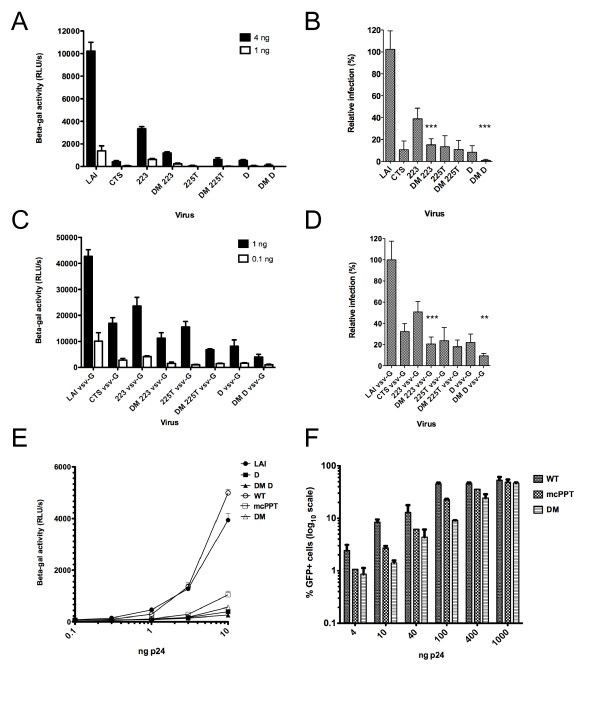
Figure 2.
Single-cycle titration assay in P4-CCR5 cells indicate an increased infectivity defect of DNA Flap double mutant viruses compared with cPPT or CTS single mutants. (A) P4-CCR5 cells were infected with 4 ng or 1 ng p24 of HIV-1 wild-type envelope and infectivity was measured 48 h p.i by tat transactivation of the beta-gal promoter (mean of triplicates +/- SD representative of two independent experiments). (B) Relative infection of the DNA Flap mutant viruses compared with wild-type LAI virus (mean of three independent experiments carried out in triplicate over a range of viral concentrations +/- SD). Statistical relevance was calculated using paired t test to compare cPPT single mutant viruses with their corresponding DM virus, *** p < 0.001. (C) P4-CCR5 cells were infected with 1 ng or 0.1 ng p24 of HIV-1 VSV-G and infectivity was measured 48 h p.i by Tat transactivation of the beta-gal promoter (mean of triplicates +/- SD representative of three independent experiments). (D) Relative infection of the DNA Flap mutant viruses compared with wild-type LAI virus (mean of three independent experiments carried out in triplicate +/- SD). Statistical relevance was calculated using paired t test to compare cPPT single mutant viruses with their corresponding DM virus, *** p < 0.001. (E) P4-CCR5 cells were infected with wild-type env NL4-3 viruses from the Hu et al., 2010 study (WT, mcPPT, DM) in parallel with our wild-type and mutant LAI viruses (LAI, D, DM D). Results show the mean beta-galactosidase activity of duplicates +/- SD and are representative of three independent experiments. (F) GHOST3 cells were infected with increasing doses of viruses from the Hu et al. study [16]. Infectivity was assessed at 48 h p.i using flow cytometry. Results show the mean percentage of GFP positive cells of three independent experiments.