Abstract
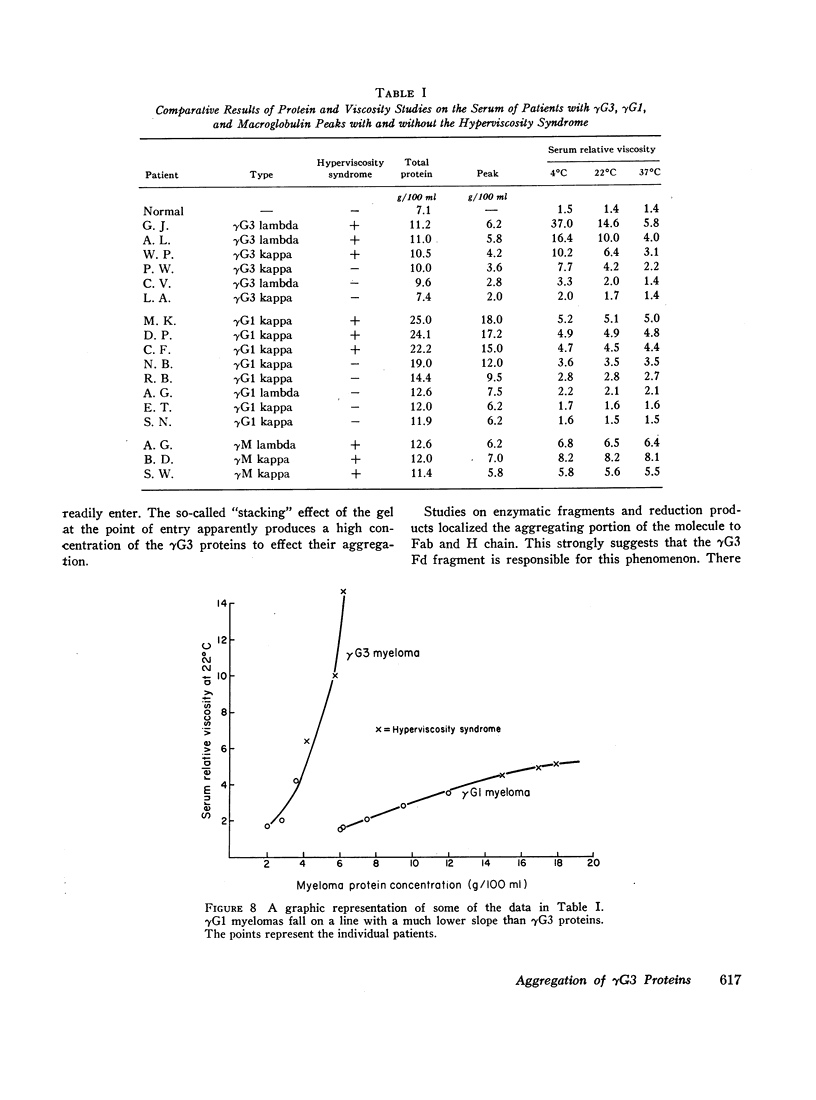
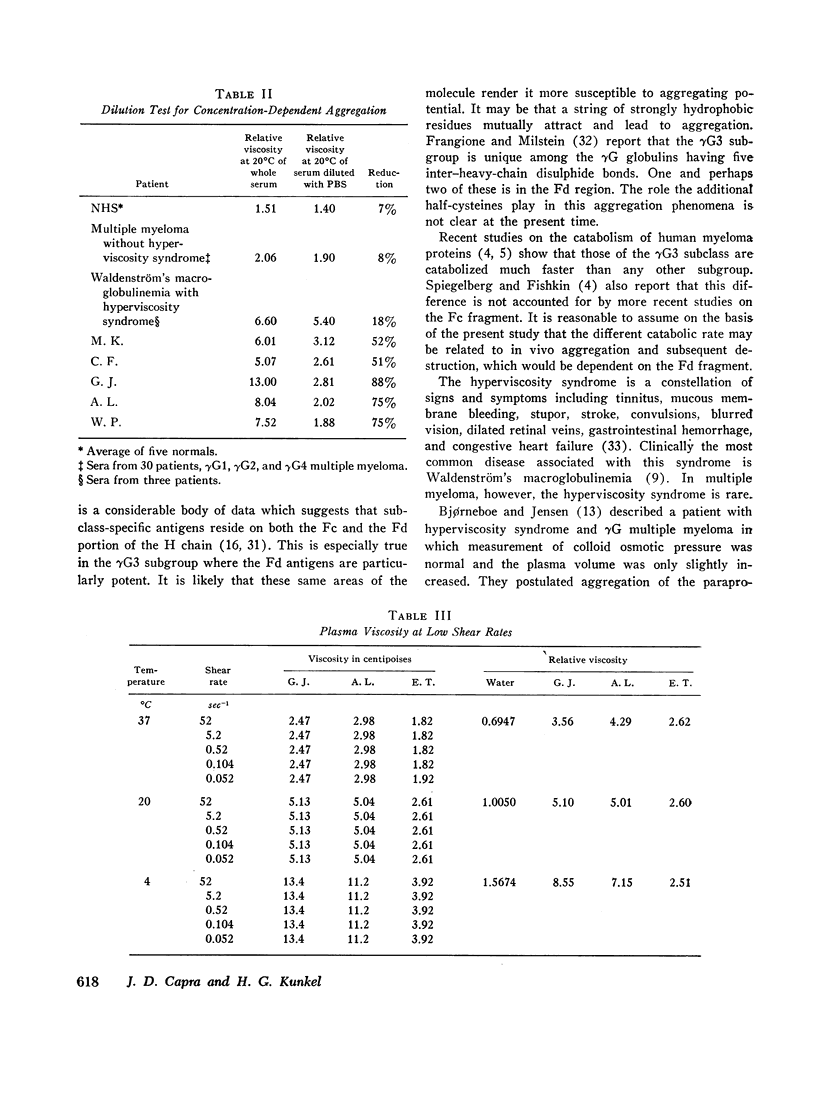
Studies on the sera and isolated proteins from 14 patients with γG3 multiple myeloma revealed a concentration- and temperature-dependent aggregation which was not encountered in 26 sera from patients with multiple myeloma involving other γG subgroups. When the γG3 myeloma sera were diluted and characterized by analytical ultracentrifugation, complex formation was minimal. However, when these sera were examined undiluted, marked complex formation was observed. Studies on the isolated proteins, their enzymatic fragments, as well as their heavy and light polypeptide chains localized the aggregating sites to the Fd fragment of the heavy chains. The findings were also documented by acrylamide-gel electrophoresis and capillary tube viscometry.
The hyperviscosity syndrome was observed in six patients: three with γG3 myeloma and three with γG1 myeloma. In the latter group extreme protein concentrations appeared essential for the development of the clinical symptoms. The γG3 cases, however, because of the aggregation phenomenon, showed the syndrome at relatively low protein concentrations.
Full text
PDF


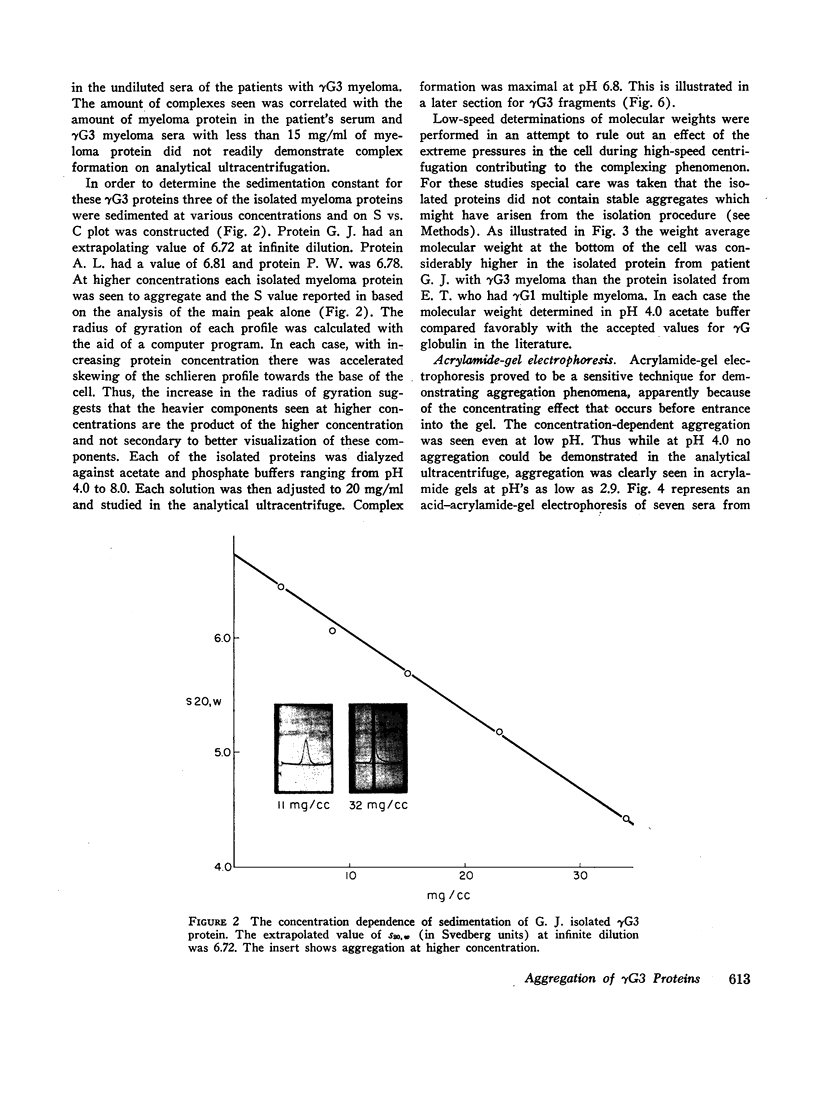
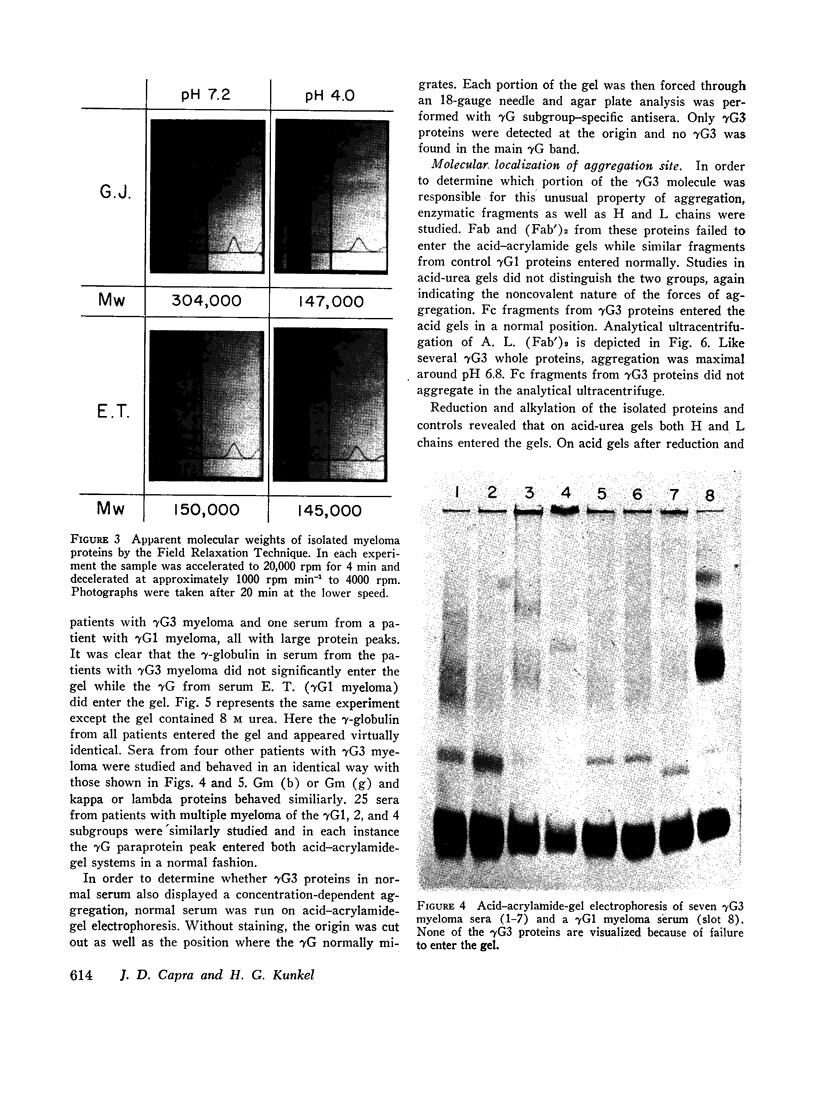
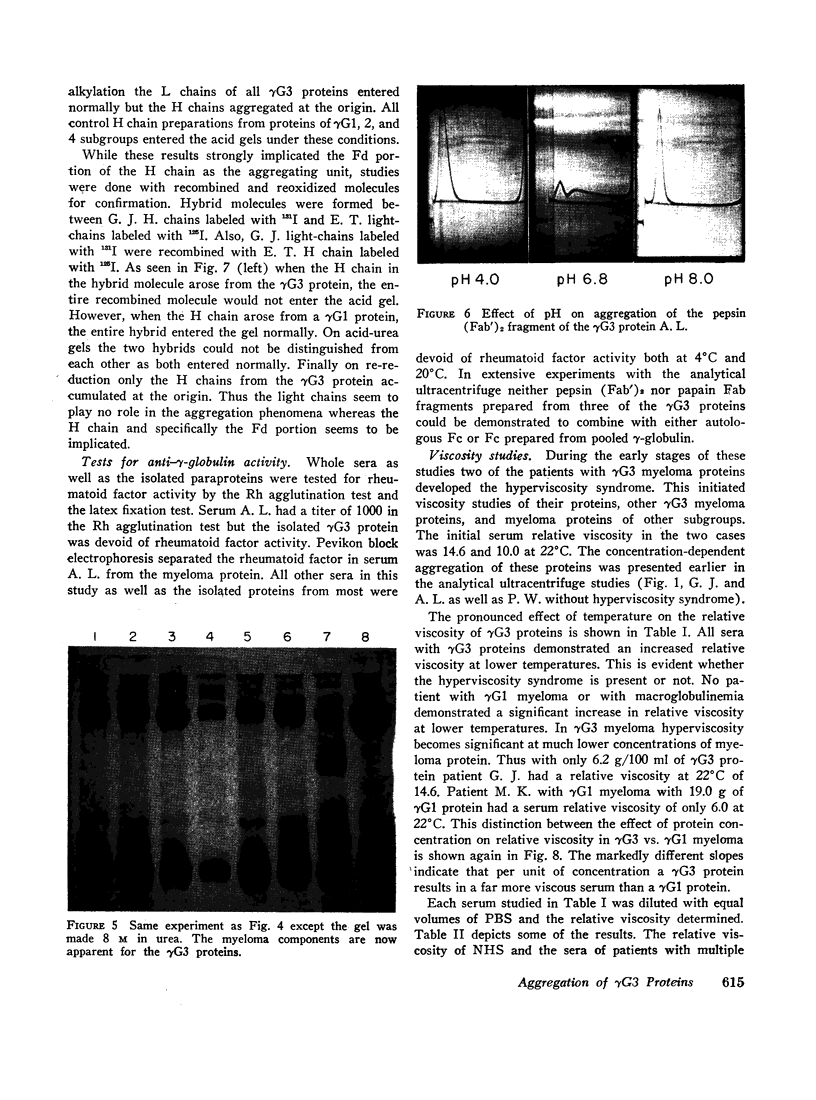
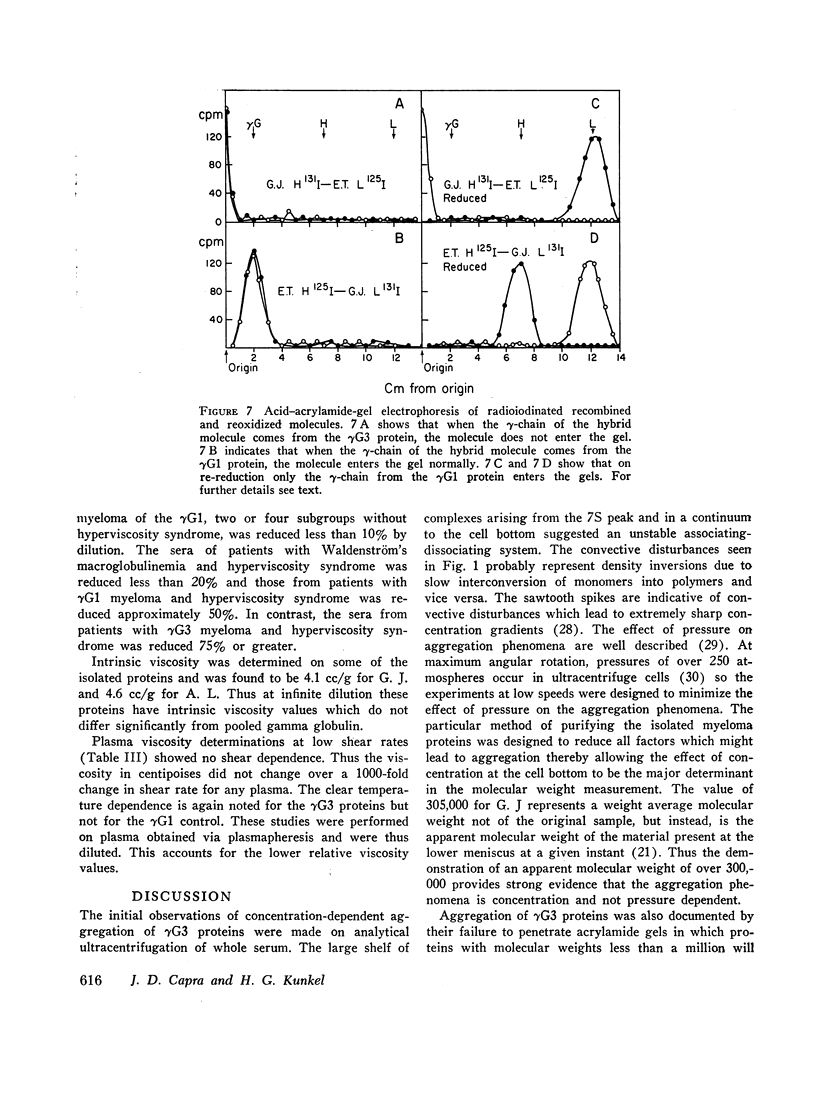



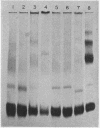
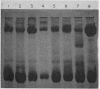
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorneboe M., Jensen K. B. A case of myelomatosis with normal colloid osmotic pressure in spite of extremely high serum protein concentration. (Hyperviscosity syndrome due to aggregation of myeloma globulin molecules?). Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;445:212–215. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARM S., KURLAND G. S. Tube flow behavior and shear stress-shear rate characteristics of canine blood. Am J Physiol. 1962 Sep;203:417–421. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Usami S., Taylor H. M., Lundberg J. L., Gregersen M. I. Effects of hematocrit and plasma proteins on human blood rheology at low shear rates. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):81–87. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH H. F., MORTON J. I. Human serum macroglobulins and dissociation units. I. Physicochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):1107–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., BARTH W. F., SOLOMON A. SERUM HYPERVISCOSITY SYNDROME. JAMA. 1965 May 10;192:464–467. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080190030008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L. SERUM PROTEIN DISORDERS CAUSING CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN MALIGNANT NEOPLASTIC DISEASE. J Chronic Dis. 1963 Jul;16:703–712. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(63)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C. Variations in the S-S bridges of immunoglobins G: interchain disulfide bridges of gamma G3 myeloma proteins. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):893–906. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M., KUNKEL H. G. H CHAIN SUBGROUPS OF MYELOMA PROTEINS AND NORMAL 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:253–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kohler P. F., Terry W. D., Franklin E. C. Human monoclonal gamma G-cryoglobulins with anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1875–1884. doi: 10.1172/JCI105878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E. M., Raymond S. Gel electrophoresis: a new catalyst for acid systems. Anal Biochem. 1969 Feb;27(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. On the stability of myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2834–2847. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEGELES G., SIA C. L. AN ULTRACENTRIFUGAL FIELD RELAXATION METHOD FOR MOLECULAR WEIGHTS. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:906–909. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochwa S., Smith E., Brownell M., Wasserman L. R. Aggregation of IgG globulin in vivo. II. Physicochemical properties of the isolated protein. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):277–285. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp W. L., Beirne G. J., Burns R. O. Hyperviscosity syndrome in multiple myeloma. Am J Med. 1967 Jul;43(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Natvig J. B., Joslin F. G. A "Lepore" type of hybrid gamma-globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):144–149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRILL E. W., GILLILAND E. R., COKELET G., SHIN H., BRITTEN A., WELLS R. E., Jr Rheology of blood and flow in the microcirculation. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Mar;18:255–260. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLINS D. E., EDELMAN G. M. RECONSTITUTION OF 7S MOLECULES FROM L AND H POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS OF ANTIBODIES AND GAMMA-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1964 May 1;119:789–815. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH E., KOCHWA S., WASSERMAN L. R. AGGREGATION OF IGG GLOBULIN IN VIVO. I. THE HYPERVISCOSITY SYNDROME IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Am J Med. 1965 Jul;39:35–48. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEEL A. E. The laboratory diagnosis of macroglobulinaemia by viscometry. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 Jan;8:86–90. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somer T. The viscosity of blood, plasma and serum in dys- and paraproteinemias. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;456:1–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gammaG-immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. I. Catabolism of gammaG-myeloma proteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2323–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI105917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY W. D., FAHEY J. L. SUBCLASSES OF HUMAN GAMMA-2-GLOBULIN BASED ON DIFFERENCES IN THE HEAVY POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):400–401. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAERMAN J. P., JOHNSON L. B., MANDY W., FUDENBERG H. H. MULTIPLE MYELOMA WITH TWO PARAPROTEIN PEAKS: AN INSTRUCTIVE CASE. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Jan;65:18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER M. V., VAUGHAN J. H. Use of anti-Rh sera for demonstrating agglutination activating factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 May;92(1):198–200. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS D. E., REISFELD R. A. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS IN POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS: EXTENSION TO NEW CONDITIONS OF PH AND BUFFER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]