Abstract
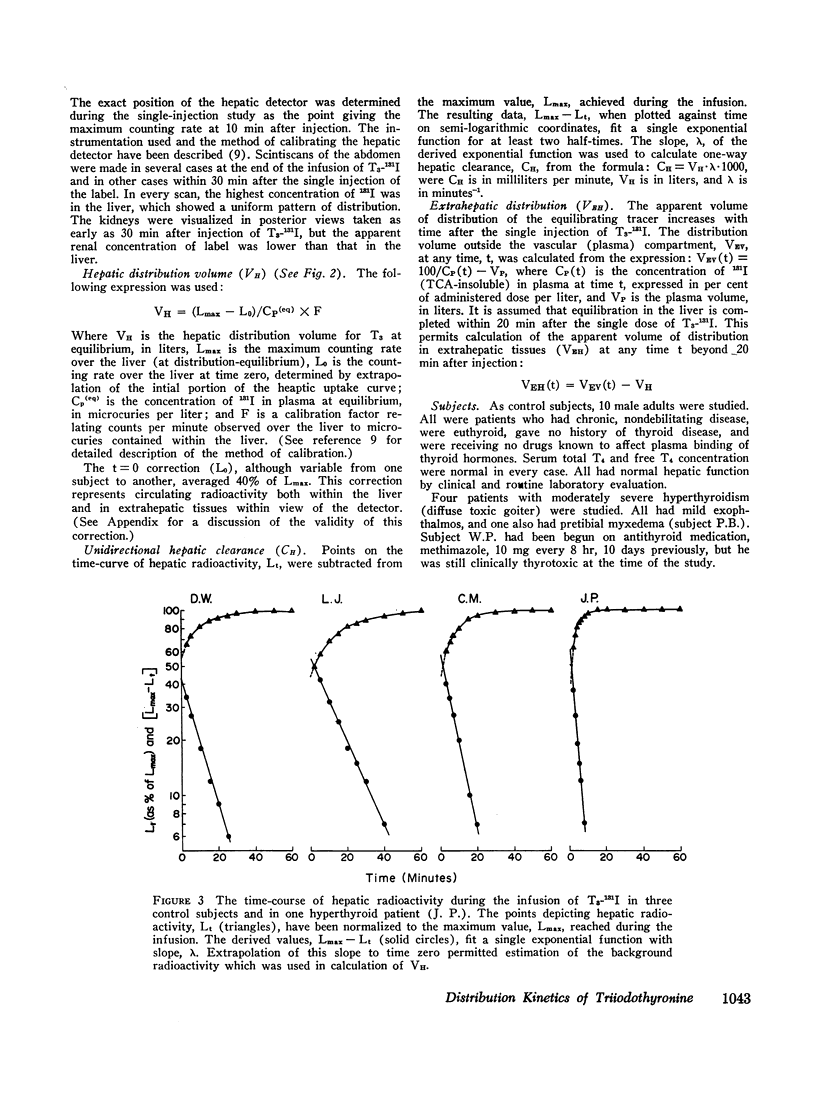
The kinetics of distribution of 3,3′,5-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3) have been studied employing both a single-injection and a continuous infusion of T3-131I. External monitoring of radioactivity in the liver during the infusion permitted estimation of the hepatic distribution volume (VH) and the one-way hepatic clearance (CH) of the hormone. Among 10 euthyroid control subjects, VH averaged 2.07 liters ±0.50 (SD), and the mean value for CH, 231 ml of plasma per min (±64). In three euthyroid men whose plasma showed decreased binding capacity by thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) abnormally high VH and CH values were found, the increase in CH being proportional to the decrease in binding activity by plasma proteins. Among all 13 subjects, there was a high correlation (+ 0.86) between CH and the proportion of free hormone in plasma, measured in vitro.
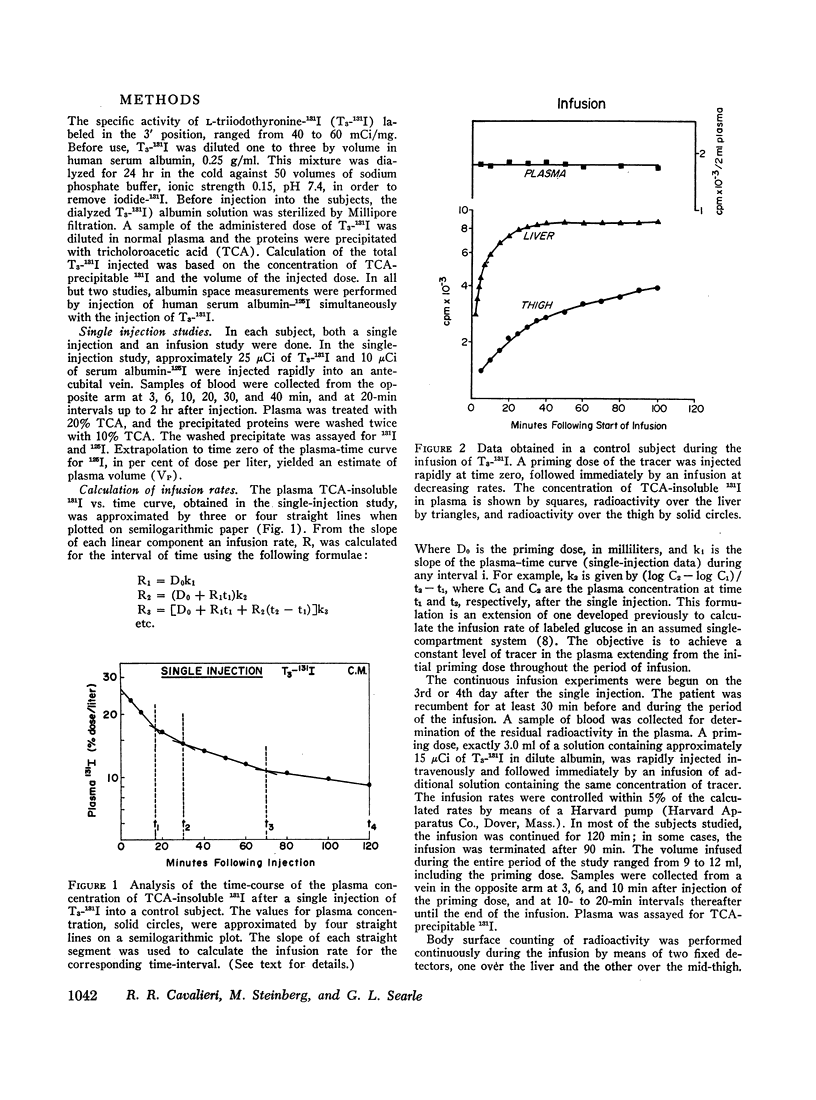
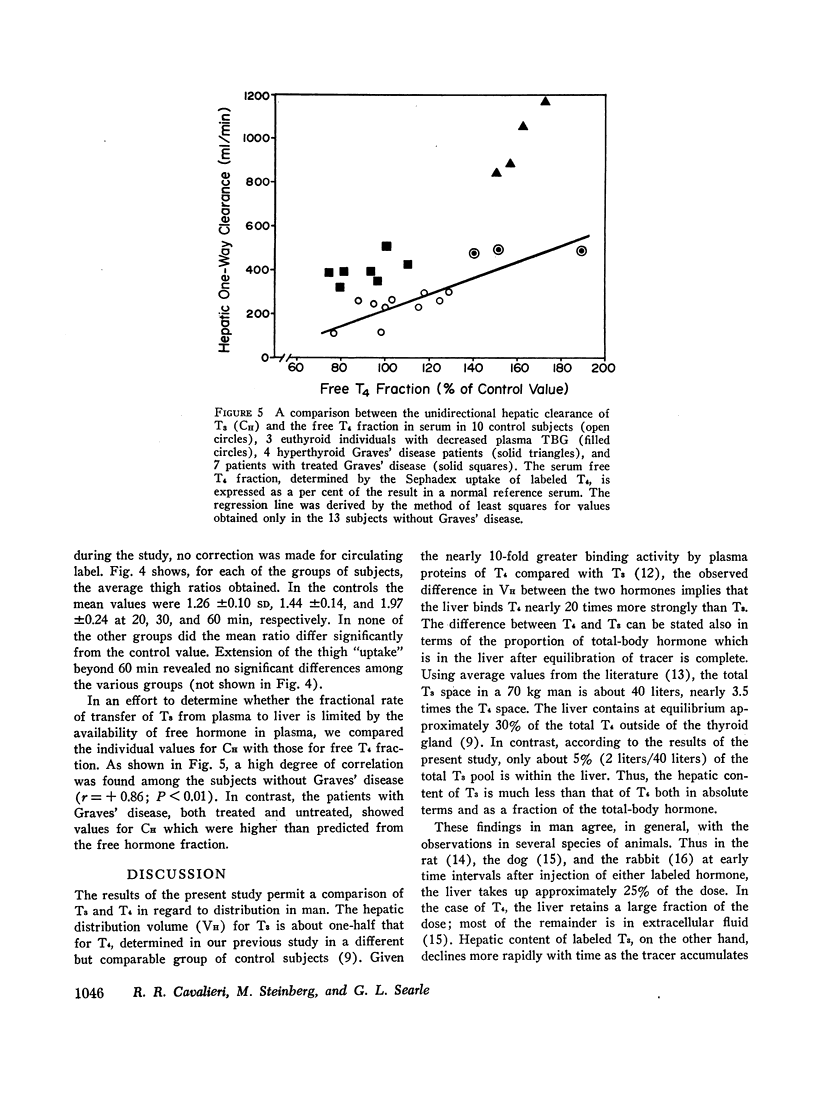
In four patients with hyperthyroid Graves' disease VH ranged from 3.2 to 4.2 liters and CH was elevated in every case, averaging 989 ml/min. The increase in CH in this group was out of proportion to the elevation of free hormone fraction in plasma. Seven patients who were either euthyroid or hypothyroid after treatment of Graves' disease showed a slight but significant increase in CH compared with the euthyroid controls without Graves' disease. The percentage of free hormone in the plasma of the treated group was normal or low and therefore could not explain the persistent elevation in unidirectional hepatic clearance observed.
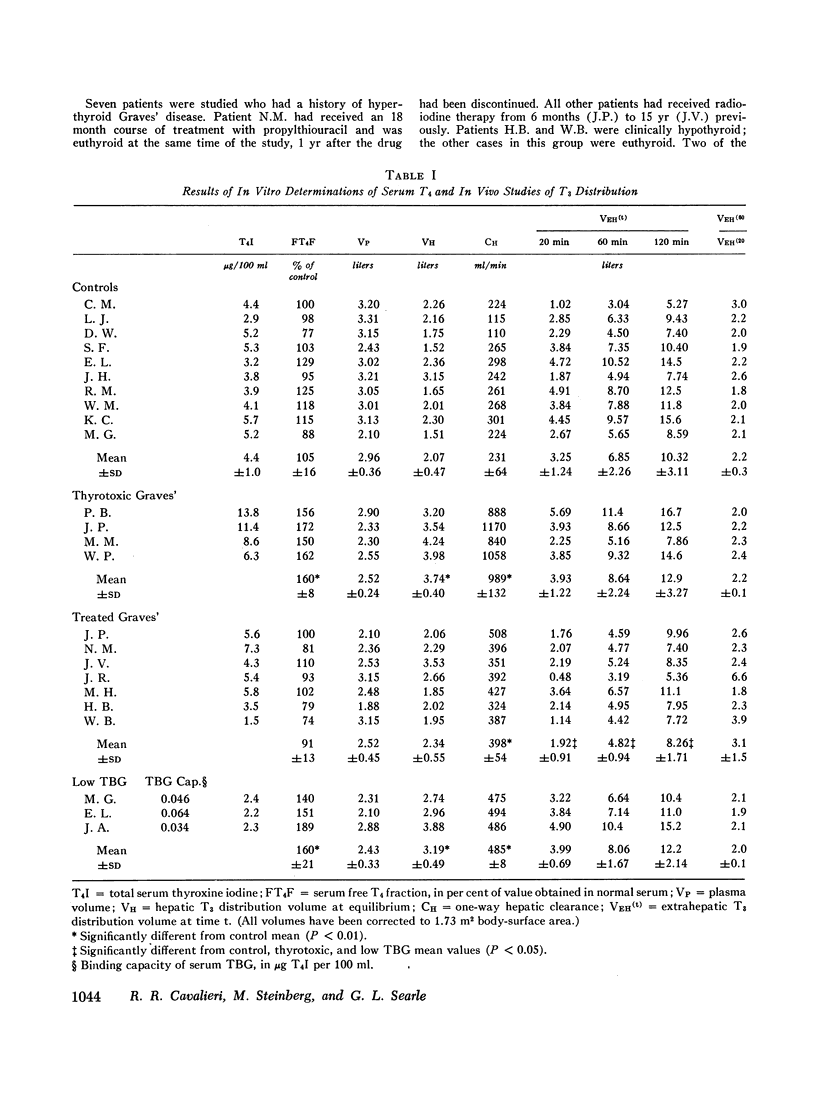
The rate of accumulation of labeled T3 in the tissues of the thigh during the interval from 10 to 60 min of the sustaining infusion of tracer was slow compared to the rate of equilibration in the liver and did not differ significantly among the various groups studied. These latter findings suggest that in slowly equilibrating tissues such as the thigh the kinetics of T3 distribution are relatively insensitive to alterations in hormone-binding activity by plasma proteins.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown-Grant K., Tata J. R. The distribution and metabolism of thyroxine and 3:5:3'-triiodothyronine in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1961 Jun;157(1):157–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Castle J. N., Searle G. L. A simplified method for estimating free-thyroxine fraction in serum. J Nucl Med. 1969 Sep;10(9):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Searle G. L. The kinetics of distribution between plasma and liver of 131-I-labeled L-thyroxine in man: observations of subjects with normal and decreased serum thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):939–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI105409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER D. A., ODDIE T. H. WHOLE-BODY COUNTING OF 131-I-LABELED TRIIODOTHYRONINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:733–739. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregerman R. I., Solomon N. Acceleration of thyroxine and triiodothyronine turnover during bacterial pulmonary infections and fever: implications for the functional state of the thyroid during stress and in senescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jan;27(1):93–105. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES I. B., DOBYNS B. M. The metabolism of triiodothyronine in Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Jan;20:68–80. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Regulation of the peripheral metabolism of the thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:353–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Studies of thyroid function and the peripheral metabolism of I 131-labeled thyroxine in patients with treated Graves disease. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1603–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI103753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E., Dawber N. A., Lee G. Y. A new method for measuring the free thyroid hormone in human serum and an analysis of the factors that influence its concentration. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1679–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS J. D., BRANNON E. S., HOLLAND B. C. A correlative study of the cardiac output and the hepatic circulation in hyperthyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1950 Aug;29(8):1069–1077. doi: 10.1172/JCI102338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musa B. U., Kumar R. S., Dowling J. T. Role of thyroxine-binding globulin in the early distribution of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 May;29(5):667–674. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-5-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauman J. A., Nauman A., Werner S. C. Total and free triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1346–1355. doi: 10.1172/JCI105627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Dowling J. T. Studies of peripheral thyroxine distribution in thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2000–2015. doi: 10.1172/JCI105887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Bernstein G., Hasen J. Estimation of rapidly exchangeable cellular thyroxine from the plasma disappearance curves of simultaneously administered thyroxine-131-I and albumin-125-I. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):762–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI105577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILEGGI V. J., LEE N. D., GOLUB O. J., HENRY R. J. Determination of iodine compounds in serum. I. Serum thyroxine in the presence of some iodine contaminants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Oct;21:1272–1279. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-10-1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE J., MICHEL R. On the peripheral metabolism of thyroid hormones. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr 23;86:454–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARLE G. L., STRISOWER E. H., CHAIKOFF I. L. Glucose pool and glucose space in the normal and diabetic dog. Am J Physiol. 1954 Feb;176(2):190–194. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., LASHOF J. C., MAN E. B. Disappearance from serum of I131-labeled l-thyroxine and l-triiodothyronine in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Invest. 1954 Jul;33(7):1031–1035. doi: 10.1172/JCI102970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Bellabarba D., Newman E. S., Brenner M. A. Determination of triiodothyronine concentration in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1150–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI106072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Formation of iodoprotein during the peripheral metabolism of 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine-125I in the euthyroid man and rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):685–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI106026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANARSDEL P., Jr, HOGNESS J. R., WILLIAMS R. H., ELGEE N. Comparative distribution and fate of I131-labeled thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1954 Sep;55(3):332–343. doi: 10.1210/endo-55-3-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISWELL J. G., CORONHO V. Disappearance of I-131-triiodo-thyronine from the plasma in the presence of fever. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Jun;22:657–659. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-6-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeber K. A., Hecker E., Ingbar S. H. The effects of an acute load of thyroxine on the transport and peripheral metabolism of triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):650–654. doi: 10.1172/JCI106276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninovich A. A., Farach H., Ezrin C., Volpé R. Lack of significant binding of L-triiodothyronine by thyroxine-binding globulin in vivo as demonstrated by acute disappearance of 131-I-labeled triiodothyronine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Aug;45(8):1290–1301. doi: 10.1172/JCI105436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninovich A. A., Volpe R., Ezrin C. Effects of variations of thyroxine-binding globulin capacity on the disappearance of triiodothyronine from the plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Dec;29(12):1601–1607. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-12-1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



