Abstract
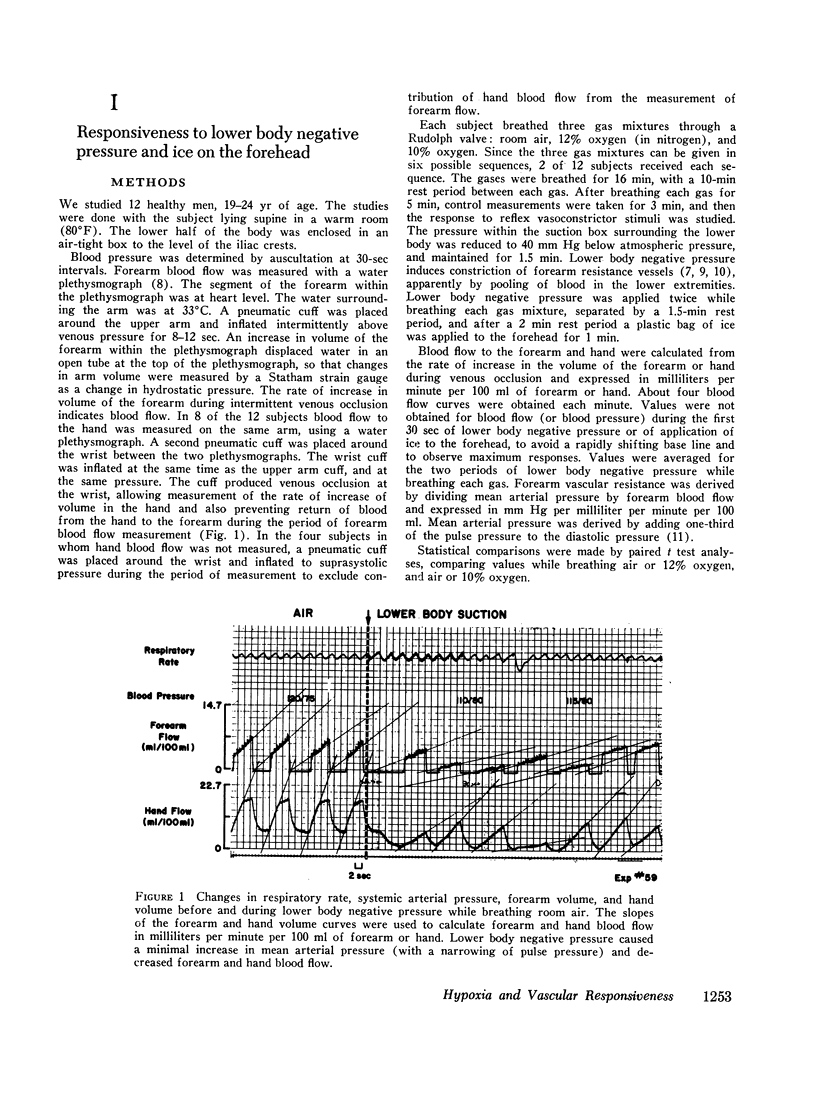
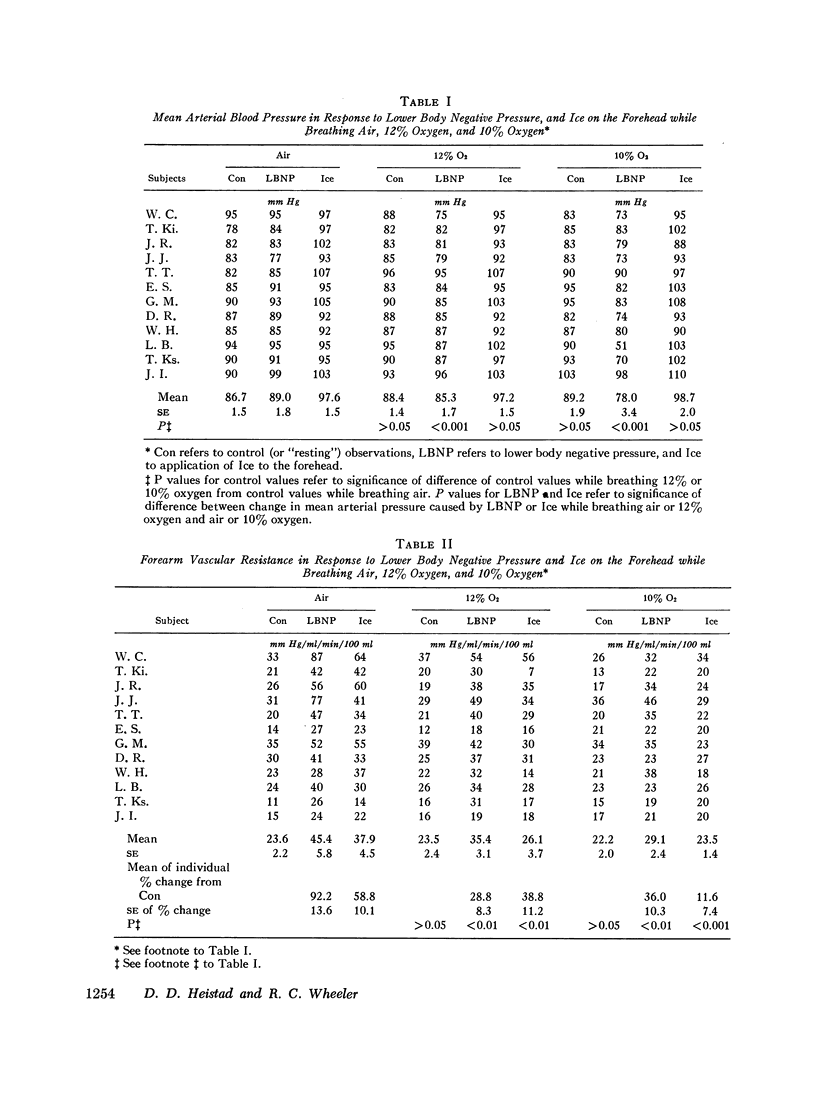
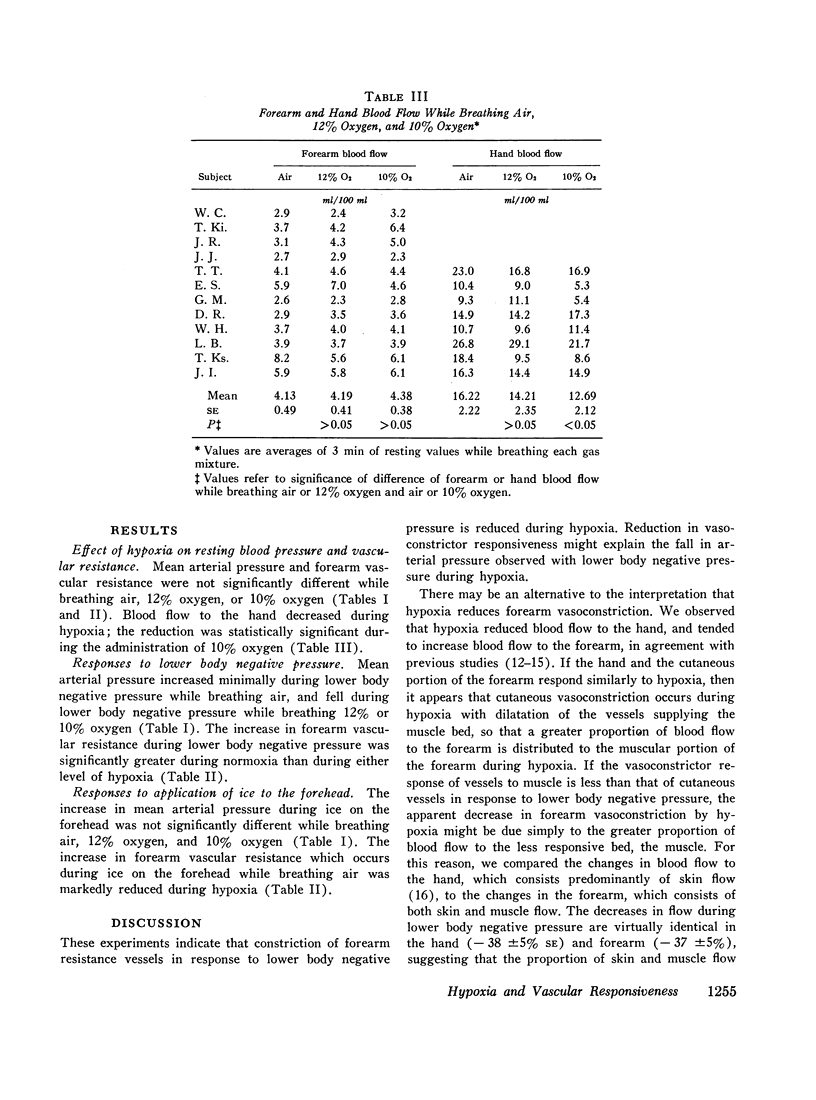
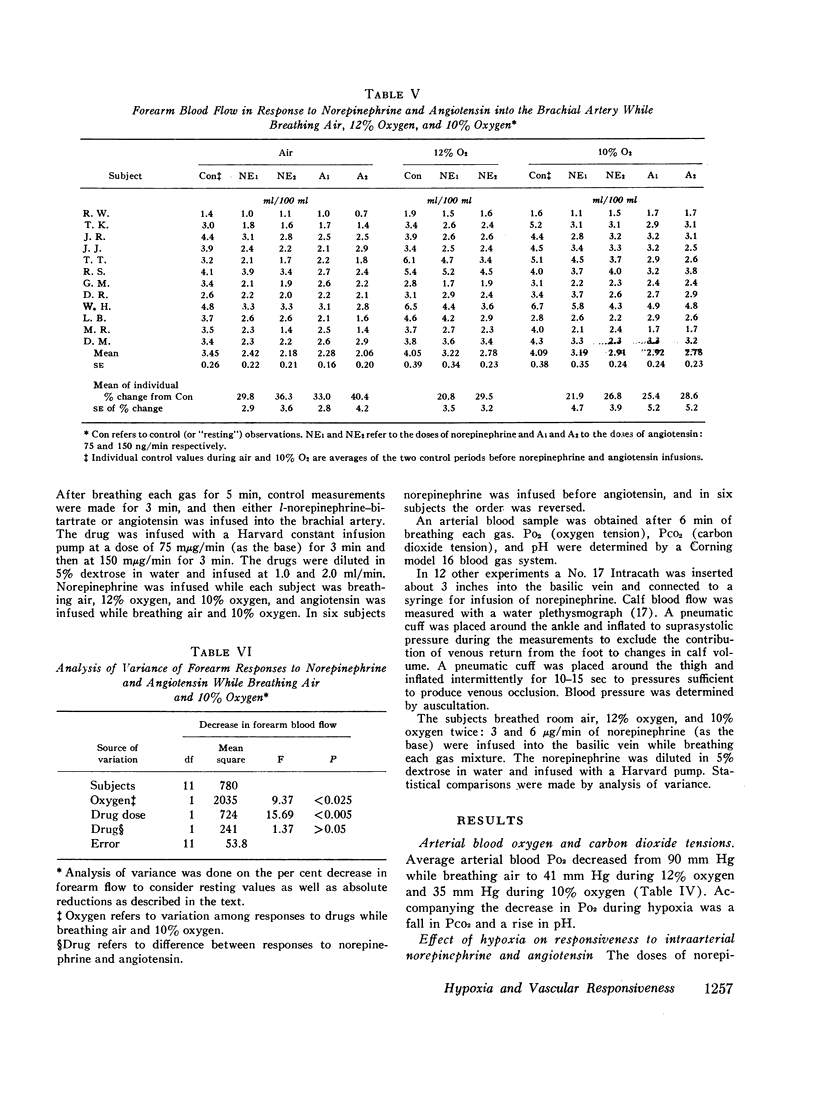
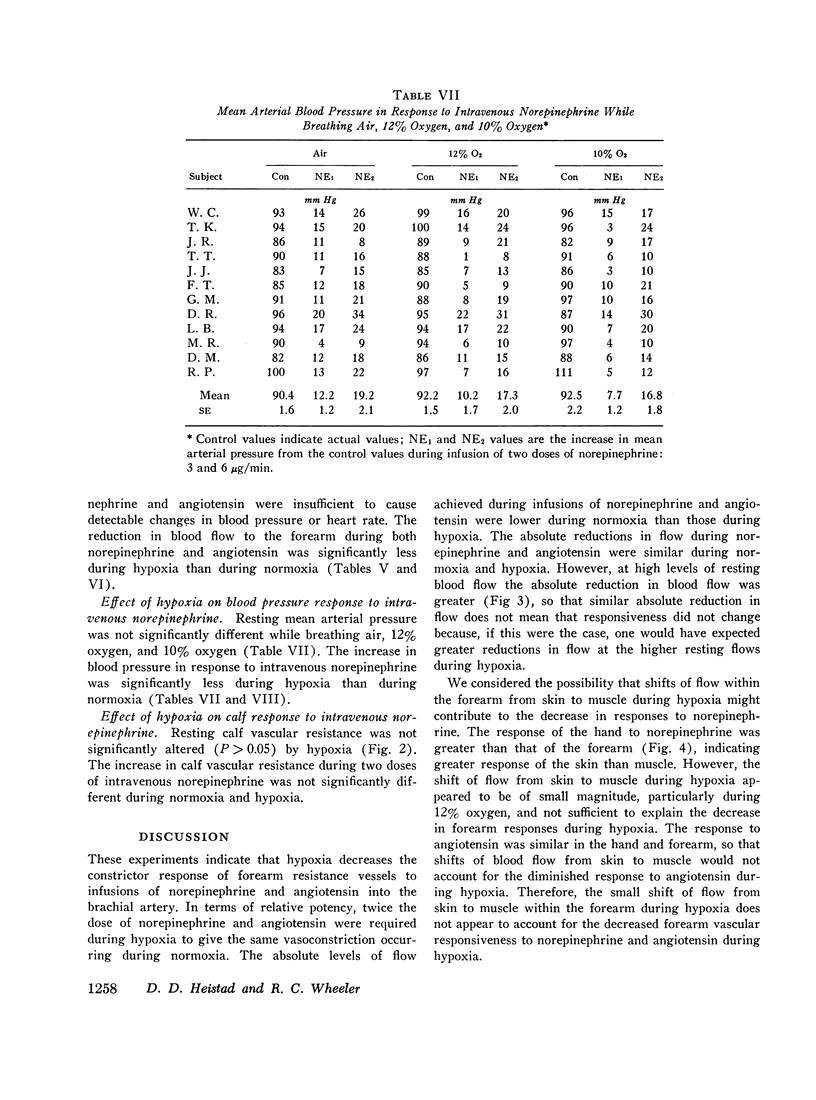
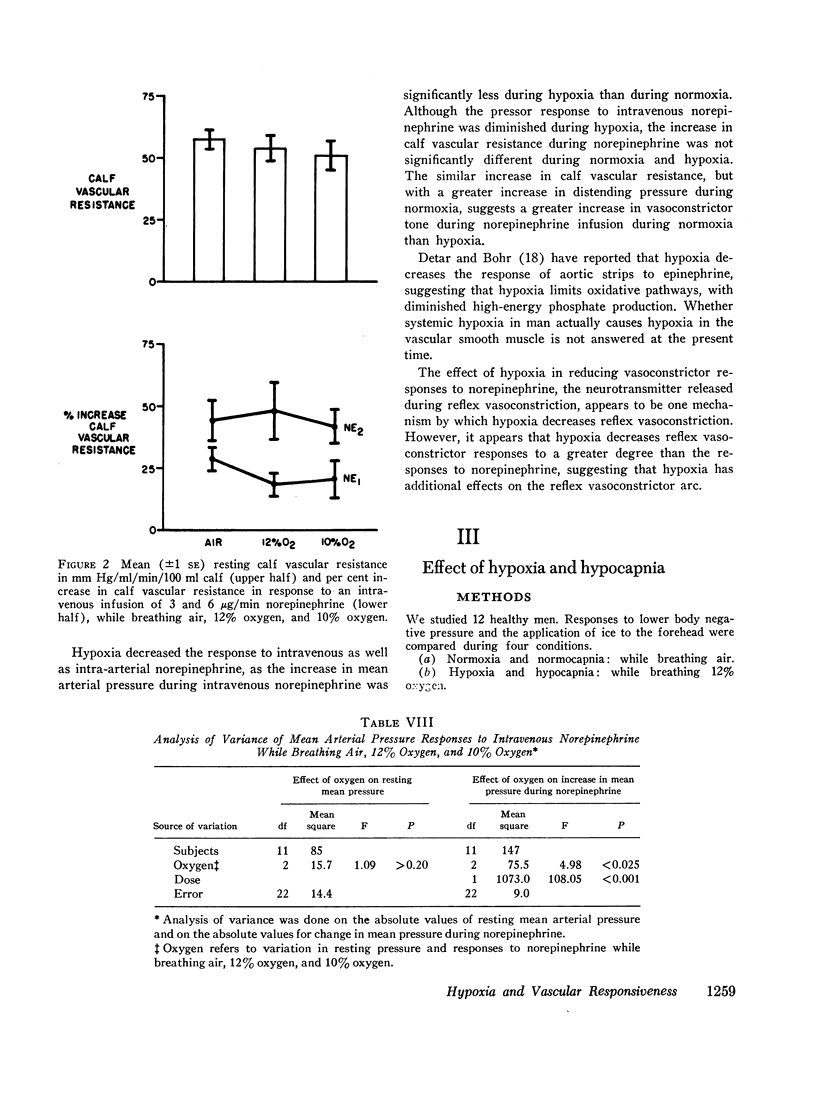
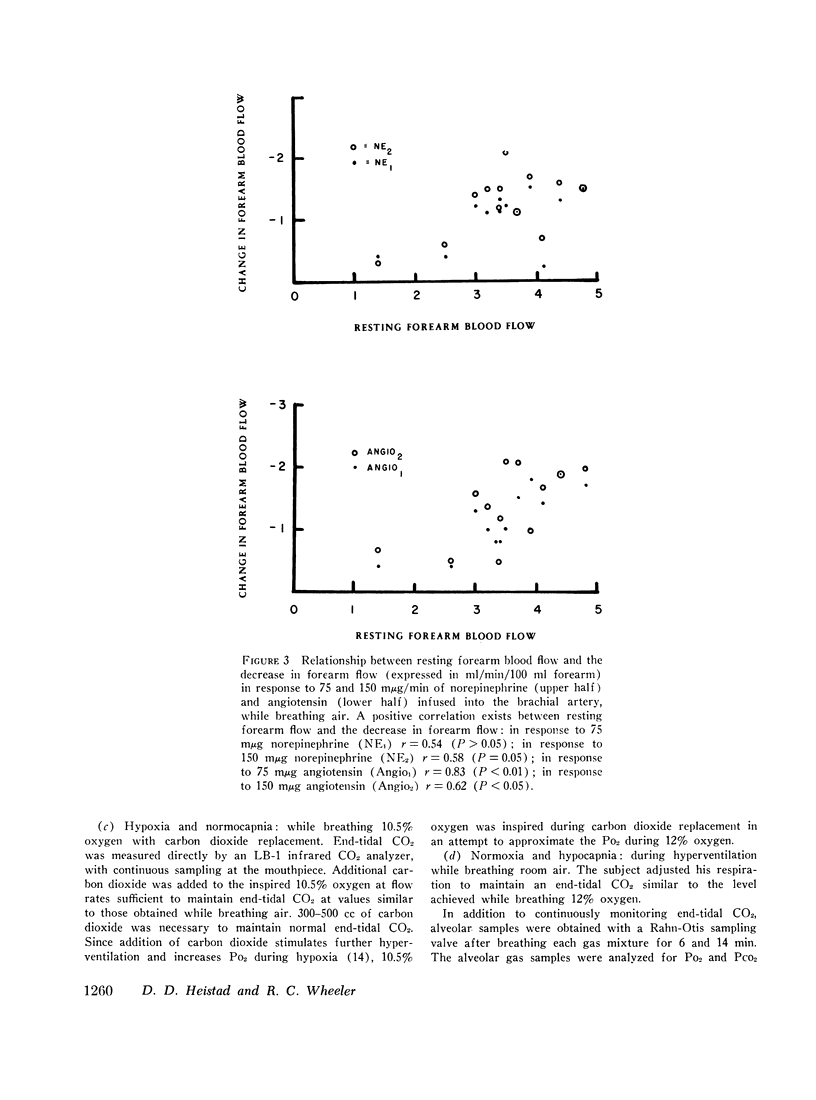
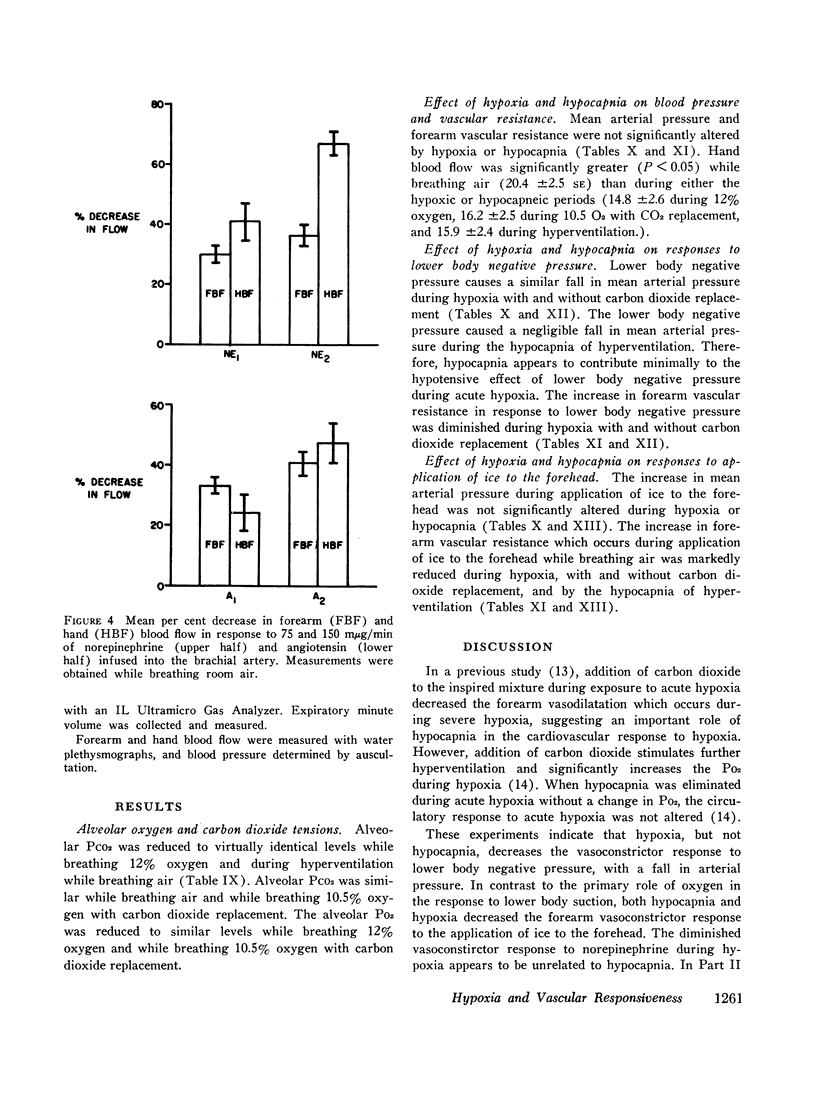
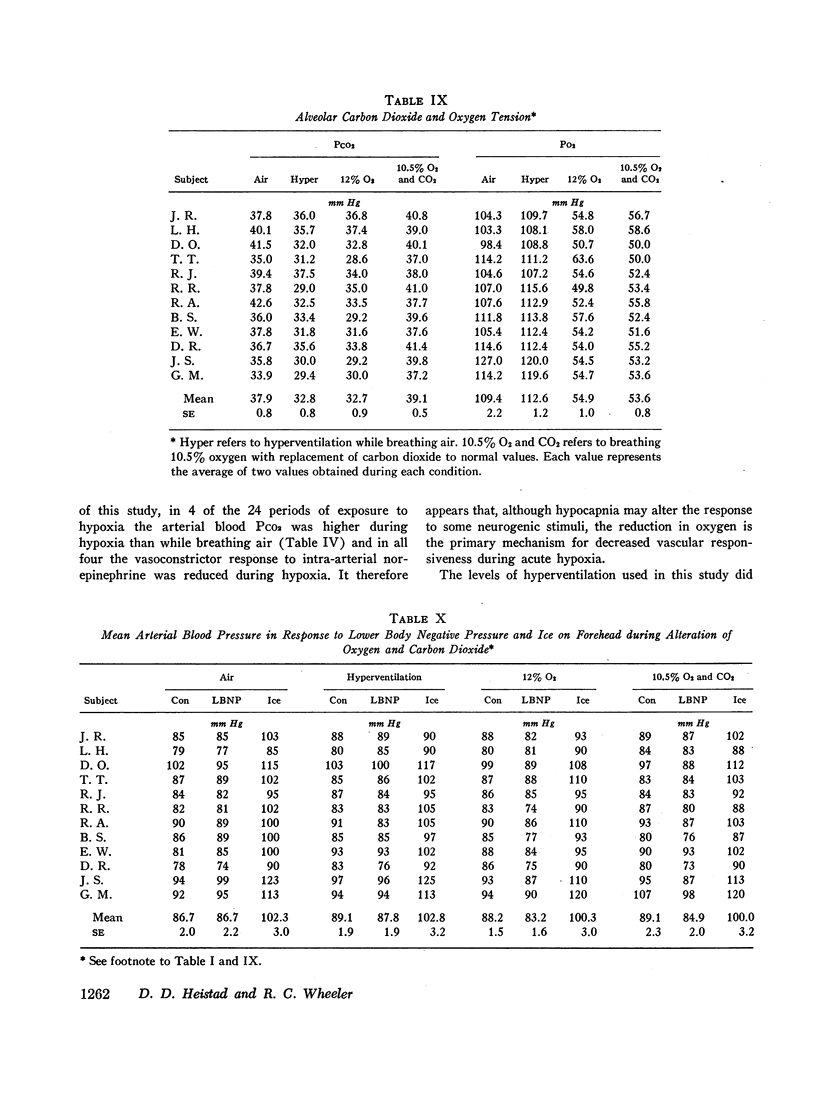
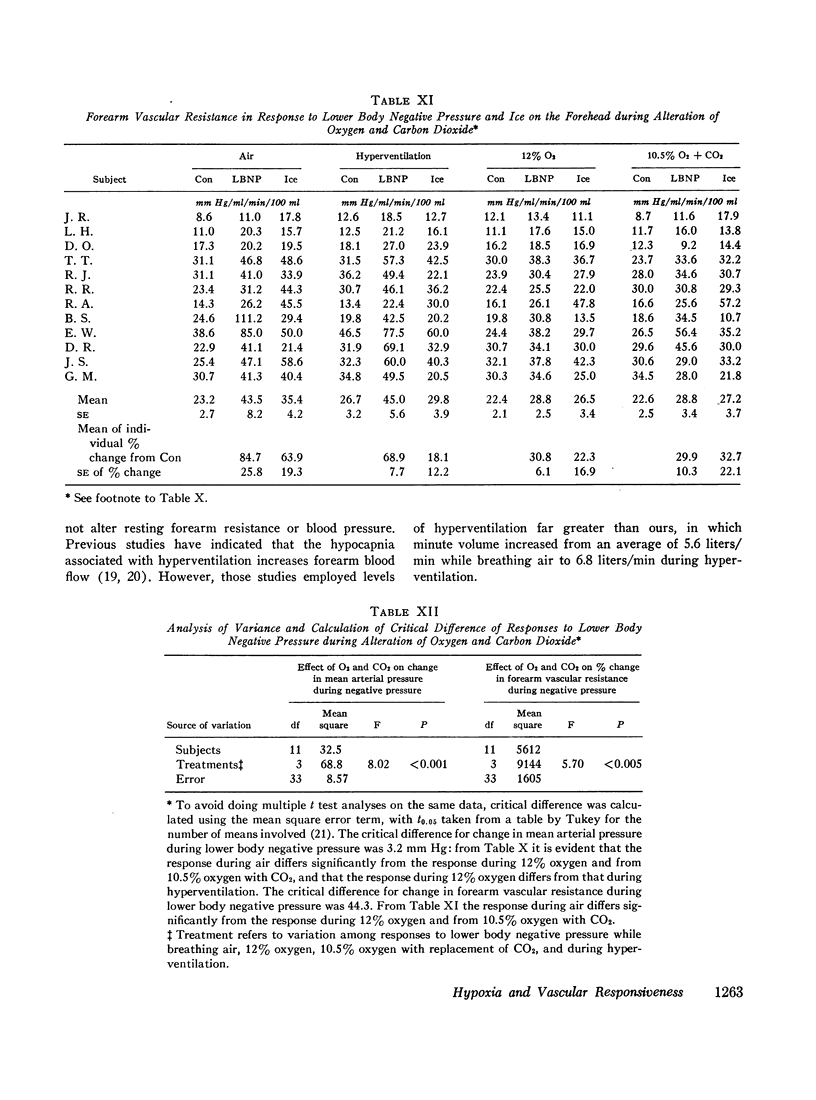
An effect of hypoxemia on vascular responsiveness and blood pressure regulation has not been demonstrated in man. The response of forearm resistance vessels to several vasoconstrictor stimuli was compared during normoxia and acute hypoxia. Forearm vasoconstrictor responses to lower body negative pressure and to the application of ice to the forehead, which are neurogenic stimuli, were decreased during acute hypoxia. Lower body negative pressure caused a decrease in mean arterial pressure during hypoxia, but not during normoxia. Because norepinephrine is the neurotransmitter released during reflex vasoconstriction, we considered the possibility that decreased responsiveness to norepinephrine might be one mechanism for diminished responses to lower body negative pressure and ice on the forehead during hypoxia. Hypoxia decreased the response of forearm resistance vessels to infusions of norepinephrine and angiotensin into the brachial artery. In addition, the effectiveness of intravenous infusions of norepinephrine in elevating mean arterial pressure was decreased during hypoxia. Since exposure to acute hypoxia stimulates hyperventilation and hypocapnia, experiments were done to determine the contribution of hypocapnia during hypoxia to the decreased vasoconstriction. The results indicate that hypocapnia may diminish the vascular response to some stimuli, but the reduction in oxygen appears to be the primary mechanism for decreased vasoconstrictor responses during acute hypoxia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK J. E., RODDIE I. C. The mechanism of the changes in forearm vascular resistance during hypoxia. J Physiol. 1958 Sep 23;143(2):226–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brick I., Hutchison K. J., Roddie I. C. The effect of beta adrenergic receptor blockade on the vasodilator response in the forearm to voluntary hyperventilation. J Physiol. 1966 Dec;187(3):645–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Goei J. S., Greenfield A. D., Plassaras G. C. Circulatory responses to simulated gravitational shifts of blood in man induced by exposure of the body below the iliac crests to sub-atmospheric pressure. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):607–627. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman J. D., Kelly P. Hyperventilation and human calf blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1966 Nov;211(5):1255–1260. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.5.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley R. J., Greenfield A. D., Plassaras G. C., Stephens D. The interrelation of thermoregulatory and baroreceptor reflexes in the control of the blood vessels in the human forearm. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):628–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detar R., Bohr D. F. Oxygen and vascular smooth muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):241–244. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenmure A. C., Murdoch W. R., Beattie A. D., Marshall J. C., Cameron A. J. Circulatory and metabolic effects of oxygen in myocardial infarction. Br Med J. 1968 Nov 9;4(5627):360–364. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5627.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marticorena E., Ruiz L., Severino J., Galvez J., Peñaloza D. Systemic blood pressure in white men born at sea level: changes after long residence at high altitudes. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Mar;23(3):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90516-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. W., Kontos H. A., Raper A. J., Patterson J. L., Jr Modification by beta-adrenergic blockade of the circulatory respones to acute hypoxia in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):77–85. doi: 10.1172/JCI105513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. W., Kontos H. A., Shapiro W., Patterson J. L., Jr Role of hypocapnia in the circulatory responses to acute hypoxia in man. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):22–26. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner N. S., Jr, Costin J. C. Role of O2 and K+ in abolition of sympathetic vasoconstriction in dog skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1969 Aug;217(2):438–444. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.2.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



