Abstract
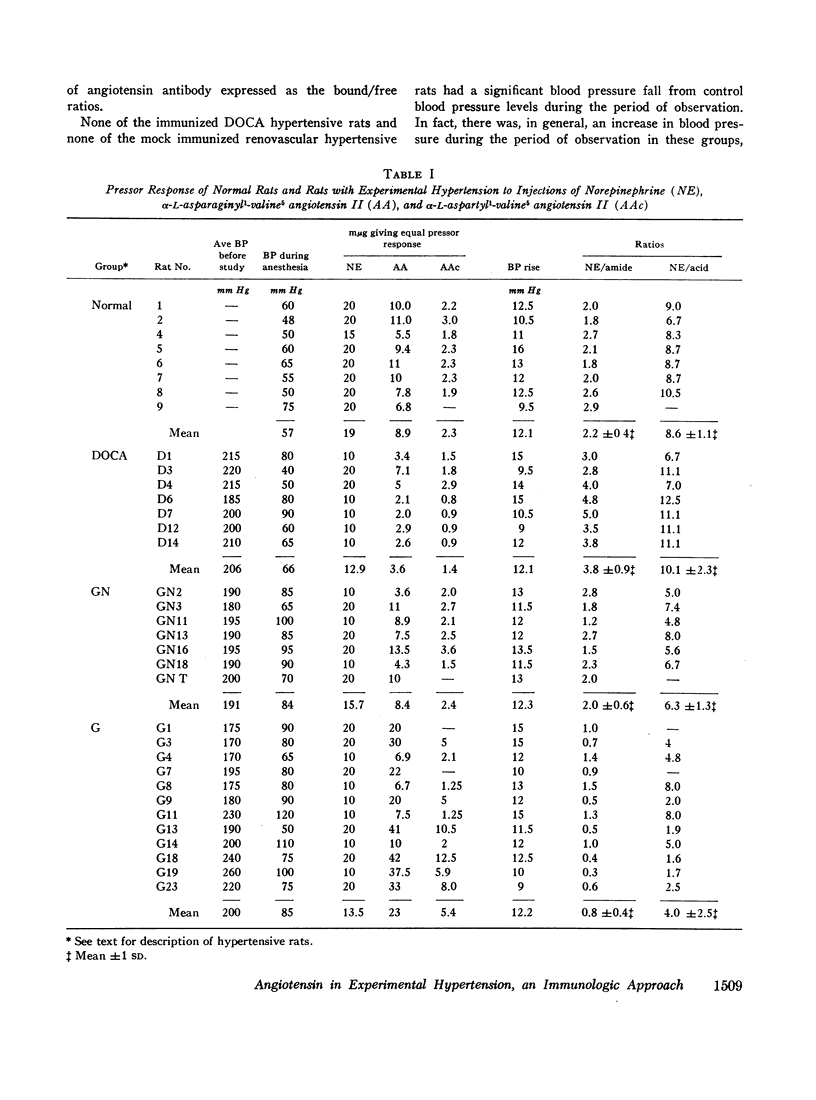
The role of angiotensin in three forms of experimental hypertension was assessed in rats. First, the acute blood pressure response to injected angiotensin amide and angiotensin acid was determined. Rats made hypertensive with deoxycorticosterone and saline showed exaggerated responses; rats made hypertensive by clipping one renal artery showed depressed responses; and rats made hypertensive by clipping one renal artery and contralateral nephrectomy showed normal responsivity to angiotensin amide but depressed responsivity to angiotensin acid. These findings suggested that different mechanisms may be involved in the three types of hypertension studied.
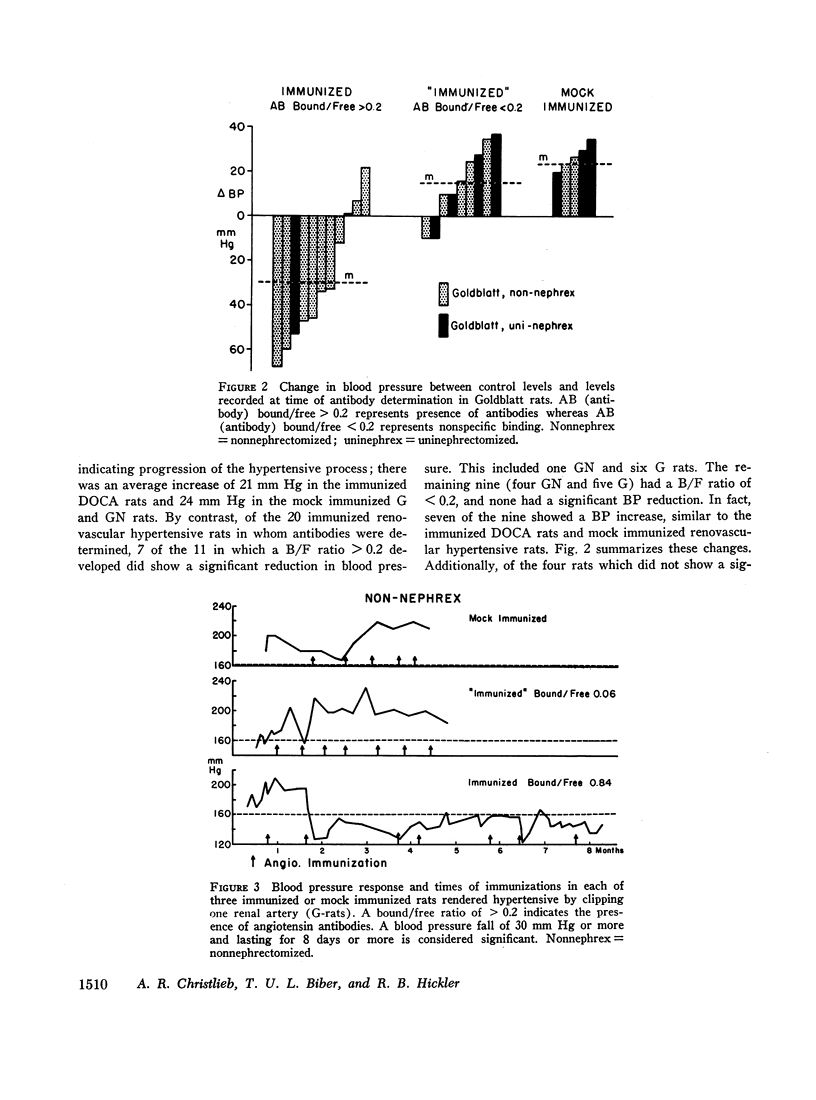
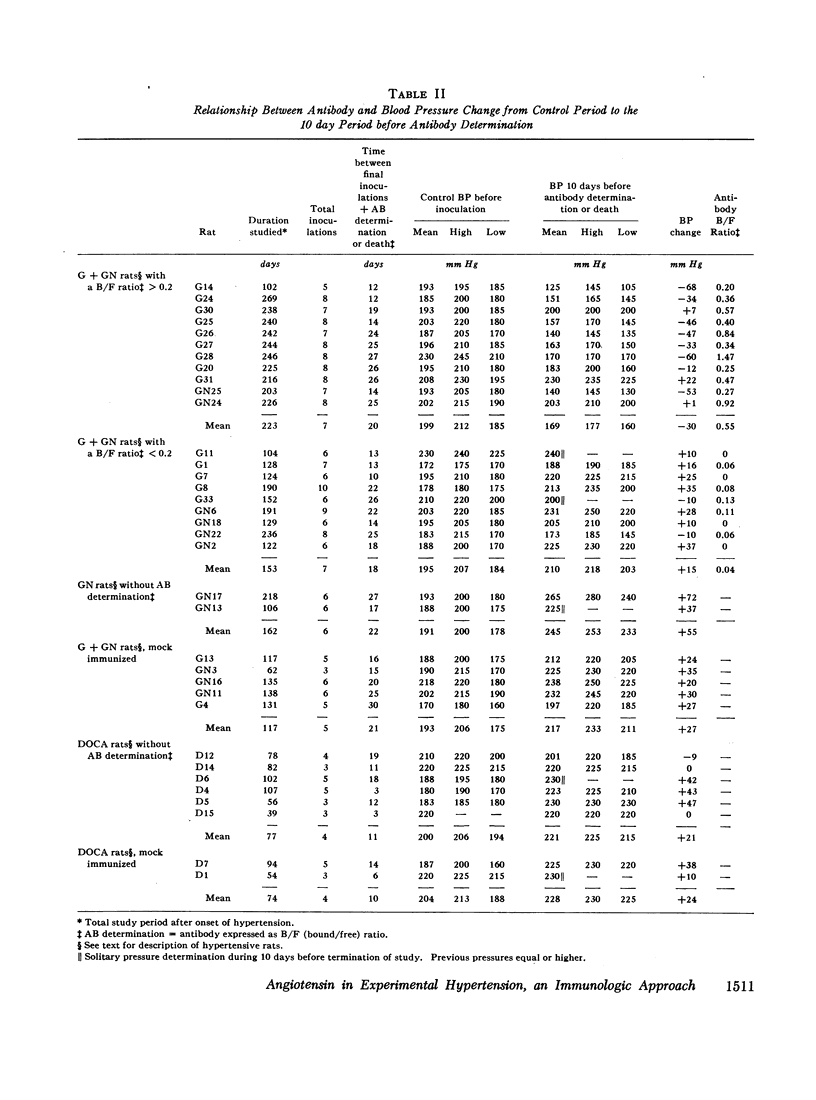
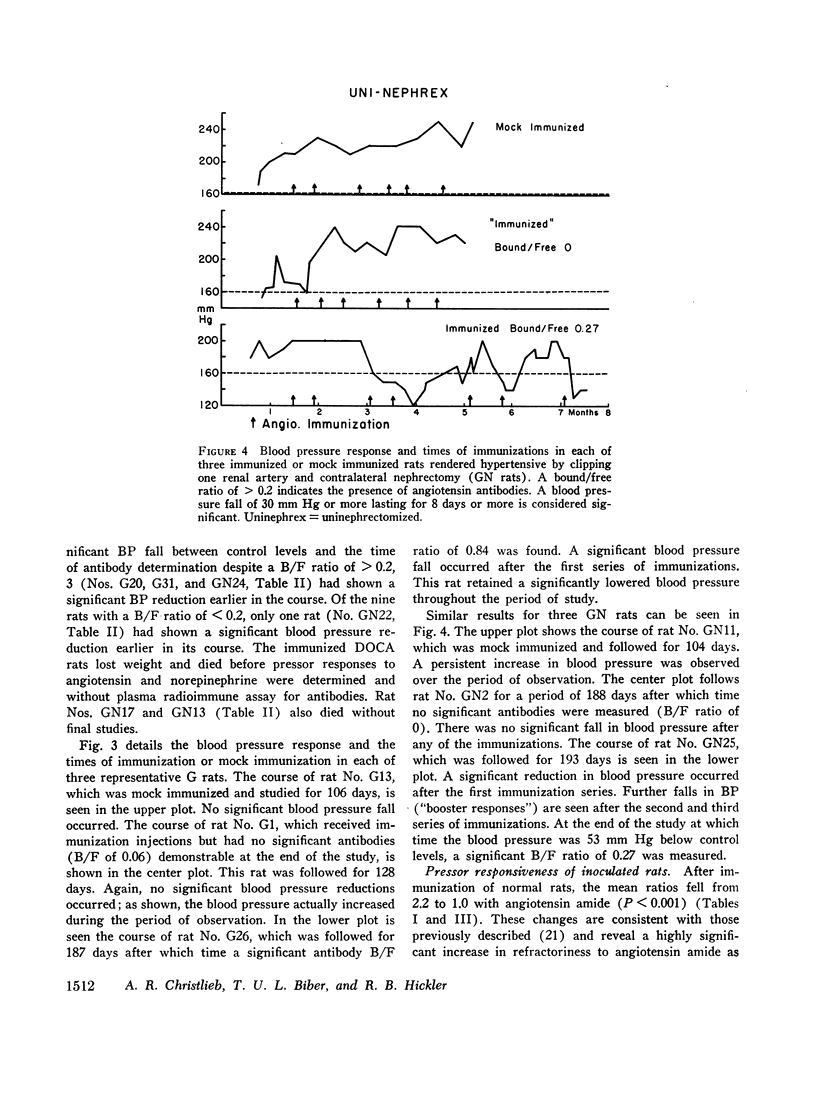
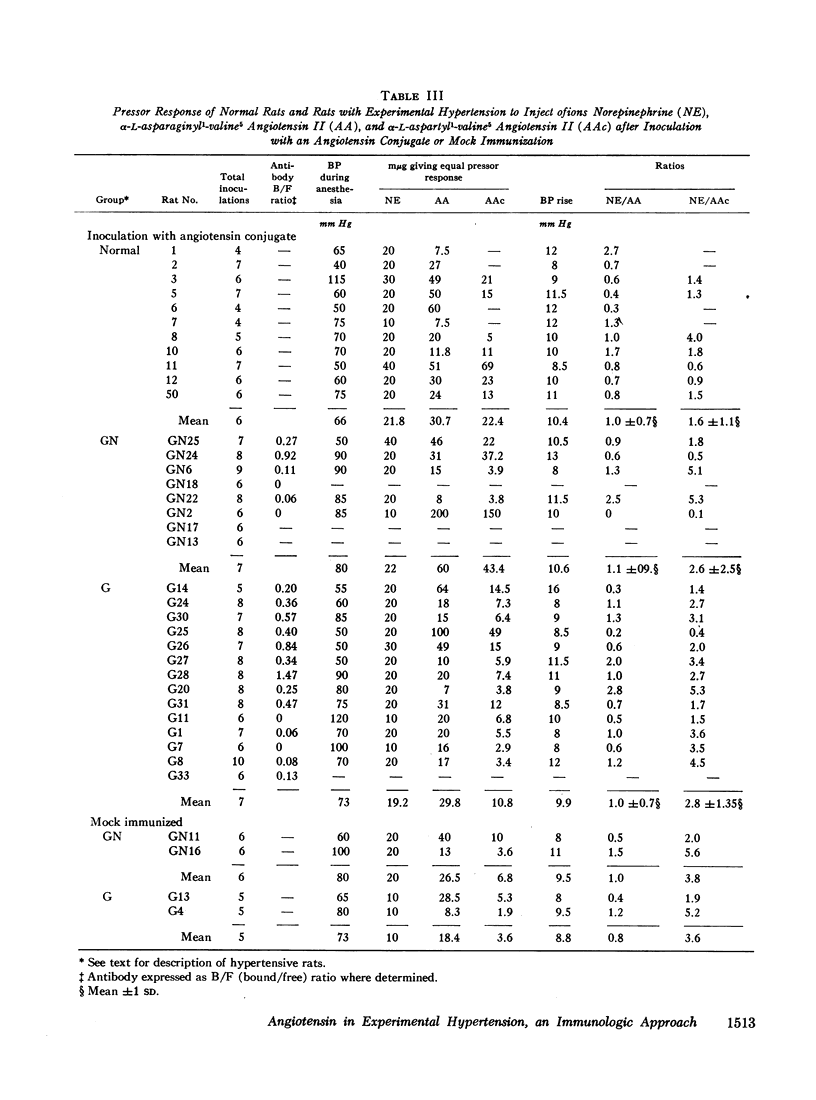
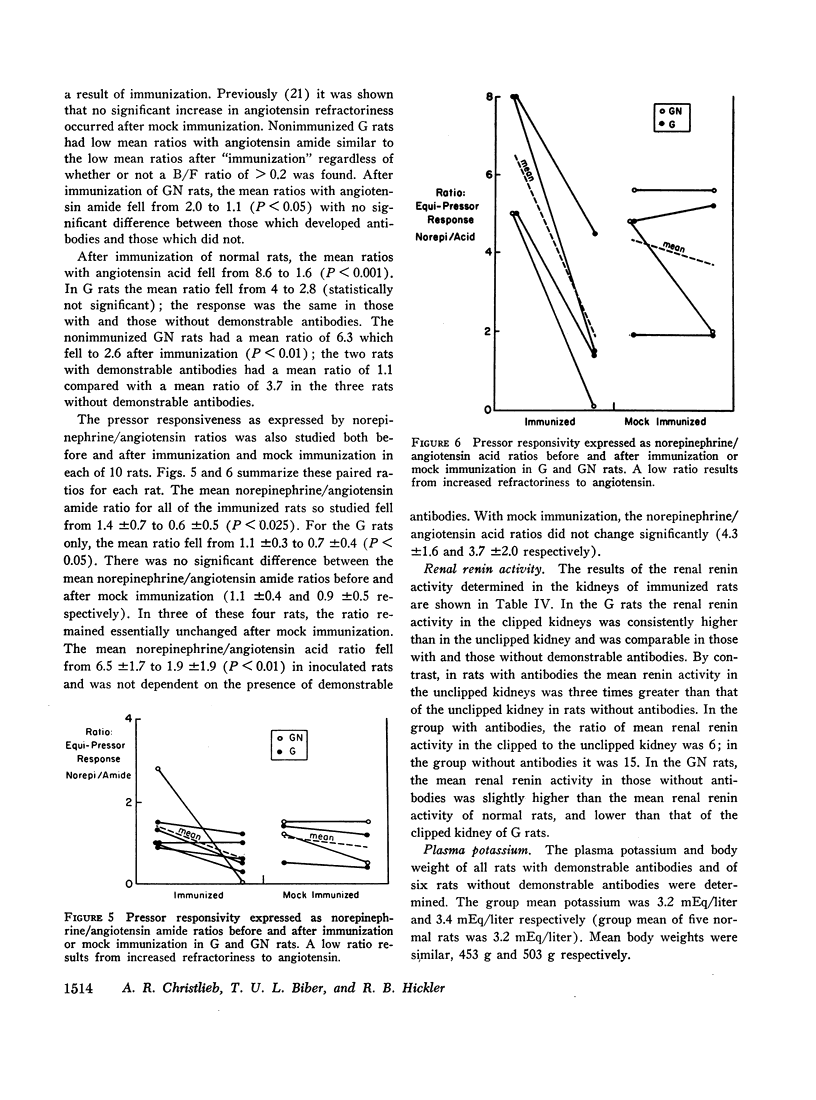
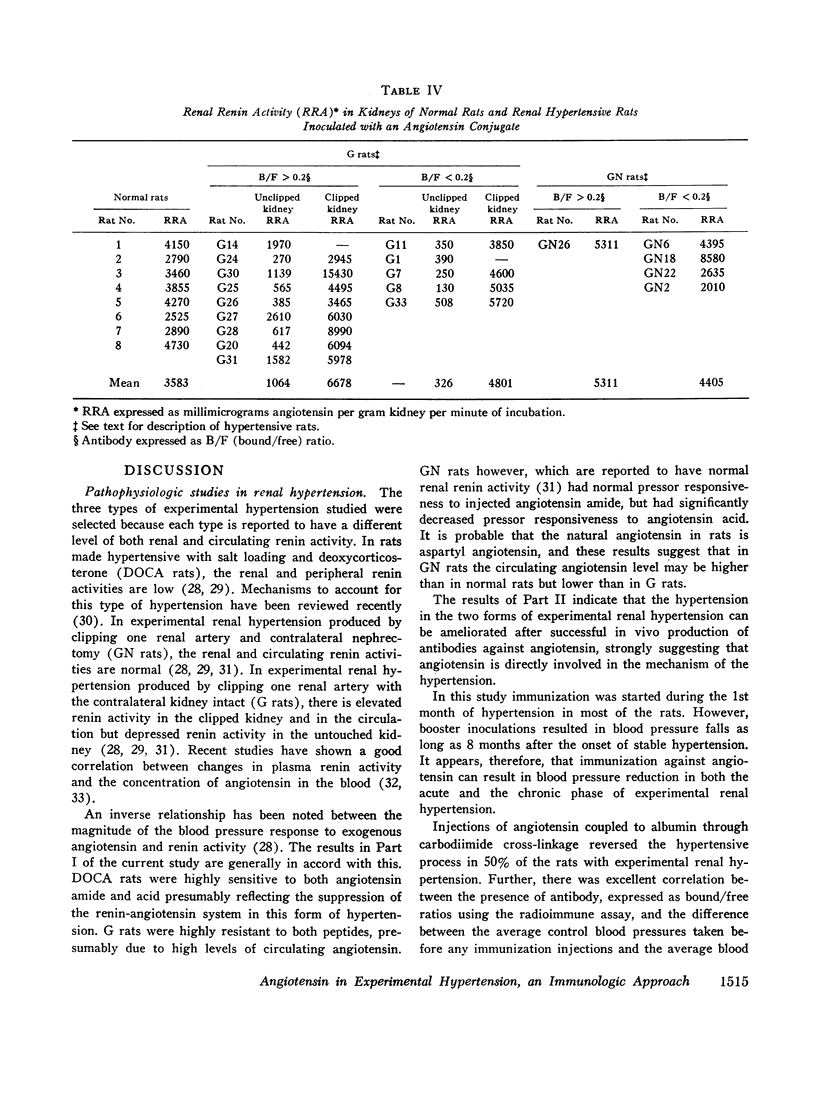
To assess the role of angiotensin in these hypertensive rats the blood pressure response, the presence of antibodies determined by radioimmune techniques, and the degree of refractoriness to injected angiotensin after immunization with angiotensin were studied. None of six rats made hypertensive by deoxycorticosterone and saline, and none of five mock immunized rats with renal hypertension of both types had a fall in blood pressure. By contrast, of the 20 rats with both types of renal hypertension in which antibody determinations were made, 11 had developed a significant antibody titer, of which seven showed a significant reduction in blood pressure at the time of antibody determination, and three of the remaining four had a significant blood pressure reduction earlier in their course. None of the nine renal hypertensive rats without demonstrable antibodies had a reduced blood pressure at the time of antibody determination, and only one had an earlier reduction in blood pressure. The renal hypertensive rats were all refractory to injected angiotensin after immunization.
These results suggest a primary role for angiotensin in both forms of renal hypertension.
Full text
PDF
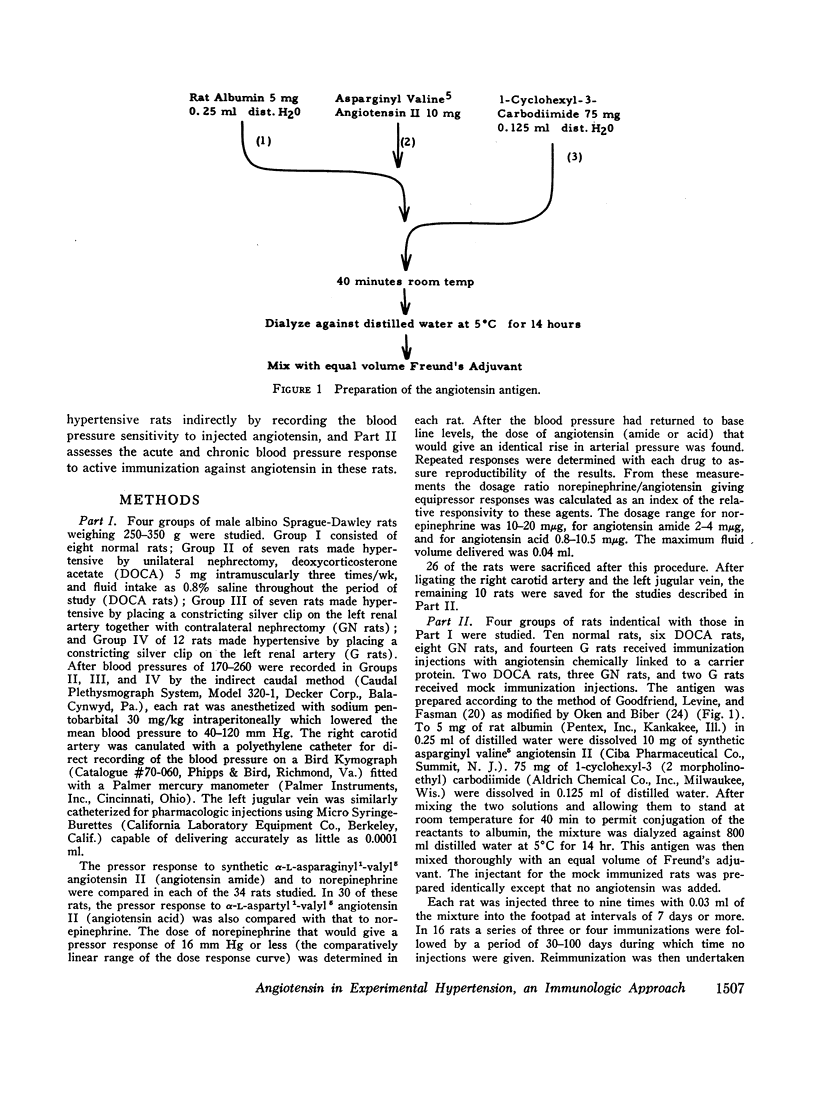




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATTISTO J. R., CHASE M. W. IMMUNOLOGICAL UNRESPONSIVENESS TO SENSITIZATION WITH SIMPLE CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS; A SEARCH FOR ANTIBODY-ABSORBING DEPOTS OF ALLERGEN. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:1021–1035. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATTISTO J. R., MILLER J. Immunological unresponsiveness produced in adult guinea pigs by parenteral introduction of minute quantities of hapten or protein antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Oct;111:111–115. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battisto J. R., Bloom B. R. Mechanism of immunologic unresponsiveness: a new approach. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaufox M. D., Birbari A. E., Hickler R. B., Merrill J. P. Peripheral plasma renin activity in renal-homotransplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 24;275(21):1165–1168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611242752105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R., Ménard J., Genest J. A micromethod for measurement of renin in the plasma and kidney of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;45(5):881–890. doi: 10.1139/y67-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. J., Lever A. F., Robertson J. I., Hodge R. L., Lowe R. D., Vane J. R. Concurrent measurement of renin and angiotensin in the circulation of the dog. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):853–855. doi: 10.1038/215853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CADE R., PERENICH T. SECRETION OF ALDOSTERONE BY RATS. Am J Physiol. 1965 May;208:1026–1030. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.5.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEODHAR S. D., HAAS E., GOLDBLATT H. PRODUCTION OF ANTIRENIN TO HOMOLOGOUS RENIN AND ITS EFFECT OF EXPERIMENTAL RENAL HYPERTENSION. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:425–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEODHAR S. D. Immunologic production of antiangiotensin. I. Preparation of angiotensin-protein complex antigen. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:419–427. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEODHAR S. D. Immunologic production of antiangiotensin. II. Production and detection of antiangiotensin. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:429–439. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich F. M. Immunogenicity of synthetic angiotensin II. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;30(5):497–506. doi: 10.1159/000229834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOYER M. A. The effect of nephrectomy and adrenalectomy upon the blood pressure in hypertensive and normotensive rats. Clin Sci. 1951 Nov;10(4):405–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFRIEND T. L., LEVINE L., FASMAN G. D. ANTIBODIES TO BRADYKININ AND ANGIOTENSIN: A USE OF CARBODIIMIDES IN IMMUNOLOGY. Science. 1964 Jun 12;144(3624):1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3624.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS F., BRUNNER H., ZIEGLER M. RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM, ALDOSTERONE, AND SODIUM BALANCE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1965;21:119–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS F., SCHAECHTELIN G., BRUNNER H., PETERS G. THE ROLE OF THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM IN BLOOD PRESSURE REGULATION AND KIDNEY FUNCTION. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 25;90:258–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfriend T., Fasman G., Kemp D., Levine L. Immunochemical studies of angiotensin. Immunochemistry. 1966 May;3(3):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER E., PAGE L. B., JACOBY G. A. SYNTHESIS OF ANTIGENIC BRANCH-CHAIN COPOLYMERS OF ANGIOTENSIN AND POLY-L-LYSINE. Biochemistry. 1965 Apr;4:693–698. doi: 10.1021/bi00880a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMER O. M. Studies on renin antibodies. Circulation. 1958 Apr;17(4 Pt 2):648–652. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J. I., SKOM J. H., WAKERLIN G. E. Pathogenesis of spontaneous and pyelonephritic hypertension in the dog. Circ Res. 1957 Mar;5(2):137–143. doi: 10.1161/01.res.5.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREMEN S. H., WAKERLIN G. E. Renin and antirenin in treatment of long term experimental renal hypertension in the dog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):99–104. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARAGH J. H., ANGERS M., KELLY W. G., LIEBERMAN S. Hypotensive agents and pressor substances. The effect of epinephrine, norepinephrine, angiotensin II, and others on the secretory rate of aldosterone in man. JAMA. 1960 Sep 17;174:234–240. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03030030014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARIEB N. J., MULROW P. J. ROLE OF THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM IN THE REGULATION OF ALDOSTERONE SECRETION IN THE RAT. Endocrinology. 1965 Apr;76:657–664. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-4-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSON G. M., KASHII C., MATSUNAGA M., PAGE I. H. HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE PRODUCED BY HOMOLOGOUS RENIN. Science. 1964 Jul 10;145(3628):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3628.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken D. E., Biber T. U. Biologically effective immunization against angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):791–795. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOLI D., BRUNNER H., PETERS G., GROSS F. Changes in renin content in kidneys of renal hypertensive rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jan;109:142–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen S., Smeby R. R., Bumpus F. M. Antihypertensive effect of an isolated phospholipid. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):337–341. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallotton M. B., Page L. B., Haber E. Radioimmunoassay of angiotensin in human plasma. Nature. 1967 Aug 12;215(5102):714–715. doi: 10.1038/215714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKERLIN G. E. Antibodies to renin as proof of the pathogenesis of sustained renal hypertension. Circulation. 1958 Apr;17(4 Pt 2):653–657. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.4.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKERLIN G. E., BIRD R. B., BRENNAN B. B., FRANK M. H., KREMEN S., KUPERMAN I., SKOM J. H. Treatment and prophylaxis of experimental renal hypertension with renin. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 May;41(5):708–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



