Abstract
Disease control programmes for an influenza pandemic will rely initially on the deployment of antiviral drugs such as Tamiflu, until a vaccine becomes available. However, such control programmes may be severely hampered by logistical constraints such as a finite stockpile of drugs and a limit on the distribution rate. We study the effects of such constraints using a compartmental modelling approach.
We find that the most aggressive possible antiviral programme minimizes the final epidemic size, even if this should lead to premature stockpile run-out. Moreover, if the basic reproductive number R0 is not too high, such a policy can avoid run-out altogether. However, where run-out would occur, such benefits must be weighed against the possibility of a higher epidemic peak than if a more conservative policy were followed.
Where there is a maximum number of treatment courses that can be dispensed per day, reflecting a manpower limit on antiviral distribution, our results suggest that such a constraint is unlikely to have a significant impact (i.e. increasing the final epidemic size by more than 10%), as long as drug courses sufficient to treat at least 6% of the population can be dispensed per day.
Keywords: mathematical modelling, influenza, pandemic, antiviral treatment
1. Introduction
The H5N1 virus, with its demonstrated virulence in humans, has drawn widespread attention to the threat of an influenza pandemic (Li et al. 2004; Beigel et al. 2005). Should the virus acquire the ability to easily infect humans, the resulting pandemic would have far-reaching consequences.
Although vaccines are an important means of control for seasonal influenza, with the emergence of a novel pandemic strain, no effective vaccine would be available for at least the first six months (Fedson 2003; Webby & Webster 2003). During this period, control strategies would depend largely on social distancing (e.g. closure of schools and workplaces; UK Health Departments 2005; US Department of Health and Human Services 2005) and stockpiles of antiviral drugs, such as Tamiflu (oseltamivir phosphate).
The role envisaged for Tamiflu in current pandemic plans is chiefly to relieve symptoms in infected individuals. However, there has also been discussion on the use of antiviral drugs for targeted prophylaxis (Longini et al. 2005; McCaw & McVernon in press). In this paper we shall concentrate on the former, assuming that an antiviral stockpile would be intended mainly for treatment rather than prophylaxis. Clinical trials with seasonal influenza have shown Tamiflu to reduce infectiousness and the infectious period (Treanor et al. 2000; Ward et al. 2005), as long as treatment commences within the first 48 hours of symptoms developing. The efficacy of Tamiflu against H5N1 is not yet known; nonetheless, by lowering infection rates, the use of Tamiflu in the community also offers an opportunity to limit the pandemic impact, for example by reducing the overall number of cases.
Previous modelling work on antiviral drugs has addressed such issues as the treatment of health care workers and children (Barnes et al. in press). Ferguson et al. (2005) and Longini et al. (2005) used intensive numerical simulations to consider the effect of targeted antiviral treatment, in combination with other intervention strategies. However, simpler compartmental models have the advantage of being more transparent (Arino et al. 2006). Gani et al. (2005) used this approach to consider optimal targeting strategies for various stockpile sizes. Such models can also be more amenable to understanding the effect of uncertainties such as the efficacy of antiviral drugs. In this paper we use this approach to consider the implications of antiviral run-out, as well as the effect of limited manpower in antiviral distribution.
2. Public health issues
In the ideal antiviral (AV) scenario, there is an unlimited stockpile, a capability to treat an unlimited number of cases per day and a perfectly efficacious drug. None of these will apply in practice, and this prompts the following questions: for given infection and drug efficacy parameters, what stockpile would be sufficient? With a stockpile that is potentially insufficient, is it preferable to adopt an ‘aggressive’ AV programme, dispensing treatment to as many infected cases as possible, or a more ‘conservative’ one, limiting the distribution rate to try and avoid run-out? If there were a limit on the number of cases that can be treated per day, would this have a significant impact?
Once a pandemic-capable strain evolves and starts to spread widely, containment would be unfeasible. We therefore concentrate on the use of antiviral drugs to reduce the impact of a pandemic. In particular, in the absence of reliable data on the effect of AV treatment on hospitalizations, we consider primarily its effect in reducing the overall attack rate (final epidemic size). Additionally, we consider the effect of an AV programme in mitigating the ‘peak pandemic impact’, which includes the following factors: (i) reducing the peak prevalence eases the pressure on public health services; (ii) delaying the epidemic peak affords more time to acquire vaccines or to replenish the AV stock.
3. The basic model
We use a compartmental modelling approach, as developed by Kermack & McKendrick (1927). We write S for the proportion of the population that is susceptible, IT for the proportion who are infected and receiving treatment, IN for the proportion who are infected and not receiving treatment, RT for the proportion who have recovered via treatment and RN for those who have recovered without treatment.
Regarding AV distribution, an ideal scenario might be that all infected cases receive treatment within 48 hours of developing symptoms. This is infeasible in practice; a certain proportion of cases would be asymptomatic (Couch et al. 1971), and thus tend to escape detection before they can infect others. Moreover, for a very limited stockpile, a policy decision may be taken to preferentially treat those most at risk from secondary complications, such as the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions (UK Health Departments 2005). We write α for the proportion of infected cases receiving treatment within 48 hours of symptoms. This quantity, the ‘AV coverage’, provides a convenient way of representing the AV programme.
We assume that the effect of treatment is to reduce the infectious period, so that those receiving treatment recover in 1/γT days, and the remainder of infected cases recover in 1/γN days, where γT>γN. The model is summarized schematically in figure 1; we assume a constant population size and neglect births and deaths. For simplicity, we do not explicitly include disease-related deaths—to do so is equivalent to modifying the definition of γN and γT to include removal of infected cases due to mortality (i.e. writing them as recovery rate + death rate), and this does not alter the qualitative behaviour of the model. Where disease-related deaths may be significant, all variables are interpreted as proportions of the initial population size.
Figure 1.
Summary of the basic model, where f=β(IT+IN). A proportion α of infected cases receive treatment (class IT) and recover in 1/γT days. The remainder of infected cases (class IN) recover in 1/γN days, where γT>γN.
The governing equations are as follows:
| (3.1) |
| (3.2) |
| (3.3) |
| (3.4) |
where β is the infection rate and denotes dS/dt. Seeding the epidemic by a small perturbation IN0 to the disease-free state in class IN, the initial conditions are
| (3.5) |
For simplicity, we take S0≈1, IN0≈0 in the calculations to follow. The number of AV courses that have been dispensed at any given time is RT+IT (i.e. a sum of those recovered and those recovering through treatment), and so a stockpile sufficient to treat a proportion M of the population is exhausted when RT+IT=M. Where this occurs in the numerical calculation, we set α=0 for all subsequent time.
4. Reproductive numbers
The basic reproductive number R0 is the average number of secondary cases arising from one index case, in a wholly susceptible population. We define the ‘treated’ reproductive number Rα as the corresponding quantity, but, in the presence of an AV programme, with AV coverage α. Following van den Driessche & Watmough (2002), the next-generation matrix is
| (4.1) |
Since this has rank 1, its spectral radius is equal to its trace, giving
| (4.2) |
There are two possibilities for a pandemic-capable strain: Rα<1<R0 and 1<Rα<R0. The first corresponds to successful containment and is a particularly simple case, where IT, IN remain small and S≈1 throughout. In this paper we concentrate instead on the second scenario, that is where an epidemic still occurs in the presence of an AV programme, but with a smaller reproductive number than in the case of no treatment.
5. Parameters
We note that the lower γT is, the less efficacious the drug is in reducing the infectious period (i.e. residence time in the infected class). We follow Gani et al. (2005) in assuming that the effect of antiviral treatment is to reduce the infectious period from 4 to 2.5 days. In other words, γN=0.25, γT=0.4.
It is not possible to determine R0 in advance for a pandemic strain. From past pandemics, however, R0 has been well approximated by the reproductive number in the early stages of disease spread, when there was almost no immunity in the population. For the second ‘autumn’ wave of the 1918 pandemic, the reproductive number has been estimated to be 2–3 using excess mortality (Mills et al. 2004) and daily case notification data (Chowell et al. 2007). For the first wave, it has been estimated at 1.5 (Chowell et al. 2006). Accordingly, we consider a range of values for R0: 1.5, 2 and 3, corresponding to values for β: 0.375, 0.5 and 0.75, respectively.
6. Minimum required stockpile: constant α
We first consider the minimum sufficient stockpile for given infection and AV parameters. This is the same as the total AV usage with an unlimited stockpile, which we denote by U=limt→∞RT. Adding equations (3.1) and (3.2) gives . Integrating and letting t→∞ yields
| (6.1) |
where is the serologic attack rate (final epidemic size). As shown in appendix A.1, equation (6.1) can be used to show that is a solution of the equation
| (6.2) |
allowing us to determine U as a function of α in (6.1). We note that equation (6.2) is analogous to the final-size equation for an ‘untreated’ epidemic as discussed, for example, by Murray (1989, p. 614), where Rα is replaced by R0. Figure 2 shows plots of U(α), for different values of R0. For a given stockpile M and AV coverage α, run-out occurs if M exceeds U(α).
Figure 2.
Plots of AV usage U (or minimum required stockpile) versus coverage α, for different values of R0.
It is of interest to note that U(α) is not necessarily a monotonically increasing function of α, i.e. that an aggressive AV policy is not necessarily linked with a higher overall AV usage than a more conservative one. In particular, in figure 2 when R0 is sufficiently low (e.g. R0=1.5, 2) there is a turning point in U(α), where it is maximum. However, when R0 is sufficiently high (e.g. R0=3), an increase in AV coverage α is always associated with an increase in overall AV usage.
This has the following implications for a limited stockpile M. Consider the situation illustrated in figure 3a, where there exists a turning point in U(α) in the range 0<α<1, and the stockpile M is less than the maximum possible AV usage but greater than the AV usage with 100% coverage (i.e. U(1)). Then there are precisely two values of α, say α1, α2, where α1<α2, such that U(α)=M. Therefore, run-out may be avoided by a sufficiently aggressive programme (i.e. α>α2), as well as by a sufficiently conservative programme (i.e. α<α1). This is significant from a disease control point of view: it is straightforward to show, using equations (4.2) and (6.2), that, as long as run-out is avoided, increasing α decreases the attack rate , by lowering the treated reproductive number, Rα. Thus, the former aggressive strategy above represents the more efficient use of a stockpile M, delivering a lower attack rate.
Figure 3.
Illustration of different run-out scenarios. (a) Stockpile of 10% and R0=1.5. There are precisely two values of AV coverage, marked α1 and α2, such that U(α)=M. Run-out may be avoided by α<α1 or by α>α2. (b) Stockpile of 30% and R0=2, 3. Here R0 is sufficiently large for the antiviral usage U(α) to be monotonically increasing with respect to α. Run-out can be avoided only by a sufficiently low AV coverage.
On the other hand, when M is less than U(1), there is precisely one value of α for which U(α)=M, as illustrated in figure 3b. In this case, run-out can only be avoided by a sufficiently conservative programme.
We can show that, with R0>1, U(α) has a turning point in the range 0<α<1, if and only if
| (6.3) |
The r.h.s. is the drug efficacy in reducing infectiousness: it is the reduction, due to treatment, in the average number of secondary cases arising from one clinical case. This result is derived in appendix A.2. If R0 is sufficiently high to invalidate this inequality, then, with a limited stockpile, R0 is too high with respect to the drug efficacy for it to be possible to avoid run-out by maximizing α.
7. Run-out scenario: general α
We now consider the implications of run-out. Figure 4 shows a plot of attack rate versus α, for the parameters used in figure 3a. The attack rate is monotonically decreasing with respect to α, except for an interval where it is constant. Figure 3a confirms that this interval is associated with AV run-out.
Figure 4.
Attack rate versus AV coverage α. For R0=1.5 and a stockpile M=0.1.
Indeed, it can be shown analytically that the attack rate in a run-out scenario is a solution of the equation
| (7.1) |
where
| (7.2) |
This result is derived in appendix A.1.2 and is indeed independent of the AV coverage α. Regarding the role of the constant A, we note that when A=1 we recover the familiar expression for the attack rate for an epidemic without any AV treatment (Murray 1989, p. 614). Moreover, parameters associated with the AV programme (β, M, γT) are all contained in A. Thus, A represents the effect of the AV programme, on reducing the attack rate.
However, in a run-out scenario, α can affect the epidemic peak properties. Figure 5 shows numerical plots for the epidemic peak timing and its height; it suggests that, in this model, increasing α can have the effect of delaying the epidemic peak, as well as reducing its height.
Figure 5.
Numerical plots of epidemic peak properties, where prevalence is IT+IN. The ‘kinks’ in both plots arise because, for sufficiently high α, the epidemic peak occurs after run-out. Parameters: γT=0.4, γN=0.25, M=0.2 and R0=0.25. (a) Peak height and (b) peak timing.
8. Extended model
In order to explore the robustness of these results, the calculations above have been extended to a more biologically detailed model, one that explicitly incorporates the clinical course of infection, as well as broadening the possible effects of AV treatment. Cases of influenza can start being infectious before developing symptoms. Moreover, some infections are subclinical, i.e. never developing symptoms. Longini et al. (2005) estimate the mean latent period (i.e. time from infection to infectiousness) to be 1.2 days, and that individuals subsequently develop symptoms after an average of 0.7 days. It is also estimated that 33% of infected cases will be subclinical.
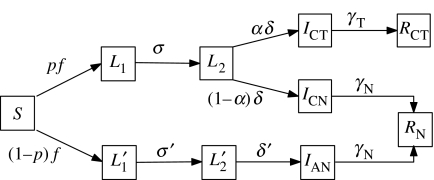
Accordingly, we assume that a proportion p of infected cases ultimately develop clinical symptoms. These cases are first latent (class L1), and after 1/σ days become infectious but pre-symptomatic (class L2). Subsequently, after 1/δ days, they develop symptoms: a proportion α of these cases receives treatment (class ICT) to recover in 1/γT days. The remainder (class ICN) recover in 1/γN days, where again 0<γN<γT. Overall, therefore, we assume that cases without symptoms do not receive treatment.
The subclinical cases follow a similar course to clinical cases, being first latent (class ) and after 1/σ′ days becoming infectious (class ). After another 1/δ′ days, they enter class IAN, who are also subclinical and infectious. Although there is no clinical distinction between and IAN, we use this structure to preserve symmetry between the clinical and subclinical courses of infection. Infected cases in class IAN recover in 1/γN days.
We assign an infection rate βN to all cases that are infectious but without symptoms, i.e. classes L2, and IN; these infected cases receive no treatment. Moreover, we now assume that the effect of AV treatment is not only to reduce the infectious period, but also to reduce infectiousness. Thus, we assign infection rates βCT and βCN to classes ICT and ICN, respectively, where 0<βCT<βCN.
This model is summarized in figure 6. The model equations are
| (8.1) |
| (8.2) |
| (8.3) |
| (8.4) |
| (8.5) |
| (8.6) |
where
| (8.7) |
If the disease is seeded by a perturbation in the class L1 (say) to the disease-free state, then the initial conditions are
| (8.8) |
Once again, for simplicity in the analytical calculations, we shall take S0≈1, L1≈0. We note that the basic model is a limiting case of the extended model: the former can be retrieved from the latter by taking p=1, βCT=βCN=β and letting σ, δ→∞ in (8.1)–(8.7).
Figure 6.
Schematic illustration of the extended model, where .
9. Reproductive numbers
Setting α=0, we follow van den Driessche & Watmough (2002) once again to find R0. As in the basic model, the next-generation matrix has rank 1, so that the spectral radius is equal to its trace, giving
| (9.1) |
Similarly, when α is non-zero, we find for the treated reproductive number,
| (9.2) |
10. Minimum required stockpile
We assume constant α and an unlimited stockpile. As shown in appendix A.1.1, the total AV usage is given by
| (10.1) |
and the overall attack rate is a solution of the equation
| (10.2) |
the same as equation (6.2) for the basic model. The discussion for the basic model, on the maximum in U(α) and the possibility of avoiding run-out with a sufficiently high α, also applies here. In particular, we have that, with R0>1, U(α) has a turning point in the range 0<α<1 if and only if
| (10.3) |
as derived in appendix A.2. If R0 is sufficiently high to invalidate this inequality, then U(α) is monotonically increasing for 0≤α≤1 and it is not possible to avoid run-out by maximal coverage. Here again the important parameters are R0 and the drug efficacy in reducing infectiousness, where the relevant measure of drug efficacy is the reduction, due to treatment, in the average number of secondary cases arising from a single clinical case.
11. Run-out scenario
Relaxing the assumption of constant α, it can be shown that, where a stockpile sufficient to treat a proportion M of the population is exhausted before the end of the epidemic, the overall attack rate is a solution of the equation
| (11.1) |
where
| (11.2) |
A derivation of this result is given in appendix A.1.2. Once again we have that, after run-out, the attack rate depends not on the AV coverage, but on the stockpile, and the drug efficacy in reducing infectiousness.
However, the behaviour of the epidemic peak shows an interesting departure from the basic model. Assuming constant α once again, we consider ICT+ICN, the proportion of the population that is symptomatic, since it is these infected cases that pose the most immediate challenge to health services. Figure 7a,b shows numerical plots of the epidemic peak height and the peak timing, respectively, where we have used Longini's parameter estimates, stated above, for illustration. Comparing peak timing with figure 5b, it appears to remain true in the extended model that, whether the stockpile is exhausted or not, a higher AV coverage leads to a delayed epidemic peak. However, considering the peak height, whereas in figure 5a it is a decreasing function of α, figure 7a shows an example of a case where peak height can also slightly increase with increasing coverage. This effect also occurs with different values of σ and is stronger with smaller values of δ. It occurs only where the stockpile is exhausted, but suggests a potential trade-off, in an aggressive AV programme, for the benefits of minimizing the number of cases and delaying the epidemic peak.
Figure 7.
Numerical plots of epidemic peak properties for the extended model, measuring ICT+ICN. The ‘kinks’ arise because, for sufficiently high α, the peak occurs after run-out. (a) Peak height versus AV coverage. In the run-out range (α>0.32), peak height is an increasing function of α. (b) Peak timing in days versus AV coverage. Parameters: p=0.67, σ=σ′=1/1.2, δ=δ′=1/0.7, γT=0.4, γN=0.25, βCT=0.3, βCN=0.6, βN=0.39, M=0.1 and R0=2.5.
12. Limited distribution capacity
We now consider the case of a maximum in the number of treatment courses that can be dispensed per day, due to limits on manpower. We refer to this as a ‘limited distribution capacity’. Returning to the basic model, when there are few infected cases at the beginning of an epidemic, a proportion α0 receive treatment. As the epidemic progresses, however, there is a limit C to the number of doses of treatment that can be dispensed per day, as a proportion of the population. In other words, we require
| (12.1) |
A convenient choice of such α is
| (12.2) |
When C→∞ we have constant α=α0, which will be our baseline in discussing the effect of finite C. We also assume an unlimited stockpile, since the post-run-out results above apply for any α, and hence also hold in this case.
Assuming R0=2, attack rates were computed numerically for different values of α0 and C and are plotted in figure 8a. The attack rate can depend sensitively on C, when the latter is sufficiently small. This is because a decrease in α during the course of an epidemic is self-reinforcing: it leads to an increase in infections, compared with the case of constant α, which in turn reduces α still further.
Figure 8.
(a) Calculated attack rate versus distribution capacity C, for different values of α0. (b) Prevalence versus time under a limited distribution capacity, α0=0.6, for different values of C. Parameters: γN=0.25, γT=0.4 and R0=2.
However, if C is sufficiently high, it has no significant effect on the attack rate, nor on the course of the epidemic, as shown by a comparison of the cases C=0.25 and 0.1 in figure 8b. To quantify this, we say that a limited distribution capacity ‘fails’ if it results in an increase in the attack rate of greater than 10%, compared with the case of unlimited distribution capacity (constant α). We choose this figure as an estimated lower bound on the increase in attack rate that may be considered significant in terms of policy. Numerically, for a given α0 we calculate the value of C yielding a 10% increase in the attack rate, and maximize this over α0, to give Cfail. Thus, for given AV and infection parameters, any AV programme capable of dispensing treatment to at least a proportion Cfail of the population would avoid failure, whatever the value of α0. Figure 9 shows plots of Cfail versus R0, for different values of γT. In all of the curves, Cfail is a decreasing function of R0 if the latter is sufficiently high, and this is because in such cases there is little percentage difference in attack rate between the cases of limited and unlimited distribution capacity. Overall, figure 9 suggests that, with R0 in the range of 1–3 estimated from past pandemics, distribution ‘failure’ would be avoided as long as there is a capability of distributing drugs to at least 6% of the population per day. This value is decreased by taking a threshold higher than 10% for failure and vice versa.
Figure 9.
Minimum required distribution capacity Cfail, to ensure that attack rate is within 10% of the case of unlimited distribution capacity, versus R0, for different values of γT. The ‘termination’ of each curve is where R0 is sufficiently high that the percentage difference in attack rate between even the two most extreme cases, C=0 and C→∞, is less than 10%. γN=0.25.
13. Summary
Much of the previous modelling work on the use of AVs in a pandemic has concentrated on containment at the source (Ferguson et al. 2005; Longini et al. 2005), and on the use of drugs in conjunction with other interventions such as case isolation and air traffic reduction (Flahault et al. 2006; Colizza et al. 2007). Should containment fail, however, a widespread AV programme by itself would have a ‘society-wide’ effect by reducing the disease reproductive number, and such an effect has also been noted by Gani et al. (2005). Using a simple model we have explored some implications of this effect, with two types of logistical constraints: a limited stockpile and a limited distribution capacity.
We find that the most aggressive possible AV programme can offer several benefits: first, it minimizes the overall attack rate, even if it should lead to run-out. A conservative programme, while avoiding run-out, would dispense fewer courses of treatment overall, without the society-level benefit of widespread aggressive AV treatment and would thus result in a higher epidemic size. Second, if R0 is not too high, a sufficiently aggressive AV programme can avoid run-out altogether, by lowering disease spread to such an extent that the required AV stockpile is also sufficiently lowered. We have derived a condition on R0, in terms of the drug efficacy, for this to be possible. Third, our numerical results suggest that, whether run-out occurs or not, an aggressive AV policy would delay the epidemic peak. In practical terms, this could buy valuable time for the development of an effective vaccine, or to replenish the stockpile.
Nonetheless, an aggressive AV policy is not without risk: where it would lead to run-out, we have seen an instance of an aggressive programme leading to a higher epidemic peak than a more conservative one. Such an effect would place a greater peak burden on health services, and further work is required to determine under which conditions this effect could occur. Another potential issue with an aggressive programme, which we have not considered in detail here, is the emergence of drug resistance (Lipsitch et al. 2007). Indeed, cases have been recorded of resistance of H5N1 against Tamiflu in humans (De Jong et al. 2005). The benefits discussed above must therefore be weighed against the possibility of these effects occurring.
Even with an unlimited stockpile, however, an AV programme would be constrained by an upper limit on the number of treatment courses that can be dispensed per day. We have found that the attack rate and peak prevalence can increase significantly, if this ceiling in distribution is reached; however, for the parameters we have adopted here, a capability of dispensing courses of drugs to at least 6% of the population per day should avoid this occurring. This low threshold suggests that, in practice, it would be unlikely for a limited distribution capacity to be a significant issue.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support for this project from the James Martin 21st Century School at Oxford University.
Appendix A. Technical supporting information
Note. The basic model is a limiting case of the extended model presented above: the former follows from the latter by allowing σ, δ→∞, and setting p=1, βCT=βCN=β. For brevity, we therefore present the following derivations for the extended model only, and briefly show how the results from the basic model can be obtained from these.
A.1 Final epidemic size
Relaxing the assumption of constant α, we derive a ‘final-state equation’ that is valid, whether the stockpile is exhausted or not. We work on equations (8.1)–(8.6) of the extended model. For simplicity in the calculations to follow, we shall approximate the initial conditions by S≈1 and all other variables being 0 at t=0. Dividing (8.1) by S and integrating,
| (A1) |
The first integral term on the r.h.s. is proportional to RCT, from (8.6). Letting t→∞, and noting that ,
| (A2) |
To find the remaining terms on the r.h.s., we note, from (8.1)–(8.5), that
| (A3) |
| (A4) |
| (A5) |
| (A6) |
Integrating each of these equations in turn, letting t→∞ and noting that all infected classes tend to 0 in this limit,
| (A7) |
| (A8) |
Substituting these terms into (A 2) and recalling (9.1) yield the final-state equation
| (A9) |
As an aside, we can show with the same working that this equation applies also for the basic model, but with βCN=βCT=β.
It is now straightforward to distinguish between the cases of sufficient and insufficient stockpiles.
A.1.1 Sufficient stockpile
Where the stockpile avoids exhaustion, we have, from (8.1)–(8.4),
| (A10) |
Assuming now constant α, integrating and letting t→∞, we find
| (A11) |
By definition, the l.h.s. is U(α), and so this is a derivation of equation (10.1) for the overall AV usage. Substituting (A 11) into (A 9) and rearranging,
| (A12) |
where Rα is given by (9.2). The corresponding result (6.2) for the basic model is obtained by taking Rα given in (4.2).
A.1.2 Insufficient stockpile
Where a stockpile sufficient to treat a proportion M of the population is exhausted before the end of the epidemic, we have simply . Substituting into (A 9) and rearranging this gives
| (A13) |
where
| (A14) |
independent of α. The corresponding result (7.1), (7.2) for the basic model is obtained by taking βCN=βCT=β, and R0 as given in (4.2).
A.2 Maximizing antiviral usage with respect to α
We seek to maximize
| (A15) |
where p is a constant, set to unity in the basic model, is given by (A 12), and Rα by (9.2).
First, it follows from (A 15) that dU/dα=0 when
| (A16) |
Differentiating both and Rα with respect to α yields, respectively,
| (A17) |
| (A18) |
Using (A 18) in the r.h.s. of (A 17), substituting for using (A 16) and rearranging this gives
| (A19) |
Substituting for into (A 12),
| (A20) |
Using (9.2) to eliminate Rα in (A 20) and rearranging, we can thus express the value of α at a turning point of U(α) as
| (A21) |
For R0≥1, this is a strictly increasing function of R0, and αmax=0 when R0=1. It follows that, with R0≥1, we have 0<αmax<1 if and only if
| (A22) |
The corresponding condition (6.3) for the basic model is obtained by taking p=1, βCN=βCT=β.
References
- Arino J, Brauer F, van den Driessche P, Watmough J, Wu J. Simple models for containment of a pandemic. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2006;3:453–457. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2006.0112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, B., Glass, K. & Becker, N. G. In press. The role of health care workers and antiviral drugs in the control of pandemic influenza. Math. Biosci ( 10.1016/j.mbs.2007.02.008). [DOI] [PubMed]
- Beigel J.H, et al. Avian influenza A (H5N1) in humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1374–1385. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra052211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowell G, Ammon C.E, Hengartner N.W, Hyman J.M. Transmission dynamics of the great influenza pandemic of 1918 in Geneva Switzerland: assessing the effects of hypothetical interventions. J. Theor. Biol. 2006;241:193–204. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2005.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowell G, Nishiura H, Bettencourt L.M.A. Comparative estimation of the reproduction number for pandemic influenza from daily case notification data. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2007;4:155–166. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2006.0161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizza V, Barrat A, Barthelemy M, Valleron A.J, Vespignani A. Modeling the worldwide spread of pandemic influenza: baseline case and containment interventions. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e13. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch R.B, Douglas R.G, Jr, Fedson D.S, Kasel J.A. Correlated studies of a recombinant influenza-virus vaccine. 3. Protection against experimental influenza in man. J. Infect. Dis. 1971;124:473–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.5.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong M.D, et al. Oseltamivir resistance during treatment of influenza A (H5N1) infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:2667–2672. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa054512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedson D.S. Pandemic influenza and the global vaccine supply. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003;36:1552–1561. doi: 10.1086/375056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson N.M, Cummings D.A, Cauchemez S, Fraser C, Riley S, Meeyai A, Iamsirithaworn S, Burke D.S. Strategies for containing en emerging influenza pandemic in southeast Asia. Nature. 2005;437:209–214. doi: 10.1038/nature04017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flahault A, Vergu E, Coudeville L, Grais R.F. Strategies for containing a global influenza pandemic. Vaccine. 2006;24:6751–6755. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.05.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gani R, Hughes H, Fleming D, Griffin T, Medlock J, Leach S. Potential impact of antiviral drug use during influenza pandemic. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005;11:1355–1362. doi: 10.3201/eid1109.041344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermack W.O, McKendrick A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. A. 1927;115:700–721. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1927.0118. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li K.S, et al. Genesis of a highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1 influenza virus in eastern Asia. Nature. 2004;430:209–213. doi: 10.1038/nature02746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsitch M, Cohen T, Murray M, Levin B. Antiviral resistance and the control of pandemic influenza. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longini I.M, Jr, Nizam A, Xu S, Ungchusak K, Hanshaoworakul W, Cummings D.A.T, Halloran M.E. Containing pandemic influenza at the source. Science. 2005;309:1083–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.1115717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaw, J. M. & McVernon, J. In press. Prophylaxis or treatment? Optimal use of an antiviral stockpile during an influenza pandemic. Math. Biosci ( 10.1016/j.mbs.2007.02.003). [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mills C.E, Robins J.M, Lipsitch M. Transmissibility of 1918 pandemic influenza. Nature. 2004;432:904–906. doi: 10.1038/nature03063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J.D. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 1989. Mathematical biology. [Google Scholar]
- Treanor J, et al. Efficacy and safety of the oral neuraminidase inhibitor Oseltamivir in treating acute influenza. JAMA. 2000;283:1016–1024. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.8.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UK Health Departments 2005 Pandemic flu—UK influenza pandemic contingency plan See. http://www.dh.gov.uk/assetRoot/04/12/17/44/04121744.pdf.
- US Department of Health and Human Services 2005 HHS pandemic influenza plan See. http://www.hhs.gov/pandemicflu/plan/pdf/HHSPandemicInfluenzaPlan.pdf.
- van den Driessche P, Watmough J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibris for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002;180:29–48. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P, Small I, Smith J, Suter P, Dutkowski R. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and its potential for use in the event of an influenza pandemic. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005;55(Suppl. S1):i5–i21. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webby R.J, Webster R.G. Are we ready for pandemic influenza? Science. 2003;302:1519–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1090350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]