Abstract
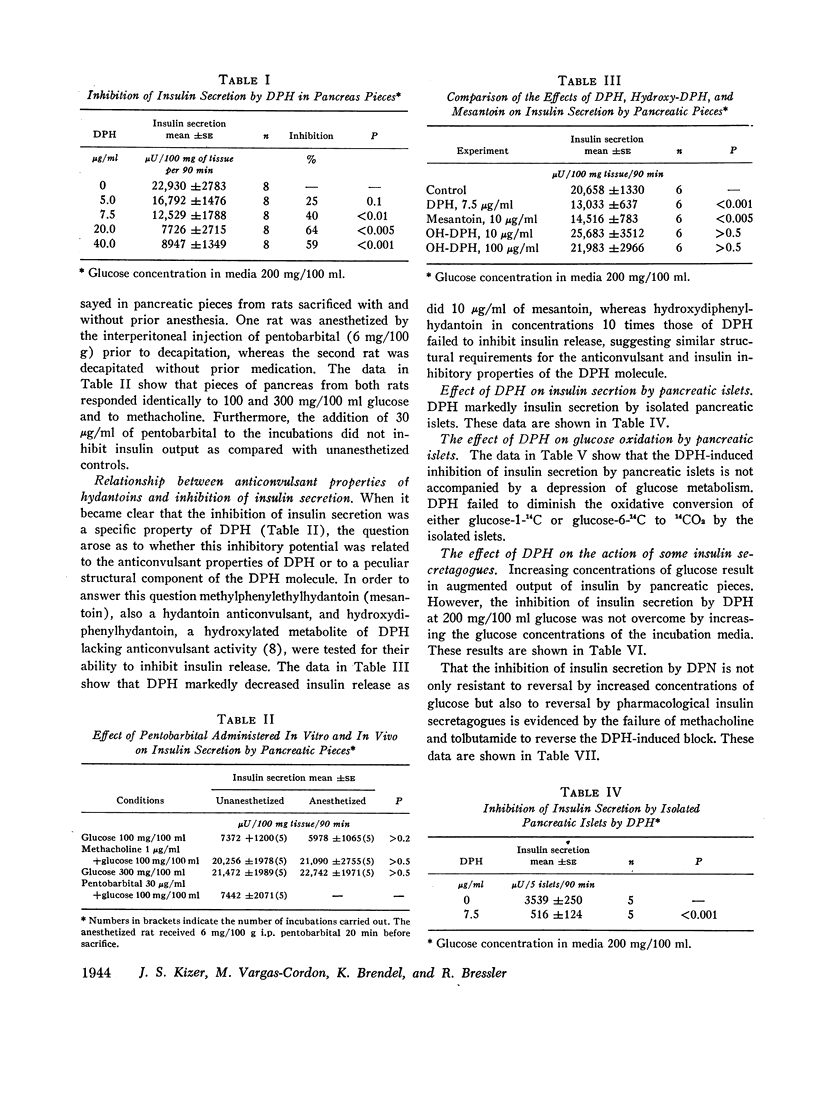
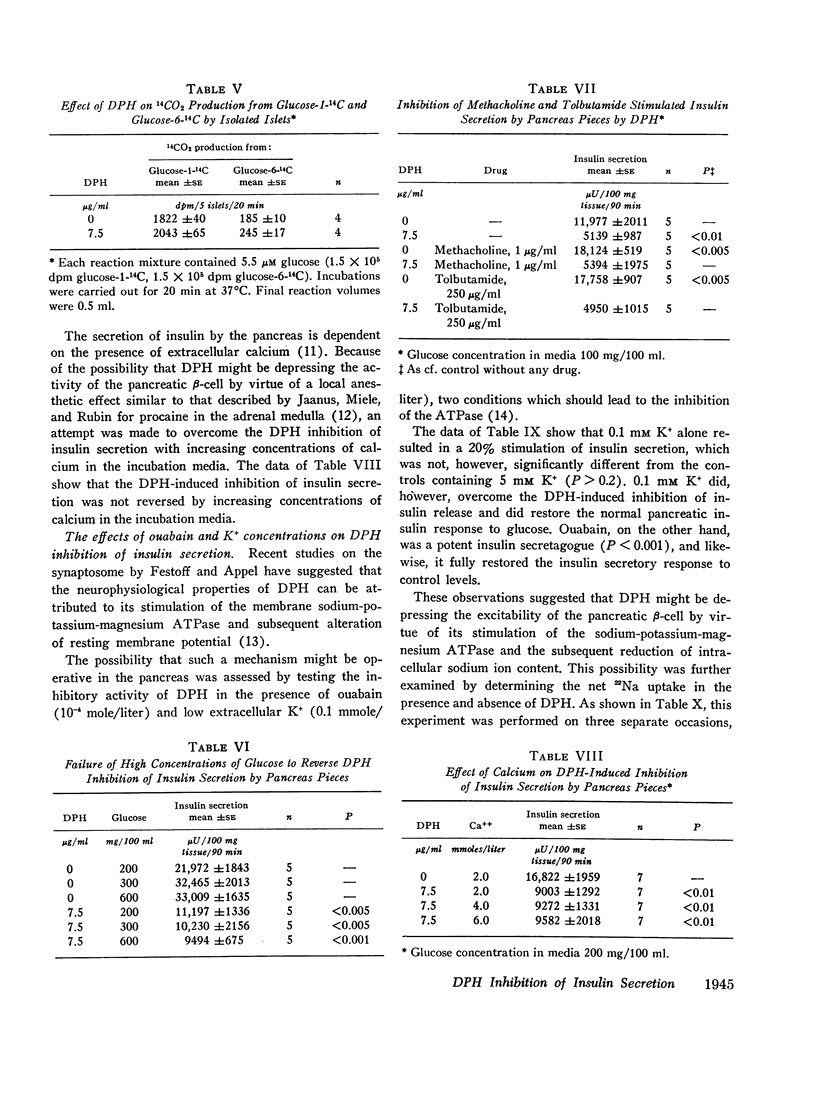
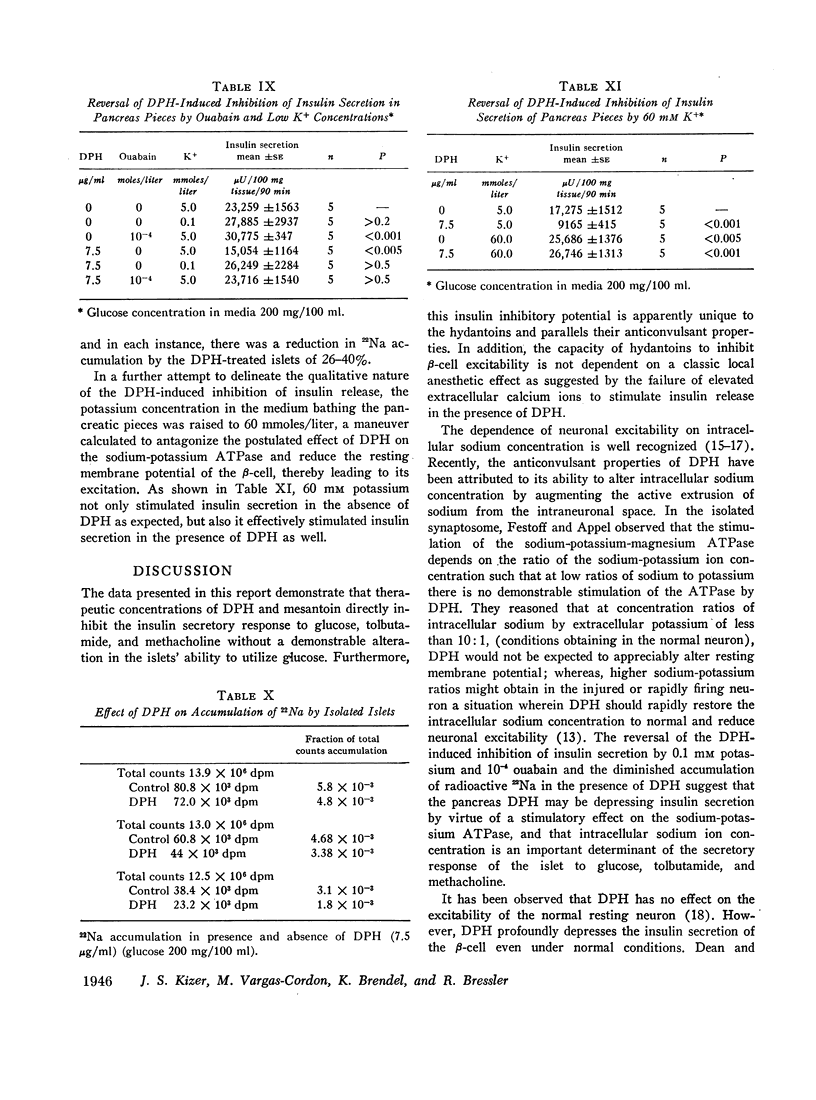
Glucose intolerance has been observed following diphenylhydantoin (DPH) intoxication. Because of this association between DPH and hyperglycemia, the effect of DPH on insulin release in vitro using preparations of isolated islets of Langerhans and pancreatic pieces was examined. In concentrations identical with those considered necessary for adequate anticonvulsant therapy in man, DPH markedly decreases the insulin secretory response of pancreatic pieces to methacholine, 1 μg/ml, tolbutamide, 250 μg/ml, and glucose, 200 mg/100 ml, without any demonstrable alteration in the oxidative conversion of glucose-1-14C or glucose-6-14C to 14CO2 by isolated islets. This DPH-induced inhibition of insulin secretion is not reversed by higher concentrations of glucose (600 mg/100 ml) or by increasing concentrations of extracellular calcium ion (4-6 mmoles/liter). 0.1 mM potassium and 10-4 M ouabain, however, effectively restore the DPH-induced block of insulin secretion in pancreatic pieces. 60 mM potassium ion, on the other hand, not only restores the insulin secretory response to glucose (200 mg/100 ml) but results in an added stimulation of insulin secretion in the presence of DPH. In the presence of DPH, 22Na accumulation by isolated islets is decreased by 26-40% as compared with controls. Such evidence is considered to indirectly support the postulate that the electrophysiological properties of DPH on the pancreas are due to a stimulation of the membrane sodium-potassium-magnesium ATPase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTLER T. C. The metabolic conversion of 5, 5-diphenyl hydantoin to 5-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenyl hydantoin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Jan;119(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belton N. R., Etheridge J. E., Jr, Millichap J. G. Effects of convulsions and anticonvulsants on blood sugar in rabbits. Epilepsia. 1965 Sep;6(3):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1965.tb03792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I., Cohen M. W. The action of sodium pump inhibitors on neuromuscular transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 9;170(1021):381–399. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I., Cohen M. W. The influence of internal sodium on the behaviour of motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 9;170(1021):401–421. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn R. D., Kennedy J. W., Blackmon J. R. The hemodynamic effects of diphenylhydantoin. Am Heart J. 1967 Apr;73(4):500–505. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(67)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Requirement for calcium ion in insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):174–178. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):389–390. doi: 10.1038/219389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festoff B. W., Appel S. H. Effect of diphenylhydantoin on synaptosome sodium-potassium-ATPase. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2752–2758. doi: 10.1172/JCI105956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUND M., JORGENSEN R. S., KUEHL V. SERUM DIPHENYLHYDANTOIN (PHENYTOIN) IN AMBULANT PATIENTS WITH EPILEPSY. Epilepsia. 1964 Mar;5:51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1964.tb04345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H. A new method for the measurement in vitro of pancreatic insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 Jan;80(1):99–108. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millichap J. G. Hyperglycemic effect of diphenylhydantoin. N Engl J Med. 1969 Aug 21;281(8):447–447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196908212810816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchnik S., Venosa R. A. Role of sodium ions in the response of the frequency of miniature end-plate potentials to osmotic changes in the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1969 Apr 12;222(5189):169–171. doi: 10.1038/222169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B. H., Samaan N. A. Hyperglycemia with relative hypoinsulinemia in diphenylhydantoin toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 10;281(2):91–92. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907102810208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said D. M., Fraga J. R., Reichelderfer T. E. Hyperbglycemia associated with diphenylhydantoin (Dilantin) intoxication. Med Ann Dist Columbia. 1968 Mar;37(3):170–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



