliGV | |
| Transcription | 39 K (Spli44), lef-11 (Spli45), p47 (54), lef-6 (Spli 65), lef-5 (Spli73), lef-4 (Spli83), vlf (Spli94), lef-9 (Spli104), lef-8 (Spli119) | p26 (Ac136), pe38 (Ac153) |
| Replication | ie (Spli7), lef-2 (Spli28), dUTPase (Spli47), lef-1 (Spli58), dbp (Spli66), 38 k (Spli74), hel-1 (Spli77), dna pol (Spli98), lef-3 (Spli100), pnk/pnl (Spli105), dna ligase (Spli107), hel-2 (Spli116), me53 (Spli132) | ptp (Ac1), lef-7 (Ac125), ie0 (Ac147-0), nudix (Ac38), ie2 (Ac151), pnk polynucelotide kinase (Ac33), rr1 (Cp127), rr2 (Cp128) |
| Structural | granulin (Spli1), pk (Spli3), p10-1 (Spli4), odv-e18 (Spli10), odv-e56 (Spli13), pep (Spli18), p10-2 (Spli19), efp (Spli22), pif-3 (Spli24), p1 3(Spli34), pif-2 (Spli35), cg30-1 (Spli48), p74 (Spli52), vp24capsid (Spli56), p10-3 (Spli59), pif-1 (Spli60), bv/odv-c42 (Spli71), p6.9 (Spli72), pif-4 (Spli76), odv-e25 (Spli78), p33 (Spli80), vp39 capsid (Spli84), odv-ec27 (Spli85), vp91capsid (Spli89), tlp20 (Spli90), gp41 (Spli92), desmop (Spli99), fp (Spli106), cg30-2 (Spli122), odv-e66 (Spli123), vp1054 (Spli129) | bv/odv-e26 (Ac16), pkip (Ac24), gp64 (Ac128), vp80,vp87 (Ac104), exon-0 (Ac141) |
| Auxiliary | p49 (Spli11), iap-3 (Spli16), bro-1 (Spli17), lef-10 (Spli128), mp-nase (Spli33), ubi (Spli41), dna photolyase (Spli46), bro-2 (Spli49), bro-3 (Spli50), fgf-1 (Spli62), iap-5 (Spli103), bro-4 (Spli109), bro-5 (Spli112), bro-6 (Spli113), fgf-2 (Spli114), alk-exo (Spli115), fgf-3 (Spli131) | p94 (Xecn21), cathepsin (Xecn58), sod (Xecn68), chitinase (Xecn103), gp37 (Xecn107), ctl (Xecn127), enhancin-1 (Xecn150), enhancin-2 (Xecn152), enhancin-3 (Xecn154), enhancin-4 (Xecn166), lef-12 (Ac41) |
| Unknown | Spli2, Spli5, Spli6, Spli8, Spli9, Spli12, Spli14, Spli15, Spli20, Spli21, Spli23, Spli25, Spli26, Spli27, Spli29, Spli31, Spli32, Spli36, Spli37, Spli38, Spli39, Spli42, Spli43, Spli53, Spli55, Spli57, Spli64, Spli67, Spli68, Spli69, Spli70, Spli79, Spli81, Spli82, Spli86, Spli87, Spli91, Spli93, Spli95, Spli96, Spli97, Spli101, Spli102, Spli108, Spli110, Spli111, Spli117, Spli118, Spli120, Spli124, Spli125, Spli126, Spli127, Spli130 | |
| SpliGV unique | Spli30, Spli40, Spli51, Spli61, Spli63, Spli75, Spli88, Spli121, Spli133 |
SpliGV lacks genes for enzymatic functions in nucleotide metabolism, such as the large (rr1) and small (rr2) subunits of ribonucleotide reductase, but it does have the deoxyuridyltriphosphate (dUTPase) gene (Table 2). These enzymes are found in several baculoviruses and are involved in nucleotide metabolism. They catalyze the reduction of host cell rNTPs to dNTPs [1].
Many genes required for late gene transcription have been described, including lef-4, lef -6, lef -8, lef -9, lef -10, lef -11, 39 k, p47, and vlf-1 [28]. All of these genes are found in SpliGV (Table 2). Generally, these genes are more conserved than the early transcription activators [29]. The lef-6 genes of GVs are smaller than the lef-6 genes of NPVs (86–102 amino acids vs. 138–187 amino acids).
SpliGV structural genes
The most conserved baculovirus structural protein is polyhedrin/granulin (93% maximal amino acid identity), the major component of OBs [30]. SpliGV lacked homologs of two structural genes, the p80/87-capsid gene and ORF 1629 (p78/73). The p80/87-capsid gene is also absent from the other sequenced GVs. A putative ORF 1629 (Xecn2) has been identified in XecnGV (Xecn2), although it is less than half the size of the NPV ORFs and has similarity concentrated only around a conserved proline-rich region [20]. Except for HearGV, all of the GVs have a Xcen2 homolog with similarity in the first 65 aa of the amino-terminal region of the protein but show no similarity to ORF 1629 and do not contain a proline-rich region. Pep is found on the surface of the OBs and is important for the formation of polyhedra, as it stabilizes them and prevents them from fusing [31]. SpliGV does have a pep (Spli18) that shares 55% amino acid identity with its homolog from XecnGV, Xecn18 (Table 2).
Occlusion-derived viruses (ODVs) contain more than 10 different envelope proteins. Five of these, denoted pif-1, pif-2, pif-3, pif-4, and p74, have been identified as essential for per os infection of insect larvae [32]–[36]. All five proteins are highly conserved in Baculoviridae and are encoded by the so-called core genes [32], [37]–[39]. These PIF proteins function in the early stage of virus infection, and deletion of any of these pif genes leads to a block in infection prior to viral gene expression in midgut epithelial cells [33], [35], [40]. All five genes involved in per os infectivity were present in SpliGV (Table 2). In the SpliGV genome, p74 encodes a small, truncated protein (144 aa) containing the conserved C-terminal region of the XcenGV p74 (Xcen77) gene (43% identity over 140 aa), but the p74 of SpliGV is substantially shorter than that of XcenGV (144 aa vs. 710 aa).
In NPV-infected cells, P10 forms fibrillar structures in the nucleus and cytoplasm [21]. This protein is implicated in OB morphogenesis and disintegration of the nuclear matrix, resulting in the dissemination of OBs [41]. P10 proteins from different baculoviruses are characterized by the size differences in their shared domains, and their sequences are generally poorly conserved [17]. Three XcenGV ORFs (Xcen5, Xcen19, and Xcen83) present similarities to p10. Homologs of these three ORFs are present in PlxyGV (Plxy2, Plxy21, and Plxy50), and Hashimoto et al. [19] suggested that they are all p10 homologs. SpliGV contained homologs of the three putative p10 genes of XcenGV, which are Spli4, Spli19, and Spli59 (Table 2). They showed maximal similarity to Xcen5, Xcen19, and Xcen83, respectively. Whereas Spli4 (p10–1) and Spli19 (p10–2) have a proline-rich domain and a heptad sequence, Spli59 (p10–3) has only a heptad sequence significantly smaller than that of Xcen83 (97 vs. 182 amino acids). The close association of P10 and the polyhedron envelope has been well documented in many NPVs, and it has been known that the presence of P10 is essential for the formation of the polyhedron envelope [17]. In some GVs, the functional association of PEP and P10 might have been conserved in a single protein [1]. Further work must be done to fully understand the role of the different p10 homologs in SpliGV.
SpliGV auxiliary genes
Auxiliary genes are not essential for viral replication, but they do provide some selective advantages [42]. SpliGV does not contain either a chitinase or a cathepsin gene. It appears that baculoviruses encode these enzymes to aid breakdown of insect tissues at the end of infection to release OBs into the environment and thereby aid their horizontal spread. SpliGV-infected larvae do not lyse at the end of infection. The cadavers of S. litura larvae infected by SpliGV appeared smaller than normal larvae, as if they had lost much water, and they were very soft.
Enhancin is a metalloproteinase that disrupts the insect peritrophic membrane, facilitating the initiation of infection [43], [44]. These genes were first found in GV OBs, which can enhance the infection of some NPVs. Also referred to as viral enhancing or synergistic factors, enhancins were first identified and isolated by Tanada and colleagues [45]. Enhancin genes have been found in several GVs, including HearGV [46], PsunGV [46], TnGV [47], XecnGV [20], AgseGV (GenBank: AY522332), and ChfuGV (GenBank: AAG33872). The first GV genome to be completely sequenced, that of XecnGV, was found to have four different enhancin genes [20]. In contrast, no enhancin homolog is present in SpliGV.
Superoxide dismutase (sod) is a well-conserved gene of baculoviruses. This gene is presumably involved in the removal of free radicals but is non-essential, and its role in the virus life cycle is not known [48]. Of all of the GVs that have been sequenced to date, SpliGV is not the only one to lack sod; sod is also not found in a few NPV genomes.
Ubiquitin is the most conserved auxiliary gene and is present in all sequenced baculovirus genomes. The main function of cellular ubiquitin is to signal protein degradation [49]. Viral ubiquitin is nonessential, and its role is unclear [50]. SpliGV contains a homolog of ubiquitin, Spli41 (Table 2).
Another SpliGV ORF of interest is Spli46, a homolog of the DNA photolyase gene (Table 2). DNA photolyase genes encode photoactive enzymes that are involved in the repair of UV-damaged DNA [51]. To date, in the sequenced baculoviruses other than SpliGV, photolyase genes are found only in ChchNPV and Trichoplusia ni NPV (TnNPV).
Inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP)
Apoptosis represents an important virus-host interaction process that probably influences viral pathogenesis. As an antiviral response in multicellular organisms, apoptosis can limit viruses in the suicide cells, thereby reducing the yield of progeny viruses, which results in abortive infection [52], [53]. Although many viruses, including baculoviruses, can trigger apoptosis in infected cells, they can synthesize proteins that prevent apoptosis [54]–[57]. Baculoviruses possess two families of genes that suppress apoptosis, the p35/p49 family and the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family. P35 was the first antiapoptotic baculovirus protein discovered, and it has only been indentified in AcMNPV, Bombyx mori NPV (BmNPV), SpliMNPV, and Maruca vitrata MNPV (MaviMNPV) [58]–[60]. A larger p35 homolog, p49, has been found in some baculoviruses [57], [60]. P49 has a similar three-dimensional structure and the same mode of action as P35. However, P49 is able to inhibit initiator caspases that P35 is unable to inhibit [57], [61], [62]. All baculoviruses have been found to contain IAP homologs. The IAP-3 protein of CpGV was the first member of the baculovirus IAP family to be indentified [56]. IAP homologs generally contain two baculovirus IAP repeats (BIR), which are associated with binding to apoptosis-inducing proteins, and a C-terminal zinc finger-like (RING) Cys/His motif [54], [56], [63]. According to amino acid sequence similarity, baculovirus IAPs can be divided into five types, named iap-1 through iap-5 [21]. There are two IAP genes, iap-3 (Spli16) and iap-5 (Spli103), and one p49 (Spli11) gene in the genome of SpliGV (Table 2).
Baculovirus repeated ORFs (bro genes)
One to sixteen copies of bro are present in all lepidopteran and dipteran NPVs sequenced to date and in some of GVs. They comprise a highly repetitive and conserved gene family that is widespread among insect DNA viruses [64]. Gene expression, nucleic acid binding activity, nucleosome association, protein localization and protein trafficking have been characterized for some NPV bro genes and proteins, but the functions of bro gene products in the baculovirus life cycle are still unclear [64]–[68]. SpliGV has 6 bro genes, named bro-1 to bro-6 based on their order in the genome, including homologs of XecnGV bro-a (Xecn60), bro-b (Xecn76), bro-e (Xecn130), and bro-f (Xecn131) (Table 2). In SpliGV, there are two adjacent pairs of bro ORFs (bro-2 and bro-3; bro-5 and bro-6). Interestingly, the bro-1, bro-4, and bro-6 genes are all homologs of Xecn60 (Table 2). The bro-3 gene of SpliGV encodes a small, truncated protein (67 aa) containing the conserved N-terminal region of the Xecn76 homolog.
Materials and Methods
Viral DNA extraction
The granules produced in larval cadavers were purified by a standard method [69]. To extract virus DNA, the purified granules were resuspended in 0.1 M sodium carbonate solution [0.1 M Na2CO3, 0.17 M NaCl, 0.01 M EDTA (pH 10.9)] and incubated at 37°C overnight with 0.5 mg/ml proteinase K (Sigma) and 1% SDS. A further extraction with phenol and chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24∶1) was performed, and the DNA was ethanol precipitated. The DNA was resuspended in TE buffer [10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8; 1 mM EDTA].
Sequencing and sequence analysis of SpliGV genomic DNA
The complete nucleotide sequence of SpliGV genomic DNA was determined using a shotgun strategy on an ABI Model 3700 sequencer (PE-Applied Biosystems, USA). The SpliGV DNA sequence was determined at least six times, and additional assessments were carried out for ambiguous sequences using gene-specific primers. Putative coding regions of the SpliGV genome were predicted using FGENESV0 (http://www.softberry.com/berry.phtml) [70] and the NCBI ORF finder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html) by locating translation start and stop codons of ORFs of 50 or more amino acids. Dot plot sequence comparisons were generated with Advanced PipMaker (http://pipmaker.bx.psu.edu/cgi-bin/pipmaker?advanced). Predicted amino acid sequence identities were obtained from the results of protein database searches using the standard protein-protein BLAST algorithm (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). The genomic DNA sequence was deposited in GenBank under the accession number NC990503.
Phylogenetic analysis
For phylogenetic analysis, 24 genes from 30 NPVs and 10 GVs, which all have homologs in the SpliGV genome, were obtained from GenBank. Phylogenetic analysis was carried out using the maximum-parsimony (MP) method [71] incorporated in the parsimony program PAUP (Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony and Other Methods) version 4.0 b10 program [72]. The reliability of the trees was tested with bootstrap re-sampling using 1,000 replicates.
Total RNA extraction and RT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from infected S. litura larvae with TRIZOL® Reagent (Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed using AccuPower® RT/PCR PreMix (Bioneer, Korea) with SpliGV unique gene primer sets (Table S2). One microgram of total RNA and 20 pmol reverse primers were mixed, incubated at 70°C for 5 min and placed on ice. The incubated mixtures and 20 pmol forward primers were transferred to an AccuPower® RT/PCR PreMix tube, and the reaction volumes were brought up to 20 microliters with DEPC-DW. cDNA synthesis reactions and DNA PCR reactions were performed under the following temperature cycles: one cycle at 42°C for 60 min; 94°C for 5 min; one cycle at 94°C for 30 sec, 50°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 90 sec; 33 cycles at 94°C for 30 sec, 55°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 90 sec; and 1 cycle at 94°C for 30 sec, 55°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 7 min.
Supporting Information
Predicted SpliGV ORFs by BLAST Search.
(DOC)
Primers used to confirm new SpliGV genes.
(DOC)
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (No. PJ008036), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea. YW, QL, XYT, and JBP were supported by 2nd stage of the Brain Korea 21 project. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Lange M, Jehle JA. The genome of the Cryptophlebia leucotreta granulovirus. Virology. 2003;317:220–236. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Martignoni ME, Iwai PJ. A catalogue of viral diseases of insects, mites and ticks. In: Burges HD, editor. Microbial Control of Pests and Plant Diseases. New York & London: Academic Press; 1981. pp. 879–911. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Murphy FA, Fauquet CM, Bishop DHL, Ghabrial SA, Jarvis AW, et al. Virus Taxonomy - 6th Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Arch Virol Suppl. 1995;10:1–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Regenmortel MHV, Carstens EB, Estes MK, Lemon SM, Maniloff J, et al. San Diego: Academic Press; 2000. Virus Taxonomy-Seventh Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1162 p. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jehle JA, Blissard GW, Bonning BC, Cory JS, Herniou EA, et al. On the classification and nomenclature of baculoviruses: a proposal for revision. Arch Virol. 2006;151:1257–1266. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0763-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Theilmann DA, Bissard GW, Bonning B, Jehle JA, O'Reilly DR, et al. Baculovirudae. In: Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA, editors. Virus Taxonomy: Eighth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. London: Academic Press; 2005. pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zanotto PMD, Kessing BD, Maruniak JE. Phylogenetic interrelationships among baculoviruses - evolutionary rates and host associations. J Invertebr Pathol. 1993;62:147–164. doi: 10.1006/jipa.1993.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bulach DM, Kumar CA, Zaia A, Liang BF, Tribe DE. Group II nucleopolyhedrovirus subgroups revealed by phylogenetic analysis of polyhedrin and DNA polymerase gene sequences. J Invertebr Pathol. 1999;73:59–73. doi: 10.1006/jipa.1998.4797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Federici BA. Baculovirus pathogenesis. In: Miller LK, editor. The Baculoviruses. New York: Plenum Press; 1997. pp. 33–59. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jehle JA, Lange M, Wang H, Hu Z, Wang Y, et al. Molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis of baculoviruses from Lepidoptera. Virology. 2006;346:180–193. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nakai M, Goto C, Kang W, Shikata M, Luque T, et al. Genome sequence and organization of a nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from the smaller tea tortrix, Adoxophyes honmai. Virology. 2003;316:171–183. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2003.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang XX, Liang ZP, Peng HY, Zhang ZX, Tang XC, et al. Characterization and partial genome sequence analysis of Clostera anachoreta granulovirus. Virus Res. 2005;113:36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shim HJ, Choi JY, Li MS, Wang Y, Roh JY, et al. A novel recombinant baculovirus expressing insect neurotoxin and producing occlusion bodies that contain Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxin. J Asia-Pac Entomol. 2009;12:217–220. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rashidan KK, Nassoury N, Giannopoulos PN, Mauffette Y, Guertin C. Identification, characterization and phylogenic analysis of conserved genes within the odvp-6e/odv-e56 gene region of Choristoneura fumiferana granulovirus. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;37:206–212. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2004.37.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Salama HS, Dimetry NZ, Salem SA. On the host preference and biology of the cotton leaf worm Spodoptera littoralis. J Appl Entmol. 1971;67:261–266. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Armes NJ, Wightman JA, Jadhav DR, Rao GVR. Status of insecticide resistance in Spodoptera litura in Andhra Pradesh, India. Pestic Sci. 1997;50:240–248. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Escasa SR, Lauzon HA, Mathur AC, Krell PJ, Arif BM. Sequence analysis of the Choristoneura occidentalis granulovirus genome. J Gen Virol. 2006;87:1917–1933. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81792-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Harrison RL, Popham HJ. Genomic sequence analysis of a granulovirus isolated from the Old World bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Virus Genes. 2008;36:565–581. doi: 10.1007/s11262-008-0218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hashimoto Y, Hayakawa T, Ueno Y, Fujita T, Sano Y, et al. Sequence analysis of the Plutella xylostella granulovirus genome. Virology. 2000;275:358–372. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hayakawa T, Ko R, Okano K, Seong SI, Goto C, et al. Sequence analysis of the Xestia c-nigrum granulovirus genome. Virology. 1999;262:277–297. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Luque T, Finch R, Crook N, O'Reilly DR, Winstanley D. The complete sequence of the Cydia pomonella granulovirus genome. J Gen Virol. 2001;82:2531–2547. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-82-10-2531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wormleaton S, Kuzio J, Winstanley D. The complete sequence of the Adoxophyes orana granulovirus genome. Virology. 2003;311:350–365. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang Y, Choi JY, Roh JY, Woo SD, Jin BR, et al. Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of Spodoptera litura granulovirus. J Microbiol. 2008;46:704–708. doi: 10.1007/s12275-008-0133-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rapp JC, Wilson JA, Miller LK. Nineteen baculovirus open reading frames, including LEF-12, support late gene expression. J Virol. 1998;72:10197–10206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.12.10197-10206.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Friesen PD. Regulation of baculovirus early gene expression. In: Miller LK, editor. The Baculoviruses. New York: Plenum Press; 1997. pp. 141–170. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lu A, Krell PJ, Vlak JM, Rohrmann GF. Baculovirus and replication. In: Miller LK, editor. The Baculoviruses. New York: Plenum Press; 1997. pp. 171–192. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuzio J, Pearson MN, Harwood SH, Funk CJ, Evans JT, et al. Sequence and analysis of the genome of a baculovirus pathogenic for Lymantria dispar. Virology. 1999;253:17–34. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lu A, Miller LK. Regulation of baculovirus late and very late gene expression. In: Miller LK, editor. The Baculoviruses. New York: Plenum Press; 1997. pp. 193–216. [Google Scholar]
- 29.IJkel WFJ, van Strien EA, Heldens JGM, Broer R, Zuidema D, et al. Sequence and organization of the Spodoptera exigua multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J Gen Virol. 1999;80:3289–3304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-12-3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rohrmann GF. Baculovirus structural proteins. J Gen Virol. 1992;73:749–761. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bateman A, Coin L, Durbin R, Finn RD, Hollich V, et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:D138–141. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fang M, Nie Y, Harris S, Erlandson MA, Theilmann DA. Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus core gene ac96 encodes a per os infectivity factor (PIF-4). J Virol. 2009;83:12569–12578. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01141-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Faulkner P, Kuzio J, Williams GV, Wilson JA. Analysis of p74, a PDV envelope protein of Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus required for occlusion body infectivity in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1997;78:3091–3100. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-12-3091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kikhno I, Gutierrez S, Croizier L, Croizier G, Ferber ML. Characterization of pif, a gene required for the per os infectivity of Spodoptera littoralis nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:3013–3022. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-12-3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ohkawa T, Washburn JO, Sitapara R, Sid E, Volkman LE. Specific binding of Autographa californica M nucleopolyhedrovirus occlusion-derived virus to midgut cells of Heliothis virescens larvae is mediated by products of pif genes Ac119 and Ac022 but not by Ac115. J Virol. 2005;79:15258–15264. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15258-15264.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pijlman GP, Pruijssers AJ, Vlak JM. Identification of pif-2, a third conserved baculovirus gene required for per os infection of insects. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:2041–2049. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Braunagel SC, Summers MD. Molecular biology of the baculovirus occlusion-derived virus envelope. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:1084–1095. doi: 10.2174/138945007782151315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Herniou EA, Olszewski JA, Cory JS, O'Reilly DR. The genome sequence and evolution of baculoviruses. Annu Rev Entomol. 2003;48:211–234. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.48.091801.112756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.van Oers MM, Vlak JM. Baculovirus genomics. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:1051–1068. doi: 10.2174/138945007782151333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Haas-Stapleton EJ, Washburn JO, Volkman LE. P74 mediates specific binding of Autographa californica M nucleopolyhedrovirus occlusion-derived virus to primary cellular targets in the midgut epithelia of Heliothis virescens Larvae. J Virol. 2004;78:6786–6791. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.6786-6791.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.van Oers MM, Vlak JM. The baculovirus 10-kDa protein. J Invertebr Pathol. 1997;70:1–17. doi: 10.1006/jipa.1997.4675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.O'Reilly DR. Auxiliary genes of baculoviruses. In: Miller LK, editor. The Baculoviruses. New York: Plenum Press; 1997. pp. 267–300. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Derksen ACG, Granados RR. Alteration of a lepidopteran peritrophic membrane by baculoviruses and enhancement of viral infectivity. Virology. 1988;167:242–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wang P, Granados RR. Observations on the presence of the peritrophic membrane in larval Trichoplusia ni and its role in limiting baculovirus infection. J Invertebr Pathol. 1998;72:57–62. doi: 10.1006/jipa.1998.4759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tanada Y, Himeno M, Omi EM. Isolation of a factor, from the capsule of a granulosis virus, synergistic for a nuclear-polyhedrosis virus of the armyworm. J Invertebr Pathol. 1973;21:31–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(73)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Roelvink PW, Corsaro BG, Granados RR. Characterization of the Helicoverpa armigera and Pseudaletia unipuncta granulovirus enhancin genes. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:2693–2705. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-11-2693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hashimoto Y, Corsaro BG, Granados RR. Location and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the viral enhancing factor of the Trichoplusia ni granulosis virus. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:2645–2651. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tomalski MD, Eldridge R, Miller LK. A baculovirus homolog of a Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene. Virology. 1991;184:149–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90831-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Haas AL, Katzung DJ, Reback PM, Guarino LA. Functional characterization of the ubiquitin variant encoded by the baculovirus Autographa californica. Biochemistry. 1996;35:5385–5394. doi: 10.1021/bi9524981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Reilly LM, Guarino LA. The viral ubiquitin gene of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus is not essential for viral replication. Virology. 1996;218:243–247. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.van Oers MM, Lampen MH, Bajek MI, Vlak JM, Eker AP. Active DNA photolyase encoded by a baculovirus from the insect Chrysodeixis chalcites. DNA Repair (Amst) 2008;7:1309–1318. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hay S, Kannourakis G. A time to kill: viral manipulation of the cell death program. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:1547–1564. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-7-1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Roulston A, Marcellus RC, Branton PE. Viruses and apoptosis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999;53:577–628. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Birnbaum MJ, Clem RJ, Miller LK. An apoptosis-inhibiting gene from a nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a polypeptide with Cys/His sequence motifs. J Virol. 1994;68:2521–2528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2521-2528.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Clem RJ, Fechheimer M, Miller LK. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science. 1991;254:1388–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.1962198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Crook NE, Clem RJ, Miller LK. An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J Virol. 1993;67:2168–2174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2168-2174.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Du Q, Lehavi D, Faktor O, Qi Y, Chejanovsky N. Isolation of an apoptosis suppressor gene of the Spodoptera littoralis nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Virol. 1999;73:1278–1285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.2.1278-1285.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ayres MD, Howard SC, Kuzio J, Lopez-Ferber M, Possee RD. The complete DNA sequence of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1994;202:586–605. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gomi S, Majima K, Maeda S. Sequence analysis of the genome of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Gen Virol. 1999;80:1323–1337. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-5-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pang Y, Yu J, Wang L, Hu X, Bao W, et al. Sequence analysis of the Spodoptera litura multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. Virology. 2001;287:391–404. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pei Z, Reske G, Huang Q, Hammock BD, Qi Y, et al. Characterization of the apoptosis suppressor protein P49 from the Spodoptera littoralis nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:48677–48684. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208810200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zoog SJ, Schiller JJ, Wetter JA, Chejanovsky N, Friesen PD. Baculovirus apoptotic suppressor P49 is a substrate inhibitor of initiator caspases resistant to P35 in vivo. EMBO J. 2002;21:5130–5140. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vucic D, Kaiser WJ, Harvey AJ, Miller LK. Inhibition of reaper-induced apoptosis by interaction with inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:10183–10188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bideshi DK, Renault S, Stasiak K, Federici BA, Bigot Y. Phylogenetic analysis and possible function of bro-like genes, a multigene family widespread among large double-stranded DNA viruses of invertebrates and bacteria. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:2531–2544. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kang W, Kurihara M, Matsumoto S. The BRO proteins of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus are nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins that utilize the CRM1-mediated nuclear export pathway. Virology. 2006;350:184–191. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kang W, Suzuki M, Zemskov E, Okano K, Maeda S. Characterization of baculovirus repeated open reading frames (bro) in Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Virol. 1999;73:10339–10345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.12.10339-10345.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kang WK, Imai N, Suzuki M, Iwanaga M, Matsumoto S, et al. Interaction of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus BRO-A and host cell protein laminin. Arch Virol. 2003;148:99–113. doi: 10.1007/s00705-002-0902-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zemskov EA, Kang W, Maeda S. Evidence for nucleic acid binding ability and nucleosome association of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus BRO proteins. J Virol. 2000;74:6784–6789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.6784-6789.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.O'Reilly DR, Miller LK, Luckow VA. New York: W.H.Freeman & Company; 1992. Baculovirus Expression Vector: A Laboratory Manual. 368 p. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Solovyev VV, Salamov AA. INFOGENE: a database of known gene structures and predicted genes and proteins in sequences of genome sequencing projects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:248–250. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Fitch WM. Toward Defining Course of Evolution - Minimum Change for a Specific Tree Topology. Syst Zool. 1971;20:406–416. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Swfford DL. PAUP*. 2003. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods) Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA (on disk)
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Predicted SpliGV ORFs by BLAST Search.
(DOC)
Primers used to confirm new SpliGV genes.
(DOC)