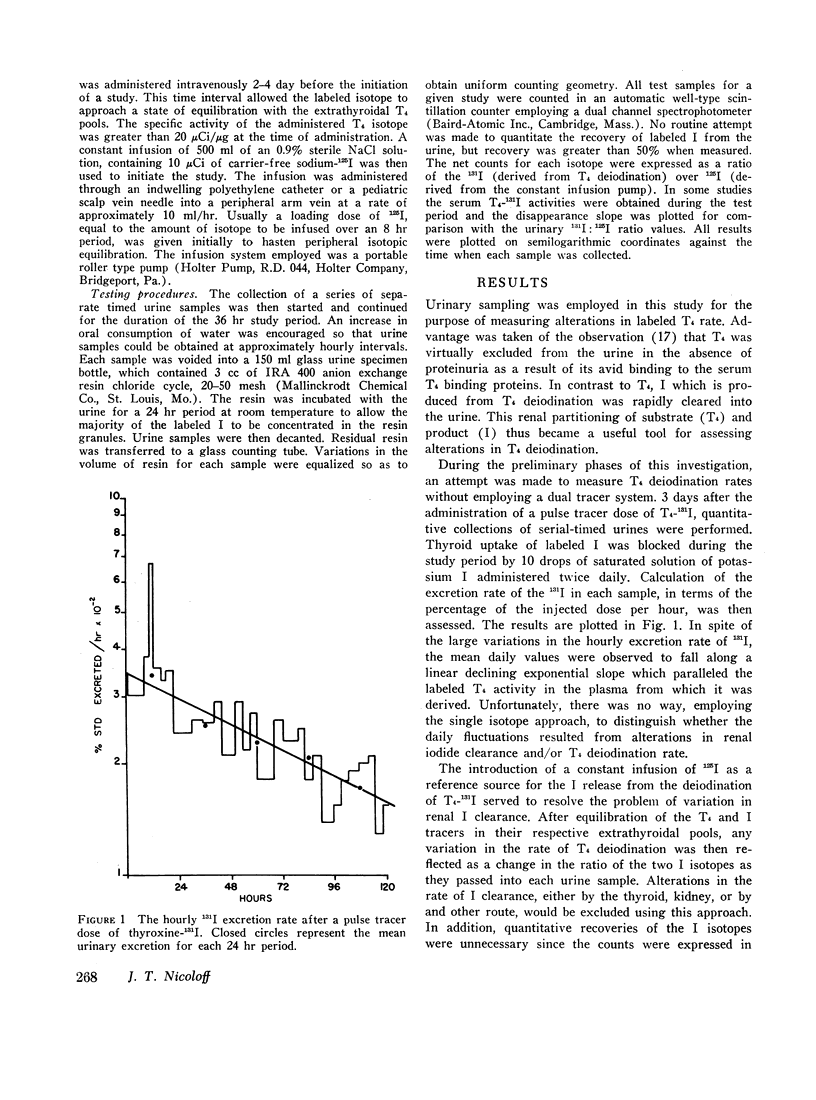
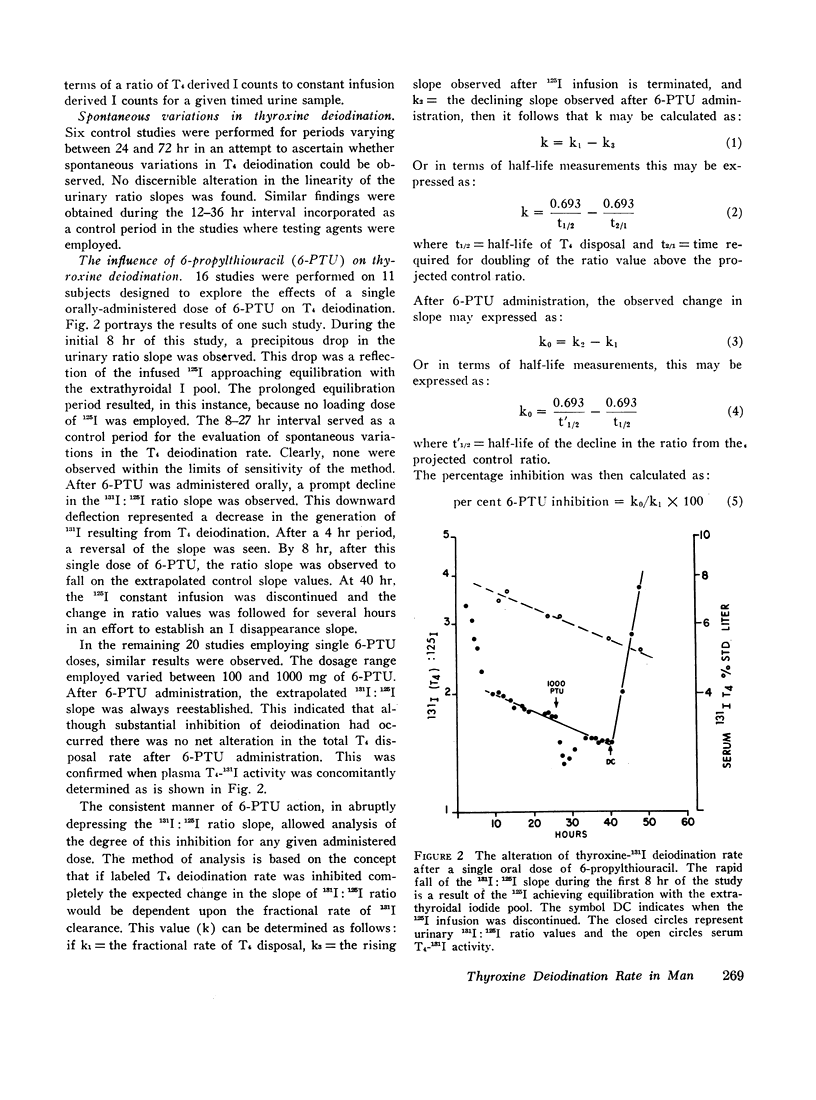
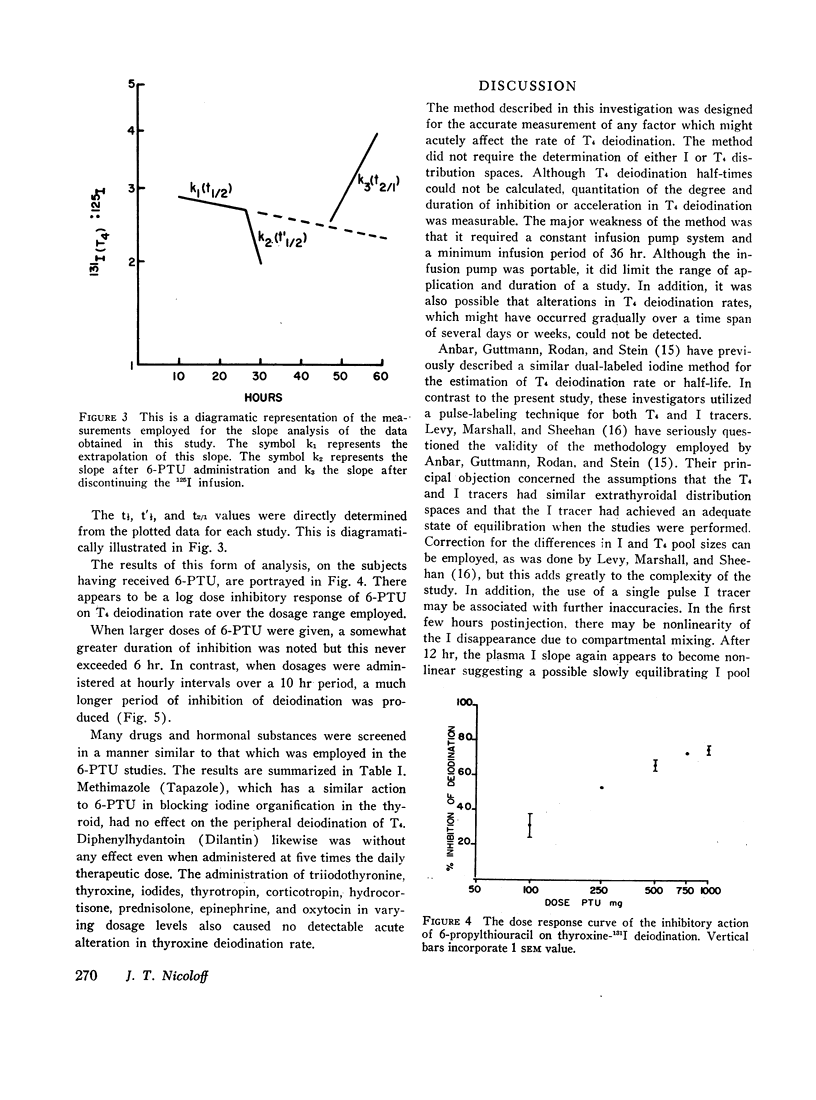
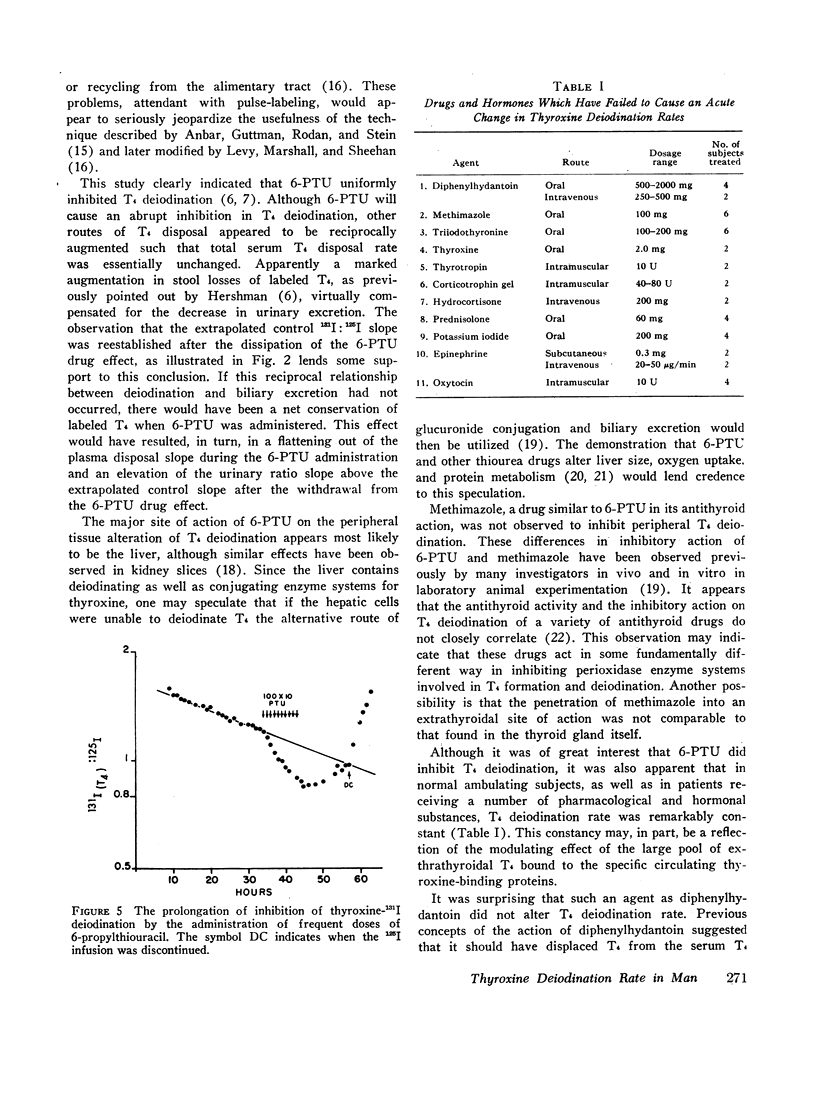
Abstract
A newly devised dual labeled iodine isotopic method is described for the detection and quantitation of alterations in thyroxine (T4) deiodination rate in man. This method employs the principle of a constant 125I infusion to serve as a reference source for the generation of 131I derived from the deiodination of T4-131I. Measurement of these two iodide isotopes are made in serially timed urine collections and are expressed in terms of a ratio value. Using this technique, it was possible to measure accurately the effects of a single dose of 6-propylthiouracil (6-PTU) in producing inhibition of T4 deiodination in euthyroid subjects. It was also possible to assess the time of onset, duration of action, and degree of inhibition produced by 6-PTU. Employing single doses of 6-PTU, ranging from 100 to 1000 mg, there was found to be a log dose relationship with a degree of inhibition observed in T4 deiodination. In control studies T4 deiodination rate was found to be constant for periods ranging up to 72 hr in normal ambulating subjects. The acute administration of many other agents was employed in an attempt to alter the T4 deiodination rate. These included diphenylhydantoin, methimazole, triiodothyronine, thyroxine, thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), hydrocortisone, predinsolone, potassium iodide, epinephrine, and oxytocin. No detectable change in T4 deiodination rate was observed with these agents in the dosage ranges employed in this study. The lack of any observable alteration in the T4 deiodination rate in response to this array of drugs and hormones appears to indicate that the availability of T4 to intracellular sites of deiodination and possibly action is well modulated to resist abrupt changes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anbar M., Guttmann S., Rodan G., Stein J. A. The determination of the rate of deiodination of thyroxine in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1986–1991. doi: 10.1172/JCI105305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arango G., Mayberry W. E., Hockert T. J., Elveback L. R. Total and free human serum thyroxine in normal and abnormal thyroid states. Mayo Clin Proc. 1968 Jul;43(7):503–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAVERMAN L. E., INGBAR S. H. Effects of propylthiouracil and thiouracil on the metabolism of thyroxine and several of its derivatives by rat kidney slices in vitro. Endocrinology. 1962 Nov;71:701–712. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-5-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein G., Hasen J., Oppenheimer J. H. Turnover of 131-I-thyroxine in patients subjected to surgical trauma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 May;27(5):741–744. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-5-741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein G., Oppenheimer J. H. Factors influencing the concentration of free and total thyroxine in patients with nonthyroidal disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Feb;26(2):195–201. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W., Schussler G. C. Decreased serum free thyroxine concentration in patients treated with diphenylhydantoin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Feb;28(2):181–186. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREINKEL N., INGBAR S. H. ACTH, cortisone and the metabolism of iodine. Metabolism. 1956 Nov;5(6 Pt 1):652–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth E. D., Rives K., Becker D. V. Nonthyroidal action of propylthiouracil in euthyroid, hypothyroid and hyperthyroid man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Mar;26(3):239–246. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-3-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALTON V. A., INGBAR S. H. A photoactivated flavin-induced degradation of thyroxine and related phenols. Endocrinology. 1962 Feb;70:210–220. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-2-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALTON V. A., INGBAR S. H. The mechanism of protein iodination during the metabolism of thyroid hormones by peripheral tissues. Endocrinology. 1961 Jul;69:30–38. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregerman R. I., Solomon N. Acceleration of thyroxine and triiodothyronine turnover during bacterial pulmonary infections and fever: implications for the functional state of the thyroid during stress and in senescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jan;27(1):93–105. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHMAN J. M. EFFECT OF 5- AND 6-PROPYLTHIOURACIL ON THE METABOLISM OF L-THYROXINE IN MAN. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Feb;24:173–179. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-2-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHMAN J. M., VAN MIDDLESWORTH L. Effect of antithyroid compounds on the deiodination of thyroxine in the rat. Endocrinology. 1962 Jul;71:94–100. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-1-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays M. T., Solomon D. H. Effect of epinephrine on the peripheral metabolism of thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1114–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI106068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D., Meek J. C., Manning R. T. Determination of free thyroxine in serum of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. N Engl J Med. 1967 Apr 20;276(16):900–902. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196704202761604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Regulation of the peripheral metabolism of the thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:353–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Studies of thyroid function and the peripheral metabolism of I 131-labeled thyroxine in patients with treated Graves disease. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1603–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI103753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E., Dawber N. A., Lee G. Y. A new method for measuring the free thyroid hormone in human serum and an analysis of the factors that influence its concentration. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1679–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine C. H. Effect of exercise on thyroxine degradation in athletes and non-athletes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jul;28(7):942–948. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-7-942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. P., Marshall J. S., Sheahan M. G. Theoretical and practical considerations of thyroxine deiodination rates in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 May;28(5):633–643. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-5-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza D. M., Flock E. V., Owen C. A., Jr, Paris J. Effect of 5,5'-diphenylhydantoin on the metabolism of L-thyroxine-131-I in the rat. Endocrinology. 1966 Jul;79(1):106–118. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-1-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Dowling J. T. Studies of peripheral thyroxine distribution in thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2000–2015. doi: 10.1172/JCI105887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., FISHER L. V., NELSON K. M., JAILER J. W. Depression of the serum protein-bound iodine level by diphenylhydantion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Mar;21:252–262. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-3-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SURKS M. I. DETERMINATION OF FREE THYROXINE IN HUMAN SERUM: A THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:785–793. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., TAVERNETTI R. R. Displacement of thyroxine from human thyroxine-binding globulin by analogues of hydantoin. Steric aspects of the thyroxinebinding site. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2213–2220. doi: 10.1172/JCI104680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., TAVERNETTI R. R. Studies on the thyroxine-diphenylhydantoin interaction: effect of 5,5'-diphenylhydantoin on the displacement of L-thyroxine from thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Endocrinology. 1962 Sep;71:496–504. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-3-496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Bernstein G., Hasen J. Estimation of rapidly exchangeable cellular thyroxine from the plasma disappearance curves of simultaneously administered thyroxine-131-I and albumin-125-I. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):762–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI105577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H. Role of plasma proteins in the binding, distribution and metabolism of the thyroid hormones. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 23;278(21):1153–1162. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805232782107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY J. B. Deiodination of the iodinated amino acids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr 23;86:417–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., CHODOS R. B. Radiothyroxine turnover studies in myxedema, thyrotoxicosis, and hypermetabolism without endocrine disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jul;35(7):806–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI103333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SURKS M. I., OPPENHEIMER J. H. POSTOPERATIVE CHANGES IN THE CONCENTRATION OF THYROXINE-BINDING PREALBUMIN AND SERUM FREE THYROXINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:794–802. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J., STANDAERT M. E., RALL J. E. Thyroxine displacement from serum proteins and depression of serum protein-bound iodine by certain drugs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1373–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI104368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATVIN M. B., WANNEMACHER R. W., Jr, BANKS W. L., Jr EFFECTS OF THIOURACIL AND OF THYROIDECTOMY OF LIVER PROTEIN METABOLISM. Endocrinology. 1964 Jun;74:878–884. doi: 10.1210/endo-74-6-878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



