Abstract
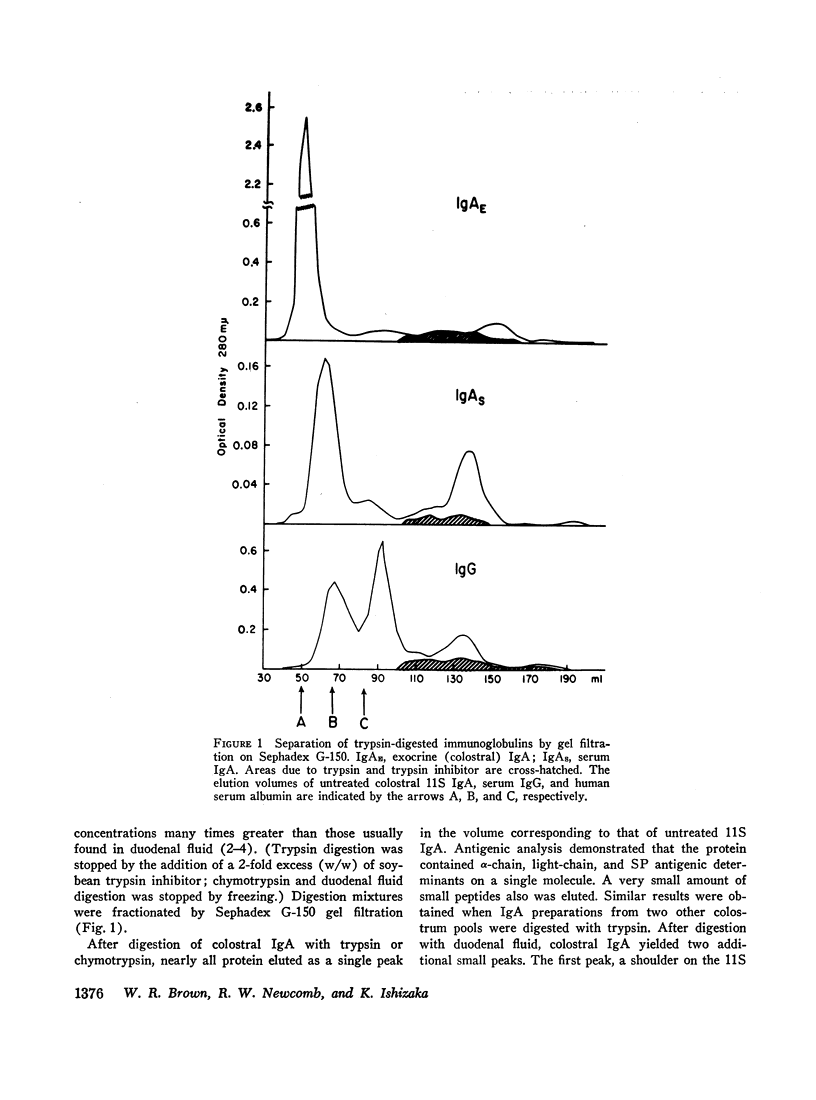
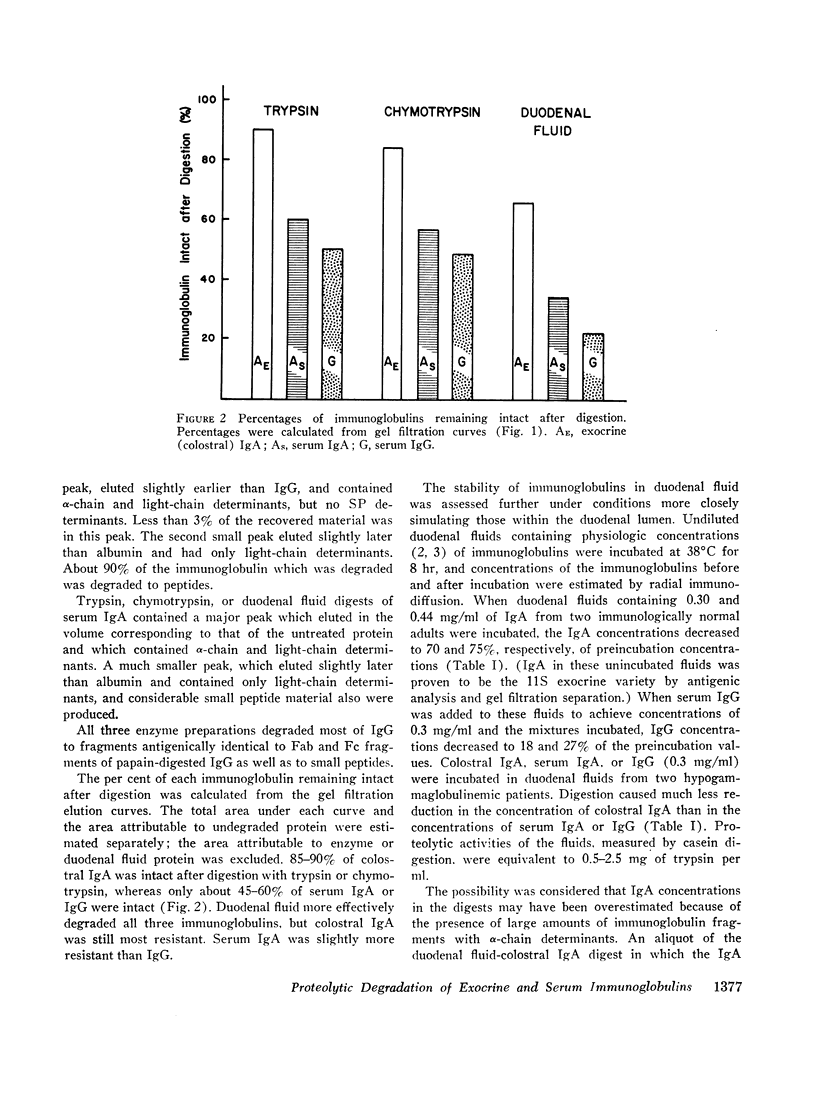
The susceptibility of exocrine and serum immunoglobulins and antibodies to proteolytic degradation was assessed. Colostral and duodenal fluid exocrine 11S IgA, monomeric serum IgA, and IgG were digested with trypsin, chymotrypsin, or duodenal fluid. Exocrine IgA was more resistant to digestion than were the serum immunoglobulins. Under conditions of the experiments, most of colostral IgA retained its 11S quaternary structure, including the secretory piece; the portion degraded was reduced almost entirely to peptides.
The superior resistance of exocrine IgA was also demonstrated by digestion of serum IgG and nasal exocrine IgA diphtheria antitoxins with trypsin or duodenal fluid. Selective precipitation of trypsin-digested antitoxins with antibodies to heavy chains, light chains, or secretory piece revealed that the differences in susceptibility to digestion were due to differences in lability of the Fc portions of the IgA and IgG antibody molecules. The Fc portions of IgG antibody molecules were degraded or cleaved from the Fab units of the molecules, whereas the Fc-like portions of IgA antibody molecules remained associated with their Fab-like units and the secretory piece. On the other hand, trypsin treatment did not affect the antigen binding ability of the Fab parts of either the exocrine IgA or IgG antibodies.
The Fc-like portions of exocrine IgA may be protected from tryptic degradation by the quaternary structure of the 11S molecules, which includes a dimer of 7S IgA subunits and the secretory piece.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger R., Ainbender E., Hodes H. L., Zepp H. D., Hevizy M. M. Demonstration of IgA polioantibody in saliva, duodenal fluid and urine. Nature. 1967 Apr 22;214(5086):420–422. doi: 10.1038/214420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Immunoglobulins of intestinal fluids. Gastroenterology. 1969 Sep;57(3):368–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHODIRKER W. B., TOMASI T. B., Jr GAMMA-GLOBULINS: QUANTITATIVE RELATIONSHIPS IN HUMAN SERUM AND NONVASCULAR FLUIDS. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1080–1081. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederblad G., Johansson B. G., Rymo L. Reduction and proteolytic degradation of immunoglobulin A from human colostrum. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Abel C. A., Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G. A subclass of human gamma-A-globulins (gamma-A2) which lacks the disulfied bonds linking heavy and light chains. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1223–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONG R., PALMER J. L., NISONOFF A. UNIVALENCE OF HALF-MOLECULES OF RABBIT ANTIBODY. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:603–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Borsos T., Rapp H. C'-1 fixation by human isoagglutinins: fixation of C'-1 by gamma-G and gamma-M but not by gamma-A antibody. J Immunol. 1966 Nov;97(5):716–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. F., Boesman M. I., Michaels R. H. Bacterial and viral coproantibodies in breast-fed infants. Pediatrics. 1967 Feb;39(2):202–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K., DeVald B. L. Human IgG and IgA diphtheria antitoxins in serum, nasal fluids and saliva. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):215–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K. Human diphtheria antitoxin in immunoglobulin classes IgG and IgA. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):40–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb R. W., Normansell D., Stanworth D. R. A structural study of human exocrine IgA globulin. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):905–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Keonil P. Immunoglobulins in human small intestinal fluid. Gastroenterology. 1969 Mar;56(3):522–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S. Radioactive single radial diffusion: a method for increasing the sensitivity of immunochemical quantification of proteins in agar gel. Bull World Health Organ. 1969 Apr;40(4):613–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROHENLOHER R. E. The degradation of human gamma-globulin by trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jun;101:456–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Danon F., Hurez D., Mihaesco E., Preud'homme J. L. Alpha-chain disease: a new immunoglobulin abnormality. Science. 1968 Dec 20;162(3860):1396–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3860.1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Mihaesco E., Hurez D., Mihaesco C., Preud'homme J. L., Rambaud J. C. Immunochemical studies in four cases of alpha chain disease. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2374–2389. doi: 10.1172/JCI106204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- South M. A., Cooper M. D., Wollheim F. A., Hong R., Good R. A. The IgA system. I. Studies of the transport and immunochemistry of IgA in the saliva. J Exp Med. 1966 Apr 1;123(4):615–627. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAERMAN J. P., HEREMANS J. F., VAERMAN C. STUDIES OF THE IMMUNE GLOBULINS OF HUMAN SERUM. I. A METHOD FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS ISOLATION OF THE TREE IMMUNE GLOBULINS (GAMMA-SS, GAMMA-IM AND GAMMA-1A) FROM INDIVIDUAL SMALL SERUM SAMPLES. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Fudenberg H. H., Vaerman C., Mandy W. J. On the significance of the heterogeneity in molecular size of human serum gamma A-globulins. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. D., Williams R. C., Jr Two distinct groups of immunoglobulin A(IgA) revealed by peptic digestion. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2409–2416. doi: 10.1172/JCI106207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


