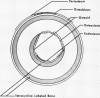
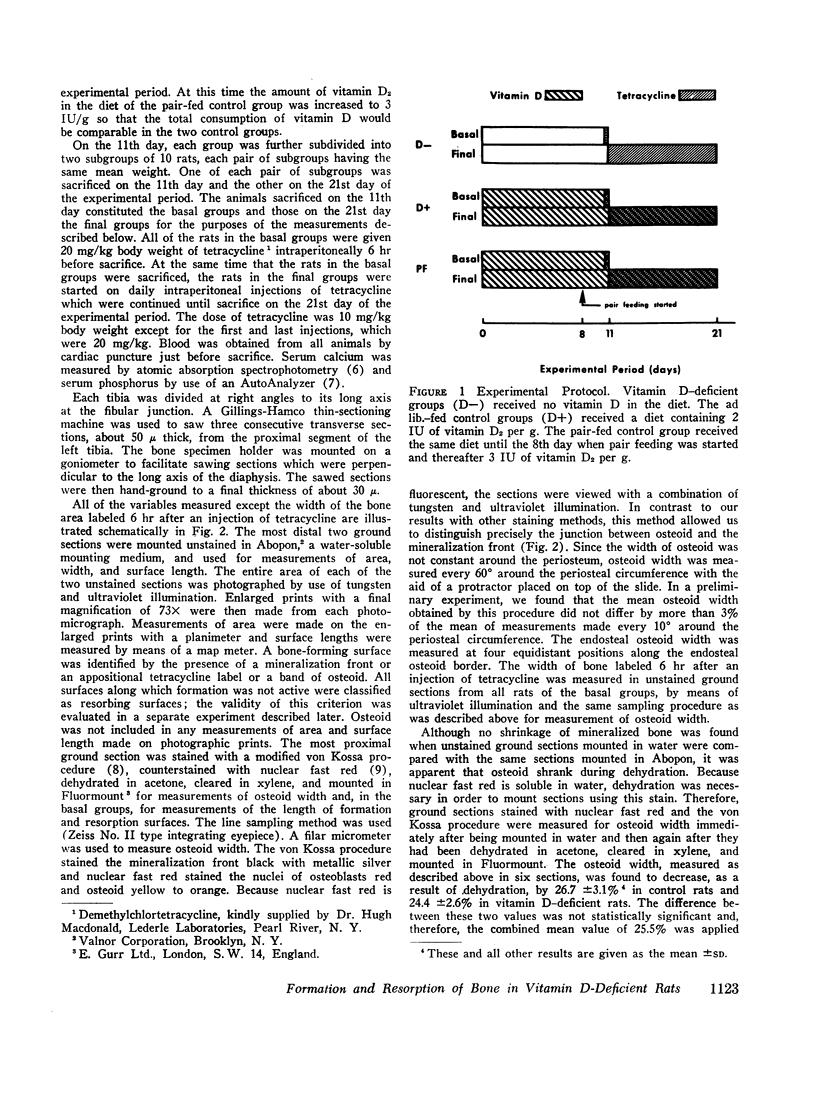
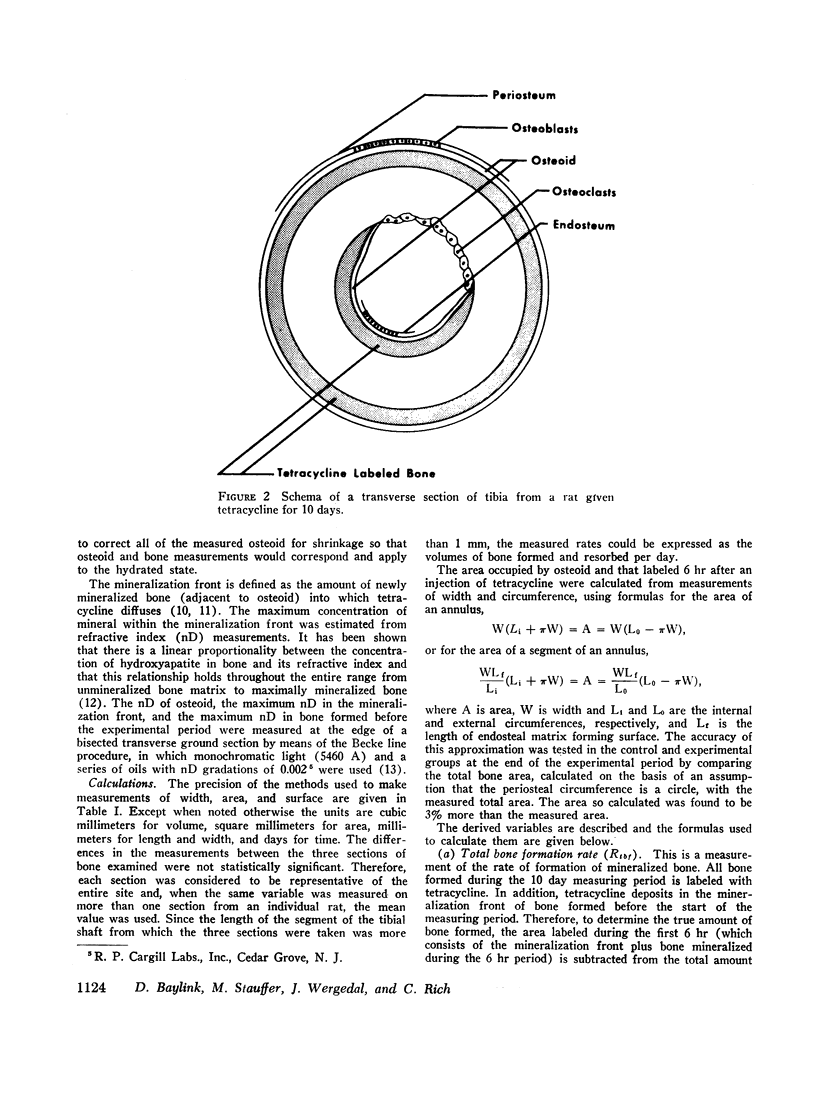
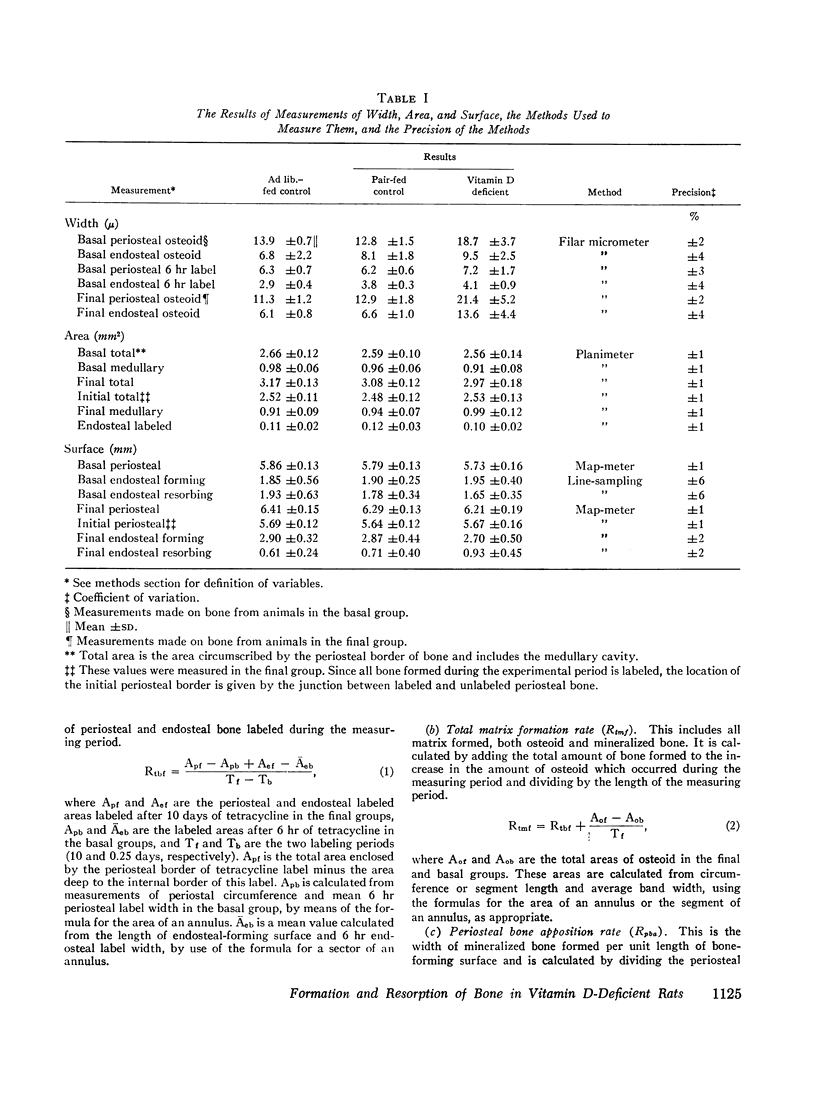
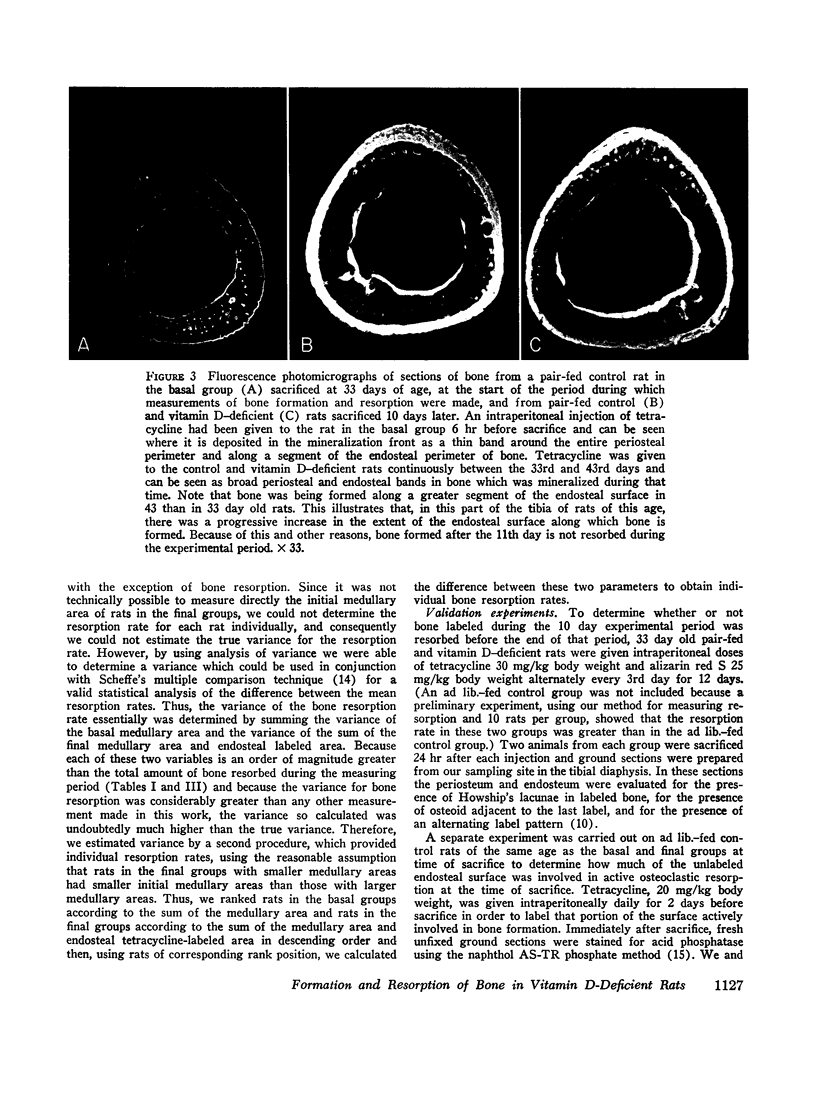
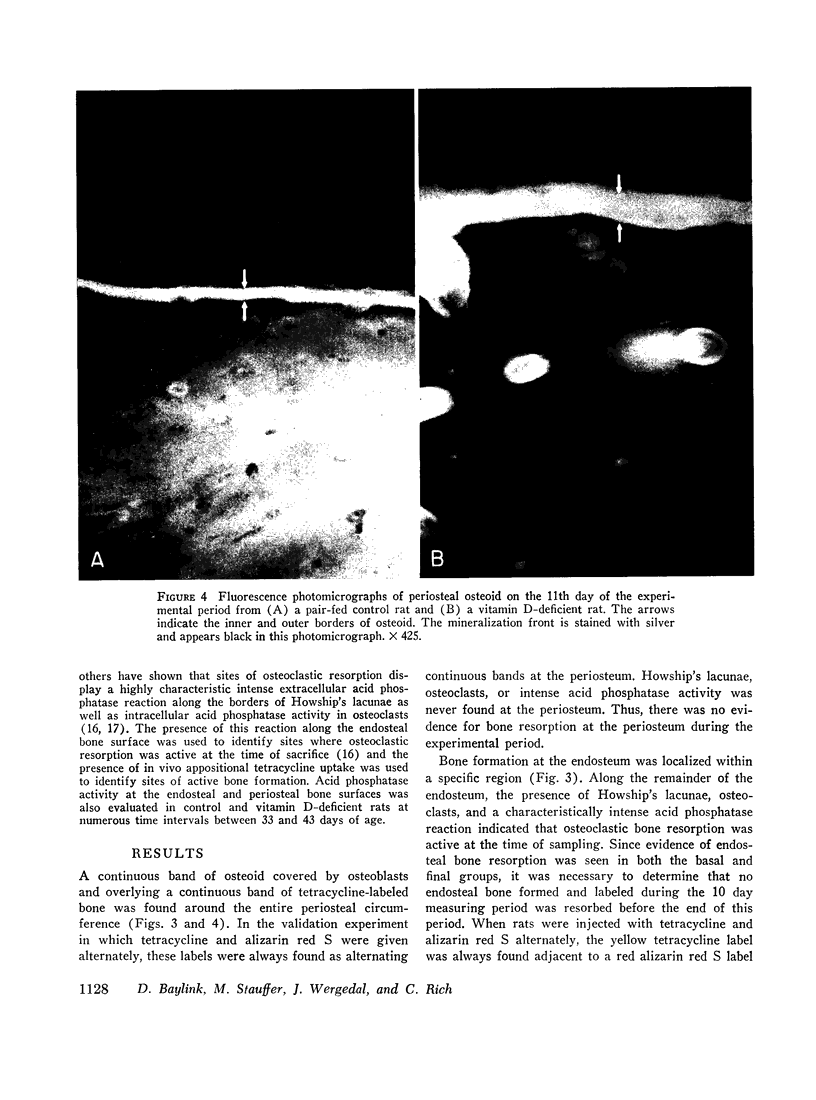
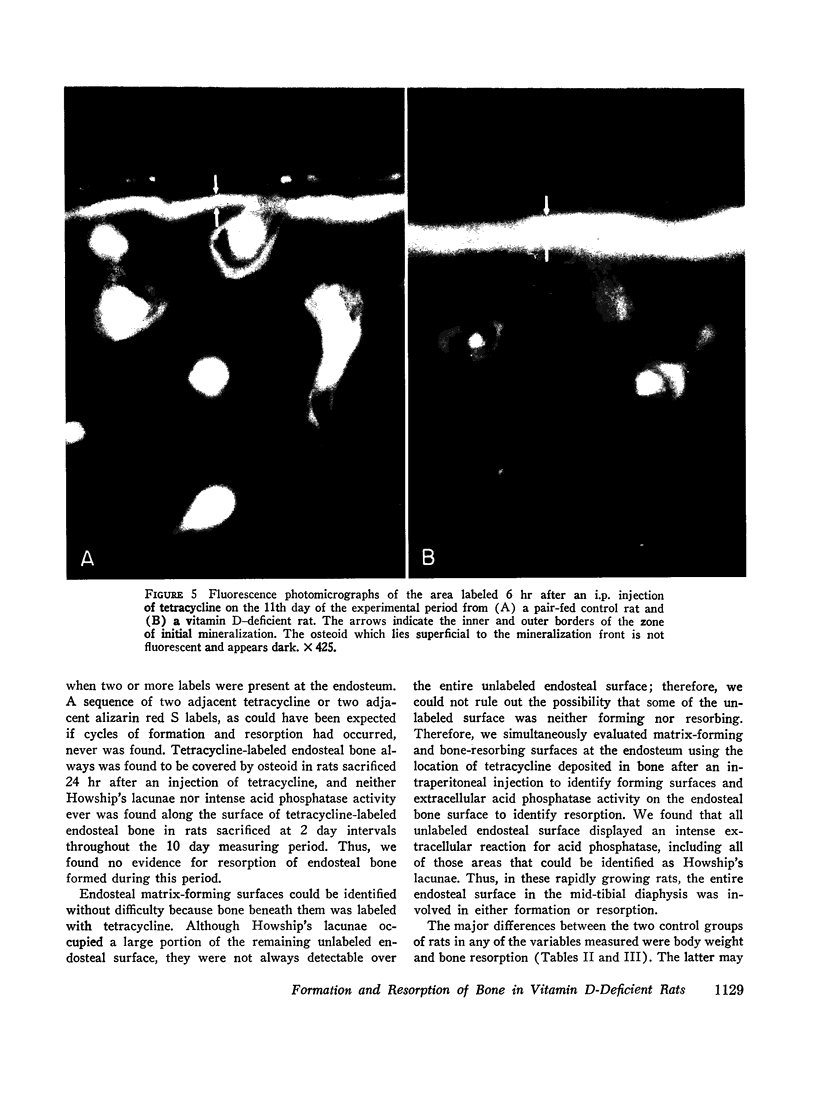
Abstract
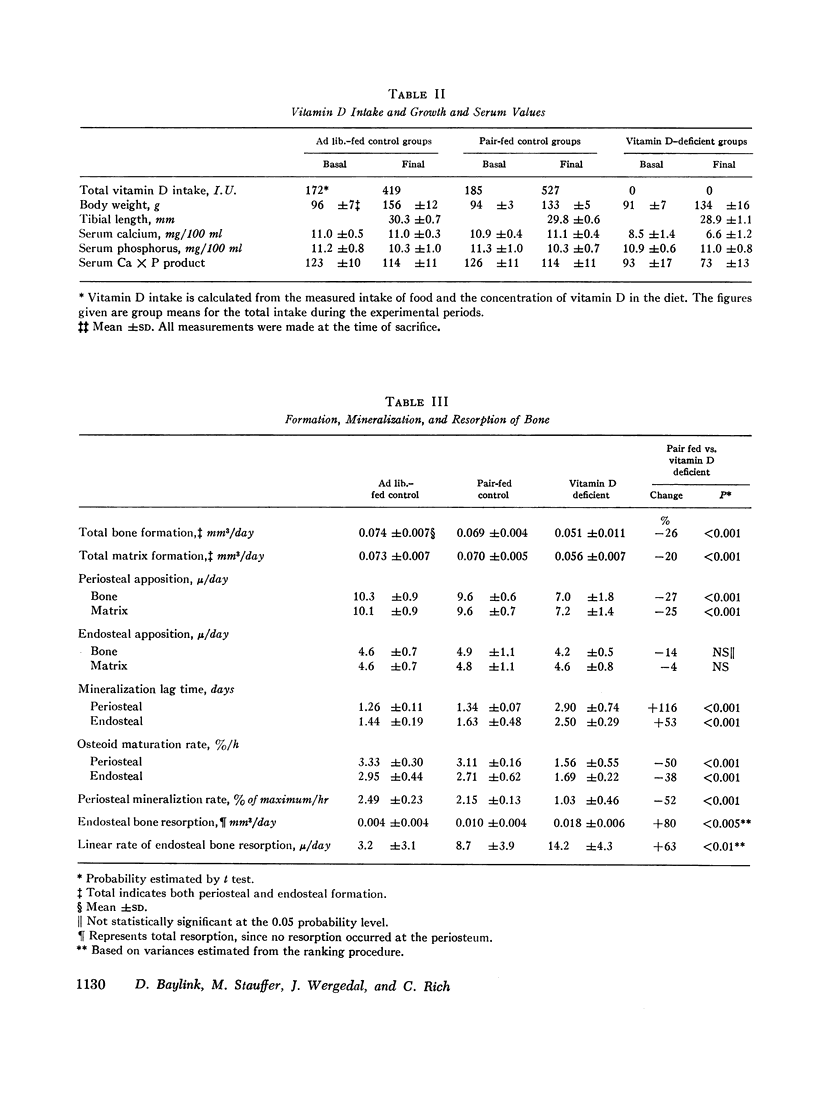
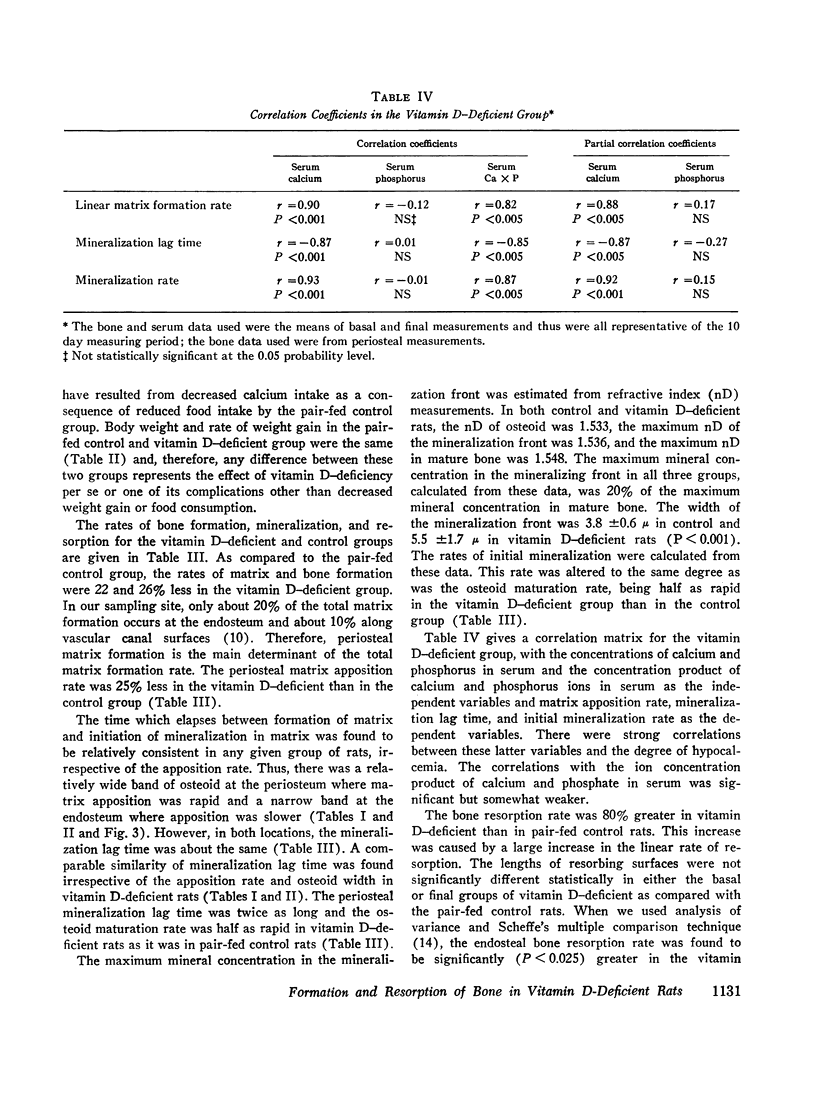
Quantitative histologic methods have been devised to measure several processes dealing with formation and mineralization of matrix and bone resorption. In vitamin D-deficient rats, the total osteoblastic matrix formation rate was 20% less and the total osteoclastic bone resorption rate was 80% more than in pair-fed control rats. These changes were found to be primarily because of changes in the rates of matrix formation and of bone resorption per unit area of forming or resorbing surfaces rather than to changes in the areas of these surfaces. The rate of maturation of osteoid and the rate of initial mineralization both were reduced to half of normal in the vitamin D-deficient rats. These variables related to matrix formation and mineralization were significantly correlated with the concentration of calcium but not with the concentration of phosphate in serum. The occurrence of hypocalcemia is interpreted as the consequence, both of reduced calcium absorption and of inadequate resorptive response of bone cells to homeostatic stimuli, such that, although bone resorption was greater than normal, it did not adequately compensate for the reduced intestinal absorption.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASCENZI A., FABRY C. Technique for dissection and measurement of refractive index of osteones. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Aug;6(1):139–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.6.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUBERT J. P., MILHAUD G. [Method for the measurement of the principal routes of calcium metabolism in man]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 25;39:122–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au W. Y., Bartter F. C. Effect of vitamin D on in vitro bone calcium metabolism. Endocrinology. 1966 Jun;78(6):1100–1104. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-6-1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTONE M. S. Histochemical demonstration of acid phosphatases with naphthol AS-phosphates. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1958 Sep;21(3):523–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylink D. J., Bernstein D. S. The effects of fluoride therapy on metabolic bone disease. A histologic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1967 Nov-Dec;55:51–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylink D., Morey E., Rich C. Effect of calcitonin on the rates of bone formation and resorption in the rat. Endocrinology. 1969 Feb;84(2):261–269. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhart J. M., Jowsey J. Morphologic evidence of osteomalacia in the parathyroidectomized dog. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Oct;41(10):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canas F., Brnd J. S., Neuman W. F., Terepka A. R. Some effects of vitamin D 3 on collagen synthesis in rachitic chick cortical bone. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1092–1096. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER R., HARRISON M., IBBERTSON K. The rate of calcium turnover in bone. Measurement by a tracer test using stable strontium. Q J Med. 1960 Jan;29:85–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDELMAN C. S., MORSE A., IRVING J. T. THE ENZYME HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE OSTEOCLASTS OF NORMAL AND "IA" RATS. Am J Anat. 1964 Sep;115:363–375. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001150209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER-STEINBERG M. Ground substance, bone salts, and cellular activity in bone formation and destruction. Am J Anat. 1951 Nov;89(3):347–379. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000890302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVING J. T. A histological staining method for sites of calcification in teeth and bone. Arch Oral Biol. 1959 Oct;1:89–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(59)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. J. Bone remodeling in puppies with experimental rickets. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jul;70(1):94–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols G., Jr, Flanagan B., Veer J. van der S. Distortions of bone cell metabolism in uremia and their cause. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Nov;124(5):530–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN H., DELUCA H., ARNAUD C., HAWKER C., VONSTEDINGK M. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VITAMIN D AND PARATHYROID HORMONE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1940–1946. doi: 10.1172/JCI104880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wergedal J. E., Baylink D. J. Distribution of acid and alkaline phosphatase activity in undemineralized sections of the rat tibial diaphysis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Dec;17(12):799–806. doi: 10.1177/17.12.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wergedal J. E. Enzymes of protein and phosphate catabolism in rat bone. I. Enzyme properties in normal rats. Calcif Tissue Res. 1969;3(1):55–66. doi: 10.1007/BF02058645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K., Jett S., Frost H. M. Bone resorption rates in rib in physiological, senile, and postmenopausal osteoporoses. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 May;69(5):810–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]