Abstract
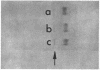
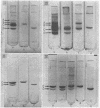
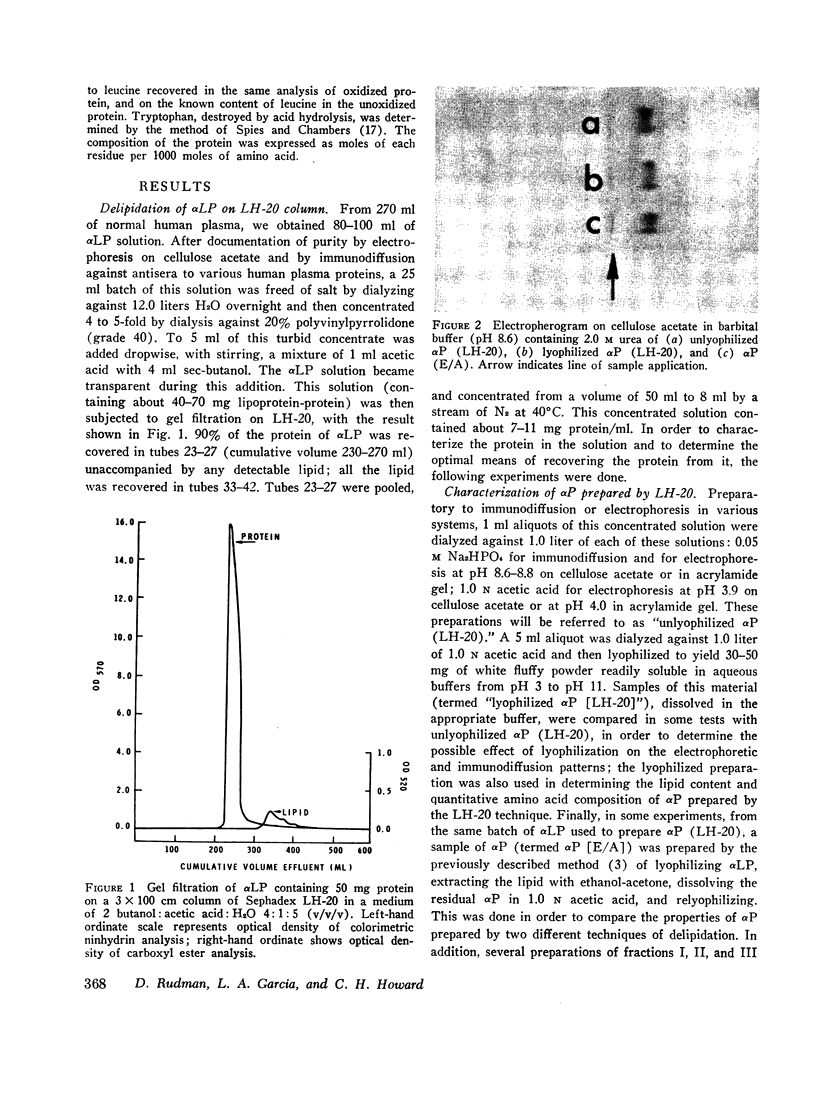
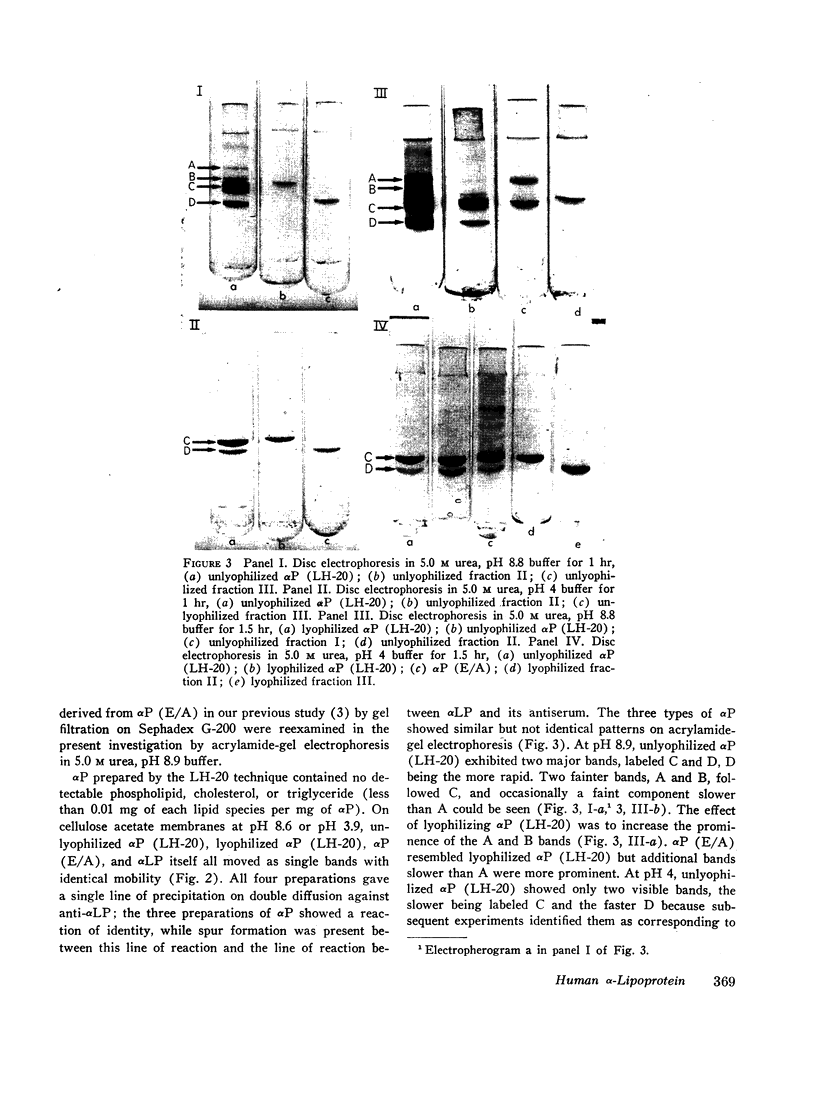
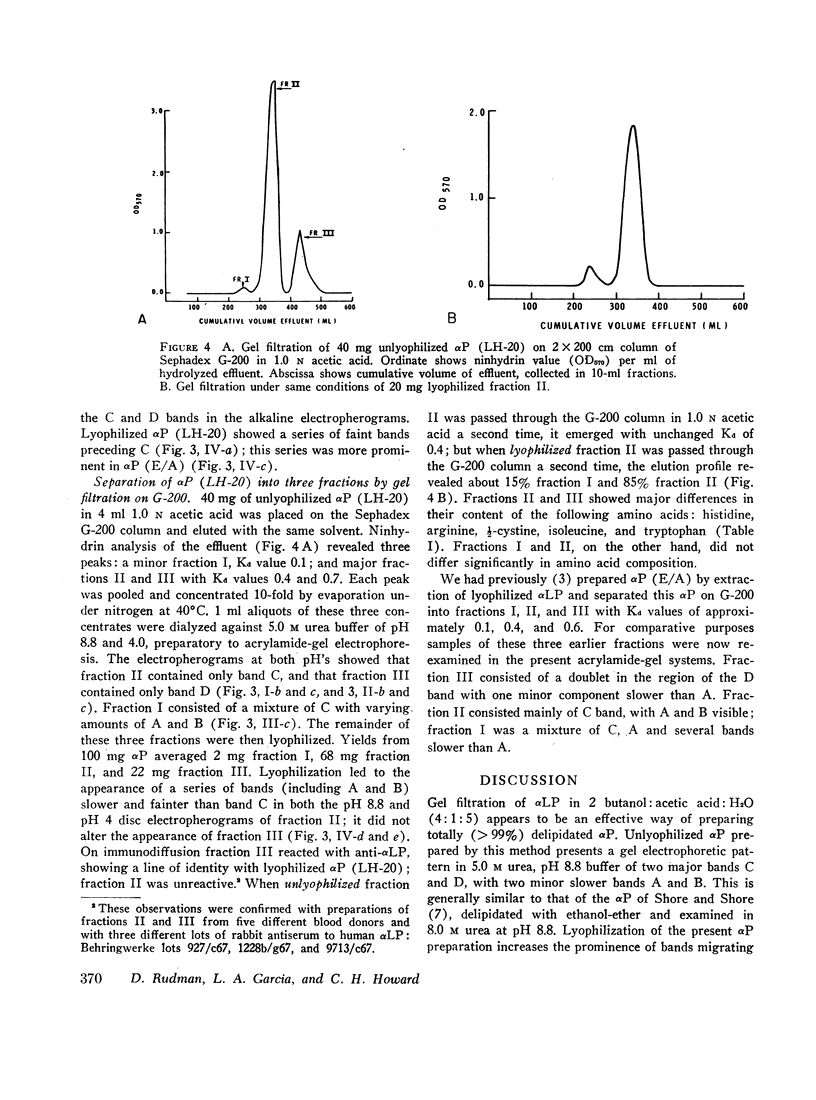
Human plasma alpha lipoprotein (αLP) was totally delipidated by gel filtration on Sephadex LH-20 in a medium of 2 butanol:acetic acid:H2O, 4:1:5. The resulting alpha protein (αP) exhibited two major bands, labeled C and D, on acrylamide-gel electrophoresis in 5.0 M urea at pH 8.8 or 4.0. Minor bands labeled A and B, also present, were shown to be aggregates of C which form when the latter is lyophilized. The C and D components were isolated in pure form from αP (prepared by LH-20 chromatography of αLP) by gel filtration of this protein on Sephadex G-200 in a medium of 1.0 N acetic acid: the C component emerged with a distribution coefficient (Kd) of 0.4, and the D component with a coefficient of 0.7. From each 100 mg of αP, 68 mg of C and 22 mg of D were isolated. 3 mg of a minor fraction with Kd 0.1, containing A and B components as well as C, were also obtained. D but not C reacts with rabbit antiserum to human αLP. C and D differ substantially in content of arginine, histidine, ½-cystine, isoleucine, and tryptophan.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Peptides obtained by tryptic hydrolysis of performic acid-oxidized ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):623–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M., FREDERICKSON D. S. The nature of the proteins associated with dog ano human chylomicrons. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):562–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL H. L., PFLUKE M. L., CALLERAMI J. The colorimetric estimation of serum fatty esters. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 May;4(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Garcia L. A., Abell L. L., Akgun S. Observations on the protein components of human plasma high- and low-density lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3136–3148. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCANU A., LEWIS L. A., PAGE I. H. Studies on the antigenicity of beta- and alpha-lipoproteins of human serum. J Exp Med. 1958 Aug 1;108(2):185–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. Forms of human serum high density lipoprotein protein. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):295–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. Heterogeneity in protein subunits of human serum high-density lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2773–2777. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V., Shore B. Some physical and chemical studies on the protein moiety of a high-density (1.126-1.195 g-ml) lipoprotein fraction of human serum. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1962–1969. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V., Shore B. Some physical and chemical studies on two polypeptide components of high-density lipoproteins of human serum. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3396–3403. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodhi H. S., Gould R. G. Combination of delipidized high density lipoprotein with lipids. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1205–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler P. H., Wallach D. F. Isolation of lipid-free plasma membrane proteins by gel filtration on Sephadex LH-20 using 2-chloroethanol-water as solvent. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 2;135(2):371–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]