Abstract
IgG and IgM metabolism was evaluated in 10 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 10 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and in seven normal volunteers. The biological half-lives of purified IgG and IgM, labeled with 131I and 125I, respectively, were determined by serial measurements of radioactivity in the blood and urine with a gamma well counter, and by serial counts of total body radioactivity in a total body counting chamber.
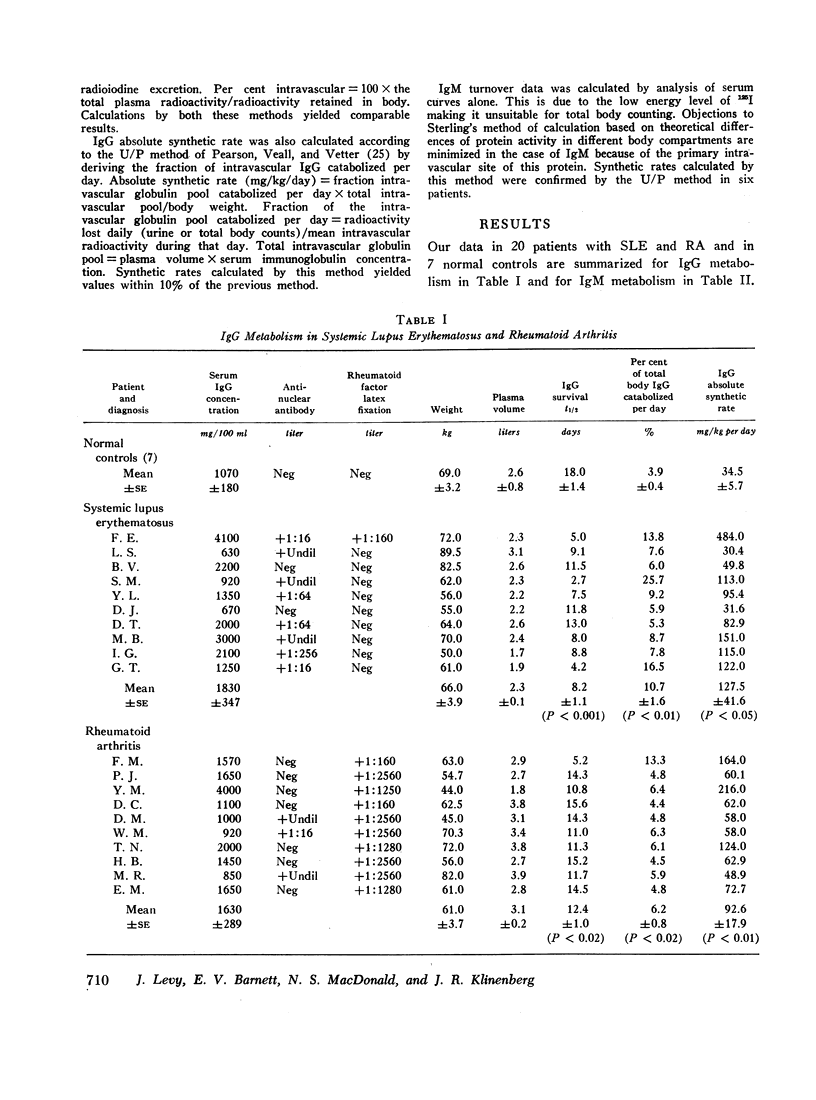
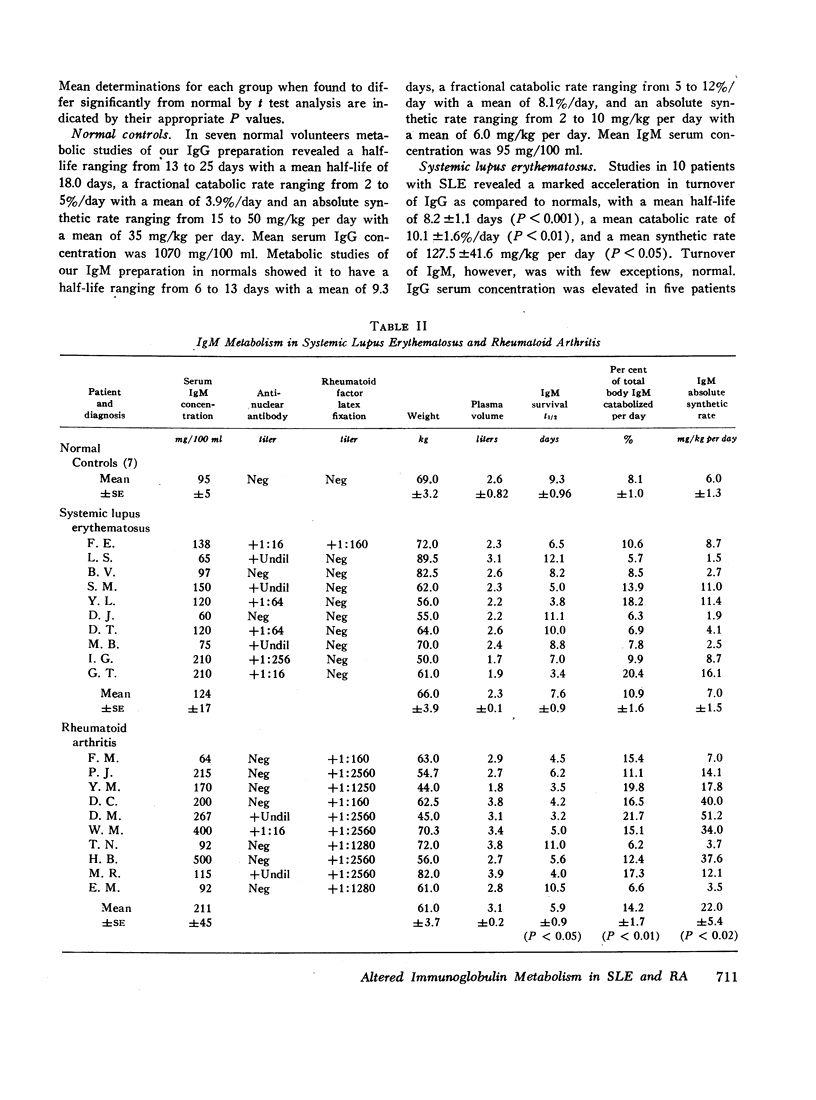
The mean survival half-life for IgG in patients with SLE was 8.2 days as compared to an average of 18 days in normal controls. An average of 10.1% of total body IgG was catabolized daily compared to a mean of 3.9% in normal controls. Turnover of IgM in patients with SLE was, with very few exceptions, normal. In contrast, patients with rheumatoid arthritis revealed a milder abnormality of IgG metabolism, but markedly abnormal IgM catabolism with a mean half-life averaging 5.9 days as compared to 9.3 days in control subjects. An average of 14.2% of total body IgM was catabolized daily in patients with RA as compared to 8.1% in normal controls.
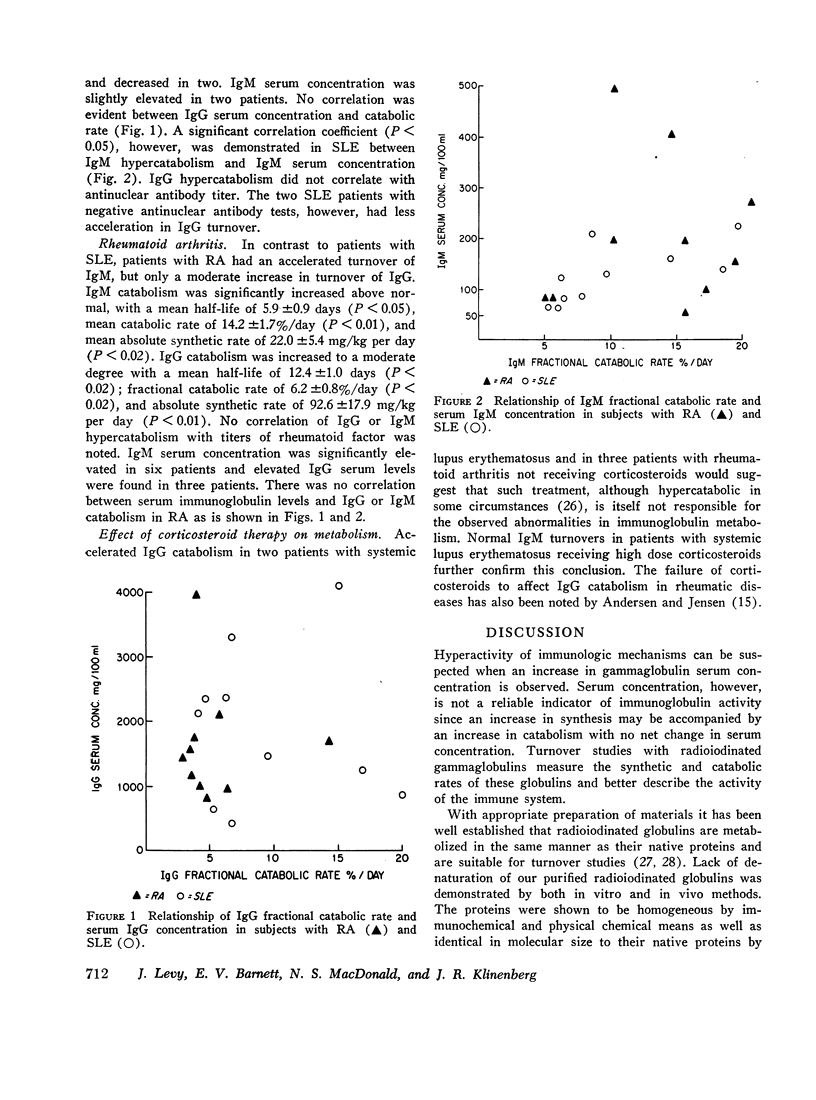
Our data suggest that there are basic differences between patients with RA and SLE in the synthesis and catabolism of IgG and IgM not readily apparent from serum IgG and IgM concentration. Abnormal IgG and IgM metabolism may be related to underlying immunological mechanisms in these diseases. Immunoglobulin turnover studies appear to be an additional means for the characterization of rheumatic diseases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen S. B. Metabolism of gammaG-globulin in chronic leukaemia. Acta Haematol. 1965 Jul;34(1):44–50. doi: 10.1159/000209429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arden J., Mullinax F., Waller M. Immunoglobulin levels in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with rheumatoid factor titers, clinical stage and disease duration. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Jun;10(3):228–234. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNETT E. V., CONDEMI J. J., LEDDY J. P., VAUGHAN J. H. GAMMA-2, GAMMA-1A AND GAMMA-1M ANTINUCLEAR FACTORS IN HUMAN SERA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jun;43:1104–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI104995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTH W. F., WOCHNER R. D., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. METABOLISM OF HUMAN GAMMA MACROGLOBULINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jun;43:1036–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI104987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., SCHREIBER S. S., POST J. Tracer experiments with I131 labeled human serum albumin: distribution and degradation studies. J Clin Invest. 1953 Aug;32(8):746–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI102789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J., Normansell D., Rowe D. S. The metabolism of autologous IgM and 19S rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 May;4(5):537–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., FREEMAN T. Metabolic heterogeneity of human gamma-globulin. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:475–487. doi: 10.1042/bj0760475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass R. M., Mongan E. S., Jacox R. F., Vaughan J. H. Immunoglobulins G, A, and M in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to serum complement titer, latex titer, antinuclear antibody, and manifestations of clinical disease. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Oct;69(4):749–756. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-4-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., TALMAGE D. W., MAURER P. H., DEICHMILLER M. The half-life on homologous gamma globulin (antibody) in several species. J Exp Med. 1952 May;95(5):313–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRIVSHOLM A. Turnover rate of myeloma proteins in serum and urine determined after intravital labelling with glycine--1--C--14. Acta Med Scand. 1961 May;169:503–507. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1961.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez C. J., Caggiano V., Kochwa S., Wasserman L. R. Antigenic heterogeneity of reduced and alkylated subunits of human monoclonal macroglobulins. J Immunol. 1968 Dec;101(6):1159–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., HORBETT A. P. Human gamma globulin fractionation on anion exchange cellulose columns. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2645–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., ROBINSON A. G. FACTORS CONTROLLING SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION. J Exp Med. 1963 Nov 1;118:845–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Structural differences between macroglobulins belonging to two serologically distinguishable subclasses. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4203–4211. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Two serologically distinguishable subclasses of mu-chains of human macroglobulins. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):810–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABUZDA T. G. The turnover and distribution of I-131-labeled myeloma and macroglobulin proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Jan;59:65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARBOE M., DEVERILL J., GODAL H. C. ANTIGENIC HETEROGENEITY OF WALDENSTROEM TYPE GAMMA-M-GLOBULINS. Scand J Haematol. 1965;2:137–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVENS W. P., Jr, DICKENSHEETS J., BIERLY J. N., EBERHARD T. P. The half-life of I131 labeled normal human gamma globulin in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Immunol. 1954 Oct;73(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. B. Some comments on the catabolism of IgM. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;22(1):27–28. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPINCOTT S. W., KORMAN S., FONG C., STICKLEY E., WOLINS W., HUGHES W. L. Turnover of labeled normal gamma globulin in multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 1960 Apr;39:565–572. doi: 10.1172/JCI104069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS J. A., CALKINS E., COHEN A. S. The plasma disappearance time and catabolic half-life of I-131-labeled normal human gamma globulin in amyloidosis and inrheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1961 Oct;40:1926–1934. doi: 10.1172/JCI104418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcolongo R., Jr, Carcassi A., Frullini F., Bianco G., Bravi A. Levels of serum immunoglobulins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1967 Sep;26(5):412–418. doi: 10.1136/ard.26.5.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. The behavior of I 131-labeled plasma proteins in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Aug 30;70(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb35374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLESEN H. TURNOVER STUDIES WITH IODINE-LABELED GAMMA-MACROGLOBULIN AND ALBUMIN. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:497–510. doi: 10.1080/00365516309079778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLHAGEN B., BIRKE G., PLANTIN L. O., AHLINDER S. ISOTOPE STUDIES OF GAMMAGLOBULIN CATABOLISM IN COLLAGEN DISORDERS. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1963;9:88–93. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1963.9.issue-1-4.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S. EVIDENCE FOR SPECIES' DIFFERENCES IN THE EFFECT OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION ON GAMMA-GLOBULIN CATABOLISM. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:967–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S., FAHEY J. L. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GAMMA-GLOBULIN METABOLISM AND LOW SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN IN GERMFREE MICE. J Immunol. 1964 Jul;93:81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. Clinical and experimental metabolism of normal 6.6s gamma-globulin in normal subjects and in patients with macroglobulinemia and multiple myeloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K. The turnover rate of serum albumin in man as measured by I131-tagged albumin. J Clin Invest. 1951 Nov;30(11):1228–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI102542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salky N. K., Mills D., Di Luzio N. R. Activity of the reticuloendothelial system in diseases of altered immunity. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Dec;66(6):952–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gammaG-immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. I. Catabolism of gammaG-myeloma proteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2323–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI105917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truax W. E., McCoy J. Gamma globulin catabolism by the kidney. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Winter;23(4):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN J. H., ARMATO A., GOLDTHWAIT J. C., BRACHMAN P., FAVOUR C. B., BAYLES T. B. A study of gamma globulin in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):75–85. doi: 10.1172/JCI103065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Barnett E. V., Leddy J. P. Autosensitivity diseases. Immunologic and pathogenetic concepts in lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and hemolytic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1966 Dec 22;275(25):1426–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196612222752507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veys E. M., Claessens H. E. Serum levels of IgG, IgM, and IgA in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Sep;27(5):431–440. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDMANN T. A., SCHWAB P. J. IGG (7 S GAMMA GLOBULIN) METABOLISM IN HYPOGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA: STUDIES IN PATIENTS WITH DEFECTIVE GAMMA GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS, GASTROINTESTINAL PROTEIN LOSS, OR BOTH. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1523–1533. doi: 10.1172/JCI105259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Drews G., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. Accelerated breakdown of immunoglobulin G (IgG) in myotonic dystrophy: a hereditary error of immunoglobulin catabolism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):321–329. doi: 10.1172/JCI105346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. The role of the kidney in the catabolism of Bence Jones proteins and immunoglobulin fragments. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):207–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


