Abstract
Six normal men were fed formula diets containing either highly saturated fat (cocoa butter, iodine value 32) or polyunsaturated fat (corn oil, iodine value 125). The sterol balance technique was used to compare the changes in serum cholesterol concentration with the excretion of fecal steroids. The method used for the analysis of fecal steroids was chemical, with a final identification and quantification by gas-liquid chromatography. It was confirmed that the chemical method for fecal steroid analysis was accurate and reproducible.
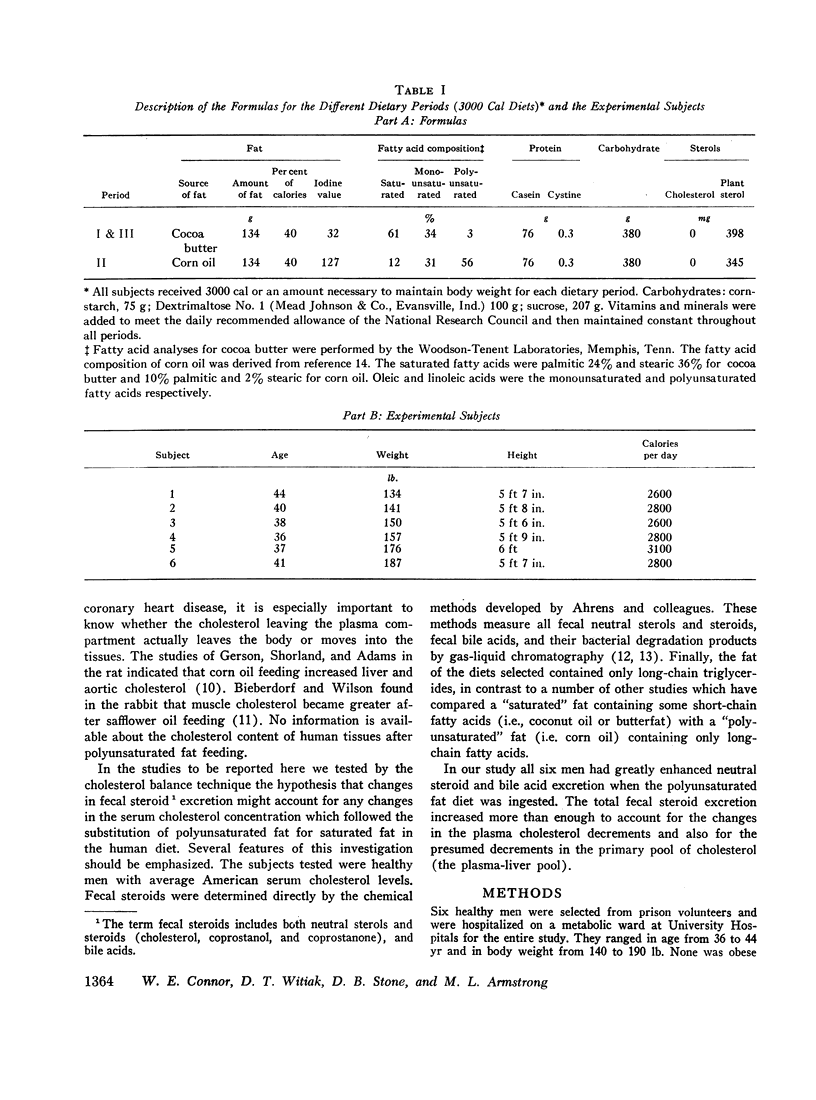
The three dietary periods were each 3 wk in length. In sequence, cocoa butter (period I), corn oil, and cocoa butter (period III) were fed at 40% of the total calories. All diets were cholesterol free, contained similar amounts of plant sterols, and were identical in other nutrients.
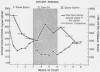
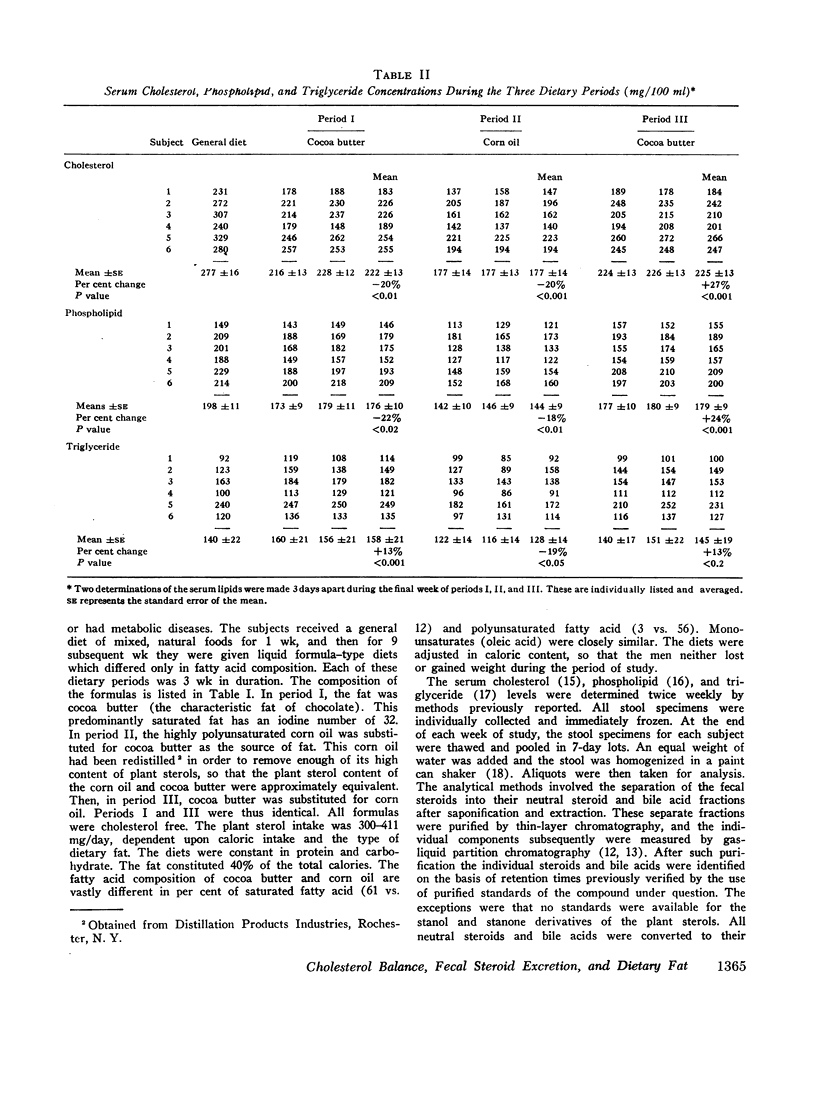
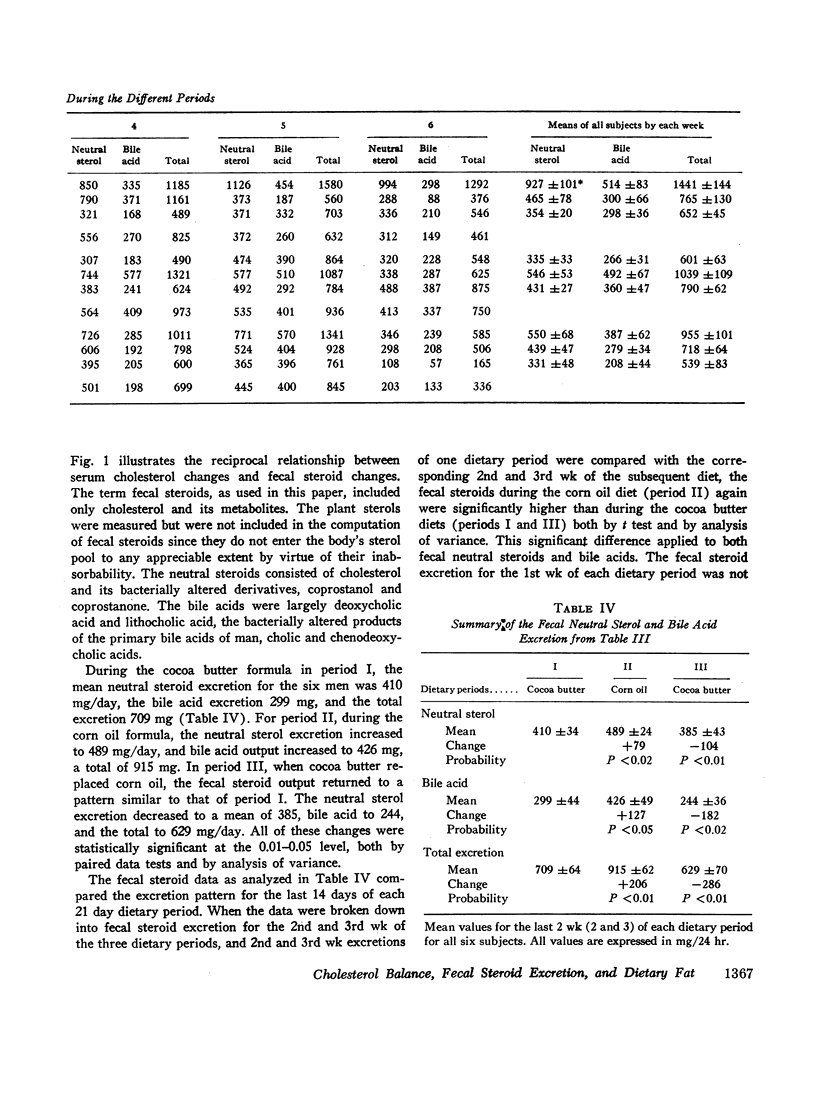
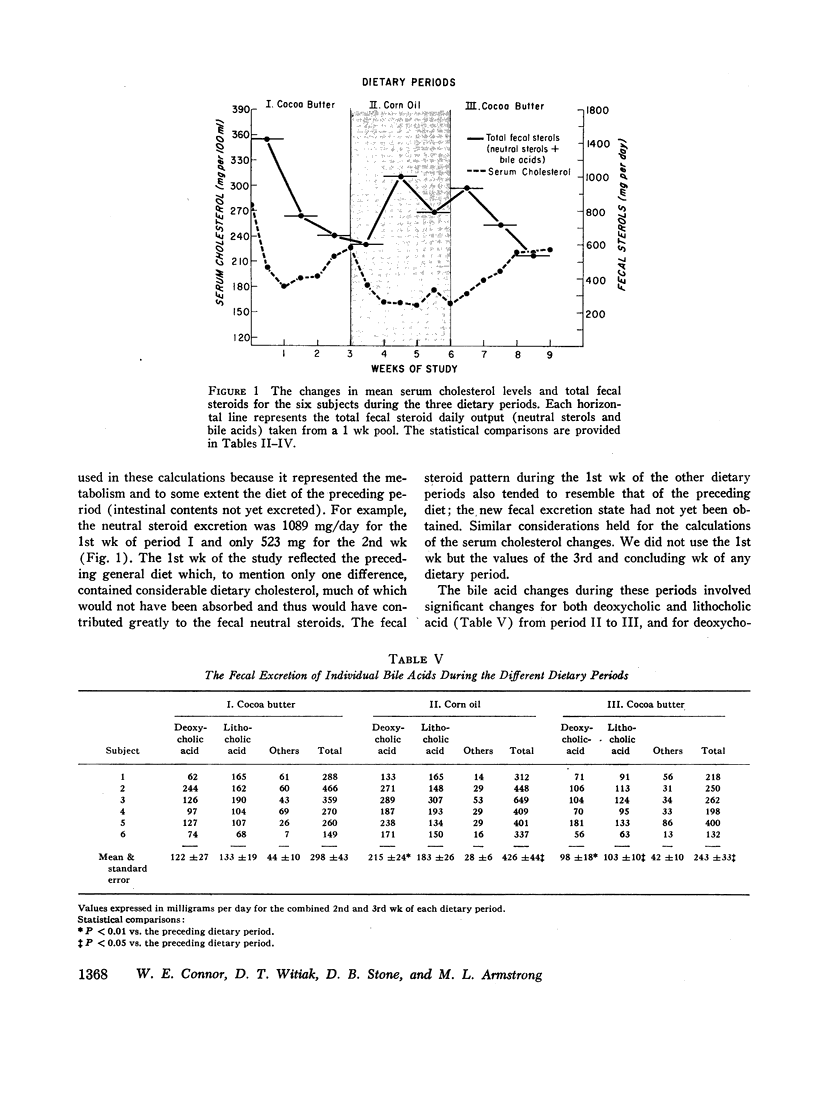
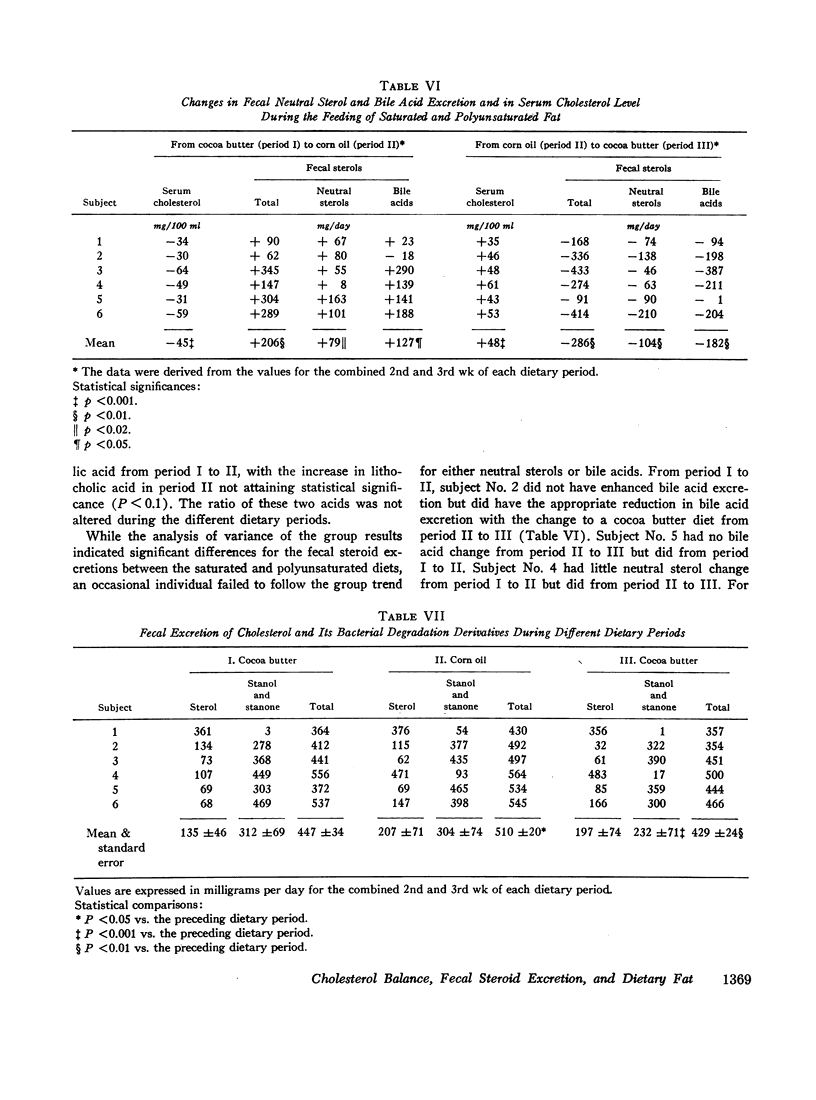
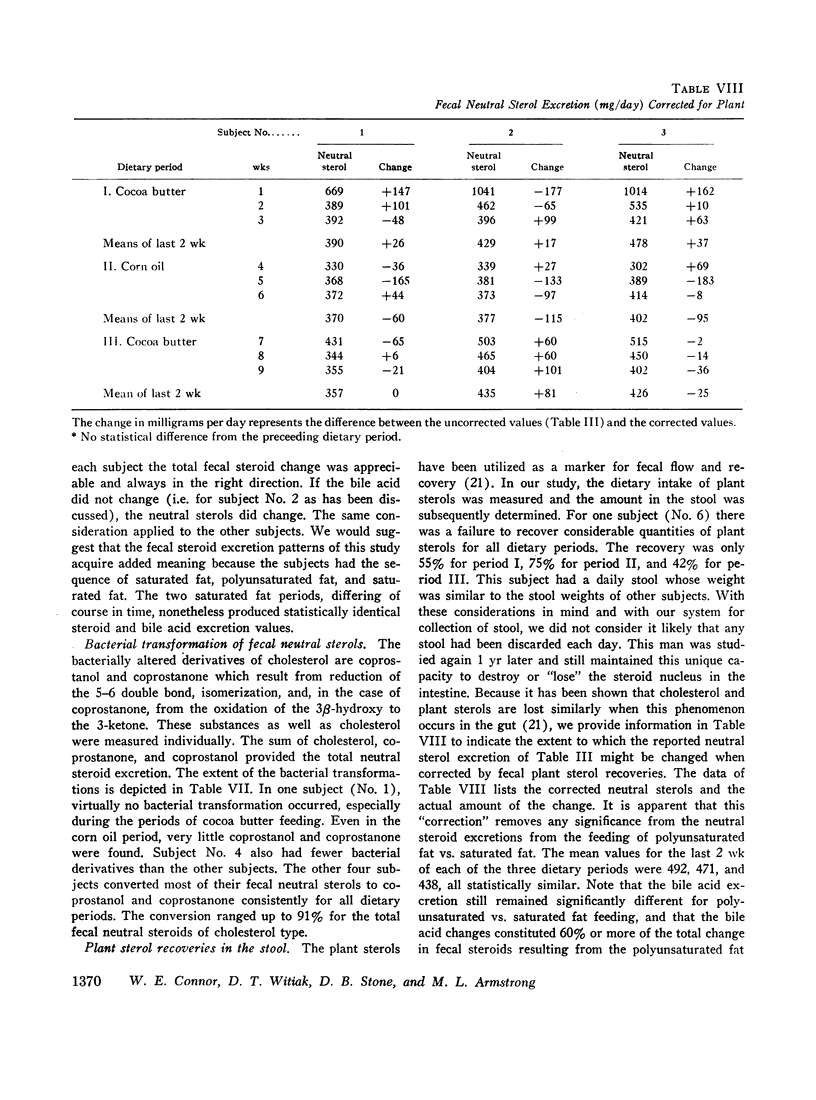
Corn oil had a hypocholesterolemic effect. Mean serum cholesterol concentrations were 222 mg/100 ml (cocoa butter, period I), 177 during corn oil, and 225 after the return to cocoa butter. Individual fecal steroids were determined from stools pooled for 7 days. Both neutral steroids and bile acids were altered significantly by dietary polyunsaturated fat. The change in bile acid excretion was considerably greater than the change in neutral steroids. Corn oil caused a greater fecal excretion of both deoxycholic and lithocholic acids. The total mean excretion (milligrams per day) of fecal steroids was 709 for cocoa butter (period I), 915 for corn oil, and 629 for the second cocoa butter period.
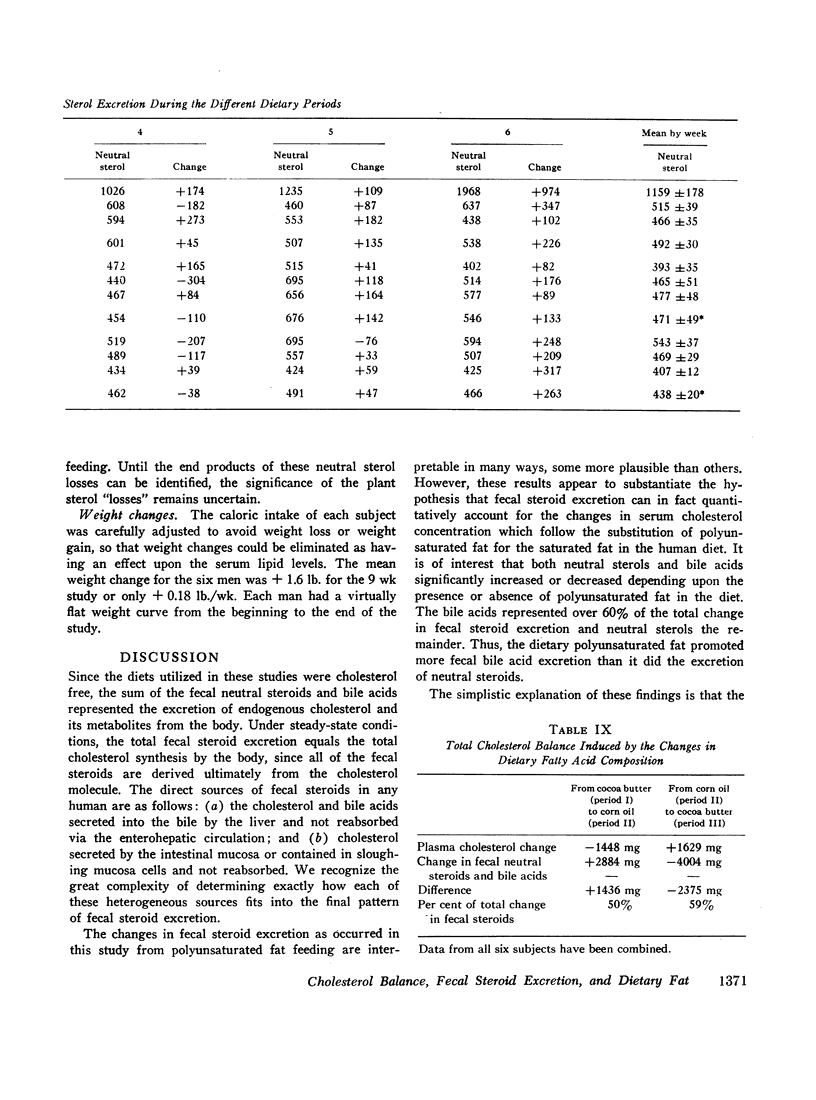
The enhanced total fecal steroid excretion by the polyunsaturated fat of corn oil created a negative cholesterol balance vis-à-vis the saturated fat of cocoa butter. The hypocholesterolemic effect of polyunsaturated fat was associated with total fecal sterol excretion twice greater than the amount of cholesterol calculated to leave the plasma. This finding suggested possible loss of cholesterol from the tissues as well.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AHRENS E. H., Jr, INSULL W., Jr, BLOMSTRAND R., HIRSCH J., TSALTAS T. T., PETERSON M. L. The influence of dietary fats on serum-lipid levels in man. Lancet. 1957 May 11;272(6976):943–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AVIGAN J., STEINBERG D. Effects of saturated and unsaturated fat on cholesterol metabolism in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Apr;97(4):814–816. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. S., Kuksis A., Beveridge J. M. Excretion of bile acids by three men on corn oil and butterfat diets. Can J Biochem. 1966 Oct;44(10):1377–1388. doi: 10.1139/o66-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avigan J., Steinberg D. Sterol and bile acid excretion in man and the effects of dietary fat. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1845–1856. doi: 10.1172/JCI105292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieberdorf F. A., Wilson J. D. Studies on the mechanism of action of unsaturated fats on cholesterol metabolism in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1834–1844. doi: 10.1172/JCI105291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNOR W. E., STONE D. B., HODGES R. E. THE INTERRELATED EFFECTS OF DIETARY CHOLESTEROL AND FAT UPON HUMAN SERUM LIPID LEVELS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1691–1696. doi: 10.1172/JCI105044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYER R. L., TAMMES A. R., ROUTH J. I. The determination of phosphorus and phosphatase with N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN I. S., LEIBMAN J. Anatomy of body water and electrolytes. Am J Med. 1959 Aug;27:256–277. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENEROTH P., HELLSTROEM K., RYHAGE R. IDENTIFICATION AND QUANTIFICATION OF NEUTRAL FECAL STEROIDS BY GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY AND MASS SPECTROMETRY: STUDIES OF HUMAN EXCRETION DURING TWO DIETARY REGIMENS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Apr;5:245–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERICKSON B. A., COOTS R. H., MATTSON F. H., KLIGMAN A. M. THE EFFECT OF PARTIAL HYDROGENATION OF DIETARY FATS, OF THE RATIO OF POLYUNSATURATED TO SATURATED FATTY ACIDS, AND OF DIETARY CHOLESTEROL UPON PLASMA LIPIDS IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2017–2025. doi: 10.1172/JCI105076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSON T., SHORLAND F. B., ADAMS Y. The effects of corn oil on the amounts of cholesterol and the excretion of sterol in the rat. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:584–591. doi: 10.1042/bj0810584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSMITH G. A., HAMILTON J. G., MILLER O. N. Lowering of serum lipid concentrations: mechanisms used by unsaturated fats, nicotinic acid, and neomycin: excretion of sterols and bile acids. Arch Intern Med. 1960;105:512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Cholesterol ester metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1965 Oct;45(4):747–839. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Noble R. P. Turnover of plasma cholesterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):231–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI105719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr An evaluation of the relative merits of two methods for measuring the balance of sterols in man: isotopic balance versus chromatographic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1503–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI105457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Dietary beta-sitosterol as an internal standard to correct for cholesterol losses in sterol balance studies. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):374–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUST H. L., BEVERIDGE J. M. Effect of varying type and quantity of dietary fat on the fecal excretion of bile acids in humans subsisting on formula diets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOVER A., GORDON R. S., Jr Procedure for quantitative analysis of faces with special reference to facal fatty acids. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS B. Effect of certain dietary oils on bile-acid secretion and serum-cholesterol. Lancet. 1958 May 24;1(7030):1090–1092. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91847-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIETTINEN T. A., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. M. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL DIETARY AND FECAL NEUTRAL STEROIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:411–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. B., Anderson J. T., Taylor H. L., Keys A., Frantz I. D., Jr Effect of dietary fat on the fecal excretion of cholesterol and its degradation products in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1517–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI105845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRITZ N., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. STEROL BALANCE IN MAN AS PLASMA CHOLESTEROL CONCENTRATIONS ARE ALTERED BY EXCHANGES OF DIETARY FATS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1482–1493. doi: 10.1172/JCI105255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodhi H. S., Wood P. D., Schlierf G., Kinsell L. W. Plasma, bile and fecal sterols in relation to diet. Metabolism. 1967 Apr;16(4):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz N., Mishkel M. A. Effects of dietary fats on plasma lipids and lipoproteins: an hypothesis for the lipid-lowering effect of unsaturated fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):78–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI105976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Micromethod for the direct determination of serum triglycerides. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDENHEUVEL F. A. The origin, metabolism, and structure of normal human serum lipoproteins. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Sep;40:1299–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]