Abstract
Regional cerebral oxygen utilization rate is measured in vivo by the following method:
A small volume of blood with radioactive oxygen-15-tagged hemoglobin is rapidly injected into the internal carotid artery of the patient under study. The first injection is followed by the injection carried out under identical circumstances but with blood labeled with water-15O. After each injection, the distribution of the radioactive label in the brain is measured and recorded, as a function of time, by six collimated scintillation probes placed over the subject's head. The recording, subsequent to the first injection, reflects (a) the arrival of the labeled oxygen into the tissues, (b) its partial conversion into water of metabolism, and (c) the washout of labeled water from the brain. The ratio of the amount of labeled water formed to the amount of oxygen perfusing the tissues, which can be derived from the recording, is a measure of fractional oxygen utilization. The second injection provides a measure of blood flow by the interpretation of the washout of labeled water from brain tissues. The product, fractional oxygen utilization × blood flow × arterial oxygen content, gives a measure of oxygen utilization rate. Some aspects of the validity of this method are tested by the injection of a nondiffusible indicator, carboxyhemoglobin-15O.
Regional cerebral oxygen utilization rates for a series of patients with cerebral pathology are reported.
Full text
PDF

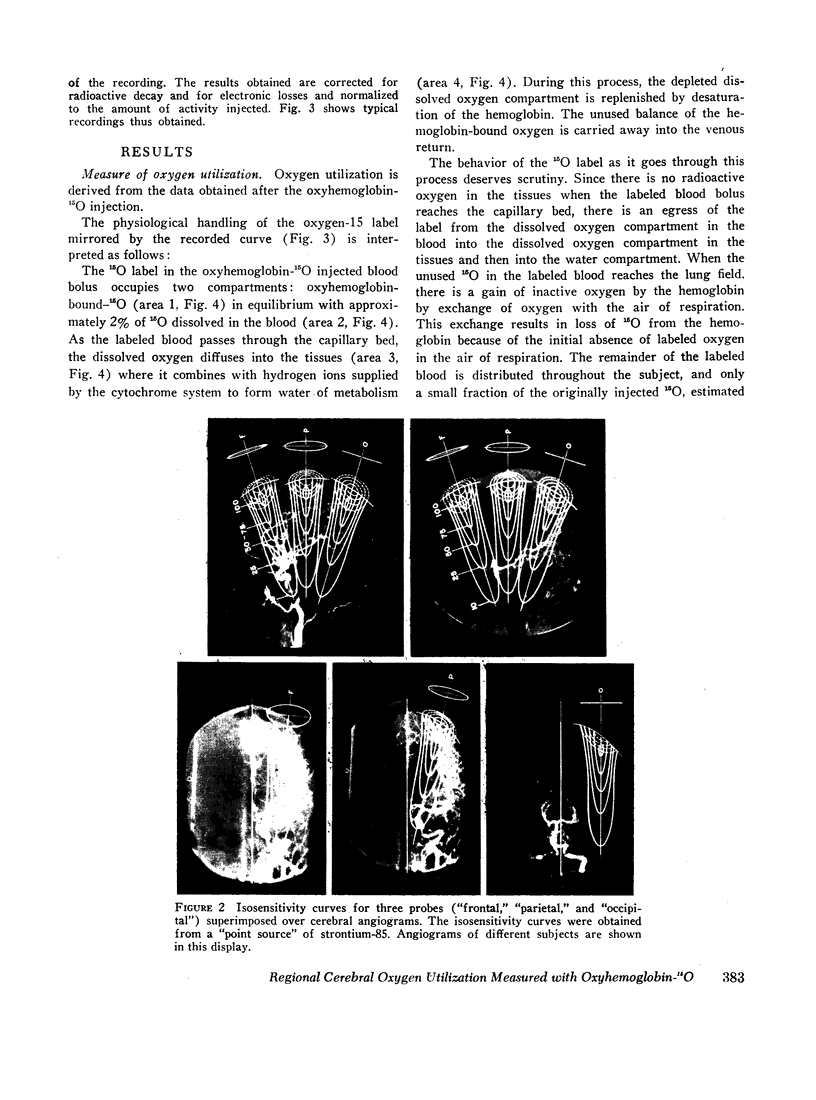
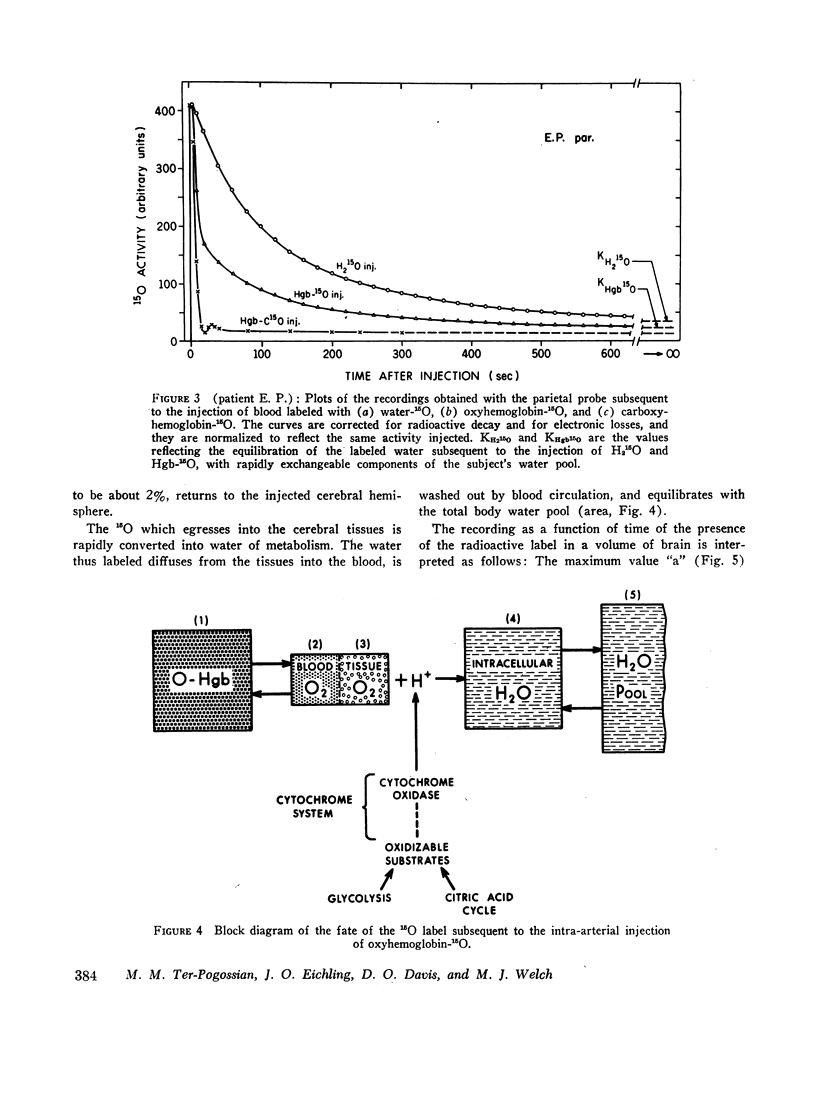
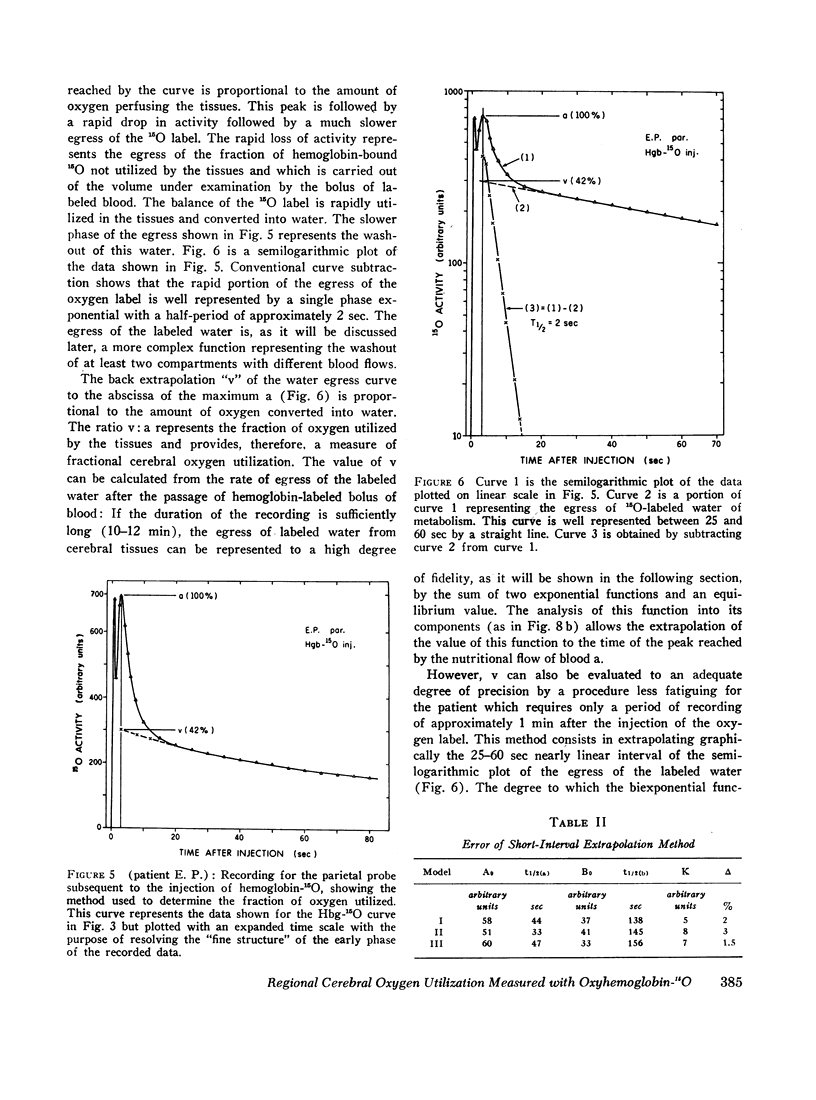


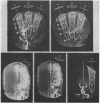
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS F. E., KENYON K., KIRK J. A rapid titrimetric method for determining the water content of human blood. Science. 1953 Sep 4;118(3062):276–277. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3062.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoedt-Rasmussen K., Skinhoj E. In vivo measurements of the relative weights of gray and white matter in the human brain. Neurology. 1966 May;16(5):515–520. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Schmidt C. F. THE EFFECTS OF ALTERED ARTERIAL TENSIONS OF CARBON DIOXIDE AND OXYGEN ON CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND CEREBRAL OXYGEN CONSUMPTION OF NORMAL YOUNG MEN. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):484–492. doi: 10.1172/JCI101995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Schmidt C. F. THE NITROUS OXIDE METHOD FOR THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW IN MAN: THEORY, PROCEDURE AND NORMAL VALUES. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):476–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI101994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN N. A. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in man. Physiol Rev. 1959 Apr;39(2):183–238. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ter-Pogossian M. M., Eichling J. O., Davis D. O., Welch M. J., Metzger J. M. The determination of regional cerebral blood flow by means of water labeled with radioactive oxygen 15. Radiology. 1969 Jul;93(1):31–40. doi: 10.1148/93.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. J., Ter-Pogossian M. M. Preparation of short half-lived radioactive gases for medical studies. Radiat Res. 1968 Dec;36(3):580–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. EQUATIONS FOR MEASURING BLOOD FLOW BY EXTERNAL MONITORING OF RADIOISOTOPES. Circ Res. 1965 Apr;16:309–321. doi: 10.1161/01.res.16.4.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]