Abstract
Various in vitro and in vivo experimental models have been used for the discovery of genes and pathways involved in melanoma and other types of cancer. However, in many cases, the results from various tumor models failed to be validated successfully in clinical studies. Limited information is available on how closely these models reflect the in vivo physiological conditions. In this study, a comprehensive genomics approach was used to systematically compare the expression patterns of snap frozen samples obtained from patients with primary melanoma, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastases, and compare these patterns to those of their corresponding cell lines and tumor xenografts in nude mice. The GE Healthcare 20k human genome array was used and the expression data was normalized and analyzed using GeneSpring 7.2 software. Based on the expression analysis, the correlation rate between the snap frozen primary patient samples vs. derived cell lines was 66%, with 1687 differentially expressed genes. The correlation rate between the snap frozen primary patient samples and the tumor xenografts was 75%, with 1,374 differentially expressed genes, and the correlation rate comparing tumor xenografts to derived cell lines ranged between 58% and 84%. These results demonstrated significant gene expression differences between tumor materials with different in vitro and in vivo growth microenvironments. Such studies can help us to distinguish between genes up- or down-regulated as a result of the microenvironment and those stably expressed independently of the tumor milieu. With the extensive use of cell lines and xenografts in cancer research, the information obtained using our approach may help to better interpret results generated from different tumor models by understanding common differences, as well as similarities at the gene expression level, information that may have important practical and biological implications.
Keywords: Melanoma, expression profiling, connexin 43, metastasis
The mortality rate of melanoma patients is still on the rise despite extensive research efforts. Recent technologies applying high throughput genomics to cancer research have been successfully utilized in melanoma research, identifying key molecular gene targets such as microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1(BRAF), and neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 9 (NEDD9) (1-5). The molecular and cellular mechanisms of many genes have been successfully validated in vivo. However, in other cases, the functional significance of such targets has failed to be confirmed in vivo, despite a strong in vitro phenotype. This may reflect the intrinsic and/or extrinsic differences in some tumor models used for such studies. In the case of melanoma, it is known that the disease development not only involves genetic and epigenetic changes that take place within the cell, but also involves processes determined collectively by tumor micro-environmental factors, including cell-cell interactions with a plethora of surrounding stromal elements. Currently, very limited information is available in regard to the distinct genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation and expression in these models.
Over the years, cancer biologists have utilized many different tumor models in order to gain an improved understanding of the processes involved in human cancer. One of the most important sources of in vitro models that is still in use today is the NCI-60 cell line panel, used for drug screening, target discovery and validation (6-13). However, in many cases, the functional significance of these genes found in vitro is poorly consistent with those identified in in vivo models. It is well-known that the tumor micro-environment can have a tremendous influence upon gene expression (14). Culture conditions and long-term cell passaging are known to greatly change the gene expression patterns for such artificial environments (15, 16). Currently, there is a lack of systematic analysis of the differences among the available research models that are in use. In many cases, the desired phenotype cannot be replicated in vivo due to the intrinsic differences in the model system. Therefore, it is important to understand the fundamental differences of tumor models in different situations in order to inform and guide gene targets and validation efforts.
To systematically address this issue, a comprehensive gene expression profiling-based analysis was employed to investigate the gene expression differences utilizing melanoma as a model system. This is an ideal system for such examination due to the extensive biobanking efforts of the surgical oncologists in obtaining freshly procured samples followed by immediate cryopreservation. Additionally, an attempt was made to grow and expand daughter melanoma cell lines in vitro whenever enough tissue was available. Utilizing these cell lines, further experiments were performed in several xenograft models, comparing the results of each of these tissue samples for evidence of differences in gene expression. In addition, to further validate this approach, a well characterized pair of melanoma cell lines (FEMX-1 and FEMX-V) with different in vivo metastatic potentials and their corresponding tumor xenografts were also used (17).
Materials and Methods
Tumor specimens
Surgically procured tumor samples from patients with primary cutaneous and metastatic melanoma were obtained under an Investigational Review Board (IRB) approved tissue procurement protocol (MCC#13448, IRB#101751; PSM# 990914-JM, 020318-JM). The tumor specimens were macrodissected and cryopreserved within 5 minutes, being careful to avoid any surrounding, non-neoplastic stromal tissue. All the samples were cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen and stored within the Tissue Procurement Laboratory of the Moffitt Cancer Center, securely de-identified through a centralized database.
Cell lines and tissue culture
Freshly excised melanoma samples were placed into culture media RPMI 1640 with 5% FCS. The expansion of daughter cell lines was performed utilizing previously published techniques (18, 19). All the cell lines were split and serially passaged less than 10 times and characterized by flow cytometry and/or cytospin preparation for cellular confirmation of melanoma cell purity (data not shown). Three cell lines were used in this study, one was derived from a primary melanoma, one from a brain metastasis and one from a distant subcutaneous leg metastasis. One of the best characterized melanoma cell lines, FEMX-I, and its derivative, FEMX-V. which were established and described previously were subsequently investigated (17). These paired cell lines were derived a decade ago from the same patient with lymphnode metastatic melanoma. FEMX-I was the first generation of the clonal variants selected by in vivo experiments that exhibited a strongly aggressive capability of metastasis. FEMX-V was derived from the fifth consecutive generation of metastases developing after injection of isolated cells into a recipient mouse. The FEMX-V cells have no metastatic potential (17). The molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying this change in metastatic capacity have not been systematically investigated, but with high throughput gene expression analysis this is now possible. A comprehensive gene expression analysis of the FEMX-I and FEMX-V cells grown in vitro and xenografts in nude mice was performed. These cell lines were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2, in RPMI 1640 (Invitrogen Inc. Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone. Logan, UT, USA). The xenografts were grown as described previously (20). In brief, the cells were detached at 80-90% confluence with 2 mM EDTA or trypsin-EDTA (0.1% trypsin and 2mM EDTA) solution, washed with calcium- and magnesium-free Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline solution (CMF-DPBS), counted using a hemacytometer and resuspended in ice-cold Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS) to a final concentration of 107 cells/ml. The cells, 1×106 (0.1 ml), were injected subcutaneously into the scapular region of 3 weeks old, female athymic mice (Harlan Sprague-Dawley, Indianapolis, IN, USA), using a 27 gauge needle affixed to a 1 cc syringe. The tumor size was measured weekly by Vernier calipers. After the mean tumor diameter reached 10 mm, the mice were euthanized and the tumors were removed for further analysis. The animals were maintained under the guidelines of the National Institute of Health and the University of South Alabama. All the protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of South Alabama. Food and water were provided ad libitum.
RNA isolation and purification
The samples were homogenized in Trizol (Invitrogen Inc.). The 100 Ìl of 1-bromo-3-chloropropane (BCP) solution (Molecular Research Center, Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA) was added to the samples. After 2 minutes vortexing, the samples were incubated for 3 minutes at room temperature. The upper aqueous phase containing the RNA from each sample was transferred to a new tube and centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 7 minutes. Equal volume of 100% isopropanol (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added and precipitation was performed at −80°C for 60 minutes. After centrifuging at 14,000 rpm for 7 minutes at 4°C, the supernatant was removed and 1 ml of 75% ethanol was added for washing. The pellet of each sample was air dried and eluted with nuclease-free water. The samples were treated with DNase to avoid potential DNA contamination, 15 Ìl DNase treatment mix (2 Ìl RQ1 RNase-Free DNase, 11 Ìl RQ1 DNase 10X Reaction Buffer and 2 Ìl RNasin Plus RNase Inhibitor, Promega, Madison, WI, USA) was incubated with each sample in 100 Ìl volume at 37°C for 30 minutes. Then 115 Ìl UltraPureì phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1, Invitrogen Inc.) was added. After 2 minutes of vortexing, the samples were centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 7 minutes. The upper aqueous phase was carefully taken out and mixed with 2 volumes of 100% ethanol and 1/10 volume of 3M sodium scetate pH 5.5 (Ambion Inc., Austin, TX, USA). The samples were held at room temperature for 15-30 minutes, then centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 7 minutes. After removing the supernatant, 1 ml of 75% ethanol was added for washing, centrifuging was repeated and then the pellets were air dried. The samples were dissolved in nuclease-free water. A NanoDrop ND-100 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA) was used to determine the concentration of all the samples.
Gene expression analysis via microarray
The CodeLink UniSet Human 20 K Oligo Bioarray (Amersham Biosciences, NJ, USA), containing approximately 20,289 gene probes, was used to generate the gene expression profiles for all the samples examined. The procedure has been described in detail previously (21, 22). In brief, double-stranded cDNAs were generated using 2 Ìg of total RNA from each sample. All the reagents and protocols were provided by GE Healthcare/Amersham Biosciences except for special indication. After purification, the double-stranded cDNAs were used as templates to generate cRNA via an in vitro transcription reaction using T7 RNA polymerase and biotin-11-UTP (Perkin-Elmer, Boston, MA, USA). The biotin-labeled cRNA (10 Ìg) was fragmented and hybridized to the CodeLink UniSet Human 20 K Oligo Bioarray. The arrays were stained with Cy5-streptavadin. After washing, the dried slides were scanned by Axon GenePix Professional 4200A microarray scanner under Genepix Pro 5.1 software (Molecular Devices Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The images were grided by Codelink 4.1 software (GE-Healthcare/Amersham Biosciences) and exported to GeneSpring Software 7.2 (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
GeneSpring software allows multifilter comparisons using data from different experiments to perform the normalization, the generation of restriction lists and the functional classification of the differentially expressed genes. Utilizing the Cross-Gene Error Model, normalization was applied in two steps: “per chip normalization” in which each measurement was divided by the 50th percentile of all measurements in its array and “per gene normalization” in which all the samples were normalized against the specific samples (controls). The data was filtered by flags. The expression profiles of the different groups were compared using one-way ANOVA with cut-off p<0.05. Comparisons of the gene lists across the different groups were performed using Venn diagrams and clustering function using Genespring.
Statistical analysis
All the statistical analyses were performed by JMP 6.0 software (SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA). All the normalized data from tumor tissue, cell lines and tumor xenografts were analyzed to determine the correlation coefficient of expression. P-values of <0.05 were interpreted as statistically significant.
Results
Clustering analysis of expression profiles among three sets of melanoma models
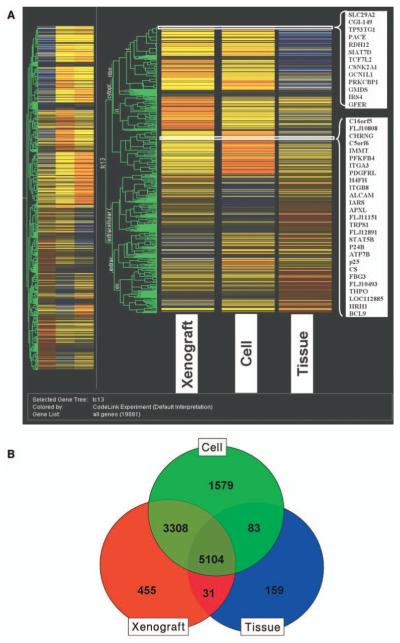
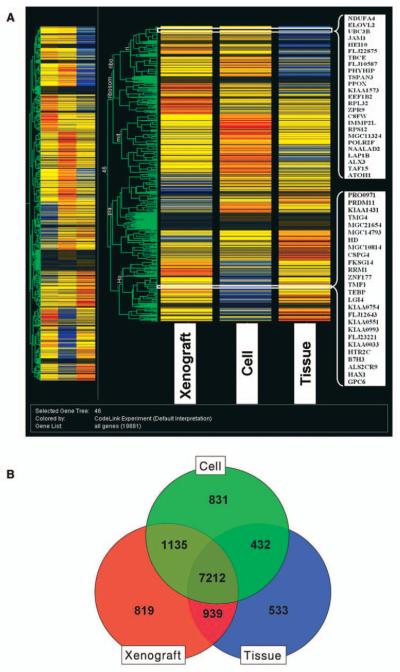
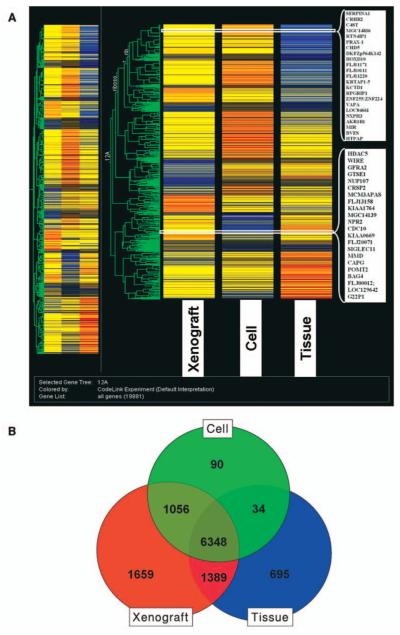
The genes clustered from the primary melanoma models (snap frozen, xenograft and cell line) are shown in Figure 1A. Gene clustering analysis showed that the expression profiles of the melanoma cells and those from human xenografts had more similarities in gene expression compared to the freshly procured tumor samples. Venn diagram analysis (Figure 1B) was utilized to discover the overlapping and unique gene sets among the three samples. Between the melanoma xenografts and the snap frozen tissues 5,135 overlapping genes were found and between the melanoma tumor xenografts and the cell lines8,412 overlapping genes were found. The clustering analysis of the models generated from the brain melanoma metastasis (Figure 2A) and Venn diagram analysis (Figure 2B) were also obtained. The clustering analysis showed that the cell lines and the xenografts had more similarities than the original tumor sample. There were 8,151 overlapping genes between the melanoma xenograft and the snap frozen tissues and 8,347 overlapping genes between melanoma tumor xenografts and cell lines. With the models from the distant (leg) metastasis, the clustering analysis (Figure 3A) showed a close similarity between the cell lines and the xenografts compared to the profiles of the melanoma tissue samples. The Venn diagram analysis (Figure 3B) with the distant metastasis model (snap frozen tissue, derived cell line and xenograft) showed 7,737 overlapping genes between the melanoma xenografts and the snap frozen tissues and 7,404 overlapping genes between the melanoma tumor xenografts and the cell lines.
Figure 1.
Clustering analysis of expression of snap frozen primary melanoma, its derived cell line and tumor xenograft (A). The data was filtered by flags. The expression profiles of the different groups were compared using one-way ANOVA with cut-off p<0.05. Comparisons of gene lists across different groups were performed using Venn diagrams and clustering function using Genespring 7.2 (B).
Figure 2.
Clustering analysis of expression of snap frozen brain metastatic melanoma, its derived cell line and tumor xenograft (A). The data was filtered by flags. The expression profiles of the different groups were compared using one-way ANOVA with cut-off p<0.05. Comparisons of gene lists across different groups were performed using Venn diagrams and clustering function using Genespring 7.2 (B).
Figure 3.
Clustering analysis of expression of snap frozen distant (leg) metastatic melanoma, its derived cell line and tumor xenograft (A). The data was filtered by flags. The expression profiles of the different groups were compared using one-way ANOVA with cut-off p<0.05. Comparisons of gene lists across different groups were performed using Venn diagrams and clustering function using Genespring 7.2 (B).
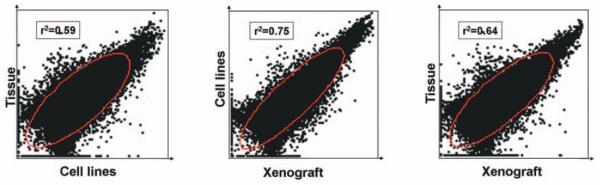
Correlations analysis based on global gene expression profiles
Next, the expression profiles were compared between the snap frozen surgical samples and their derived cell lines and the tumor xenografts based on global gene expression profiles. The weakest correlation was observed with the cell lines and snap frozen surgical tissue samples, having an overall correlation coefficient of r2=0.59 (Figure 4A). The expression profiles between the cell lines and the corresponding tumor xenografts had a correlation coefficient of r2=0.75, based upon the global gene expression profiles, which was the strongest correlation among the different comparisons (Figure 4B). The correlation between the expression profiles of the snap frozen tissue and the xenograft was r2=0.64 (Figure 4C).
Figure 4.
Correlation coefficient analysis of the expression of all normalized data from tumor tissue, cell lines and tumor xenografts. Statistical analysis was performed using JMP 6.0 software (SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA). P-values of <0.05 were interpreted as statistically significant.
Correlations analysis based on overlapping gene expression profiles
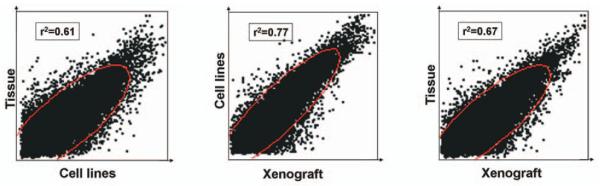
Correlation analysis was also performed based on all the overlapping genes (Figure 5). The correlation coefficient between the melanoma snap frozen tissues and its derived cell lines was r2=0.61 (Figure 5A). The correlation coefficient between the xenograft and the cell line was r2=0.77 (Figure 5B). The correlation coefficient between the tissue and the cell line was r2=0.67 (Figure 5C).
Figure 5.
Correlation coefficient analysis of the expression of all over-lapping genes from tumor tissue, cell lines and tumor xenografts. Statistical analysis was performed using JMP 6.0 software (SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA). P-values of <0.05 were interpreted as statistically significant.
Validation of prediction models using cell lines and xenografts
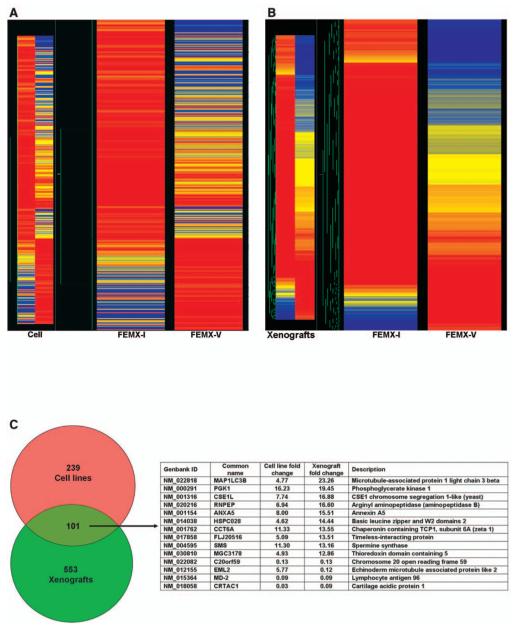
Clustering analysis was performed between the FEMX-I and FEMX-V cell lines and their xenografts (Figure 6A and 6B). Venn diagram analysis was conducted and showed that there were 367 differentially regulated genes in the FEMX-I and FEMX-V cells (Table II). In contrast, 763 genes were altered in the corresponding tumor xenografts. A Venn diagram shows 110 overlapping genes (Figure 6B, Table I). Among these, the tumor susceptibility gene 101 (TSG101) was up-regulated in both model systems. There were 653 non-overlapping genes in the xenografts that were uniquely expressed (Table III). Among these, gap junction protein, alpha 1 (connexin 43), was over-expressed >400-fold in the FEMX-I tumor xenografts compared to the FEMX-V tumor xenografts. However, this gene was not found to be significantly different in gene expression for the daughter cell lines.
Figure 6.
Clustering analysis of expression of melanoma cell lines FEMX-I and FEMX-V and their derived tumor xenografts (A). The data was filtered by flags. The expression profiles of the different groups were compared using one-way ANOVA with cut-off p<0.05. Comparisons of gene lists across different groups were performed using Venn diagrams and clustering function using Genespring 7.2 (B).
Table II. Non-overlapping differentially regulated genes comparison between FEMX-I and FEMX-V cell lines.
| GenBank ID | Common name |
Fold change |
Description | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated | ||||
| NM_032380 | EFG2 | 36.70 | Mitochondrial elongation factor G2 | Protein biosynthesis; translational elongation |
| NM_000175 | GPI | 36.50 | Glucose phosphate isomerase | Carbohydrate metabolism; gluconeogenesis; glycolysis; hemostasis; humoral immune response; neurogenesis |
| NM_006297 | XRCC1 | 34.50 | X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 1 |
Single strand break repair |
| D42045 | DCLRE1A | 33.33 | DNA cross-link repair 1A (PSO2 homolog, S. cerevisiae) |
|
| NM_001990 | EYA3 | 31.14 | Eyes absent homolog 3 (Drosophila) | Development; metabolism; morphogenesis; visual perception |
| NM_016478 | HSPC216 | 28.97 | Nuclear interacting partner of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) |
|
| NM_016355 | LOC51202 | 26.51 | DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 47 | RNA metabolism |
| AL137581 | FLJ34497 | 25.16 | Hypothetical protein FLJ34497 | |
| D83781 | NUP160 | 25.01 | Nucleoporin 160 kDa | Mrna-nucleus export; transport |
| NM_018412 | ST7 | 24.89 | Suppression of tumorigenicity 7 | |
| NM_016343 | CENPF | 23.73 | Centromere protein F, 350/400ka (mitosin) | DNA replication and chromosome cycle; regulation of mitosis |
| NM_002627 | PFKP | 23.39 | Phosphofructokinase, platelet | Glycolysis |
| NM_016292 | TRAP1 | 23.35 | Heat shock protein 75 | Protein folding |
| NM_021078 | GCN5L2 | 19.94 | GCN5 general control of amino-acid synthesis 5-like 2 (yeast) |
Chromatin remodeling; protein amino acid acetylation; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_006819 | STIP1 | 19.65 | Stress-induced-phosphoprotein 1 (Hsp70/Hsp90-organizing protein) |
Response to stress |
| NM_020998 | MST1 | 19.49 | Macrophage stimulating 1 (hepatocyte growth factor-like) |
Blood coagulation; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_004922 | SEC24C | 19.41 | SEC24 related gene family, member C (S. cerevisiae) |
ER to Golgi transport; intracellular protein transport |
| NM_005381 | NCL | 19.22 | Nucleolin | Nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_006746 | SCML1 | 18.47 | Sex comb on midleg-like 1 (Drosophila) | Morphogenesis |
| NM_018255 | ELP2 | 17.94 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 interacting protein 1 |
|
| NM_058179 | PSA | 16.20 | Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 | L-serine biosynthesis; metabolism; pyridoxine biosynthesis |
| NM_015954 | LOC51071 | 15.69 | Unr-interacting protein | |
| AW293890 | THRAP3 | 14.71 | Thyroid hormone receptor associated protein 3 | |
| NM_006796 | AFG3L2 | 14.56 | AFG3 atpase family gene 3-like 2 (yeast) | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_007355 | HSPCB | 14.18 | Heat shock 90 kDa protein 1, beta | Positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthesis; protein folding; response to unfolded protein |
| NM_016223 | PACSIN3 | 12.76 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons 3 |
Endocytosis; negative regulation of endocytosis |
| NM_002902 | RCN2 | 12.58 | Reticulocalbin 2, EF-hand calcium binding domain | |
| NM_014390 | p100 | 11.98 | Staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_013436 | NCKAP1 | 11.88 | NCK-associated protein 1 | Apoptosis; central nervous system development |
| NM_019005 | FLJ20323 | 11.71 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20323 | |
| NM_004315 | ASAH | 11.63 | N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase (acid ceramidase) 1 |
Ceramide metabolism; fatty acid metabolism |
| NM_000918 | P4HB | 11.54 | Procollagen-proline, 2-oxoglutarate 4-dioxygenase (proline 4-hydroxylase), beta polypeptide (protein disulfide isomerase; thyroid hormone binding protein p55) |
Electron transport |
| NM_021149 | COTL1 | 11.50 | Coactosin-like 1 (Dictyostelium) | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_000108 | DLD | 11.47 | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, 2-oxo-glutarate complex, branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase complex) |
Electron transport; energy pathways; glycolysis |
| NM_016026 | ARSDR1 | 11.24 | Retinol dehydrogenase 11 (all-trans and 9-cis) | Metabolism; photoreceptor maintenance; retinol metabolism |
| NM_003100 | SNX2 | 11.19 | Sorting nexin 2 | Endocytosis; intracellular protein transport; intracellular signaling cascade |
| NM_007178 | UNRIP | 11.19 | Unr-interacting protein | |
| NM_016238 | APC7 | 11.11 | Anaphase promoting complex subunit 7 | Cytokinesis; mitosis; regulation of cell cycle |
| NM_006621 | AHCYL1 | 10.74 | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-like 1 | One-carbon compound metabolism |
| BM460564 | BAG4 | 10.71 | BCL2-associated athanogene 4 | |
| NM_013236 | E46L | 10.61 | Like mouse brain protein E46 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_001798 | CDK2 | 10.56 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 | G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; cytokinesis; mitosis; positive regulation of cell proliferation; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of DNA replication; traversing start control point of mitotic cell cycle |
| NM_018899 | PCDHAC2 | 10.48 | Protocadherin alpha 5 | Cell adhesion; homophilic cell adhesion; neurogenesis |
| NM_003472 | DEK | 10.4 | DEK oncogene (DNA binding) | SRP-dependent cotranslational membrane targeting; cell growth and/or maintenance; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter; signal transduction; viral genome replication |
| NM_001415 | EIF2S3 | 10.4 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 3 gamma, 52 kDa |
Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_024586 | OSBPL9 | 10.4 | Oxysterol binding protein-like 9 | Lipid transport; steroid metabolism |
| AK056156 | TMP21 | 10.36 | Transmembrane trafficking protein | ER to Golgi transport; intracellular protein transport |
| NM_015361 | R3HDM | 10.35 | R3H domain (binds single-stranded nucleic acids) containing |
|
| AL050143 | DKFZP586B2420 | 10.30 | FLJ00133 protein | |
| NM_015367 | MIL1 | 10.26 | BCL2-like 13 (apoptosis facilitator) | Caspase activation; induction of apoptosis; regulation of apoptosis |
| NM_006337 | MCRS1 | 10.13 | Microspherule protein 1 | |
| AL136807 | SERP1 | 10.06 | Stress-associated endoplasmic reticulum protein 1 |
Plasma membrane organization and biogenesis; protein amino acid glycosylation; response to stress |
| NM_152374 | FLJ38984 | 10.03 | Hypothetical protein FLJ38984 | |
| NM_001070 | TUBG1;TUBG2 | 9.89 | Tubulin, gamma 1 | Microtubule cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; microtubule-based movement |
| NM_018356 | FLJ11193 | 9.76 | Hypothetical protein FLJ11193 | |
| AL117616 | SRI | 9.58 | Sorcin | Heart development; intracellular iron ion storage; muscle development; regulation of action potential; regulation of heart rate; regulation of striated muscle contraction; transport |
| NM_018985 | HCGIV.9 | 9.50 | HLA complex group 4 | |
| NM_002950 | RPN1 | 9.50 | Ribophorin I | Protein amino acid glycosylation |
| NM_000271 | NPC1 | 9.44 | Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 | Cholesterol transport; intracellular protein transport |
| NM_052940 | MGC8974 | 9.36 | Hypothetical protein MGC8974 | |
| NM_000687 | AHCY | 9.17 | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase | One-carbon compound metabolism |
| NM_005973 | PRCC | 9.14 | Papillary renal cell carcinoma (translocation-associated) |
Cell growth and/or maintenance |
| NM_017819 | FLJ20432 | 9.14 | RNA (guanine-9-) methyltransferase domain containing 1 |
|
| NM_002510 | GPNMB | 9.03 | Glycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb | Negative regulation of cell proliferation |
| NM_016129 | COPS4 | 8.91 | COP9 constitutive photomorphogenic homolog subunit 4 (Arabidopsis) |
|
| AB032261 | SCD | 8.85 | Stearoyl-coa desaturase (delta-9-desaturase) | Fatty acid biosynthesis |
| AK055297 | LSM11 | 8.82 | U7 snrna-associated Sm-like protein | |
| L12711 | TKT | 8.63 | Transketolase (Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome) | |
| NM_001325 | CSTF2 | 8.61 | Cleavage stimulation factor, 3′ pre-RNA, subunit 2, 64 kDa |
Mrna cleavage; mrna polyadenylation |
| U06863 | FSTL1 | 8.60 | Follistatin-like 1 | |
| NM_006644 | HSP105B | 8.55 | Heat shock 105 kDa/110 kDa protein 1 | Protein folding; response to unfolded protein |
| NM_005494 | DNAJB6 | 8.50 | Dnaj (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 6 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_001881 | CREM | 8.48 | Camp responsive element modulator | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; signal transduction |
| NM_005313 | GRP58 | 8.20 | Glucose regulated protein, 58 kDa | Electron transport; protein-ER retention; protein-nucleus import; signal transduction |
| NM_004414 | DSCR1 | 8.19 | Down syndrome critical region gene 1 | Calcium-mediated signaling; central nervous system development; circulation; signal transduction |
| NM_014992 | DAAM1 | 8.05 | Dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 1 |
Actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; cell organization and biogenesis |
| NM_006876 | B3GNT6 | 8.02 | UDP-glcnac:betagal beta-1,3- N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 6 |
Poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthesis |
| NM_016230 | b5&b5R | 7.92 | NADPH cytochrome B5 oxidoreductase | Electron transport; energy pathways; sensory perception of chemical stimulus |
| D83778 | KIAA0194 | 7.86 | KIAA0194 protein | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_014720 | SLK | 7.85 | SNF1 sucrose nonfermenting like kinase (yeast) |
Nucleotide-excision repair; protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_005146 | SART1 | 7.82 | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognised by T cells |
|
| NM_005134 | PPP4R1 | 7.81 | Protein phosphatase 4, regulatory subunit 1 | |
| NM_004127 | GPS1 | 7.76 | G protein pathway suppressor 1 | JNK cascade; cell cycle; inactivation of MAPK |
| AK055491 | DNCI2 | 7.68 | Dynein, cytoplasmic, intermediate polypeptide 2 | Microtubule-based movement |
| NM_016229 | LOC51700 | 7.64 | Cytochrome b5 reductase b5r.2 | Electron transport |
| NM_000178 | GSS | 7.59 | Glutathione synthetase | Amino acid metabolism; glutathione biosynthesis; neurogenesis; response to oxidative stress |
| NM_005565 | LCP2 | 7.56 | Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 (SH2 domain containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa) |
Immune response; intracellular signaling cascade; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway |
| NM_014287 | PM5 | 7.41 | Hypothetical protein LOC283820 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_033657 | DAP3 | 7.33 | Death associated protein 3 | Apoptosis; induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals |
| NM_012413 | QPCT | 7.28 | Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (glutaminyl cyclase) |
Protein modification |
| NM_031304 | MGC4293 | 7.26 | Hypothetical protein MGC4293 | |
| NM_013390 | TMEM2 | 7.26 | Transmembrane protein 2 | |
| NM_012164 | FBXW2 | 7.22 | F-box and WD-40 domain protein 2 | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_032737 | LMNB2 | 7.22 | Lamin B2 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_000788 | DCK | 7.19 | Deoxycytidine kinase | Nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolism; pyrimidine nucleotide metabolism |
| NM_003146 | SSRP1 | 7.12 | Structure specific recognition protein 1 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_001695 | ATP6C | 7.08 | Atpase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 42 kDa, V1 subunit C, isoform 1 |
ATP synthesis coupled proton transport; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; development |
| NM_018050 | FLJ10298 | 7.02 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10298 | |
| BC033103 | INPP5E | 6.99 | Peptidase (mitochondrial processing) alpha | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_031216 | SEC13L | 6.99 | Sec13-like protein | Intracellular protein transport |
| AB032973 | LCHN | 6.94 | LCHN protein | |
| NM_007002 | ADRM1 | 6.90 | Adhesion regulating molecule 1 | Cell adhesion |
| NM_015922 | H105E3 | 6.86 | NAD(P) dependent steroid dehydrogenase-like | Cholesterol biosynthesis; steroid biosynthesis |
| NM_003171 | SUPV3L1 | 6.77 | Suppressor of var1, 3-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) | |
| NM_004184 | WARS | 6.75 | Tryptophanyl-trna synthetase | Negative regulation of cell proliferation; protein biosynthesis; tryptophanyl-trna aminoacylation |
| NM_005826 | HNRPR | 6.69 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein R | Mrna processing |
| NM_003915 | CPNE1 | 6.66 | Copine I | Lipid metabolism; vesicle-mediated transport |
| NM_032179 | FLJ20542 | 6.66 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20542 | |
| NM_001315 | MAPK14 | 6.66 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | Antimicrobial humoral response (sensu Vertebrata); cell motility; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; chemotaxis; protein amino acid phosphorylation; protein kinase cascade; response to stress |
| NM_018142 | FLJ10569 | 6.61 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10569 | |
| BC006427 | KIAA1279 | 6.61 | Kiaa1279 | |
| NM_004749 | CPR2 | 6.53 | Transforming growth factor beta regulator 4 | G1 phase of mitotic cell cycle; cell cycle arrest; positive regulation of cell proliferation |
| NM_005765 | ATP6IP2 | 6.45 | Atpase, H+ transporting, lysosomal accessory protein 2 |
|
| NM_005499 | UBA2 | 6.45 | SUMO-1 activating enzyme subunit 2 | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_002767 | PRPSAP2 | 6.43 | Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase-associated protein 2 |
Nucleoside metabolism; nucleotide biosynthesis |
| NM_003338 | UBE2D1 | 6.28 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2D 1 (UBC4/5 homolog, yeast) |
Ubiquitin cycle; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| NM_133436 | ASNS | 6.27 | Asparagine synthetase | Asparagine biosynthesis; glutamine metabolism |
| AK057548 | LOC154790 | 6.26 | CDNA FLJ32986 fis, clone THYMU1000029 | |
| NM_001105 | ACVR1 | 6.15 | Activin A receptor, type I | Protein amino acid phosphorylation; transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway |
| NM_002444 | MSN | 6.12 | Moesin | Cell motility |
| NM_017982 | FLJ10052 | 6.11 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10052 | |
| NM_000304 | PMP22 | 6.10 | Peripheral myelin protein 22 | Mechanosensory behavior; negative regulation of cell proliferation; perception of sound; peripheral nervous system development; synaptic transmission |
| NM_000274 | OAT | 6.08 | Ornithine aminotransferase (gyrate atrophy) | Amino acid metabolism; ornithine metabolism; visual perception |
| NM_002835 | PTPN12 | 6.02 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 12 |
Protein amino acid dephosphorylation |
| NM_022758 | FLJ22195 | 6.00 | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 106 | |
| NM_015646 | RAP1B | 5.98 | RAP1B, member of RAS oncogene family | Small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_003300 | TRAF3 | 5.97 | TNF receptor-associated factor 3 | Apoptosis; induction of apoptosis; signal transduction |
| NM_017613 | DONSON | 5.95 | Downstream neighbor of SON | Biological_process unknown |
| BC023525 | C6orf69 | 5.92 | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 69 | |
| AF155110 | NY-REN-45 | 5.90 | Similar to potassium channel proteins; Homo sapiens NY-REN-45 antigen mrna, complete cds. |
|
| NM_032333 | MGC4248 | 5.84 | Hypothetical protein MGC4248 | |
| NM_005745 | BCAP31 | 5.80 | B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 | Apoptosis; immune response; intracellular protein transport |
| AK022632 | UAP1L1 | 5.70 | UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1-like 1 |
Metabolism |
| NM_002532 | NUP88 | 5.69 | Nucleoporin 88 kDa | Transport |
| NM_007158 | D1S155E | 5.66 | NRAS-related gene | Male gonad development; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_004317 | ASNA1 | 5.59 | Arsa arsenite transporter, ATP-binding, homolog 1 (bacterial) |
Anion transport; response to arsenate |
| NM_001877 | CR2 | 5.59 | Complement component (3d/Epstein Barr virus) receptor 2 |
Complement activation, classical pathway; immune response |
| AL834171 | MGC16733 | 5.58 | Hypothetical gene MGC16733 similar to CG12113 |
|
| NM_004060 | CCNG1 | 5.56 | Cyclin G1 | Cell cycle; cytokinesis; mitosis; regulation of cyclin dependent protein kinase activity |
| NM_014847 | KIAA0144 | 5.54 | NICE-4 protein | |
| NM_003600 | STK15;STK6 | 5.51 | Serine/threonine kinase 6 | Cell cycle; mitosis; protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_006559 | KHDRBS1 | 5.46 | KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 1 |
G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; RAS protein signal transduction; cell cycle arrest; cell proliferation; mrna processing |
| NM_012113 | CA14 | 5.45 | Carbonic anhydrase XIV | One-carbon compound metabolism |
| NM_005805 | POH1 | 5.21 | Synonyms: PAD1, POH1, rpn11; go_component: 26S proteasome [goid 0005837] [evidence TAS] [pmid 9374539]; go_component: cytosol [goid 0005829] [evidence IEA]; go_component: proteasome complex (sensu Eukarya) [goid 0000502] [evidence TAS]; go_process: ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism [goid 0006511] [evidence TAS] [pmid 9374539]; Homo sapiens proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-atpase, 14 (PSMD14), mrna. |
Ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| NM_018312 | C11orf23 | 5.19 | Chromosome 11 open reading frame 23 | |
| AF222345 | SUFU | 5.19 | Suppressor of fused homolog (Drosophila) | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_014321 | ORC6L | 5.16 | Origin recognition complex, subunit 6 homolog-like (yeast) |
DNA replication |
| NM_004600 | SSA2 | 5.16 | Sjogren syndrome antigen A2 (60 kDa, ribonucleoprotein autoantigen SS-A/Ro) |
Transcription from Pol III promoter |
| NM_006400 | DCTN2 | 5.15 | Dynactin 2 (p50) | Cell proliferation; microtubule-based process; mitosis |
| AL832599 | STARD4; | 5.12 | START domain containing 4, sterol regulated | Lipid transport; steroid biosynthesis |
| AB033023 | FLJ10201 | 5.11 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10201 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_021824 | NIF3L1 | 5.10 | NIF3 NGG1 interacting factor 3-like 1 (S. Pombe) | |
| NM_003896 | SIAT9 | 5.07 | Sialyltransferase 9 (CMP-neuac:lactosylceramide alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase; GM3 synthase) |
Ganglioside biosynthesis; protein amino acid glycosylation |
| NM_004568 | SERPINB6 | 5.06 | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 6 | |
| NM_020151 | STARD7 | 5.02 | START domain containing 7 | |
| NM_004368 | CNN2 | 5.00 | Calponin 2 | Cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; smooth muscle contraction |
| AJ251973 | NAV1; POMFIL3; FLJ12560; FLJ14203; KIAA1151; MGC14961; steerin-1 |
5.00 | Homo sapiens partial steerin-1 gene. | DNA methylation |
| NM_000819 | GART | 4.97 | Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase, phosphoribosylglycinamide synthetase, phosphoribosylaminoimidazole synthetase |
‘De novo’ IMP biosynthesis; purine base biosynthesis; purine nucleotide biosynthesis |
| U03851 | CAPZA2 | 4.96 | Capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 2 |
Actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; cell motility; protein complex assembly |
| U03851 | CAPZA2 | 4.75 | Capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 2 |
Actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; cell motility; protein complex assembly |
| NM_021129 | PP | 4.69 | Pyrophosphatase (inorganic) | Metabolism; phosphate metabolism |
| NM_007217 | PDCD10 | 4.68 | Programmed cell death 10 | |
| AK055660 | MTPN | 4.56 | Myotrophin | |
| Down-regulated | ||||
| NM_000800 | FGF1 | −100.00 | Fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) | Angiogenesis; cell proliferation; cell-cell signaling; morphogenesis; regulation of cell cycle; signal transduction |
| NM_020411 | GAGED2 | −100.00 | G antigen, family D, 2 | |
| AL120032 | GABRB3 | −100.00 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, beta 3 |
|
| NM_024736 | FLJ12150 | −100.00 | Hypothetical protein FLJ12150 | |
| NM_006158 | NEFL | −100.00 | Neurofilament, light polypeptide 68 kDa | |
| BC008915 | SERPINA3 | −68.97 | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 3 |
|
| NM_025181 | FLJ22004 | −59.17 | Solute carrier family 35, member F5 | |
| NM_002050 | GATA2 | −57.47 | Synonyms: NFE1B, MGC2306; GATA-binding protein 2; go_component: nucleus [goid 0005634] [evidence TAS] [pmid 1370462]; go_function: transcription activating factor [goid 0003710] [evidence E] [pmid 1370462]; go_function: transcription factor activity [goid 0003700] [evidence TAS] [pmid 8078582]; go_function: translation regulator activity [goid 0045182] [evidence IEA]; go_process: cell growth and/or maintenance [goid 0008151] [evidence TAS] [pmid 8078582]; go_process: transcription from Pol II promoter [goid 0006366] [evidence TAS] [pmid 1370462]; go_process: regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent [goid 0006355] [evidence IEA]; Homo sapiens GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2), mrna. |
|
| NM_002922 | RGS1 | −44.05 | Regulator of G-protein signalling 1 | B-cell activation; G-protein signaling, adenylate cyclase inhibiting pathway; immune response; signal transduction |
| NM_004335 | BST2 | −27.40 | Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 | Cell proliferation; cell-cell signaling; development; humoral immune response; positive regulation of I-kappab kinase/NF-kappab cascade |
| NM_007283 | MGLL | −26.81 | Monoglyceride lipase | Aromatic compound metabolism; inflammatory response; lipid metabolism |
| NM_021992 | TMSNB | −25.00 | Thymosin, beta, identified in neuroblastoma cells | Cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis |
| AL137259 | DKFZp434D0513 | −23.98 | Hydrocephalus inducing | |
| NM_024600 | FLJ20898 | −21.32 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20898 | |
| NM_152773 | MGC33212 | −16.67 | Hypothetical protein MGC33212 | |
| NM_018476 | BEX1 | −16.50 | Brain expressed, X-linked 1 | |
| NM_001187 | BAGE | −16.34 | B melanoma antigen | |
| NM_001266 | CES1 | −15.97 | Carboxylesterase 1 (monocyte/ macrophage serine esterase 1) |
Metabolism; response to toxin |
| NM_000170 | GLDC | −15.75 | Glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating; glycine decarboxylase, glycine cleavage system protein P) |
Glycine catabolism |
| NM_139177 | C17orf26 | −14.95 | Solute carrier family 39 (metal ion transporter), member 11 |
Metal ion transport |
| NM_001869 | CPA2 | −14.18 | Carboxypeptidase A2 (pancreatic) | Proteolysis and peptidolysis; vacuolar protein catabolism |
| U83115 | AIM1 | −12.77 | Absent in melanoma 1 | |
| NM_001719 | BMP7 | −12.32 | Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (osteogenic protein 1) |
Growth; skeletal development |
| NM_005574 | LMO2 | −12.02 | LIM domain only 2 (rhombotin-like 1) | Cell growth and/or maintenance; development |
| NM_004609 | TCF15 | −11.89 | Transcription factor 15 (basic helix-loop-helix) | Development; mesoderm development; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_003227 | TFR2 | −11.82 | Transferrin receptor 2 | Iron ion transport; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| AF288741 | OSBP2 | −11.81 | Oxysterol binding protein 2 | Lipid transport; steroid metabolism |
| NM_016429 | COPZ2 | −11.52 | Coatomer protein complex, subunit zeta 2 | Intracellular protein transport |
| NM_002250 | KCNN4 | −11.27 | Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 |
Defense response; ion transport; potassium ion transport |
| BC015794 | FLJ10097 | −10.47 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10097 | |
| NM_005712 | HHLA1 | −9.90 | HERV-H LTR-associating 1 | |
| NM_005978 | S100A2 | −9.90 | S100 calcium binding protein A2 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_002928 | RGS16 | −9.80 | Regulator of G-protein signalling 16 | Regulation of G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; signal transduction; visual perception |
| NM_032638 | MGC2306 | −9.35 | GATA binding protein 2 | Cell growth and/or maintenance; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription from Pol II promoter |
| BF344649 | MGC8685 | −8.85 | Tubulin, beta polypeptide paralog | |
| NM_004078 | CSRP1 | −8.47 | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 1 | |
| NM_003733 | OASL | −8.40 | 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase-like | Immune response |
| NM_006417 | MTAP44 | −8.40 | Interferon-induced protein 44 | Response to virus |
| NM006169 | NNMT | −8.20 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | |
| AL834409 | DKFZp547J144 | −8.20 | Reticulon 4 receptor-like 1 | |
| AF399547 | OR1N1; OR1N3; OR1-26 |
−7.52 | Contains transmembrane regions 2-7; Homo sapiens clone OR1N3 olfactory receptor gene, partial cds. |
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; perception of smell |
| NM_001175 | ARHGDIB | −7.25 | Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) beta | Rho protein signal transduction; actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; development; immune response; negative regulation of cell adhesion |
| AK074703 | LOC89944 | −7.09 | Hypothetical protein BC008326 | Carbohydrate metabolism |
| NM_004924 | ACTN4 | −7.04 | Actinin, alpha 4 | Cell motility |
| AI123815 | FLJ21963 | −7.04 | FLJ21963 protein | |
| NM_032261 | DKFZp434N0650 | −6.90 | Chromosome 21 open reading frame 56 | |
| NM_006993 | NPM3 | −6.85 | Nucleophosmin/nucleoplasmin, 3 | Protein folding |
| BC009033 | LOC253982 | −6.80 | Hypothetical protein LOC253982 | Peptidyl-amino acid modification |
| NM_005794 | HEP27 | −6.76 | Dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 2 |
Metabolism |
| NM_012219 | MRAS | −6.71 | Muscle RAS oncogene homolog | RAS protein signal transduction; actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; development; muscle development |
| AB067508 | KIAA1921 | −6.58 | Start codon is not identified.; Homo sapiens mrna for KIAA1921 protein, partial cds. |
|
| NM_004711 | SYNGR1 | −6.49 | Synaptogyrin 1 | |
| NM_020169 | LXN | −6.29 | Latexin protein | |
| NM_018170 | FLJ10656 | −6.21 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10656 | |
| NM_004107 | FCGRT | −6.13 | Fc fragment of igg, receptor, transporter, alpha | Immune response; pregnancy |
| NM_018265 | FLJ10901 | −6.10 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10901 | |
| NM_006302 | GCS1 | −6.06 | Glucosidase I | N-linked glycosylation; carbohydrate metabolism; oligosaccharide metabolism |
| NM_003633 | ENC1 | −5.85 | Ectodermal-neural cortex (with BTB-like domain) | Development; neurogenesis |
| NM_004583 | RAB5C | −5.81 | RAB5C, member RAS oncogene family | Intracellular protein transport; small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| AK074859 | LOC147808 | −5.71 | Similar to zinc finger protein | |
| BE615983 | STUB1 | −5.71 | STIP1 homology and U-Box containing protein 1 | |
| NM_018022 | FLJ10199 | −5.59 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10199 | |
| NM_024710 | FLJ23469 | −5.49 | Hypothetical protein FLJ23469 | Metabolism |
| NM_016202 | LOC51157 | −5.46 | Zinc finger protein 580 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| AJ011713 | TNNT1 | −5.38 | Homo sapiens TNNT1 gene, exons 12-14. | Muscle development; regulation of muscle contraction |
| NM_003283 | TNNT1 | −5.35 | Troponin T1, skeletal, slow | Muscle development; regulation of muscle contraction |
| NM_032488 | LOC84518 | −5.15 | Protein related with psoriasis | |
| AK055959 | TOM1L2 | −5.08 | Target of myb1-like 2 (chicken) | Intra-Golgi transport; intracellular protein transport |
| NM_001060 | TBXA2R | −4.98 | Thromboxane A2 receptor | G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; muscle contraction; respiratory gaseous exchange |
| NM_002514 | NOV | −4.88 | Nephroblastoma overexpressed gene | Regulation of cell growth |
| NM_000117 | EMD | −4.83 | Emerin (Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy) | Muscle contraction; muscle development |
| NM_007286 | KIAA1029 | −4.72 | Synaptopodin | |
| NM_018956 | C9orf9 | −4.67 | Chromosome 9 open reading frame 9 | |
| NM_032603 | LOXL3 | −4.67 | Lysyl oxidase-like 3 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_015681 | B9 | −4.65 | B9 protein | |
| NM_014849 | SV2 | −4.63 | Synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A | Transport |
Table I. Overlapping differentially regulated genes, FEMX-I and FEMX-V vs. the derived tumor xenografts.
| GenBank ID | Common name |
Xenograft fold change |
Cell line fold change |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated | ||||
| NM_003752 | EIF3S8 | 51.96 | 53.86 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit 8, 110 kDa |
| NM_000181 | GUSB | 47.20 | 11.92 | Glucuronidase, beta |
| NM_006111 | ACAA2 | 40.84 | 11.94 | Acetyl-Coenzyme A acyltransferase 2 (mitochondrial 3-oxoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase) |
| NM_001416 | EIF4A1 | 32.61 | 5.60 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A, isoform 1 |
| AB014540 | KIAA0640 | 31.32 | 4.98 | SWAP-70 protein |
| NM_000967 | RPL3 | 31.15 | 6.48 | Ribosomal protein L3 |
| NM_004559 | NSEP1 | 30.48 | 5.75 | Nuclease sensitive element binding protein 1 |
| NM_003405 | YWHAH | 29.89 | 15.51 | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, eta polypeptide |
| NM_002136 | HNRPA1 | 25.64 | 12.66 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 |
| NM_001402 | EEF1A1 | 23.53 | 23.74 | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1 |
| NM_022818 | MAP1LC3B | 23.26 | 4.77 | Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta |
| NM_024057 | MGC5585 | 22.39 | 4.94 | Nucleoporin Nup37 |
| NM_017812 | FLJ20420 | 20.99 | 5.42 | Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 3 |
| NM_000291 | PGK1 | 19.45 | 16.23 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 |
| NM_003418 | ZNF9 | 19.43 | 5.46 | Zinc finger protein 9 (a cellular retroviral nucleic acid binding protein) |
| NM_001316 | CSE1L | 16.88 | 7.74 | CSE1 chromosome segregation 1-like (yeast) |
| NM_020216 | RNPEP | 16.60 | 6.94 | Arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B) |
| BC008861 | ATP6D | 16.24 | 4.77 | Atpase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 38 kDa, V0 subunit d isoform 1 |
| NM_000183 | HADHB | 15.98 | 6.03 | Hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase/enoyl-Coenzyme A hydratase (trifunctional protein), beta subunit |
| NM_001154 | ANXA5 | 15.51 | 8.00 | Annexin A5 |
| AL137681 | EIF4A2 | 14.67 | 10.06 | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4AII, unspliced; Homo sapiens mrna; cdna dkfzp434m0326 (from clone dkfzp434m0326); partial cds. |
| BC021714 | PPFIBP2 | 14.47 | 6.97 | PTPRF interacting protein, binding protein 2 (liprin beta 2) |
| NM_014038 | HSPC028 | 14.44 | 4.62 | Basic leucine zipper and W2 domains 2 |
| NM_006070 | TFG | 14.43 | 10.61 | TRK-fused gene |
| NM_001762 | CCT6A | 13.55 | 11.33 | Chaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 6A (zeta 1) |
| NM_017858 | FLJ20516 | 13.51 | 5.09 | Timeless-interacting protein |
| NM_004595 | SMS | 13.16 | 11.30 | Spermine synthase |
| NM_030810 | MGC3178 | 12.86 | 4.93 | Thioredoxin domain containing 5 |
| AF134802 | CFL2 | 12.40 | 5.21 | Cofilin 2 (muscle) |
| NM_000182 | HADHA | 12.38 | 6.62 | Hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase/enoyl-Coenzyme A hydratase (trifunctional protein), alpha subunit |
| NM_016359 | ANKT | 12.36 | 11.72 | Nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 |
| NM_003142 | SSB | 11.98 | 5.77 | Sjogren syndrome antigen B (autoantigen La) |
| NM_014309 | RBM9 | 11.73 | 9.41 | RNA binding motif protein 9 |
| NM_002847 | PTPRN2 | 11.72 | 6.16 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, N polypeptide 2 |
| NM_033317 | ZD52F10 | 11.50 | 6.69 | Hypothetical gene ZD52F10 |
| NM_006743 | RBM3 | 10.81 | 5.46 | RNA binding motif protein 3 |
| NM_015679 | CLONE24922 | 10.55 | 6.87 | Trub pseudouridine (psi) synthase homolog 2 (E. Coli) |
| NM_003819 | PABPC4 | 9.93 | 6.50 | Poly(A) binding protein, cytoplasmic 4 (inducible form) |
| NM_001634 | AMD1 | 9.77 | 5.63 | Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1 |
| NM_006904 | PRKDC | 9.51 | 5.94 | Protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide |
| NM_022874 | SMN1;SMN2 | 9.44 | 4.57 | Survival of motor neuron 1, telomeric |
| NM_014062 | ART-4 | 9.40 | 9.49 | Likely ortholog of mouse nin one binding protein |
| NM_018472 | HT011 | 9.38 | 5.65 | Uncharacterized hypothalamus protein HT011 |
| NM_022337 | RAB38 | 9.19 | 5.37 | RAB38, member RAS oncogene family |
| NM_012470 | TRN-SR | 9.06 | 4.52 | Transportin 3 |
| NM_014713 | LAPTM4A | 8.91 | 4.85 | Lysosomal-associated protein transmembrane 4 alpha |
| AB037716 | KIAA1295;FLJ20831 | 8.87 | 5.63 | KIAA1295 protein |
| NM_018206 | VPS35 | 8.83 | 11.36 | Vacuolar protein sorting 35 (yeast) |
| NM_004125 | GNG10 | 8.76 | 5.07 | Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 10 |
| NM_006017 | PROML1 | 8.73 | 9.62 | Prominin 1 |
| NM_021105 | PLSCR1 | 8.41 | 9.49 | Phospholipid scramblase 1 |
| NM_031844 | HNRPU | 8.14 | 7.20 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (scaffold attachment factor A) |
| NM_002080 | GOT2 | 8.10 | 25.65 | Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 2, mitochondrial (aspartate aminotransferase 2) |
| NM_016308 | UMP-CMPK | 7.68 | 5.82 | UMP-CMP kinase |
| NM_000520 | HEXA | 7.29 | 7.95 | Hexosaminidase A (alpha polypeptide) |
| NM_004046 | ATP5A1 | 7.14 | 19.12 | ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, alpha subunit, isoform 1, cardiac muscle |
| NM_004868 | GPSN2 | 6.98 | 5.79 | Glycoprotein, synaptic 2 |
| NM_001418 | EIF4G2 | 6.82 | 24.72 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma, 2 |
| NM_016397 | TH1L | 6.77 | 5.82 | TH1-like (Drosophila) |
| AK098818 | FLJ25952 | 6.75 | 15.21 | Hypothetical protein FLJ25952 |
| NM_005704 | PTPRU | 6.53 | 14.41 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, U |
| L29065 | 6.51 | 5.78 | Human DNA-binding protein A gene, exon 2. | |
| NM_024666 | FLJ11506 | 6.46 | 11.13 | Hypothetical protein FLJ11506 |
| NM_001881 | CREM | 6.44 | 8.66 | Camp responsive element modulator |
| NM_005348 | HSPCA | 6.19 | 18.43 | Heat shock 90 kDa protein 1, alpha |
| AB037723 | ODZ4 | 6.15 | 6.52 | Odd Oz/ten-m homolog 4 |
| NM_022145 | FKSG14 | 6.00 | 6.91 | Leucine zipper protein FKSG14 |
| NM_002079 | GOT1 | 5.96 | 7.19 | Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1, soluble (aspartate aminotransferase 1) |
| NM_019006 | AWP1 | 5.87 | 8.21 | Protein associated with PRK1 |
| NM_024306 | FAAH | 5.86 | 12.89 | Fatty acid 2-hydroxylase |
| NM_001908 | CTSB | 5.46 | 4.93 | Cathepsin B |
| Down-regulated | ||||
| NM_017863 | FLJ20527 | −100.00 | −46.08 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20527 |
| AB011538 | SLIT3 | −99.01 | −7.75 | Slit homolog 3 (Drosophila) |
| NM_004106 | FCER1G | −90.91 | −75.19 | Fc fragment of ige, high affinity I, receptor for; gamma polypeptide |
| NM_003592 | CUL1 | −71.43 | 10.92 | Cullin 1 |
| NM_016608 | ALEX1 | −48.54 | −38.91 | ALEX1 protein |
| NM_002961 | S100A4 | −45.25 | −6.06 | S100 calcium binding protein A4 (calcium protein, calvasculin, metastasin, murine placental homolog) |
| NM_033292 | CASP1;COP | −28.25 | −100.00 | Caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine protease (interleukin 1, beta, convertase) |
| NM_017590 | RoXaN | −27.32 | −9.09 | Ubiquitous tetratricopeptide containing protein roxan |
| NM_014909 | KIAA1036 | −25.45 | −20.53 | Kiaa1036 |
| X07109 | PRKCB1 | −24.88 | −7.09 | Protein kinase C, beta 1 |
| BC011739 | APOBEC3C | −23.09 | −19.05 | Apolipoprotein B mrna editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3C |
| NM_001803 | CDW52 | −20.96 | −9.09 | CDW52 antigen (CAMPATH-1 antigen) |
| NM_001778 | CD48 | −17.70 | −99.01 | CD48 antigen (B-cell membrane protein) |
| NM_000237 | LPL | −16.29 | −10.38 | Lipoprotein lipase |
| NM_018659 | C17 | −14.79 | −45.25 | Cytokine-like protein C17 |
| AK025833 | CD33L3 | −11.09 | −25.13 | CD33 antigen-like 3 |
| NM_018058 | CRTAC1 | −10.99 | −33.44 | Cartilage acidic protein 1 |
| NM_015364 | MD-2 | −10.93 | −10.67 | Lymphocyte antigen 96 |
| D10537 | MPZ | −10.41 | −47.62 | Myelin protein zero (Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy 1B) |
| AL390147 | DKFZp547D065 | −10.07 | −86.21 | Family with sequence similarity 20, member C |
| AF401235 | SLC29A2 | −9.62 | −15.48 | Solute carrier family 29 (nucleoside transporters), member 2 |
| BC015510 | RGS1 | −8.85 | −34.13 | Regulator of G-protein signalling 1 |
| NM_012155 | EML2 | −8.13 | 5.77 | Echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 2 |
| AK026966 | AK3 | −7.81 | −11.93 | Adenylate kinase 3 |
| NM_030801 | MAGE-E1 | −7.63 | −20.88 | Melanoma antigen, family D, 4 |
| NM_022082 | C20orf59 | −7.58 | −7.81 | Chromosome 20 open reading frame 59 |
| NM_000483 | APOC2 | −6.94 | −26.74 | Apolipoprotein C-II |
| NM_012253 | TKTL1 | −5.95 | −17.01 | Transketolase-like 1 |
| NM_001553 | IGFBP7 | −5.62 | −17.79 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 |
| NM_004369 | COL6A3 | −5.32 | −5.38 | Collagen, type VI, alpha 3 |
Table III. Unique differentially regulated genes comparison between FEMX-I and FEMX-V tumor xenografts.
| GenBank ID | Common name |
Fold change |
Description | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated | ||||
| NM_004214 | FIBP | 507.00 | Fibroblast growth factor (acidic) intracellular binding protein |
Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway |
| NM_000165 | GJA1 | 439.00 | Gap junction protein, alpha 1, 43 kDa (connexin 43) |
Cell-cell signaling; heart development; muscle contraction; perception of sound; positive regulation of I-kappab kinase/NF-kappab cascade; transport |
| NM_014640 | KIAA0173 | 237.00 | Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family, member 4 | Protein modification |
| NM_021979 | HSPA2 | 229.00 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 2 | Male meiosis; spermatid development |
| AF300796 | CSE-C | 164.00 | Cytosolic sialic acid 9-O-acetylesterase homolog | |
| NM_012311 | KIN | 96.38 | KIN, antigenic determinant of reca protein homolog (mouse) |
|
| NM_000188 | HK1 | 93.04 | Hexokinase 1 | Glycolysis |
| NM_016113 | TRPV2 | 69.01 | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 2 |
Cation transport; sensory perception |
| NM_015610 | DKFZP434J154 | 62.59 | DKFZP434J154 protein | |
| NM_001099 | ACPP | 62.51 | Acid phosphatase, prostate | Regulation of cell cycle |
| NM_007017 | SOX30 | 60.01 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 30 | Regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter; spermatogenesis |
| NM_000167 | GK | 51.31 | Glycerol kinase | Carbohydrate metabolism; glycerol-3-phosphate metabolism |
| NM_003750 | EIF3S10 | 49.46 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit 10 theta, 150/170 kDa |
Protein biosynthesis; regulation of translational initiation |
| NM_018702 | ADAR3 | 48.50 | Adenosine deaminase, RNA-specific, B2 (RED2 homolog rat) |
Mrna editing; mrna processing |
| NM_000308 | PPGB | 48.29 | Protective protein for beta-galactosidase (galactosialidosis) |
Intracellular protein transport; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_014065 | HT001 | 44.69 | HT001 protein | |
| NM_003367 | USF2 | 43.19 | Upstream transcription factor 2, c-fos interacting | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| AK024450 | ARHT2 | 43.05 | Ras homolog gene family, member T2 | Small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_000375 | UROS | 41.01 | Uroporphyrinogen III synthase (congenital erythropoietic porphyria) |
Heme biosynthesis; uroporphyrinogen III biosynthesis |
| NM_024689 | FLJ14103 | 37.77 | Hypothetical protein FLJ14103 | |
| NM_005412 | SHMT2 | 36.17 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (mitochondrial) |
L-serine metabolism; glycine metabolism; one-carbon compound metabolism |
| NM_004862 | PIG7 | 36.14 | Lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF factor | Positive regulation of I-kappab kinase/NF-kappab cascade; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| BC002980 | SCRN2 | 34.47 | Secernin 2 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_018410 | DKFZp762E1312 | 33.04 | Hypothetical protein dkfzp762e1312 | |
| NM_032801 | JAM3 | 32.75 | Junctional adhesion molecule 3 | |
| NM_003681 | PDXK | 32.05 | Pyridoxal (pyridoxine, vitamin B6) kinase | |
| NM_022449 | RAB17 | 30.90 | RAB17, member RAS oncogene family | Intracellular protein transport; small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_002046 | GAPD | 29.98 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Glucose metabolism; glycolysis |
| NM_003900 | SQSTM1 | 28.30 | Sequestosome 1 | Endosome transport; intracellular signaling cascade; positive regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter; protein localization; regulation of I-kappab kinase/NF-kappab cascade; response to stress |
| L09674 | SLC2A2; GLUT2 | 26.57 | Human glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) gene, exon 1. |
Carbohydrate metabolism; carbohydrate transport; glucose transport |
| NM_145792 | MGST1 | 26.39 | Microsomal glutathione S-transferase 1 | |
| AK054993 | RAC1 | 26.38 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac1) |
Cell adhesion; cell motility; inflammatory response; morphogenesis; small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_002300 | LDHB | 26.03 | Lactate dehydrogenase B | Glycolysis; tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediate metabolism |
| NM_002629 | PGAM1 | 25.26 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (brain) | Glycolysis; metabolism |
| NM_002077 | GOLGA1 | 24.72 | Golgi autoantigen, golgin subfamily a, 1 | |
| NM_015640 | PAI-RBP1 | 24.27 | PAI-1 mrna-binding protein | |
| NM_005418 | ST5 | 24.19 | Suppression of tumorigenicity 5 | |
| NM_005968 | HNRPM | 23.87 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein M | |
| NM_001968 | EIF4E | 23.69 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E | Regulation of protein biosynthesis; regulation of translation; translational initiation |
| NM_001496 | GFRA3 | 23.51 | GDNF family receptor alpha 3 | Peripheral nervous system development; signal transduction |
| NM_001679 | ATP1B3 | 23.42 | Atpase, Na+/K+ transporting, beta 3 polypeptide | Potassium ion transport; sodium ion transport |
| NM_000041 | APOE | 23.30 | Apolipoprotein E | Cholesterol homeostasis; circulation; cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; induction of apoptosis; intracellular transport; learning and/or memory; lipid transport; lipoprotein metabolism; regulation of axon extension; regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity; response to reactive oxygen species; synaptic transmission, cholinergic |
| AA933967 | SPRY3 | 23.30 | Sprouty homolog 3 (Drosophila) | |
| NM_005507 | CFL1 | 22.71 | Cofilin 1 (non-muscle) | Rho protein signal transduction; actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis |
| NM_000403 | GALE | 22.55 | Galactose-4-epimerase, UDP- | Carbohydrate metabolism; galactose metabolism; nucleotide-sugar metabolism |
| NM_020162 | DDX33 | 22.48 | DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 33 | |
| NM_006170 | NOL1 | 22.35 | HOM-TES-103 tumor antigen-like | Positive regulation of cell proliferation; regulation of cell cycle |
| NM_004570 | PIK3C2G | 22.18 | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase, class 2, gamma polypeptide |
Intracellular signaling cascade |
| NM_018223 | CHFR | 21.83 | Checkpoint with forkhead and ring finger domains | |
| AK057343 | ZNF131 | 21.32 | Zinc finger protein 131 (clone phz-10) | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_001469 | G22P1 | 21.30 | Thyroid autoantigen 70 kDa (Ku antigen) | DNA ligation; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end-joining |
| NM_016372 | TPRA40 | 20.85 | Seven transmembrane domain orphan receptor | Aging; lipid metabolism |
| NM_006098 | GNB2L1 | 20.34 | Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2-like 1 |
Protein kinase C activation; signal transduction |
| NM_005216 | DDOST | 20.27 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide- protein glycosyltransferase |
N-linked glycosylation via asparagine |
| AB002376 | KIAA0378 | 19.92 | CAZ-associated structural protein | |
| NM_006821 | ZAP128 | 19.79 | Peroxisomal long-chain acyl-coa thioesterase | Acyl-coa metabolism; lipid metabolism |
| NM_000874 | IFNAR2 | 19.42 | Interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 2 | JAK-STAT cascade; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; response to virus |
| AB011173 | KIAA0601 | 19.08 | Amine oxidase (flavin containing) domain 2 | Electron transport |
| NM_002087 | GRN | 18.86 | Granulin | Cell proliferation; cell-cell signaling; positive regulation of cell proliferation; signal transduction |
| NM_006088 | TUBB2 | 18.38 | Tubulin, beta, 2 | Microtubule polymerization; microtubule-based movement |
| NM_016180 | MATP | 18.35 | Membrane associated transporter | Melanin biosynthesis from tyrosine; visual perception |
| NM_000447 | PSEN2 | 18.26 | Presenilin 2 (Alzheimer disease 4) | Apoptotic program; chromosome organization and biogenesis (sensu Eukarya); chromosome segregation; intracellular signaling cascade |
| NM_005083 | U2AF1RS1; U2AF1RS2 |
18.21 | Signal recognition particle 19 kDa | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_002455 | MTX1 | 18.13 | Metaxin 1 | Protein transport |
| NM_006791 | MRG15 | 17.90 | Mortality factor 4 like 1 | Chromatin assembly/disassembly; regulation of cell growth |
| NM_015966 | SDBCAG84 | 17.43 | Serologically defined breast cancer antigen 84 | |
| NM_005720 | ARPC1B | 17.41 | Actin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 1B, 41 kDa |
Cell motility |
| BC014110 | LOC132241 | 17.41 | Hypothetical protein LOC132241 | Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_004592 | SFRS8 | 17.18 | Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 8 (suppressor-of-white-apricot homolog, Drosophila) |
Mrna splice site selection; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_004279 | PMPCB | 17.02 | Peptidase (mitochondrial processing) beta | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_000143 | FH | 16.98 | Fumarate hydratase | Fumarate metabolism; negative regulation of cell cycle; tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| NM_002265 | KPNB1 | 16.97 | Karyopherin (importin) beta 1 | NLS-bearing substrate-nucleus import; intracellular protein transport; protein-nucleus import, docking; protein-nucleus import, translocation |
| NM_004147 | DRG1 | 16.90 | Developmentally regulated GTP binding protein 1 | Development; transcription |
| AJ223353 | H2BFB | 16.81 | Histone 1, h2bd | Chromosome organization and biogenesis (sensu Eukarya); nucleosome assembly |
| NM_005956 | MTHFD1 | 16.09 | Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent), methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase, formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase |
Amino acid biosynthesis; folic acid and derivative biosynthesis; histidine biosynthesis; methionine biosynthesis; one-carbon compound metabolism; purine nucleotide biosynthesis |
| AL049365 | MGC50853 | 16.03 | MRNA; cdna dkfzp586a0618 (from clone dkfzp586a0618) |
|
| AB007856 | FEM1B | 15.97 | Fem-1 homolog b (C. elegans) | Induction of apoptosis |
| NM_000701 | ATP1A1 | 15.93 | Atpase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 1 polypeptide sodium ion transport; sperm motility |
ATP hydrolysis coupled proton transport; hydrogen ion homeostasis; metabolism; potassium ion transport; |
| NM_004988 | MAGEA1 | 15.84 | Melanoma antigen, family A, 1 (directs expression of antigen MZ2-E) |
|
| BC030618 | LOC196463 | 15.75 | Hypothetical protein LOC196463 | |
| NM_004637 | RAB7 | 15.61 | RAB7, member RAS oncogene family | Endocytosis; intracellular protein transport; small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_001122 | ADFP | 15.54 | Adipose differentiation-related protein | |
| NM_014677 | RIMS2 | 15.28 | Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 2 | Intracellular protein transport |
| NM_004596 | SNRPA | 15.23 | Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide A | |
| AF204171 | POP3 | 15.13 | Popeye domain containing 3 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_016001 | LOC51096 | 14.93 | CGI-48 protein | |
| NM_022157 | GTR2 | 14.89 | Ras-related GTP binding C | RNA splicing; apoptosis; cell growth; cell growth and/or maintenance; small gtpase mediated signal transduction; transcription |
| AK057545 | PLDN | 14.87 | Pallidin homolog (mouse) | Synaptic vesicle docking |
| NM_000248 | MITF | 14.71 | Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor | Development; melanocyte differentiation; perception of sound; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_005273 | GNB2 | 14.66 | Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2 |
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; signal transduction |
| NM_032558 | FLJ14753 | 14.59 | Hypothetical protein FLJ14753 | Tetracycline transport |
| NM_012067 | AKR7A3 | 14.46 | Aldo-keto reductase family 7, member A3 (aflatoxin aldehyde reductase) |
Aldehyde metabolism |
| NM_005637 | SS18 | 14.28 | Synovial sarcoma translocation, chromosome 18 | Cell growth and/or maintenance |
| NM_016535 | HSPC189 | 14.07 | Zinc finger protein 581 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_020357 | PCNP | 14.05 | PEST-containing nuclear protein | |
| NM_005466 | MED6 | 14.01 | Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription, subunit 6 homolog (yeast) |
Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| AB037843 | KIAA1422 | 13.89 | Potassium channel, subfamily T, member 1 | Ion transport; potassium ion transport |
| NM_004159 | PSMB8 | 13.81 | Proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 8 (large multifunctional protease 7) |
Immune response; proteolysis and peptidolysis; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| X53305 | STMN1 | 13.76 | Stathmin 1/oncoprotein 18 | Cell growth and/or maintenance; intracellular signaling cascade |
| NM_003831 | SUDD | 13.72 | RIO kinase 3 (yeast) | Chromosome segregation |
| NM_002817 | PSMD13 | 13.67 | Proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-atpase, 13 |
|
| BC007195 | NCK2 | 13.64 | NCK adaptor protein 2 | T-cell activation; intracellular signaling cascade; negative regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of T-cell proliferation; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activity; signal complex formation |
| BC019236 | HLA-A | 13.47 | Major histocompatibility complex, class I, A | Antigen presentation, endogenous antigen; antigen processing, endogenous antigen via MHC class I; immune response |
| NM_024663 | NPEPL1 | 13.45 | Aminopeptidase-like 1 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_003883 | HDAC3 | 13.44 | Histone deacetylase 3 | Anti-apoptosis; chromatin modification; histone deacetylation; regulation of cell cycle; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_023016 | FLJ21870 | 13.43 | Septin 10 | |
| NM_005569 | LIMK2 | 13.21 | LIM domain kinase 2 | Protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_002574 | PRDX1 | 13.21 | Peroxiredoxin 1 | Cell proliferation; skeletal development |
| NM_002914 | RFC2 | 13.16 | Replication factor C (activator 1) 2, 40 kDa | DNA replication |
| NM_004071 | CLK1 | 13.08 | CDC-like kinase 1 | Cell proliferation; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of cell cycle |
| NM_012173 | FBXO25 | 13.01 | F-box only protein 25 | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_001975 | ENO2 | 12.84 | Enolase 2 (gamma, neuronal) | Glycolysis |
| NM_017920 | URG4 | 12.80 | Up-regulated gene 4 | |
| NM_018380 | DDX28 | 12.69 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20399 | |
| NM_013379 | DPP7 | 12.66 | Dipeptidylpeptidase 7 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_012179 | FBXO7 | 12.66 | F-box only protein 7 | Ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| NM_033133 | CNP | 12.62 | 2′,3′-Cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase | Cyclic nucleotide catabolism; synaptic transmission |
| NM_014575 | SCHIP1 | 12.58 | Schwannomin interacting protein 1 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_012079 | DGAT1 | 12.54 | Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase homolog 1 (mouse) |
Fat body development; triacylglycerol metabolism |
| NM_006397 | RNASEHI | 12.47 | Jun B proto-oncogene | DNA replication; RNA catabolism |
| BC002971 | CCT5 | 12.44 | Chaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 5 (epsilon) | Protein folding |
| NM_000018 | ACADVL | 12.43 | Acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, very long chain | Electron transport; energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds; fatty acid beta-oxidation; fatty acid metabolism |
| NM_002266 | KPNA2 | 12.41 | Karyopherin alpha 2 (RAG cohort 1, importin alpha 1) |
DNA metabolism; G2 phase of mitotic cell cycle; M phase specific microtubule process; NLS-bearing substrate-nucleus import; intracellular protein transport; regulation of DNA recombination |
| NM_006913 | RNF5 | 12.41 | Ring finger protein 5 | Protein ubiquitination |
| BE737594 | RBPSUH | 12.39 | Recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless (Drosophila) |
|
| NM_006367 | CAP | 12.38 | CAP, adenylate cyclase-associated protein 1 (yeast) |
Adenylate cyclase activation; establishment and/or maintenance of cell polarity; signal transduction |
| NM_012111 | C14orf3 | 12.31 | AHA1, activator of heat shock 90 kDa protein atpase homolog 1 (yeast) |
Protein folding; response to stress |
| NM_003299 | TRA1 | 12.28 | Tumor rejection antigen (gp96) 1 | Protein folding; response to stress |
| AF154121 | SLC13A3 | 12.14 | Solute carrier family 13 (sodium-dependent dicarboxylate transporter), member 3 |
Sodium ion transport |
| NM_006115 | PRAME | 12.11 | Preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma | |
| AK027480 | ZNF266; HZF1 | 12.07 | Unnamed protein product; Homo sapiens cdna FLJ14574 fis, clone NT2RM4000751, moderately similar to ZINC FINGER PROTEIN 184. |
Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_006758 | U2AF1 | 11.99 | U2(RNU2) small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 1 | RNA splicing; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_020187 | DC12 | 11.98 | DC12 protein | |
| NM_000895 | LTA4H | 11.95 | Leukotriene A4 hydrolase | Inflammatory response; leukotriene biosynthesis; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_003288 | TPD52L2 | 11.87 | Tumor protein D52-like 2 | Cell proliferation |
| NM_014501 | E2-EPF | 11.85 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2S | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_022036 | GPRC5C | 11.84 | G protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member C |
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway |
| NM_002643 | PIGF | 11.7 | Phosphatidylinositol glycan, class F (mitochondrial 3-oxoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase) |
GPI anchor biosynthesis |
| NM_006111 | ACAA2 | 11.63 | Acetyl-Coenzyme A acyltransferase 2 | Fatty acid metabolism |
| NM_018955 | UBB | 11.58 | Ubiquitin B | |
| NM_004642 | CDK2AP1 | 11.56 | CDK2-associated protein 1 | DNA-dependent DNA replication; S phase of mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of cell cycle; protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| BE967375 | RANBP9 | 11.51 | RAN binding protein 9 | |
| NM_012103 | AUP1 | 11.48 | Ancient ubiquitous protein 1 | Metabolism |
| U86453 | PIK3CD | 11.39 | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide |
Protein amino acid phosphorylation; signal transduction |
| AK025586 | SPATA13 | 11.31 | Spermatogenesis associated 13 | |
| NM_015908 | ARS2 | 11.25 | Arsenate resistance protein ARS2 | Response to arsenic |
| NM_021178 | HEI10 | 11.25 | Cyclin B1 interacting protein 1 | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_016615 | SLC6A13 | 11.23 | Solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, GABA), member 13 |
Neurotransmitter transport |
| M94345 | CAPG | 11.17 | Capping protein (actin filament), gelsolin-like | Protein complex assembly; response to pest/pathogen/parasite |
| NM_017710 | FLJ20203 | 11.17 | Synonyms: FLJ12923, FLJ23040, KIAA1606, dkfzp761i241; Homo sapiens hypothetical protein FLJ20203 (FLJ20203), mrna. |
|
| NM_052861 | MGC21675 | 11.05 | Hypothetical protein MGC21675 | |
| S68616 | SLC9A1 | 11.03 | Solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), isoform 1 (antiporter, Na+/H+, amiloride sensitive) |
Regulation of ph; sodium ion transport |
| NM_018845 | LOC55974 | 11.03 | Stromal cell protein | |
| AL117440 | PDPR | 11.01 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase regulatory subunit | Electron transport |
| BM467642 | SNTB2 | 10.91 | Syntrophin, beta 2 (dystrophin-associated protein A1, 59 kDa, basic component 2) |
|
| NM_003968 | UBE1C | 10.90 | Ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1C (UBA3 homolog, yeast) |
Proteolysis and peptidolysis; ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_003916 | AP1S2 | 10.88 | Adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 2 subunit | Endocytosis; intracellular protein transport |
| NM_001799 | CDK7 | 10.88 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (MO15 homolog, Xenopus laevis, cdk-activating kinase) |
DNA repair; cytokinesis; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of cyclin dependent protein kinase activity; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription initiation from Pol II promoter |
| NM_005596 | NFIB | 10.85 | Nuclear factor I/B | DNA replication; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| AL834255 | DKFZp586M1819 | 10.84 | Putative lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase | Metabolism |
| NM_018482 | DDEF1 | 10.77 | Synonyms: PAP, PAG2, ASAP1, ZG14P, KIAA1249; Homo sapiens development and differentiation enhancing factor 1 (DDEF1), mrna. |
Regulation of gtpase activity |
| NM_030577 | MGC10993 | 10.71 | Hypothetical protein MGC10993 | |
| NM_022095 | ZNF335 | 10.69 | Zinc finger protein 335 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_006410 | HTATIP2 | 10.66 | HIV-1 Tat interactive protein 2, 30 kDa | Anti-apoptosis; induction of apoptosis; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_015332 | KIAA1068 | 10.63 | KIAA1068 protein | |
| NM_080820 | HARS2 | 10.48 | Histidyl-trna synthetase 2 | D-amino acid catabolism |
| M23161 | MCFD2; F5F8D; SDNSF; LMAN1IP |
10.48 | Human transposon-like element mrna. | Protein transport |
| NM_015510 | DKFZp566O084 | 10.47 | DKFZP566O084 protein | Metabolism |
| NM_014186 | HSPC166 | 10.46 | COMM domain containing 9 | |
| NM_001515 | GTF2H2 | 10.46 | General transcription factor IIH, polypeptide 2, 44 kDa |
DNA repair; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_003021 | SGT | 10.44 | Small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-containing, alpha |
Biological_process unknown |
| L48722 | PTP4A2 | 10.40 | Homo sapiens (clone hh18) protein tyrosine phosphatase (ptp-IV1r) gene, 5′ end of cds. |
Protein amino acid dephosphorylation |
| NM_013393 | FTSJ2 | 10.38 | Ftsj homolog 2 (E. Coli) | Rrna processing |
| NM_006191 | PA2G4 | 10.33 | Proliferation-associated 2G4, 38 kDa | Cell cycle arrest; cell proliferation; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_016628 | WAC | 10.29 | WW domain containing adaptor with coiled-coil | |
| NM_007269 | STXBP3 | 10.26 | Syntaxin binding protein 3 | Intracellular protein transport; protein secretion |
| NM_018091 | ELP3 | 10.24 | Elongation protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | ATP synthesis coupled proton transport |
| NM_018182 | FLJ10700 | 10.22 | Hypothetical protein FLJ10700 | |
| NM_032689 | MGC13071 | 10.22 | Hypothetical protein MGC13071 | DNA metabolism; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_003759 | SLC4A4 | 10.20 | Solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 4 |
Anion transport |
| NM_032025 | CDA02 | 10.14 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eif) 2A | Regulation of protein biosynthesis; ribosome assembly |
| NM_052935 | MGC20781 | 10.14 | Hypothetical protein MGC20781 | |
| BC014130 | FBXW5 | 10.12 | F-box and WD-40 domain protein 5 | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_022039 | SHFM3 | 10.11 | Split hand/foot malformation (ectrodactyly) type 3 | Wnt receptor signaling pathway; development; embryonic limb morphogenesis; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| NM_024868 | FLJ14124 | 10.10 | Hypothetical protein FLJ14124 | |
| NM_024033 | MGC5242 | 10.09 | Hypothetical protein MGC5242 | |
| NM_001640 | APEH | 10.06 | N-acylaminoacyl-peptide hydrolase | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_000528 | MAN2B1 | 10.05 | Mannosidase, alpha, class 2B, member 1 | Carbohydrate metabolism; protein deglycosylation; protein modification |
| M93718 | NOS3 | 10.01 | Nitric oxide synthase 3 (endothelial cell) | Amino acid metabolism; cell motility; electron transport; nitric oxide biosynthesis |
| NM_016930 | STX18 | 9.98 | Syntaxin 18 | ER to Golgi transport; intracellular protein transport; vesicle docking during the process of exocytosis |
| NM_014311 | SMUG1 | 9.96 | Single-strand selective monofunctional uracil DNA glycosylase |
DNA repair |
| NM_003187 | TAF9 | 9.94 | TAF9 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 32 kDa |
Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription from Pol II promoter; transcription initiation |
| BC004170 | POLE3 | 9.92 | Polymerase (DNA directed), epsilon 3 (p17 subunit) |
DNA replication |
| NM_014323 | ZNF278 | 9.89 | Zinc finger protein 278 | Cell growth and/or maintenance; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_003678 | PK1.3 | 9.88 | Synonyms: Fmip, PK1.3; gene from NF2/ meningioma region of 22q12; placental protein 39.2; go_function: tumor suppressor [goid 0008181] [evidence TAS] [pmid 8242058]; Homo sapiens chromosome 22 open reading frame 19 (c22orf19), mrna. |
|
| NM_013232 | PDCD6 | 9.85 | Programmed cell death 6 | Apoptosis; induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals |
| NM_003782 | B3GALT4 | 9.79 | UDP-Gal:betaglcnac beta 1,3- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 4 |
Protein amino acid glycosylation |
| NM_014920 | KIAA0936 | 9.72 | Intestinal cell (MAK-like) kinase | Protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_018106 | FLJ10479 | 9.71 | Zinc finger, DHHC domain containing 4 | |
| NM_003849 | SUCLG1 | 9.70 | Succinate-coa ligase, GDP-forming, alpha subunit | Glycolysis; metabolism; tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| NM_032907 | MGC14421 | 9.69 | Bone marrow stromal cell-derived ubiquitin-like | Protein modification |
| NM_005726 | TSFM | 9.66 | Ts translation elongation factor, mitochondrial | Protein biosynthesis; translational elongation |
| NM_014046 | MRPS18B | 9.63 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S18B | Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_003364 | UP | 9.61 | Uridine phosphorylase 1 | Nucleoside metabolism |
| NM_003017 | SFRS3 | 9.49 | Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 3 | Nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_006570 | RAGA | 9.47 | Ras-related GTP binding A | Cell death; cell growth and/or maintenance; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction |
| NM_006339 | HMG20B | 9.36 | High-mobility group 20B | Establishment and/or maintenance of chromatin architecture; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| AB058716 | KIAA1813 | 9.36 | Start codon is not identified.; Homo sapiens mrna for KIAA1813 protein, partial cds. |
Superoxide metabolism |
| NM_020199 | HTGN29 | 9.35 | HTGN29 protein | |
| AK021789 | LOC146174 | 9.33 | Hypothetical protein LOC146174 | |
| NM_007008 | RTN4 | 9.32 | Reticulon 4 | Negative regulation of anti-apoptosis; negative regulation of axon extension; regulation of apoptosis |
| NM_001205 | BNIP1 | 9.27 | BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa interacting protein 1 | Anti-apoptosis |
| NM_005057 | RBBP5 | 9.22 | Retinoblastoma binding protein 5 | |
| BF698884 | DC2 | 9.21 | DC2 protein | |
| NM_004728 | DDX21 | 9.20 | DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 21 | |
| NM_014341 | MTCH1 | 9.20 | Mitochondrial carrier homolog 1 (C. elegans) | Caspase activation; ion channel clustering; positive regulation of apoptosis; regulation of signal transduction; transport |
| NM_006325 | RAN | 9.20 | RAN, member RAS oncogene family | DNA metabolism; RNA-nucleus export; intracellular protein transport; mitotic spindle assembly; protein-nucleus export; regulation of cell cycle; signal transduction; small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_018107 | FLJ10482 | 9.18 | RNA-binding region (RNP1, RRM) containing 4 | Mrna processing |
| BC012795 | CAMK2G | 9.15 | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (cam kinase) II gamma |
Insulin secretion; protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_001424 | EMP2 | 9.15 | Epithelial membrane protein 2 | Cell death; cell proliferation; development |
| BQ889085 | KIAA1164 | 9.15 | Hypothetical protein KIAA1164 | |
| NM_006917 | RXRG | 9.10 | Retinoid X receptor, gamma | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_005167 | ARHC | 9.04 | Ras homolog gene family, member C | |
| NM_002694 | POLR2C | 8.98 | Polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide C, 33 kDa |
Transcription; transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_017582 | HSA243666 | 8.95 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2Q (putative) | Ubiquitin cycle |
| NM_005141 | FGB | 8.93 | Fibrinogen, B beta polypeptide | Blood coagulation; positive regulation of cell proliferation; regulation of blood pressure |
| NM_001631 | ALPI | 8.91 | Alkaline phosphatase, intestinal | Metabolism; phosphorylation |
| NM_014371 | NAKAP95 | 8.87 | A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 8-like | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_032280 | DKFZp761J139 | 8.86 | Zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 9 | |
| NM_004128 | GTF2F2 | 8.81 | General transcription factor IIF, polypeptide 2, 30 kDa |
RNA elongation from Pol II promoter; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription initiation from Pol II promoter |
| NM_017542 | KIAA1513 | 8.79 | Pogo transposable element with KRAB domain | Anti-apoptosis |
| NM_004725 | BUB3 | 8.75 | BUB3 budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 3 homolog (yeast) |
Cell proliferation; mitosis; mitotic spindle checkpoint |
| NM_006868 | RAB31 | 8.75 | RAB31, member RAS oncogene family | Small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_025267 | MGC2744 | 8.73 | Hypothetical protein MGC2744 | Alanyl-trna aminoacylation |
| AL137398 | DKFZp434P162 | 8.73 | Similar to hypothetical protein (LOC388094), mrna | |
| AB033041 | VANGL2 | 8.73 | Vang-like 2 (van gogh, Drosophila) | |
| NM_006357 | UBE2E3 | 8.72 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2E 3 (UBC4/5 homolog, yeast) |
Ubiquitin cycle |
| AK056862 | MPHOSPH10 | 8.70 | M-phase phosphoprotein 10 (U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein) |
Rrna processing |
| NM_018235 | FLJ10830 | 8.67 | Cytosolic nonspecific dipeptidase (EC 3.4.13.18) | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_006925 | SFRS5 | 8.64 | Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 5 | Mrna splice site selection; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| AJ224162 | LIAS | 8.63 | Lipoic acid synthetase | Lipoate biosynthesis |
| NM_001069 | TUBB | 8.62 | Tubulin, beta polypeptide | |
| NM_013989 | DIO2 | 8.61 | Deiodinase, iodothyronine, type II | Thyroid hormone generation |
| NM_152417 | FLJ32370 | 8.60 | Hypothetical protein FLJ32370 | Metabolism |
| NM_016943 | TAS2R3 | 8.59 | Taste receptor, type 2, member 3 | G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; perception of taste; signal transduction |
| NM_014335 | CRI1 | 8.55 | CREBBP/EP300 inhibitory protein 1 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_018842 | LOC55971 | 8.55 | Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate | |
| NM_021826 | FLJ13149 | 8.48 | Homo sapiens hypothetical protein FLJ13149 (FLJ13149), mrna. |
Apoptosis |
| AL832304 | SLC9A9 | 8.48 | Solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), isoform 9 |
Regulation of ph; sodium ion transport |
| NM_002027 | FNTA | 8.47 | Farnesyltransferase, CAAX box, alpha | Protein amino acid farnesylation; protein amino acid geranylgeranylation; protein amino acid prenylation; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway |
| NM_005102 | FEZ2 | 8.46 | Fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 2 (zygin II) |
Axon guidance; hemopoiesis; neurogenesis; signal transduction |
| NM_030798 | WBSCR16 | 8.46 | Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosome region 16 |
Biological_process unknown |
| NM_003213 | TEAD4 | 8.44 | TEA domain family member 4 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_002431 | MNAT1 | 8.40 | Menage a trois 1 (CAK assembly factor) | DNA repair; cell cycle; protein complex assembly; regulation of cyclin dependent protein kinase activity; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_002015 | FOXO1A | 8.38 | Forkhead box O1A (rhabdomyosarcoma) | Anti-apoptosis; cell growth and/or maintenance; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_002221 | ITPKB | 8.37 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase B | Signal transduction |
| NM_017832 | FLJ20457 | 8.35 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20457 | |
| NM_002808 | PSMD2 | 8.30 | Proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-atpase, 2 |
Regulation of cell cycle |
| AB002313 | PLXNB2 | 8.26 | Plexin B2 | Development |
| NM_004462 | FDFT1 | 8.23 | Farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1 | Biosynthesis; cholesterol biosynthesis; isoprenoid biosynthesis; steroid biosynthesis |
| NM_002109 | HARS | 8.23 | Histidyl-trna synthetase | Histidyl-trna aminoacylation; protein biosynthesis |
| NM_024330 | SLC27A3 | 8.22 | Solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 3 |
Metabolism |
| NM_020350 | AGTRAP | 8.15 | Angiotensin II receptor-associated protein | |
| NM_001288 | CLIC1 | 8.15 | Chloride intracellular channel 1 | Chloride transport; ion transport |
| N28741 | HIPK2 | 8.15 | Homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 | |
| NM_004044 | ATIC | 8.09 | 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase |
Nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolism; purine nucleotide biosynthesis |
| AF052148 | G22P1 | 8.09 | Thyroid autoantigen 70 kDa (Ku antigen) | |
| AL050205 | LOC113251 | 8.08 | C-Mpl binding protein | |
| AF250920 | FOXP1 | 8.08 | Forkhead box P1 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| BC001855 | WASF2 | 8.08 | WAS protein family, member 2 | |
| NM_003311 | TSSC3 | 8.07 | Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 2 | Apoptosis; imprinting |
| AV650362 | SFRS6 | 8.01 | Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 6 | |
| NM_018492 | TOPK | 8.00 | T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase | Protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| X80199 | MLN51 | 7.98 | Cancer susceptibility candidate 3 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_007031 | HSF2BP | 7.94 | Heat shock transcription factor 2 binding protein | Spermatogenesis; transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_002254 | KIF3C | 7.88 | Kinesin family member 3C | Microtubule-based movement |
| NM_002481 | PPP1R12B | 7.88 | Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 12B |
Regulation of muscle contraction; signal transduction |
| NM_004701 | CCNB2 | 7.83 | Cyclin B2 | Cytokinesis; mitosis; regulation of cell cycle |
| NM_001722 | BN51T | 7.79 | Polymerase (RNA) III (DNA directed) polypeptide D, 44 kDa |
Regulation of cell cycle; trna metabolism; transcription |
| NM_004356 | CD81 | 7.78 | CD81 antigen (target of antiproliferative antibody 1) |
Activation of MAPK; phosphatidylinositol biosynthesis; phosphoinositide metabolism; positive regulation of 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity; positive regulation of B-cell proliferation; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; protein localization; viral entry into host cell; virion attachment, binding of host cell surface receptor |
| NM_018983 | NOLA1 | 7.77 | Nucleolar protein family A, member 1 (H/ACA small nucleolar rnps) |
Rrna processing |
| NM_003091 | SNRPB | 7.74 | Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptides B and B1 |
RNA splicing; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_022831 | FLJ12806 | 7.72 | Hypothetical protein FLJ12806 | |
| NM_005701 | RNUT1 | 7.72 | RNA, U transporter 1 | |
| NM_138443 | LOC115106 | 7.7 | Coiled-coil domain containing 5 (spindle associated) | Cell cycle; cytokinesis; mitosis |
| AL157442 | GRINA | 7.69 | Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D- asparate-associated protein 1 (glutamate binding) |
|
| NM_004269 | CRSP8 | 7.68 | Cofactor required for Sp1 transcriptional activation, subunit 8, 34 kDa |
Regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter; transcription initiation from Pol II promoter |
| NM_002149 | HPCAL1 | 7.67 | Hippocalcin-like 1 | Vesicle-mediated transport |
| NM_016033 | CGI-90 | 7.64 | CGI-90 protein | |
| NM_001398 | ECH1 | 7.64 | Enoyl Coenzyme A hydratase 1, peroxisomal | Energy pathways; fatty acid beta-oxidation; fatty acid metabolism |
| NM_001513 | GSTZ1 | 7.64 | Glutathione transferase zeta 1 (maleylacetoacetate isomerase) |
Aromatic amino acid family metabolism; phenylalanine catabolism; tyrosine catabolism |
| NM_024662 | FLJ10774 | 7.64 | N-acetyltransferase-like protein | Biological_process unknown |
| BC015882 | EZH1;HGS | 7.62 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 1 (Drosophila) | Morphogenesis; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_024619 | FLJ12171 | 7.58 | Fructosamine-3-kinase-related protein | |
| NM_002911 | RENT1 | 7.57 | Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 | Mrna catabolism, nonsense-mediated; regulation of translational termination |
| AJ005866 | SQV7L | 7.55 | Solute carrier family 35, member D2 | Biological_process unknown |
| AL834255 | DKFZp586M1819 | 7.53 | Putative lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase | Metabolism |
| NM_016491 | MRPL37 | 7.50 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L37 | Electron transport; response to oxidative stress |
| NM_000070 | CAPN3 | 7.49 | Calpain 3, (p94) | Muscle development; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_003642 | HAT1 | 7.48 | Histone acetyltransferase 1 | DNA packaging; internal protein amino acid acetylation |
| NM_006561 | CUGBP2 | 7.47 | CUG triplet repeat, RNA binding protein 2 | RNA processing; neuromuscular junction development; regulation of heart rate |
| NM_020117 | FLJ10595 | 7.44 | Leucyl-trna synthetase | Protein biosynthesis; trna aminoacylation for protein translation |
| NM_006590 | SAD1 | 7.43 | Ubiquitin specific protease 39 | RNA splicing; mrna processing; spliceosome assembly; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| NM_006349 | CG1I | 7.40 | Zinc finger, HIT domain containing 1 | |
| NM_014251 | SLC25A13 | 7.39 | Solute carrier family 25, member 13 (citrin) | Transport |
| NM_018706 | KIAA1630 | 7.36 | Dehydrogenase E1 and transketolase domain containing 1 |
Metabolism |
| NM_032361 | MGC5469 | 7.34 | THO complex 3 | Mrna-nucleus export; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome; transport |
| BC003353 | MGC5309 | 7.33 | Hypothetical protein MGC5309 | |
| NM_057158 | DUSP4 | 7.30 | Dual specificity phosphatase 4 | MAPKKK cascade; protein amino acid dephosphorylation; regulation of cell cycle |
| NM_006451 | PAIP1 | 7.29 | Poly(A) binding protein interacting protein 1 | Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_030813 | SKD3 | 7.29 | Suppressor of potassium transport defect 3 | |
| NM_001098 | ACO2 | 7.27 | Aconitase 2, mitochondrial | Citrate metabolism; energy pathways; tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| NM_032527 | KIAA1847 | 7.26 | Kiaa1847 | |
| M96739 | NHLH1 | 7.20 | Nescient helix loop helix 1 | Cell differentiation; central nervous system development; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_013374 | PDCD6IP | 7.19 | Programmed cell death 6 interacting protein | Apoptosis; signal transduction |
| NM_005572 | LMNA | 7.18 | Lamin A/C | Muscle development |
| NM_016447 | LOC51678 | 7.16 | Membrane protein, palmitoylated 6 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 6) |
Protein complex assembly |
| NM_004132 | HABP2 | 7.15 | Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | Cell adhesion; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_002814 | PSMD10 | 7.14 | Proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-atpase, 10 |
|
| NM_014629 | ARHGEF10 | 7.14 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 10 | |
| NM_003707 | RUVBL1 | 7.14 | Ruvb-like 1 (E. Coli) | DNA recombination; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter; spermatogenesis |
| NM_014551 | 384D8-2 | 7.13 | Hypothetical protein 384D8_6 | |
| AL365410 | LOC56930 | 7.12 | Clone IMAGE:4441633, mrna | |
| NM_024863 | FLJ21174 | 7.08 | Hypothetical protein FLJ21174 | |
| NM_001358 | DDX15 | 7.07 | DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 15 | Nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_138615 | DDX30 | 7.04 | DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 30 | |
| BG497672 | CD44 | 7.03 | CD44 antigen (homing function and Indian blood group system) | |
| AB020626 | KIAA0819 | 6.98 | KIAA0819 protein | |
| BE818483 | ATP1B3 | 6.96 | Atpase, Na+/K+ transporting, beta 3 polypeptide | |
| NM_032122 | DTNBP1 | 6.95 | Dystrobrevin binding protein 1 | Visual perception |
| BC021565 | SNX8 | 6.94 | Sorting nexin 8 | Intracellular protein transport; intracellular signaling cascade |
| NM_025199 | FLJ20886 | 6.94 | Synonyms: ASH, Grb3-3, EGFRBP-GRB2; isoform 1 is encoded by transcript variant 1; HT027; growth factor receptor-bound protein 3; epidermal growth factor receptor-binding protein GRB2; abundant SRC homology; go_function: SH3/SH2 adaptor protein activity [goid 0005070] [evidence TAS] [pmid 8253073]; go_process: epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [goid 0007173] [evidence TAS] [pmid 1322798]; go_process: RAS protein signal transduction [goid 0007265] [evidence TAS] [pmid 8253073]; go_process: cell shape and cell size control [goid 0007148] [evidence E]; go_process: cell-cell signaling [goid 0007267] [evidence TAS] [pmid 8253073]; go_process: intracellular signaling cascade [goid 0007242] [evidence IEA]; Homo sapiens growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2), transcript variant 1, mrna. |
|
| NM_021639 | SP192 | 6.92 | Hypothetical protein SP192 | |
| NM_001333 | CTSL2 | 6.87 | Cathepsin L2 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| D29641 | KIAA0052 | 6.86 | KIAA0052 protein | |
| AK094458 | WBP2 | 6.86 | Unnamed protein product; Homo sapiens cdna FLJ37139 fis, clone BRACE2023727, weakly similar to Human WW domain binding protein-2 mrna. |
|
| NM_014468 | VENTX2 | 6.86 | VENT-like homeobox 2 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_001769 | CD9 | 6.84 | CD9 antigen (p24) | Cell adhesion; cell motility; fusion of sperm to egg plasma membrane; paranodal junction formation; platelet activation |
| NM_002980 | SCTR | 6.83 | Secretin receptor | G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; digestion; excretion |
| NM_014907 | KIAA0967 | 6.79 | FERM and PDZ domain containing 1 | |
| NM_030673 | SEC13L1 | 6.79 | SEC13-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) | Intracellular protein transport |
| NM_007126 | VCP | 6.78 | Valosin-containing protein | Transport |
| NM_017957 | FLJ20778 | 6.77 | Epsin 3 | |
| NM_004741 | NOLC1 | 6.77 | Nucleolar and coiled-body phosphoprotein 1 | Cell cycle; mitosis; rrna processing |
| NM_012321 | LSM4 | 6.75 | LSM4 homolog, U6 small nuclear RNA associated (S. cerevisiae) |
RNA splicing; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_015638 | C20orf188 | 6.74 | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 4 associated protein |
Antigen presentation, endogenous peptide antigen; antigen processing, endogenous antigen via MHC class I; cytosol to ER transport; intracellular protein transport; peptide transport; protein complex assembly |
| NM_024960 | PANK2 | 6.73 | Pantothenate kinase 2 (Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome) |
Coenzyme A biosynthesis |
| NM_000392 | ABCC2 | 6.72 | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 2 |
Transport |
| NM_005918 | MDH2 | 6.72 | Malate dehydrogenase 2, NAD (mitochondrial) | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| NM_003795 | SNX3 | 6.71 | Sorting nexin 3 | Endocytosis; intracellular protein transport; intracellular signaling cascade |
| AK025687 | JRK | 6.70 | Jerky homolog (mouse) | Biological_process unknown |
| AK056268 | SHD | 6.69 | Src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein D |
Intracellular signaling cascade |
| NM_022839 | MRPS11 | 6.64 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S11 | Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_004896 | VPS26 | 6.62 | Vacuolar protein sorting 26 (yeast) | Intracellular protein transport; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi |
| NM_017907 | FLJ20625 | 6.57 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20625 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_023080 | FLJ20989 | 6.57 | Hypothetical protein FLJ20989 | |
| NM_032038 | LOC83985 | 6.57 | Spinster-like | Transport |
| NM_003754 | EIF3S5 | 6.55 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit 5 epsilon, 47 kDa |
Protein biosynthesis; regulation of translational initiation |
| AB002360 | MCF2L | 6.54 | MCF.2 cell line derived transforming sequence-like |
Cell growth and/or maintenance; intracellular signaling cascade |
| AB033001 | FLJ10209 | 6.54 | Phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 1 | |
| AK093442 | ZNF596 | 6.54 | Zinc finger protein 596 | |
| NM_005444 | RQCD1 | 6.53 | RCD1 required for cell differentiation1 homolog (S. Pombe) |
Sex differentiation |
| NM_015994 | ATP6M | 6.49 | Atpase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 34 kDa, V1 subunit D |
ATP synthesis coupled proton transport |
| BF984906 | LOC199800 | 6.44 | Hypothetical protein LOC199800 | |
| NM_001102 | ACTN1 | 6.43 | Actinin, alpha 1 | |
| NM_005032 | PLS3 | 6.42 | Plastin 3 (T isoform) | |
| NM_017934 | PHIP | 6.42 | Pleckstrin homology domain interacting protein | Insulin receptor signaling pathway |
| U40271 | PTK7 | 6.42 | PTK7 protein tyrosine kinase 7 | Cell adhesion; protein amino acid phosphorylation; signal transduction |
| NM_007103 | NDUFV1 | 6.40 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 1, 51 kDa |
Energy pathways; mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone |
| NM_004716 | PCSK7 | 6.40 | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 7 | Peptide hormone processing; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_000116 | TAZ | 6.39 | Tafazzin (cardiomyopathy, dilated 3A (X-linked); endocardial fibroelastosis 2; Barth syndrome) |
Heart development; metabolism; muscle contraction; muscle development |
| NM_000137 | FAH | 6.38 | Fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (fumarylacetoacetase) |
Aromatic amino acid family metabolism; phenylalanine catabolism; tyrosine catabolism |
| NM_001611 | ACP5 | 6.36 | Acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant | |
| NM_001130 | AES | 6.36 | Amino-terminal enhancer of split | Wnt receptor signaling pathway; development; organogenesis; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_020410 | CGI-152 | 6.35 | Atpase type 13A | Cation transport; metabolism |
| NM_006838 | METAP2 | 6.35 | Methionyl aminopeptidase 2 | Protein modification; proteolysis and peptidolysis; regulation of translation |
| NM_014254 | TMEM5 | 6.32 | Transmembrane protein 5 | |
| NM_024960 | PANK2 | 6.30 | Pantothenate kinase 2 (Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome) |
Coenzyme A biosynthesis |
| NM_016016 | CGI-69 | 6.29 | CGI-69 protein | Transport |
| NM_001662 | ARF5 | 6.28 | ADP-ribosylation factor 5 | Intracellular protein transport; small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_080476 | CDC91L1 | 6.27 | CDC91 cell division cycle 91-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) | GPI anchor biosynthesis |
| NM_002887 | RARS | 6.26 | Arginyl-trna synthetase | Arginyl-trna aminoacylation; protein biosynthesis |
| NM_002414 | MIC2 | 6.26 | CD99 antigen | Cell adhesion |
| AF183421 | RAB31 | 6.26 | RAB31, member RAS oncogene family | Small gtpase mediated signal transduction |
| NM_002571 | PAEP | 6.24 | Progestagen-associated endometrial protein (placental protein 14, pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, alpha uterine protein) |
Development; transport |
| NM_003574 | VAPA | 6.22 | VAMP (vesicle-associated membrane protein)- associated protein A, 33 kDa |
Positive regulation of I-kappab kinase/NF-kappab cascade |
| NM_006523 | XPNPEPL | 6.20 | Synonyms: SAMP, XPNPEP, XPNPEPL; X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P)-like; go_function: aminopeptidase activity [goid 0004177] [evidence P]; Homo sapiens X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 1, soluble (XPNPEP1), mrna. |
|
| NM_018263 | FLJ10898 | 6.17 | Additional sex combs like 2 (Drosophila) | |
| Z70703 | LOC166994 | 6.17 | Similar to ba110h4.2 (similar to membrane protein) (LOC389281), mrna |
|
| NM_003077 | SMARCD2 | 6.16 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily d, member 2 |
Chromatin remodeling; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_003977 | AIP | 6.15 | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein | Protein folding |
| AK027249 | CAPN3 | 6.15 | Calpain 3, (p94) | Muscle development; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| AB018297 | KIAA0754 | 6.15 | KIAA0754 protein | |
| AK000300 | ATP2A2 | 6.14 | Atpase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 |
|
| NM_004229 | CRSP2 | 6.14 | Cofactor required for Sp1 transcriptional activation, subunit 2, 150 kDa |
Androgen receptor signaling pathway; regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter; transcription initiation from Pol II promoter |
| AB051469 | 3-PAP | 6.14 | Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate associated protein |
Phospholipid dephosphorylation |
| NM_020533 | MCOLN1 | 6.12 | Mucolipin 1 | Cation transport |
| NM_005865 | PRSS16 | 6.12 | Protease, serine, 16 (thymus) | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_004461 | FARSL | 6.11 | Phenylalanine-trna synthetase-like, alpha subunit | Phenylalanyl-trna aminoacylation; protein biosynthesis |
| NM_021198 | NLI-IF | 6.10 | CTD (carboxy-terminal domain, RNA polymerase II, polypeptide A) small phosphatase 1 |
Biological_process unknown |
| AL833978 | HP1-BP74 | 6.10 | Hp1-bp74 | Nucleosome assembly |
| BC000050 | ART-4 | 6.10 | Likely ortholog of mouse nin one binding protein | |
| NM_000126 | ETFA | 6.09 | Electron-transfer-flavoprotein, alpha polypeptide (glutaric aciduria II) |
Electron transport |
| NM_003295 | TPT1 | 6.08 | Tumor protein, translationally-controlled 1 | |
| NM_002319 | LRRN1 | 6.06 | Leucine rich repeat neuronal 4 | Neurogenesis |
| NM_014932 | NLGN1 | 6.02 | Neuroligin 1 | Calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion; ion channel clustering; protein targeting; regulation of neuron differentiation; synaptic vesicle targeting; synaptogenesis |
| NM_013241 | FHOD1 | 6.01 | Formin homology 2 domain containing 1 | Cell organization and biogenesis |
| NM_007032 | HRIHFB2122 | 6.01 | Tara-like protein | Actin modification |
| NM_001765 | CD1C | 6.00 | CD1C antigen, c polypeptide | Antimicrobial humoral response (sensu Vertebrata) |
| AB051535 | DKFZP586K0524 | 6.00 | Zinc finger, DHHC domain containing 5 | |
| AA316117 | MACF1 | 5.98 | Microtubule-actin crosslinking factor 1 | |
| NM_014275 | MGAT4B | 5.97 | Mannosyl (alpha-1,3-)-glycoprotein beta-1,4- N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, isoenzyme B |
Carbohydrate metabolism |
| NM_004549 | NDUFC2 | 5.97 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1, subcomplex unknown, 2, 14.5 kDa |
Mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone |
| NM_021141 | XRCC5 | 5.97 | X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 5 (double-strand-break rejoining; Ku autoantigen, 80 kDa) |
DNA recombination; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end-joining; regulation of DNA repair |
| NM_138777 | LOC92399 | 5.96 | Mitochondrial ribosome recycling factor | Protein biosynthesis |
| AB007960 | SH3GLB1 | 5.95 | SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B1 | Apoptosis |
| NM_016059 | PPIL1 | 5.93 | Peptidylprolyl isomerase (cyclophilin)-like 1 | Protein folding |
| NM_002768 | PCOLN3 | 5.93 | Procollagen (type III) N-endopeptidase | Gene silencing; mitotic chromosome condensation; negative regulation of S phase of mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of transcription by glucose; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; vesicle-mediated transport |
| NM_000930 | PLAT | 5.92 | Plasminogen activator, tissue | Blood coagulation; protein modification; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_003002 | SDHD | 5.89 | Succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit D, integral membrane protein |
Electron transport; tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| NM_000581 | GPX1 | 5.86 | Glutathione peroxidase 1 | Response to oxidative stress |
| AK075559 | MGC20446; | 5.86 | Hypothetical protein MGC20446 | Electron transport |
| NM_016553 | NUP62 | 5.86 | Nucleoporin 62 kDa | Transport |
| AK023373 | GTR2; | 5.84 | Ras-related GTP binding C | RNA splicing; apoptosis; cell growth; cell growth and/or maintenance; small gtpase mediated signal transduction; transcription |
| NM_005626 | SFRS4 | 5.84 | Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 4 | RNA splicing; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| AJ237724 | SLC19A2 | 5.82 | Solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 |
Perception of sound; thiamin transport |
| NM_014730 | KIAA0152 | 5.81 | Go_component: integral to membrane [goid 0016021] [evidence IEA]; Homo sapiens KIAA0152 gene product (KIAA0152), mrna. |
|
| NM_006164 | NFE2L2 | 5.80 | Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_006196 | PCBP1 | 5.77 | Poly(rc) binding protein 1 | Mrna metabolism |
| NM_139178 | DEPC-1 | 5.76 | Prostate cancer antigen-1 | |
| AK026920 | MYO1D | 5.75 | Myosin ID | |
| NM_004814 | HPRP8BP | 5.75 | U5 snrnp-specific 40 kDa protein (hprp8-binding) RNA splicing; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome | |
| AK026373 | HNRPA2B1 | 5.74 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 | |
| NM_002123 | HLA-DQB1 | 5.73 | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1 |
Antigen presentation, exogenous antigen; antigen processing, exogenous antigen via MHC class II; immune response |
| AB046815 | KIAA1595; | 5.72 | DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 55 | |
| AA318395 | MRLC2 | 5.72 | Myosin regulatory light chain MRLC2 | |
| NM_003562 | SLC25A11 | 5.70 | Solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; oxoglutarate carrier), member 11 |
Transport |
| NM_003485 | GPR68 | 5.69 | G protein-coupled receptor 68 | G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; inflammatory response |
| NM_001731 | BTG1 | 5.68 | B-cell translocation gene 1, anti-proliferative | Cell proliferation; negative regulation of cell proliferation |
| NM_003145 | SSR2 | 5.67 | Signal sequence receptor, beta (translocon-associated protein beta) |
Cotranslational membrane targeting |
| NM_019100 | DMAP1 | 5.66 | DNA methyltransferase 1 associated protein 1 | DNA methylation; chromatin modification; negative regulation of transcription; regulation of cell growth; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_006811 | TDE1 | 5.66 | Tumor differentially expressed 1 | |
| AB023166 | CIT | 5.65 | Citron (rho-interacting, serine/threonine kinase 21) |
Intracellular signaling cascade; protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_003769 | SFRS9 | 5.65 | Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 9 | Mrna splice site selection; nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome |
| NM_031213 | MGC:5244 | 5.63 | Hypothetical protein MGC5244 | |
| NM_001757 | CBR1 | 5.62 | Carbonyl reductase 1 | Metabolism |
| NM_003364 | UP | 5.62 | Uridine phosphorylase 1 | Nucleoside metabolism |
| BC020243 | SSH1 | 5.58 | Slingshot 1 | |
| NM_015957 | LOC51074 | 5.57 | Likely ortholog of mouse monocyte macrophage 19 | |
| NM_016038 | CGI-97 | 5.56 | Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome | |
| NM_004904 | H_GS165L15.1 | 5.55 | Camp responsive element binding protein 5 | Positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; transcription from Pol II promoter |
| NM_023077 | FLJ12439 | 5.55 | Hypothetical protein FLJ12439 | |
| NM_014369 | PTPN18 | 5.55 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 18 (brain-derived) |
Protein amino acid dephosphorylation |
| AF212303 | GSTTLp28 | 5.54 | Glutathione S-transferase omega 1 | Metabolism |
| NM_004070 | CLCNKA | 5.52 | Chloride channel Ka | Chloride transport; excretion; ion transport |
| U47077 | PRKDC | 5.52 | Protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide |
DNA recombination; double-strand break repair; protein modification |
| NM_006809 | TOMM34 | 5.51 | Translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 34 | Protein-mitochondrial targeting |
| NM_004053 | BYSL | 5.50 | Bystin-like | Cell adhesion; pregnancy |
| NM_014370 | STK23 | 5.49 | Serine/threonine kinase 23 | Protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_004517 | ILK | 5.46 | Integrin-linked kinase | Cell-matrix adhesion; integrin-mediated signaling pathway; protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| NM_145255 | MRPL10 | 5.46 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L10 | |
| D43948 | KIAA0097 | 5.45 | KIAA0097 gene product | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_032772 | MGC2555 | 5.43 | Zinc finger protein 503 | |
| NM_003904 | ZNF259 | 5.42 | Zinc finger protein 259 | Cell proliferation; signal transduction |
| NM_030782 | CRR9 | 5.41 | Cisplatin resistance related protein CRR9p | |
| NM_001532 | SLC29A2 | 5.41 | Solute carrier family 29 (nucleoside transporters), member 2 |
Cell proliferation; nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolism; nucleoside transport |
| NM_022827 | FLJ21347 | 5.40 | Hypothetical protein FLJ21347 | Carbohydrate metabolism |
| NM_006303 | JTV1 | 5.39 | JTV1 gene | Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_017455 | SDFR1 | 5.33 | Stromal cell derived factor receptor 1 | |
| NM_018413 | C4ST | 5.27 | Carbohydrate (chondroitin 4) sulfotransferase 11 | |
| NM_004582 | RABGGTB | 5.27 | Rab geranylgeranyltransferase, beta subunit | Protein modification; visual perception |
| NM_004550 | NDUFS2 | 5.25 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 2, 49 kDa (NADH-coenzyme Q reductase) |
Electron transport; mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone |
| AK023089 | SLC30A7 | 5.21 | Solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 7 |
Cation transport |
| NM_033301 | RPL8 | 5.20 | Ribosomal protein L8 | Protein biosynthesis |
| NM_015524 | C6orf5 | 5.20 | Synonyms: ACT1, CIKS, c6orf5, c6orf6, MGC3581, DKFZP586G0522; isoform 2 is encoded by transcript variant 2; chromosome 6 open reading frame 6; chromosome 6 open reading frame 5; connection to IKK and SAPK/JNK; nfkb- activating protein ACT1; go_component: cellular_component unknown [goid 0008372] [evidence ND]; go_function: molecular_function unknown [goid 0005554] [evidence ND]; go_process: intracellular signaling cascade [goid 0007242] [evidence NAS] [pmid 10962033]; Homo sapiens chromosome 6 open reading frame 4 (c6orf4), transcript variant 2, mrna. |
|
| NM_004134 | HSPA9B | 5.18 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 9B (mortalin-2) | Protein folding |
| Down-regulated | ||||
| AB040935 | CerCAM | −100.00 | Cerebral endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 | Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis |
| NM_001482 | GATM | −100.00 | Glycine amidinotransferase (L-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase) |
Creatine biosynthesis |
| X07263 | MYCL1; LMYC |
−100.00 | Human l-myc gene exon 3 and 3′-flanking region. | Cell growth and/or maintenance; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| L27560 | IGFBP5 | −100.00 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 | Cell growth and/or maintenance; regulation of cell growth; signal transduction |
| AB037804 | KIAA1383 | −100.00 | KIAA1383 protein | |
| NM_002357 | MAD | −100.00 | MAX dimerization protein 1 | Cell proliferation; development; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_139136 | KCNC2 | −100.00 | Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 2 |
Cation transport; potassium ion transport |
| NM_000962 | PTGS1 | −100.00 | Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) |
Lipid metabolism; physiological process; prostaglandin biosynthesis |
| AK000416 | SLC16A5 | −100.00 | Solute carrier family 16 (monocarboxylic acid transporters), member 5 |
Monocarboxylic acid transport |
| NM_000543 | SMPD1 | −100.00 | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1, acid lysosomal (acid sphingomyelinase) |
Carbohydrate metabolism; neurogenesis; signal transduction; sphingomyelin metabolism |
| NM_016525 | UBAP | −100.00 | Ubiquitin associated protein 1 | |
| NM_005263 | GFI1 | −87.72 | Growth factor independent 1 | G1/S-specific transcription in mitotic cell cycle; viral life cycle |
| NM_001276 | CHI3L1 | −84.75 | Chitinase 3-like 1 (cartilage glycoprotein-39) | Metabolism |
| AB033076 | KIDINS220 | −80.00 | Likely homolog of rat kinase D-interacting substance of 220 kDa |
|
| Y10183 | ALCAM | −66.23 | Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule | Antimicrobial humoral response (sensu Vertebrata); cell adhesion; signal transduction |
| NM_052944 | KST1 | −62.89 | Sodium/myo-inositol cotransporter 2 | Transport |
| AL080094 | RPESP | −60.98 | RPE-spondin | |
| NM_013448 | BAZ1A | −48.78 | Bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain, 1A | Protein ubiquitination; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_017936 | FLJ20707 | −45.87 | Kiaa2010 | ATP synthesis coupled proton transport; phosphate transport |
| NM_013357 | PURG | −39.37 | Werner syndrome | |
| NM_017884 | PINX1 | −35.21 | PIN2-interacting protein 1 | Negative regulation of cell cycle; negative regulation of cell proliferation; telomerase-dependent telomere maintenance |
| NM_005900 | MADH1; DKFZP586M0622 |
−30.67 | MAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 (Drosophila) |
Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; signal transduction; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway |
| X75489 | LIPA | −29.24 | H.sapiens LIPA gene, exon 1. | |
| M97496 | GUCA2A | −28.41 | Guanylate cyclase activator 2A (guanylin) | Signal transduction |
| AK000462 | OCIA | −26.74 | Ovarian carcinoma immunoreactive antigen | |
| NM_000756 | CRH | −25.77 | Corticotropin releasing hormone | Immune response; learning and/or memory; parturition; pregnancy; signal transduction; synaptic transmission |
| NM_130467 | PAGE-5 | −25.77 | PAGE-5 protein | |
| NM_030973 | TCBAP0758 | −23.70 | Hypothetical protein TCBAP0758 | |
| NM_018324 | FLJ11106 | −21.51 | Hypothetical protein FLJ11106 | Biosynthesis |
| NM_000961 | PTGIS | −19.46 | Prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) synthase | Electron transport; lipid metabolism; prostaglandin biosynthesis |
| NM_002363 | MAGEB1 | −16.75 | Melanoma antigen, family B, 1 | |
| NM_003940 | USP13 | −16.67 | Ubiquitin specific protease 13 (isopeptidase T-3) | Ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| NM_004284 | CHD1L | −16.23 | Synonyms: CHDL, FLJ22530; go_function: ATP binding [goid 0005524] [evidence IEA]; go_function: DNA binding [goid 0003677] [evidence IEA]; go_function: ATP-dependent helicase activity [goid 0008026] [evidence IEA]; go_function: hydrolase activity [goid 0016787] [evidence IEA]; Homo sapiens chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1-like (CHD1L), mrna. |
|
| NM_030642 | APOL5 | −15.77 | Apolipoprotein L, 5 | Lipid metabolism; lipid transport |
| AK001640 | KIAA0738 | −15.77 | KIAA0738 gene product | |
| NM_016270 | KLF2 | −14.53 | Kruppel-like factor 2 (lung) | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NM_002390 | ADAM11 | −13.93 | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 11 | Integrin-mediated signaling pathway; proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_006651 | CPLX1 | −13.83 | Complexin 1 | Exocytosis; neurotransmitter transport; synaptic transmission |
| NM_006350 | FST | −13.72 | Follistatin | Development; negative regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion |
| NM_004245 | TGM5 | −13.40 | Transglutaminase 5 | Epidermis development; peptide cross-linking |
| AL512713 | DKFZp762K222 | −13.25 | Similar to hypothetical protein dkfzp762k222 (LOC401163), mrna |
|
| NM_032649 | CPGL2 | −13.18 | Carnosinase 1 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis |
| NM_022817 | PER2 | −12.79 | Period homolog 2 (Drosophila) | Circadian rhythm; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; signal transduction |
| NM_012453 | TBL2 | −11.59 | Transducin (beta)-like 2 | Biological_process unknown |
| NM_025019 | TUBA4 | −11.55 | Tubulin, alpha 4 | Microtubule-based movement |
| AL133096 | DNAJA4 | −11.42 | Dnaj (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily A, member 4 | Protein folding |
| AK000470 | LOC286434 | −11.14 | Homo sapiens cdna FLJ20463 fis, clone KAT06143. | |
| NM_024410 | ODF1 | −10.95 | Outer dense fiber of sperm tails 1 | Spermatogenesis |
| NM_000448 | RAG1 | −10.81 | Recombination activating gene 1 | DNA recombination; hemocyte development; immune response |
| AB075834 | KIAA1954; | −10.75 | Zinc finger protein 90 homolog (mouse) | |
| NM_003635 | NDST2 | −10.26 | N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase (heparan glucosaminyl) 2 |
|
| BF089733 | NRXN3 | −10.01 | Neurexin 3 | |
| NM_000451 | SHOX | −9.90 | Short stature homeobox | Development; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; skeletal development; transcription from Pol II promoter |
| BC005107 | LOC90625 | −9.71 | Chromosome 21 open reading frame 105 | |
| NM_001215 | CA6 | −9.62 | Carbonic anhydrase VI | One-carbon compound metabolism |
| NM_001917 | DAO | −9.52 | D-amino-acid oxidase | Electron transport |
| NM_138569 | MGC18257 | −9.43 | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 142 | |
| NM_024727 | FLJ23259 | −9.43 | Hypothetical protein FLJ23259 | |
| NM_021946 | FLJ11362 | −9.35 | Hypothetical protein FLJ11362 | |
| NM_001170 | AQP7 | −9.26 | Aquaporin 7 | Energy pathways; excretion; glycerol transport; water transport |
| BC007251 | MGC15504 | −8.26 | Chromosome 14 open reading frame 128 | |
| NM_005013 | NUCB2 | −7.94 | Nucleobindin 2 | |
| NM_000328 | RPGR | −7.81 | Retinitis pigmentosa gtpase regulator | Intracellular protein transport; perception of sound; visual perception |
| AL137763 | LOC57822 | −7.19 | Sister-of-mammalian grainyhead | |
| AY008283 | PORIMIN | −7.09 | Pro-oncosis receptor inducing membrane injury gene |
|
| NM_000700 | ANXA1 | −6.99 | Annexin A1 | Cell motility; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; inflammatory response; lipid metabolism |
| NM_014244 | ADAMTS2 | −6.49 | A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 2 |
Collagen catabolism |
| NM_000602 | SERPINE1 | −6.29 | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 1 |
Blood coagulation |
| X05299 | CENPB | −6.25 | Centromere protein B, 80 kDa | Centromere/kinetochore complex maturation |
| NM_002559 | P2RX3 | −6.02 | Purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 3 |
Ion transport; signal transduction |
| NM_015900 | PS-PLA1 | −5.95 | Phospholipase A1 member A | Lipid metabolism; phosphatidylserine metabolism |
| NM_016629 | LOC51323 | −5.81 | Synonyms: DR6, BM-018; death receptor 6; TNFR-related death receptor 6; Homo sapiens tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 21 (TNFRSF21), mrna. |
|
| NM_018641 | C4S2 | −5.59 | Carbohydrate (chondroitin 4) sulfotransferase 12 | Dermatan sulfate biosynthesis |
| NM_024106 | MGC2663 | −5.59 | Zinc finger protein 426 | Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent |
| AK055449 | FLJ11588 | −5.49 | Hypothetical protein FLJ11588 | |
| NM_001615 | ACTG2 | −5.43 | Actin, gamma 2, smooth muscle, enteric | Muscle development |
| NM_003287 | TPD52L1 | −5.29 | Tumor protein D52-like 1 | Biological_process unknown |
Discussion
In this study, melanoma was used as a model system to systematically investigate the expression differences among snap frozen melanoma specimens, its derived primary culture cell lines and tumor xenografts by high throughput gene expression profiling analysis. Some genes those were concordant in all the models and many other genes that were differentially regulated were identified. Based on the clustering analysis, the expression profiles of the melanoma cell lines and the xenografts had more similarities than the profile of the snap frozen tumor tissue (Figures 1-3). It may be due to the heterogeneity of the tumor tissue despite the fact that over 90% of the cells were confirmed to be melanoma. This may also reflect the true intrinsic differences of gene expression between in vitro and in vivo models. Correlation analysis revealed that the best correlation was between the cell lines and the xenografts (Figures 4B and 5B). The correlation between the cell lines and the tumor tissues was the weakest among the three comparisons (Figures 4A and 5A). A fairly high degree of gene concordance was identified between the samples, ranging from 50-80% which may provide a selection of genes for careful examination in the future for clinical correlation with patient outcomes.
To further validate this approach, a pair of well characterized melanoma cell lines FEMX-I and FEMX-V were involved this study (17). The comparison of genes expression levels between their cultured cell lines and established corresponding tumor xenografts were analyzed base on the genes profiling. No significant differences in cellular proliferation, motility, migration or invasive capacity were identified under normal culture conditions. This may reflect differences of the influence of the tumor microenvironment in vivo and the unique properties of intercellular communication during the process of tumor cell proliferation and metastasis. In order to discover genes that may be responsible for such differences, the expression profiles of the melanoma cells and the tumor xenografts. Our data revealed that there were only 101 overlapping genes between the xenografts and the cell lines (Table I), with 239 differentially expressed genes in the cell lines (Table II) and 553 uniquely expressed genes in the xenografts (Table III). Many of these genes function as cell adhesion molecules such as JAM3, connexin-43 and growth factor binding proteins such as FIBP and IGFBP-5. Someof these genes may contribute to the phenotypic differences in vivo in terms of metastatic potential. Among these genes, connexin-43 expression was found to be no different between the two cell lines, however, it was over expressed over 400-fold in the metastatic tumor xenografts (Table III). Adhesion to vascular endothelium is a crucial first step in the colonization of select target organs by blood-borne cancer cells, and connexin-43 appears to represent an important gap junction protein, having a possible further function in angiogenesis and metastasis in melanoma, glioma, colon, lung and breast cancer (23-28). It has also been suggested that gap junction proteins such as connexin-43 may contribute to a more aggressive tumor cell phenotype via the loss of normal homeostatic growth regulation. A further understanding of this mechanism may provide new insights into the pathogenesis of human melanoma (29, 30). Thus, the high in vivo expression of connexin-43 in FEMX-I compared to FEMX-V tumors may reflect the differences in metastatic capacity. These examples demonstrate how such models may be used for gene profiling studies to identify progression-associated genes in melanoma. Furthermore it may help us to distinguish between genes expressed as a result of interactions within the microenvironment in which the cells grow. In this regard, novel genomic approaches provide a unique platform to explore genes that may play a key role in melanoma tumorigenesis and metastasis, possibly leading to targeted therapeutic approaches and gene discovery in melanoma research.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by Mitchell Cancer Institute start-up fund (J. Ju), NIHR21CA114043 (J. Ju) and NIHR01MH075020 (J. Ju).
References
- 1.Garraway LA, Widlund HR, Rubin MA, Getz G, Berger AJ, Ramaswamy S, Beroukhim R, Milner DA, Granter SR, Du J, Lee C, Wagner SN, Li C, Golub TR, Rimm DL, Meyerson ML, Fisher DE, Sellers WR. Integrative genomic analyses identify MITF as a lineage survival oncogene amplified in malignant melanoma. Nature. 2005;436:117–122. doi: 10.1038/nature03664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik JH, Feng B, Brennan C, Hahn WC, Cordon-Cardo C, Wagner SN, Flotte TJ, Duncan LM, Granter SR, Chin L. Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell. 2006;125:1269–1281. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pavey S, Johansson P, Packer L, Taylor J, Stark M, Pollock PM, Walker GJ, Boyle GM, Harper U, Cozzi SJ, Hansen K, Yudt L, Schmidt C, Hersey P, Ellem KA, O’Rourke MG, Parsons PG, Meltzer P, Ringner M, Hayward NK. Microarray expression profiling in melanoma reveals a BRAF mutation signature. Oncogene. 2004;23:4060–4067. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pollock PM, Harper UL, Hansen KS, Yudt LM, Stark M, Robbins CM, Moses TY, Hostetter G, Wagner U, Kakareka J, Salem G, Pohida T, Heenan P, Duray P, Kallioniemi O, Hayward NK, Trent JM, Meltzer PS. High frequency of BRAF mutations in nevi. Nat Genet. 2003;33:19–20. doi: 10.1038/ng1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pollock PM, Meltzer PS. A genome-based strategy uncovers frequent BRAF mutations in melanoma. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:5–7. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Acton EM, Narayanan VL, Risbood PA, Shoemaker RH, Vistica DT, Boyd MR. Anticancer specificity of some ellipticinium salts against human brain tumors in vitro. J Med Chem. 1994;37:2185–2189. doi: 10.1021/jm00040a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Beutler JA, Cardellina JH, 2nd, Gray GN, Prather TR, Shoemaker RH, Boyd MR, Lin CM, Hamel E, Cragg GM. Two new cytotoxic chalcones from Calythropsis aurea. J Nat Prod. 1993;56:1718–1722. doi: 10.1021/np50100a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Erickson KL, Beutler JA, Gray GN, Cardellina JH, 2nd, Boyd MR. Majapolene A, a cytotoxic peroxide, and related sesquiterpenes from the red alga Laurencia majuscula. J Nat Prod. 1995;58:1848–1860. doi: 10.1021/np50126a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boyd MR, Farina C, Belfiore P, Gagliardi S, Kim JW, Hayakawa Y, Beutler JA, McKee TC, Bowman BJ, Bowman EJ. Discovery of a novel antitumor benzolactone enamide class that selectively inhibits mammalian vacuolar-type (H+)-atpases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297:114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nishizuka S, Charboneau L, Young L, Major S, Reinhold WC, Waltham M, Kouros-Mehr H, Bussey KJ, Lee JK, Espina V, Munson PJ, Petricoin E, 3rd, Liotta LA, Weinstein JN. Proteomic profiling of the NCI-60 cancer cell lines using new high-density reverse-phase lysate microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:14229–14234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2331323100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Staunton JE, Slonim DK, Coller HA, Tamayo P, Angelo MJ, Park J, Scherf U, Lee JK, Reinhold WO, Weinstein JN, Mesirov JP, Lander ES, Golub TR. Chemosensitivity prediction by transcriptional profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10787–10792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191368598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Weinstein JN. Spotlight on molecular profiling: “Integromic” analysis of the NCI-60 cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:2601–2605. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Weinstein JN, Pommier Y. Transcriptomic analysis of the NCI-60 cancer cell lines. C R Biol. 2003;326:909–920. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2003.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, Brennan C, Lahti-Domenici J, Huang H, Porter D, Hu M, Chin L, Richardson A, Schnitt S, Sellers WR, Polyak K. Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:17–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lo M, Bulach DM, Powell DR, Haake DA, Matsunaga J, Paustian ML, Zuerner RL, Adler B. Effects of temperature on gene expression patterns in Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai as assessed by whole-genome microarrays. Infect Immun. 2006;74:5848–5859. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00755-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mazzatti DJ, White A, Forsey RJ, Powell JR, Pawelec G. Gene expression changes in long-term culture of T-cell clones: genomic effects of chronic antigenic stress in aging and immunosenescence. Aging Cell. 2007;6:155–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fodstad O, Kjonniksen I. Microenvironment revisited: time for reappraisal of some prevailing concepts of cancer metastasis. J Cell Biochem. 1994;56:23–28. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240560106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Riker A. The isolation and culture of melanoma cell lines. In: Langdon S, editor. Cancer Cell Culture. Humana Press; Totowa: 2004. pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Riker AI, Panelli MC, Kammula US, Wang E, Wunderlich J, Abati A, Fetsch P, Rosenberg SA, Marincola FM. Development and characterization of melanoma cell lines established by fine-needle aspiration biopsy: advances in the monitoring of patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer Detect Prev. 1999;23:387–396. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1500.1999.99045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shevde LA, Samant RS, Goldberg SF, Sikaneta T, Alessandrini A, Donahue HJ, Mauger DT, Welch DR. Suppression of human melanoma metastasis by the metastasis suppressor gene, BRMS1. Exp Cell Res. 2002;273:229–239. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xi Y, Nakajima G, Schmitz JC, Chu E, Ju J. Multi-level gene expression profiles affected by thymidylate synthase and 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:68. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xi Y, Shalgi R, Fodstad O, Pilpel Y, Ju J. Differentially regulated micro-RNAs and actively translated messenger RNA transcripts by tumor suppressor p53 in colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:2014–2024. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kamibayashi Y, Oyamada Y, Mori M, Oyamada M. Aberrant expression of gap junction proteins (connexins) is associated with tumor progression during multistage mouse skin carcinogenesis in vivo. Carcinogenesis. 1995;16:1287–1297. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.6.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lin JH, Takano T, Cotrina ML, Arcuino G, Kang J, Liu S, Gao Q, Jiang L, Li F, Lichtenberg-Frate H, Haubrich S, Willecke K, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Connexin 43 enhances the adhesivity and mediates the invasion of malignant glioma cells. J Neurosci. 2002;22:4302–4311. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-11-04302.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Milde-Langosch K, Janke S, Wagner I, Schroder C, Streichert T, Bamberger AM, Janicke F, Loning T. Role of Fra-2 in breast cancer: influence on tumor cell invasion and motility. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9559-y. epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Oliveira R, Christov C, Guillamo JS, de Bouard S, Palfi S, Venance L, Tardy M, Peschanski M. Contribution of gap junctional communication between tumor cells and astroglia to the invasion of the brain parenchyma by human glioblastomas. BMC Cell Biol. 2005;6:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-6-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang W, Nwagwu C, Le DM, Yong VW, Song H, Couldwell WT. Increased invasive capacity of connexin43-overexpressing malignant glioma cells. J Neurosurg. 2003;99:1039–1046. doi: 10.3171/jns.2003.99.6.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang W, Vaccariello MA, Wang Y, Alt-Holland A, Fusenig NE, Garlick JA. Escape from microenvironmental control and progression of intraepithelial neoplasia. Int J Cancer. 2005;116:885–893. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hsu M, Andl T, Li G, Meinkoth JL, Herlyn M. Cadherin repertoire determines partner-specific gap junctional communication during melanoma progression. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 9):1535–1542. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.9.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li G, Satyamoorthy K, Herlyn M. Dynamics of cell interactions and communications during melanoma development. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13:62–70. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]