Abstract
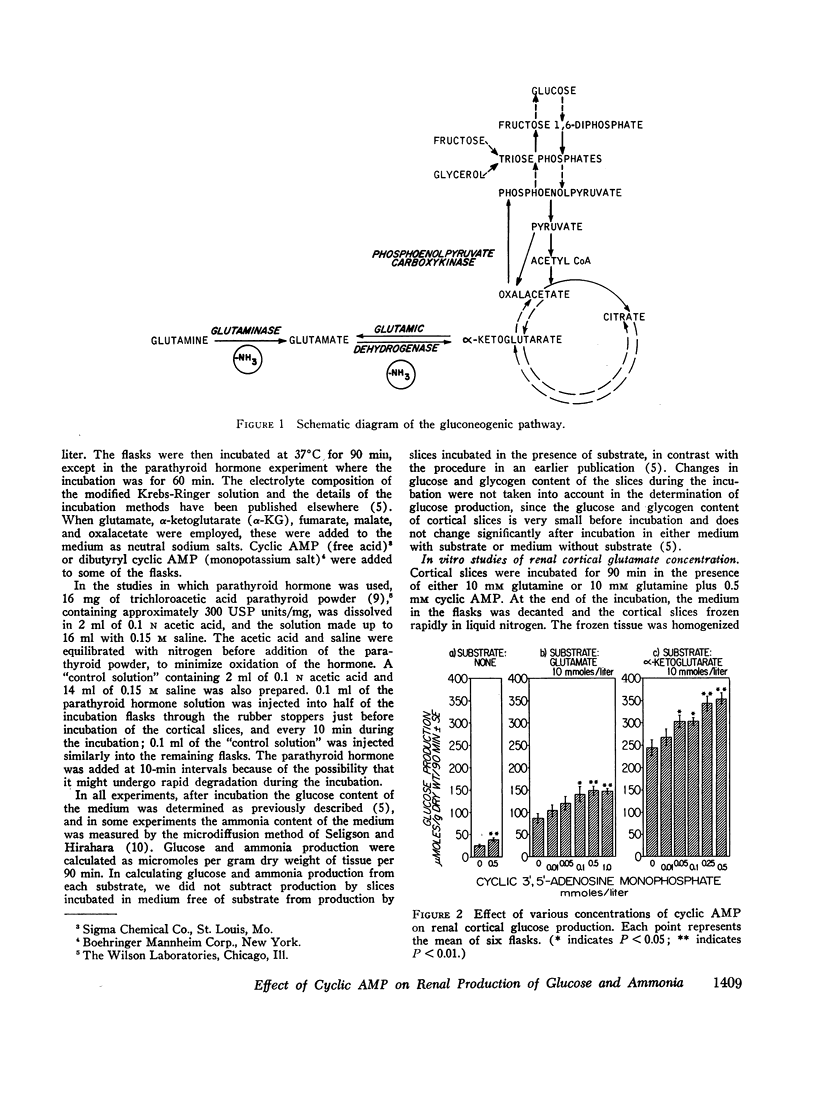
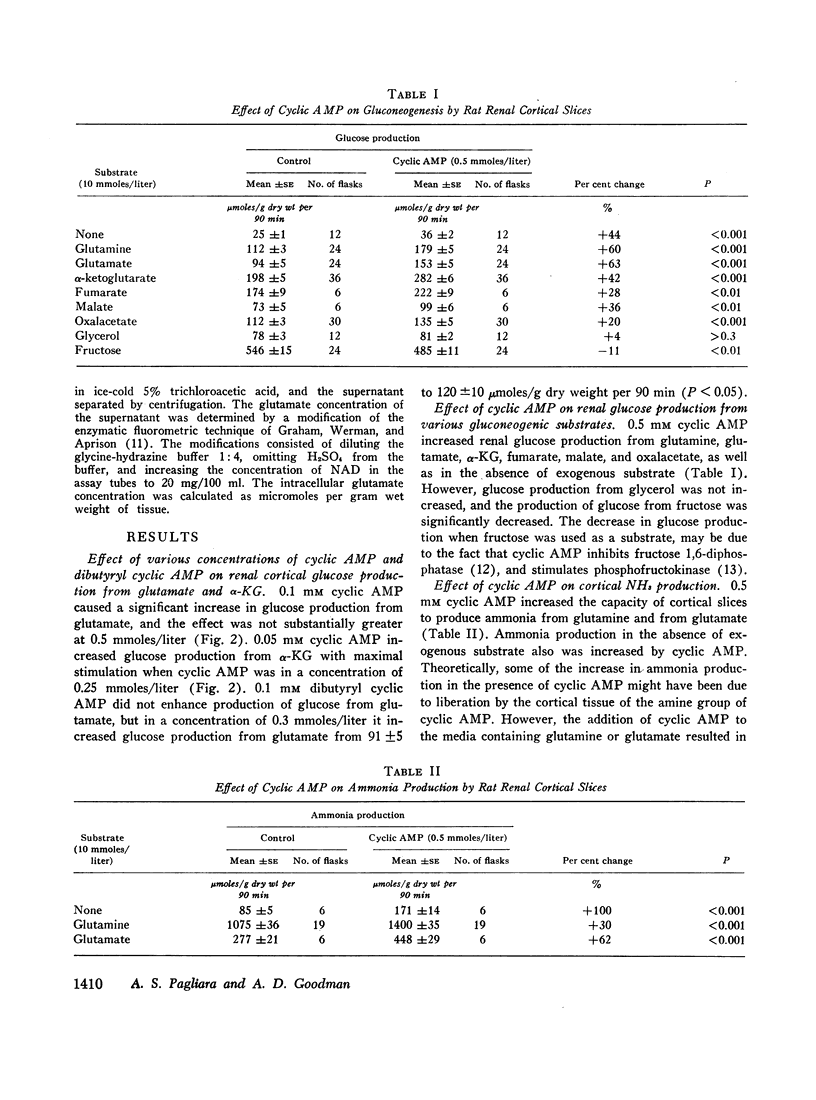
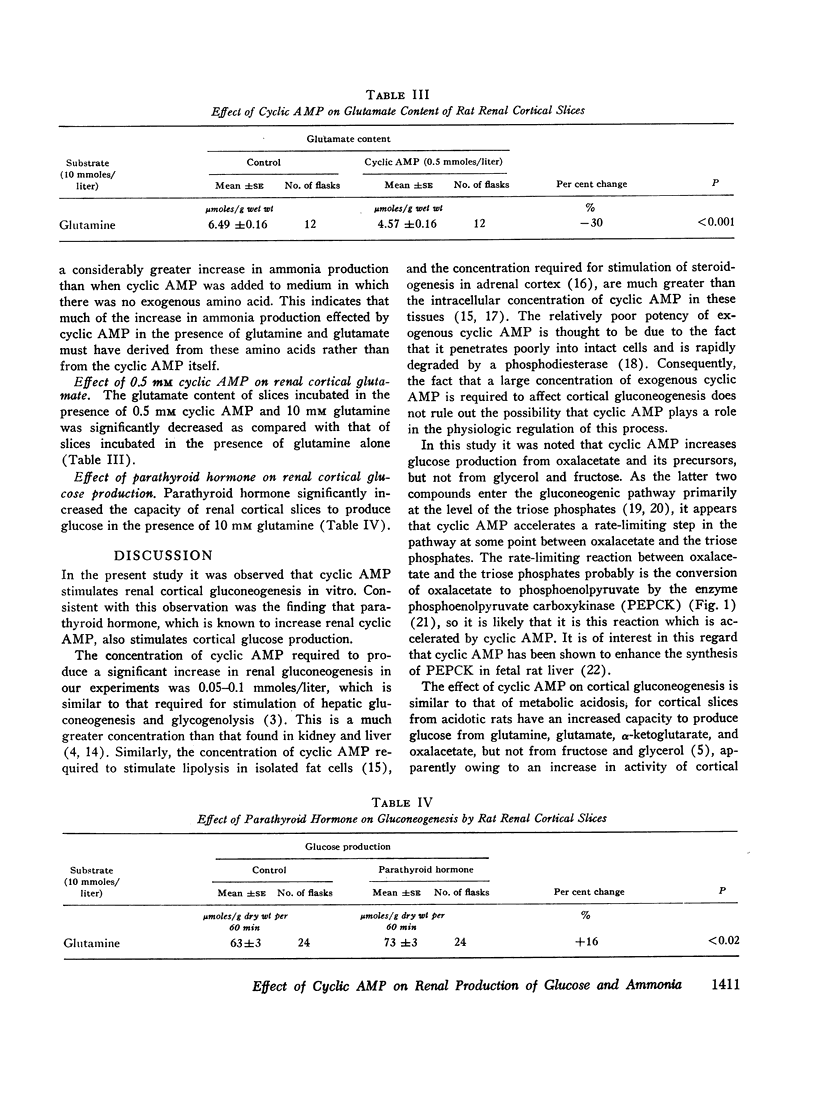
In studies employing rat renal cortical slices, the addition of adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) to the incubation medium caused an increase in production of glucose from glutamine, glutamate, α-ketoglutarate, fumarate, malate, and oxalacetate, but not from glycerol and fructose. These observations suggest that cyclic AMP accelerates a rate-limiting gluconeogenic reaction between oxalacetate and the triose phosphates. The addition to the medium of parathyroid hormone, which is known to increase renal cortical cyclic AMP, also stimulated glucose production from glutamine.
When renal cortical slices were incubated in the presence of glutamine, the addition of cyclic AMP caused a fall in tissue glutamate concentration and a rise in ammonia production, as well as an increase in gluconeogenesis. These changes are similar to those observed in renal cortex of rats with induced metabolic acidosis. The present observations are consistent with a previously advanced hypothesis that cortical gluconeogenesis, ammonia production, and glutamate concentration may be interdependent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleyne G. A., Scullard G. H. Renal metabolic response to acid base changes. I. Enzymatic control of ammoniagenesis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):364–370. doi: 10.1172/JCI105993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B., Davies J. I., Hynie S., Krishna G., Weiss B. Interrelationships of catecholamines with other endocrine systems. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):273–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES B. M. A., YUDKIN J. Studies in biochemical adaptation; the origin or urinary ammonia as indicated by the effect of chronic acidosis and alkalosis on some renal enzymes in the rat. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):407–412. doi: 10.1042/bj0520407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Jefferson L. S., Jr, Butcher R. W., Park C. R. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused liver. The effects of fasting, alloxan diabetes, glucagon, epinephrine, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and insulin. Am J Med. 1966 May;40(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. II. Effects of glucagon, catecholamines, and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4189–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. Relation of glutamate to ammonia production in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1966 Mar;210(3):661–666. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.3.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. T., Jr, Werman R., Aprison M. H. Microdetermination of glutamate in single cat spinal roots. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(10):1085–1090. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYNES R. C., Jr, KORITZ S. B., PERON F. G. Influence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on corticoid production by rat adrenal glands. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1421–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYNES R. C., Jr The activation of adrenal phosphorylase by the adrenocorticotropic hormone. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1220–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. The conversion of fructose-1-C14 and sorbitol-1-C14 to liver and muscle glycogen in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):373–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., BENNETT D. A., DE GASQUET P., GASQUET P., GASCOYNE T., YOSHIDA T. Renal gluconeogenesis. The effect of diet on the gluconeogenic capacity of rat-kidney-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0860022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendicino J., Beaudreau C., Bhattacharyya R. N. Reversible inactivation of D-fructose 1,6-diphosphatase by adenosine triphosphate and cyclic 3' ,5'-adenosine monophosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):436–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata N., Rasmussen H. Parathyroid hormone and renal cell metabolism. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3728–3733. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN H., SZE Y. L., YOUNG R. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PARATHYROID POLYPEPTIDES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2852–2857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGSON D., HIRAHARA K. The measurement of ammonia in whole blood, erythrocytes, and plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jun;49(6):962–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHRAGO E., LARDY H. A., NORDLIE R. C., FOSTER D. O. METABOLIC AND HORMONAL CONTROL OF PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE CARBOXYKINASE AND MALIC ENZYME IN RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3188–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENG C. T., KARNOVSKY M. L., LANDAU B. R., HASTINGS A. B., NESBETT F. B. Metabolism of C14-labeled glycerol and pyruvate by liver in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):705–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung D., Oliver I. T. Induction of phosphopyruvate carboxylase in neonatal rat liver by adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3231–3239. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



