Abstract
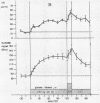
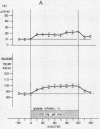
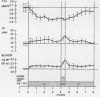
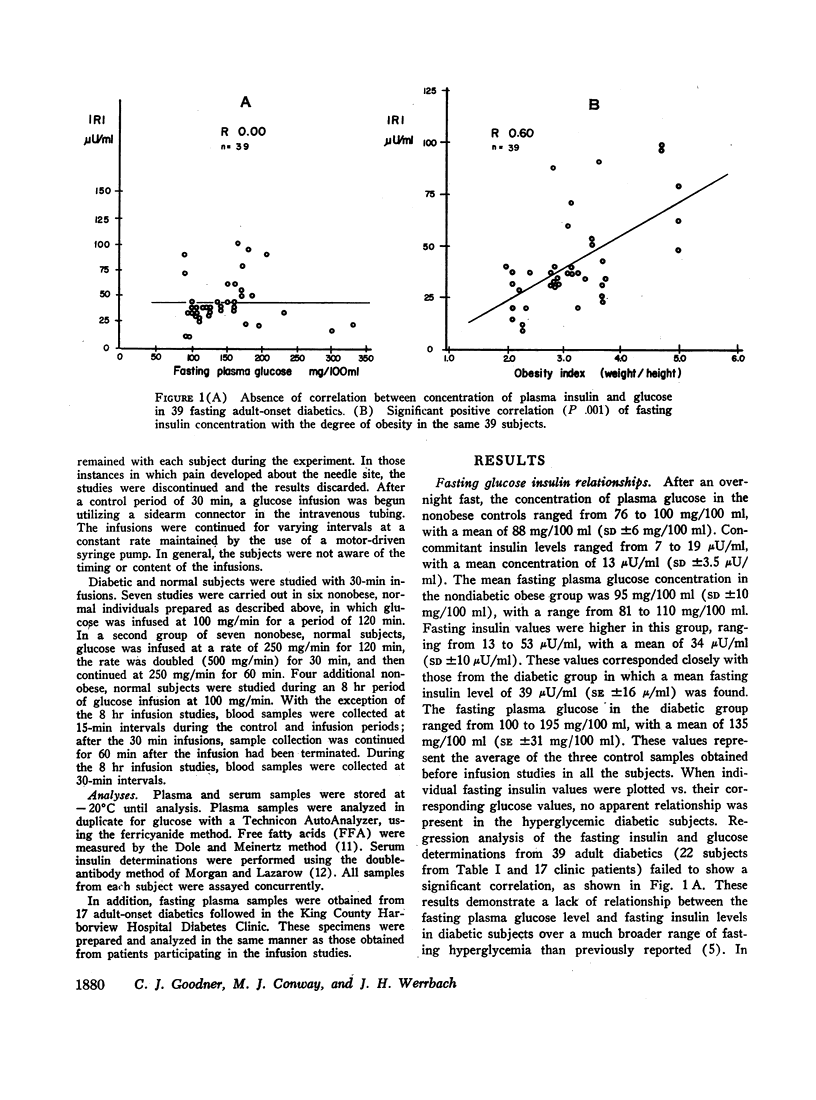
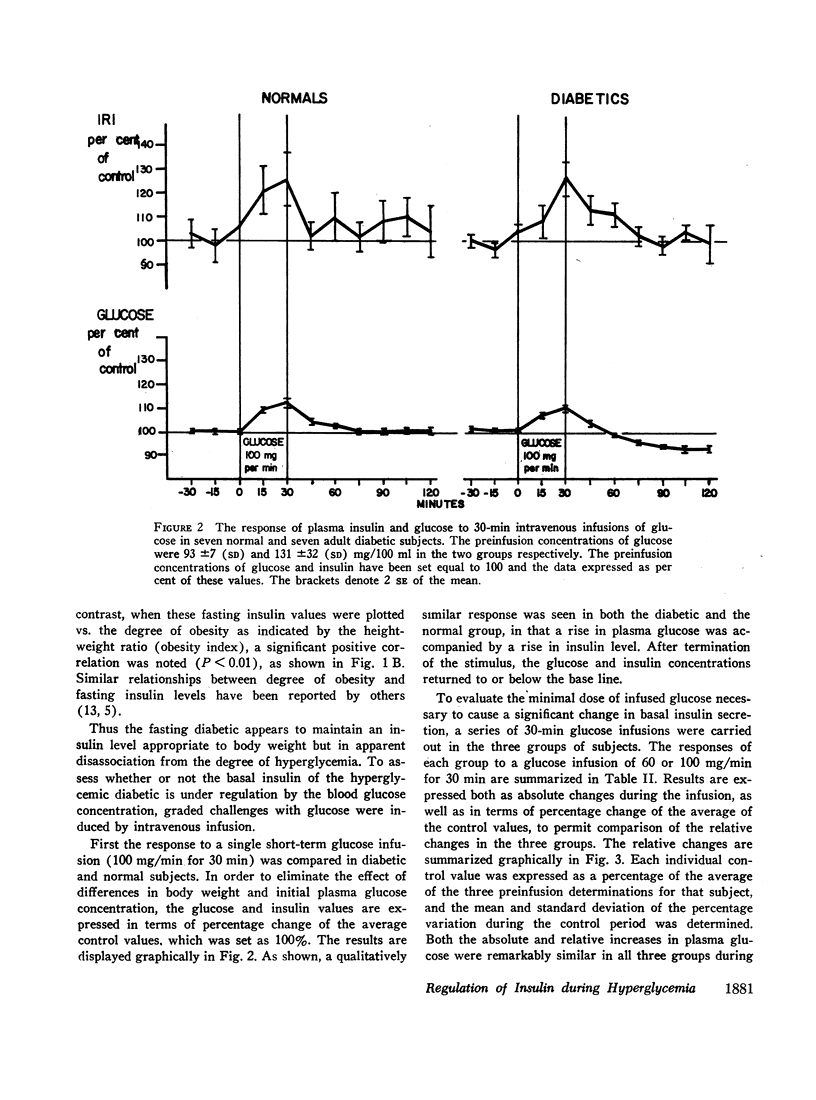
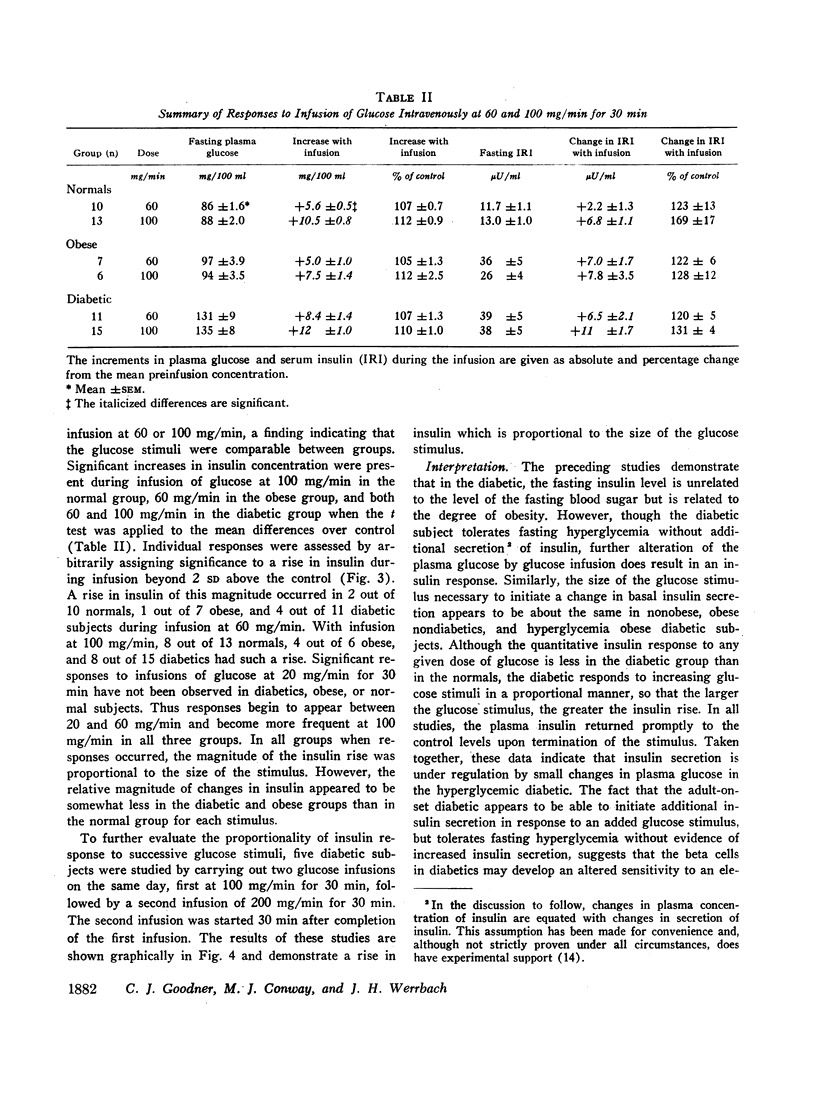
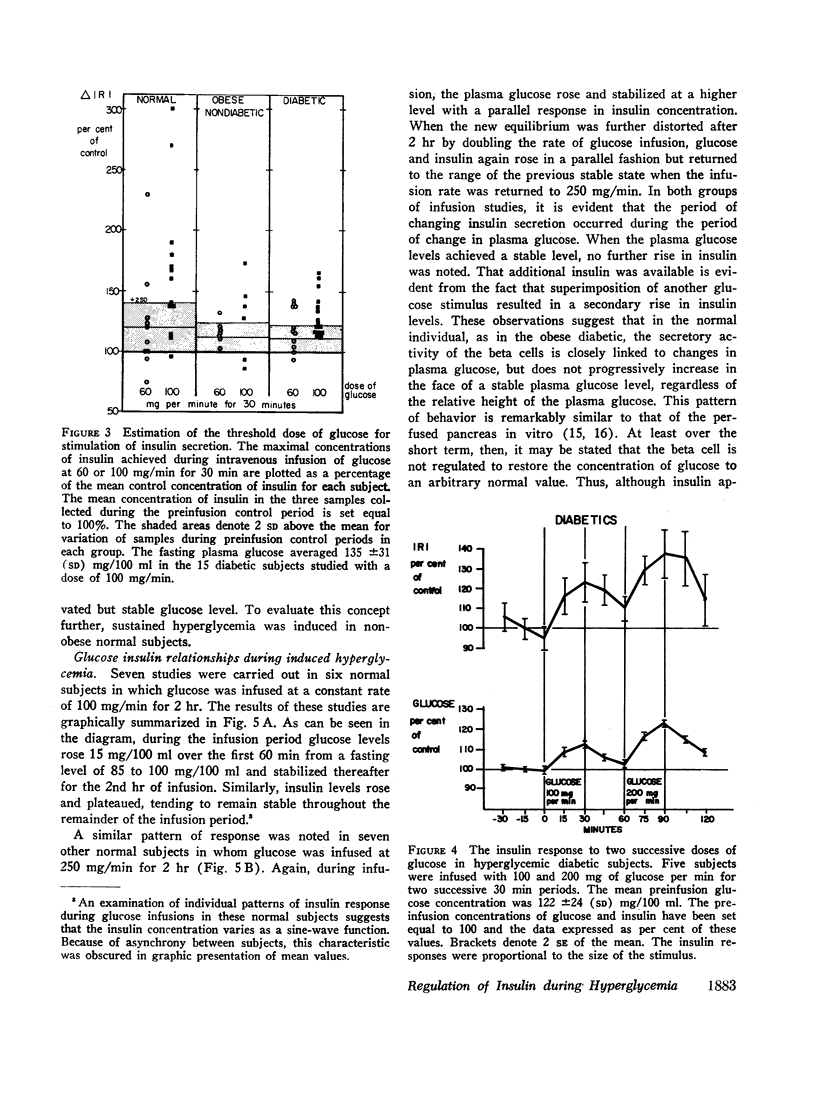
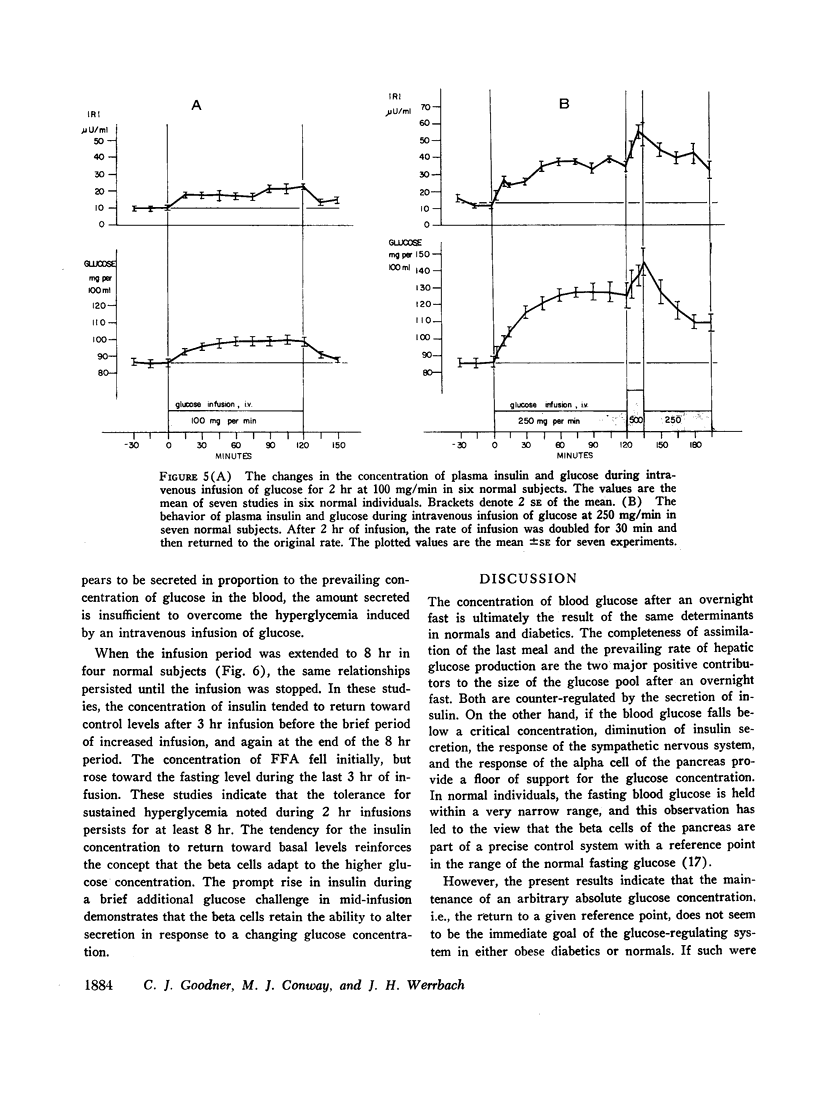
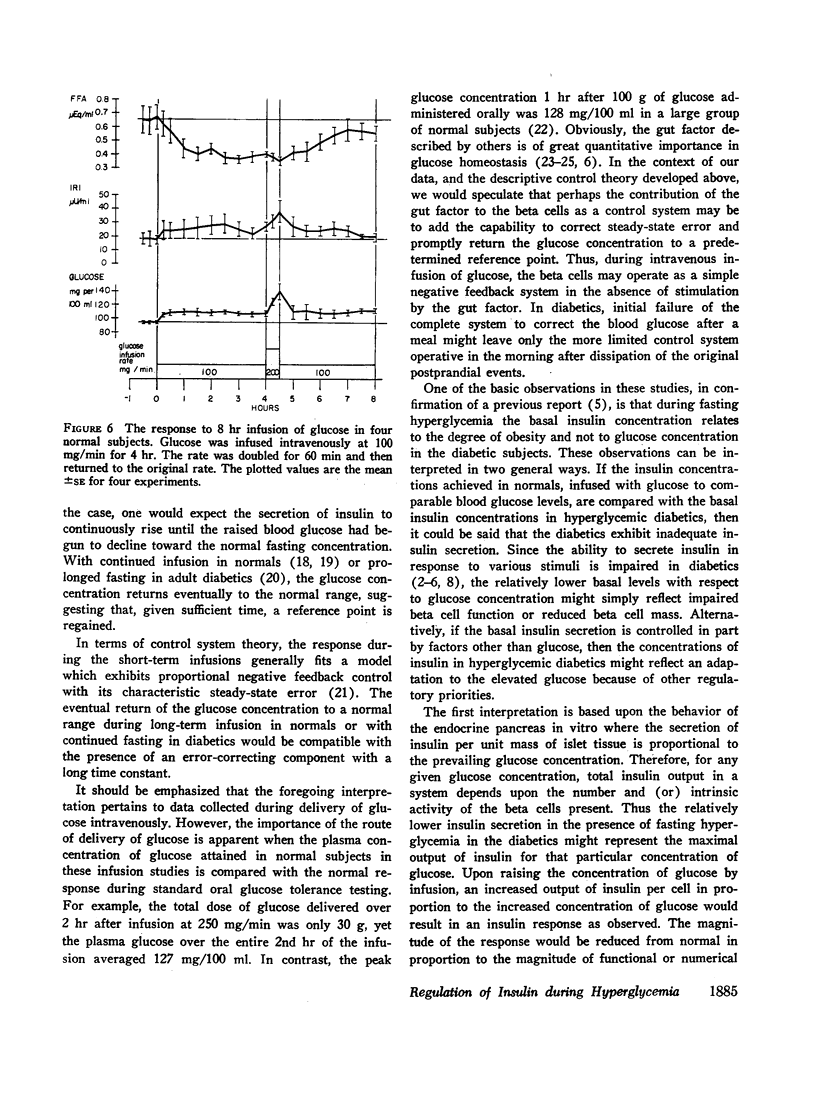
In obese adult diabetics, the concentration of insulin in venous plasma was unrelated to the degree of hyperglycemia after an overnight fast. However, in these subjects, insulin rose and fell in proportion to the magnitude of change in plasma glucose induced by small intravenous infusions of glucose. The minimal dose of glucose to cause a significant rise in insulin above the fasting level was similar in normal subjects, obese nondiabetic subjects, and in obese, hyperglycemic adult diabetics. This dose lay between infusion of 60 and 100 mg of glucose per min for 30 min. These results suggested that the secretion of insulin was under regulation by changes in blood glucose but was not stimulated in proportion to the stable raised blood glucose concentration of the hyperglycemic diabetic. Artificial hyperglycemia was induced in fasting normal subjects by constant intravenous infusion of glucose at rates of 100-250 mg of glucose per min for periods up to 8 hr. Plasma glucose rose during the 1st hr of infusion and then remained constantly elevated for up to 8 hr. The concentration of plasma insulin paralleled that of plasma glucose. During the period of constant hyperglycemia and elevated insulin, superimposition of a brief additional glucose load resulted in a prompt rise in glucose and insulin, both returning to the previous elevated levels.
Thus in normals as well as obese diabetics, stable hyperglycemia does not produce a pancreatic response sufficient to return the blood glucose to an arbitrary normal fasting concentration, yet the beta cells remain readily responsive to a change in plasma glucose. These data suggest that the beta cells do not operate as a control system with an absolute reference point when presented with systemic hyperglycemia. The behavior of the beta cells during hyperglycemia in the fasting obese adult diabetic suggests that the regulation of the basal insulin secretion may not be determined by factors directly related to the prevailing concentration of glucose. It is postulated that the beta cells adapt to hyperglycemia perhaps through the operation of controls directed toward a normal delivery of free fatty acids or some other cellular metabolic substrate during fasting.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLIE V. W. Coefficients of normal blood glucose regulation. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Sep;16:783–788. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.5.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The plasma insulin response to glucose infusion in healthy subjects and in diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):278–304. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu P. C., Conway M. J., Krouse H. A., Goodner C. J. The pattern of rsponse of plasma insulin and glucose to meals and fasting during chlorpropamide therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):757–769. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., STIMMLER L., HLAD C. J., Jr, ARAI Y. PLASMA INSULIN RESPONSE TO ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS GLUCOSE ADMINISTRATION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1076–1082. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAJANS S. S., CONN J. W. An approach to the prediction of diabetes mellitus by modification of the glucose tolerance test with cortisone. Diabetes. 1954 Jul-Aug;3(4):296-302; discussion, 302-4. doi: 10.2337/diab.3.4.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Conn J. W., Thiffault C., Knopf R. F., Guntsche E. Secretion of insulin induced by amino acids and glucose in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Feb;28(2):266–276. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODNER C. J., TUSTISON W. A. AUTONOMIC MEDIATION OF THE EFFECT OF RAISED ARTERIAL GLUCOSE UPON FREE FATTY ACIDS. Science. 1964 Nov 6;146(3645):770–772. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3645.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRODSKY G. M., BATTS A. A., BENNETT L. L., VCELLA C., MCWILLIAMS N. B., SMITH D. F. EFFECTS OF CARBOHYDRATES ON SECRETION OF INSULIN FROM ISOLATED RAT PANCREAS. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:638–644. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M. Effects of prolonged fasting on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1966 Nov;15(11):798–806. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.11.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodner C. J., Tustison W. A., Davidson M. B., Chu P. C., Conway M. J. Studies of substrate regulation in fasting. I. Evidence for central regulation of lipolysis by plasma glucose mediated by the sympathetic nervous system. Diabetes. 1967 Aug;16(8):576–589. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.8.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber A. L., Wood F. C., Jr, Williams R. H. Serum immunoreactive insulin response during prolonged glucose infusions in nondiabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):145–149. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Forsham P. H. Insulin and the pancreas. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:347–380. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAM J. H., GRODSKY G. M., FORSHAM P. H. Excessive insulin response to glucose in obese subjects as measured by immunochemical assay. Diabetes. 1963 May-Jun;12:197–204. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.3.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Boshell B. R., DiPlacido J., Roddam R. F. Insulin secretion in obesity. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 9;276(6):314–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702092760603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C. R., LAZAROW A. Immunoassay of insulin using a two-antibody system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 May;110:29–32. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Holdsworth C. D., Turner D. S. Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1317–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr A receptor mechanism for the inhibition of insulin release by epinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):86–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI105514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMEIN Q. R., WILKERSON H. L. The efficiency of screening tests for diabetes. J Chronic Dis. 1961 Jan;13:6–21. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(61)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELTZER H. S., HARRIS V. L. EXHAUSTION OF INSULOGENIC RESERVE IN MATURITY-ONSET DIABETIC PATIENTS DURING PROLONGED AND CONTINUOUS HYPERGLYCEMIC STRESS. Diabetes. 1964 Jan-Feb;13:6–13. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. P., Farquhar J. W., Silvers A., Reaven G. M. Insulin delivery rate into plasma in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):1947–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI105884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman K. E., Vaughan G. D., Timmer R. F. An in vitro method for studying insulin secretion in the perfused isolated rat pancreas. Metabolism. 1966 May;15(5):466–476. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]