Abstract
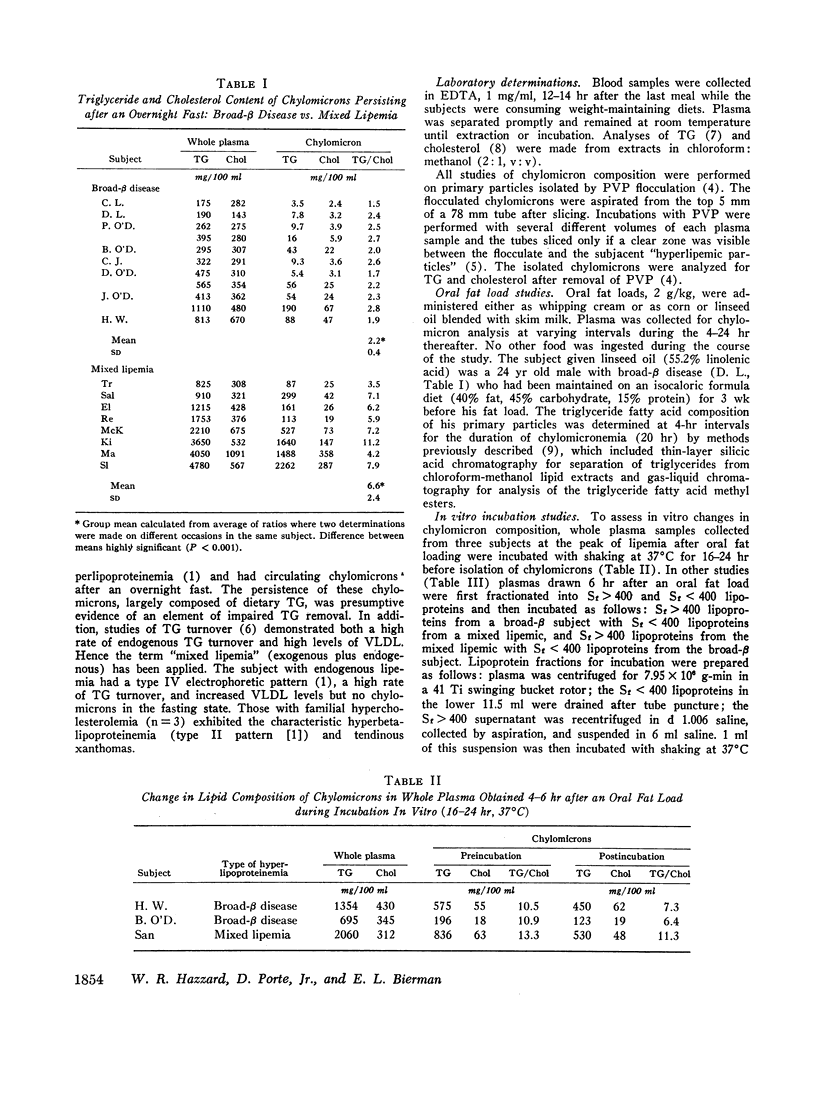
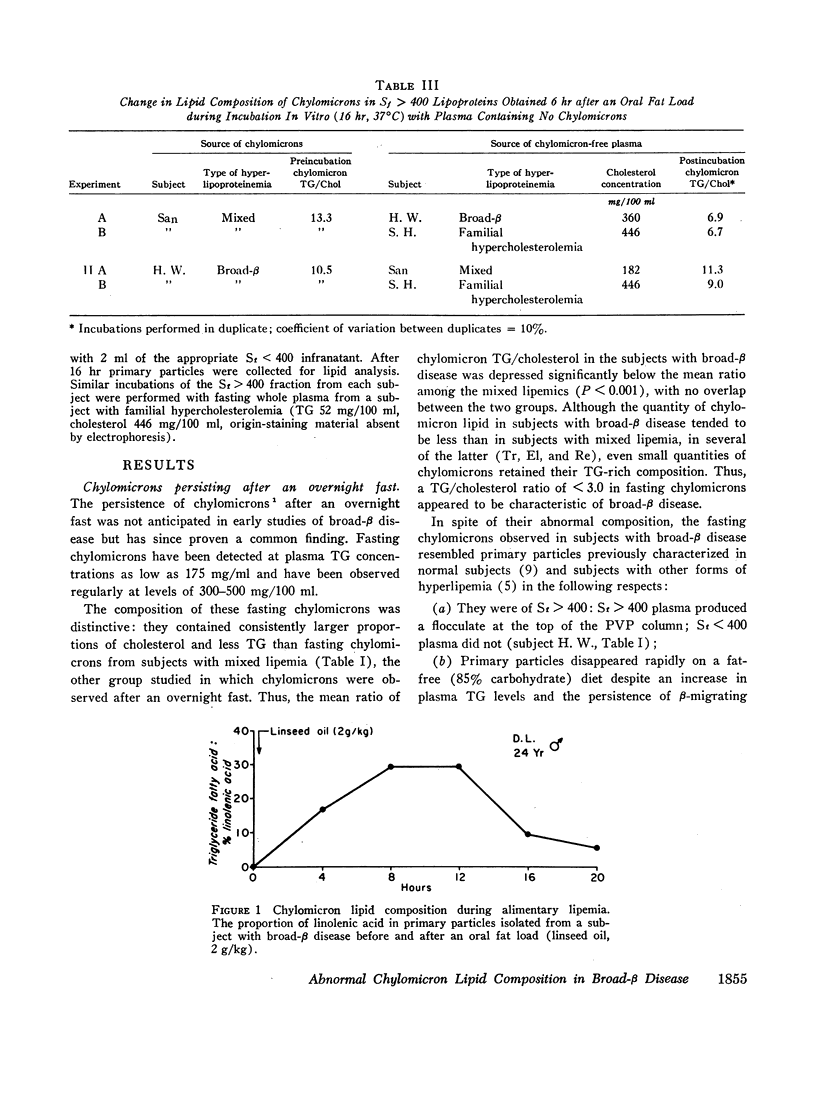
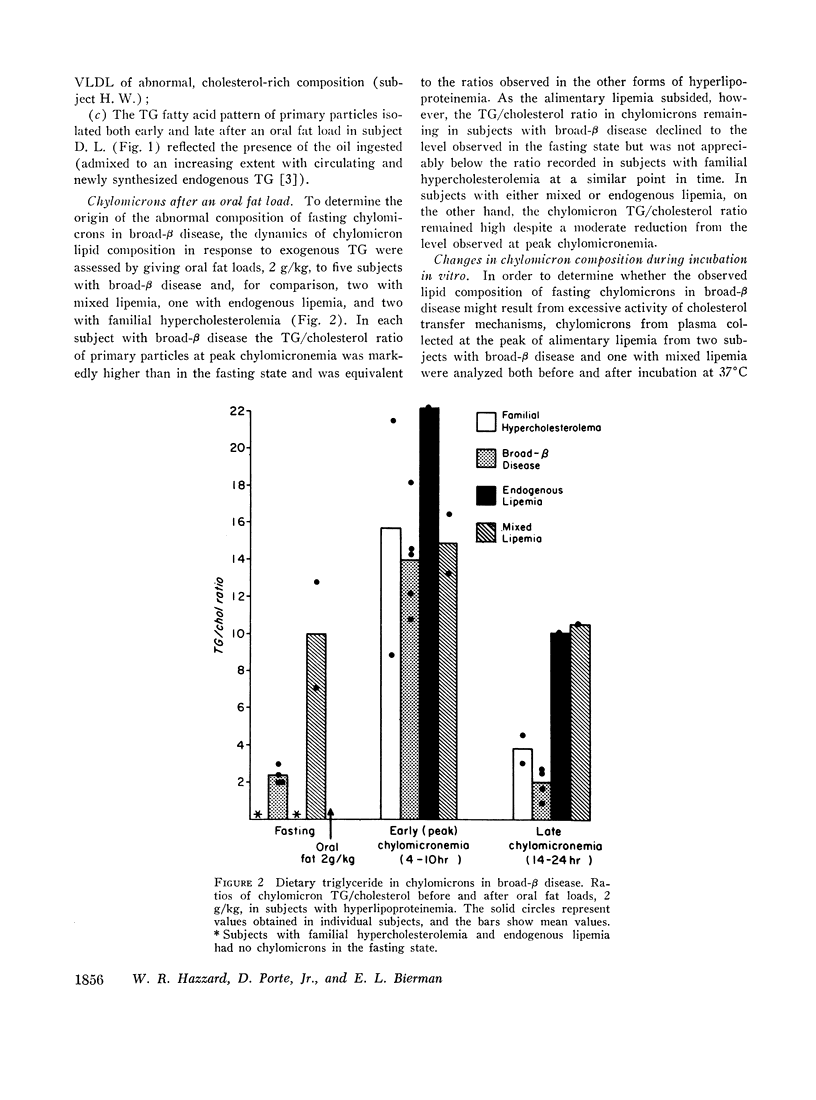
Chylomicron (primary particles) were detected by polyvinylpyrollidone (PVP) flocculation in plasma collected after an overnight fast from eight hyperlipemic subjects with broad-β disease (type III hyperlipoproteinemia). The composition of these chylomicrons was abnormal: relatively poor in triglyceride and rich in cholesterol, giving rise to a triglyceride/cholesterol ratio of < 3.0 in all cases, uniformly below the ratio in chylomicrons from eight fasting subjects with mixed lipemia. By contrast, at the peak of alimentary lipemia following an oral fat load (2 g/kg), chylomicrons from broad-β subjects had normal, triglyceride-rich composition (triglyceride/cholesterol = 14.0) and resembled chylomicrons from subjects with mixed lipemia, endogenous lipemia, and familial hypercholesterolemia after similar fat loads. As the alimentary lipemia cleared, chylomicrons remaining in broad-β subjects 14-24 hr after the fat load were again rich in cholesterol. However, a similar degree of cholesterol enrichment was observed in chylomicrons from the subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia, while only a minor increase in cholesterol was recorded in chylomicrons from subjects with mixed or endogenous lipemia. Parallel studies of changes in chylomicron composition during in vitro incubation of whole plasma and of Sf > 400 with Sf < 400 lipoproteins from subjects with the different forms of hyperlipoproteinemia revealed equal cholesterol enrichment of chylomicrons from a subject with mixed lipemia and from a subject with broad-β disease in media of equivalent cholesterol content. These experiments suggested neither excessive avidity of chylomicrons for cholesterol uptake nor excessive influence of Sf < 400 lipoproteins upon chylomicron composition in broad-β disease.
Thus, results in this study suggest that the cholesterol-rich chylomicrons observed in subjects with broad-β disease after an overnight fast may originate in the intestine as particles of normal composition (chiefly dietary triglyceride) but assume a composition which is relatively rich in cholesterol through processes of lipolysis and cholesterol transfer among circulating lipoproteins which may not be unique to broad-β disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akanuma Y., Glomset J. In vitro incorporation of cholesterol-14C into very low density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN E. L., GORDIS E., HAMLIN J. T., 3rd Heterogeneity of fat particles in plasma during alimentary lipemia. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2254–2260. doi: 10.1172/JCI104684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN E. L., HAMLIN J. T., 3rd The hyperlipemic effect of a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1961 Nov-Dec;10:432–437. doi: 10.2337/diab.10.6.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN E. L., PORTE D., Jr, O'HARA D. D., SCHWARTZ M., WOOD F. C., Jr CHARACTERIZATION OF FAT PARTICLES IN PLASMA OF HYPERLIPEMIC SUBJECTS MAINTAINED ON FAT-FREE HIGH-CARBOHYDRATE DIETS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44:261–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI105140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 2;276(5):273–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702022760507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Lindgren F. T., Bierman E. L. Very low density lipoprotein subfractions in a subject with broad-beta disease (Type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia) and a subject with endogenous lipemia (Type IV). Chemical composition and electrophoretic mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS A. V., SMITH L. EFFECT OF VERY LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS ON LIPID TRANSFER IN INCUBATED SERUM. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara D. D., Porte D., Jr, Williams R. H. Use of constant composition polyvinylpyrrolidone columns to study the interaction of fat particles with plasma. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):264–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. The effect of heparin infusion on plasma triglyceride in vivo and in vitro with a method for calculating triglyceride turnover. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Apr;73(4):631–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, O'Hara D. D., Williams R. H. Lipid composition of fat particles from normal man and patients with idiopathic hypertriglyceridemia. J Lipid Res. 1966 May;7(3):368–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARCY R. L., BERGQUIST L. M., JUNG R. C. Rapid ultramicro estimation of serum total cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1960 Jul;1:349–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


