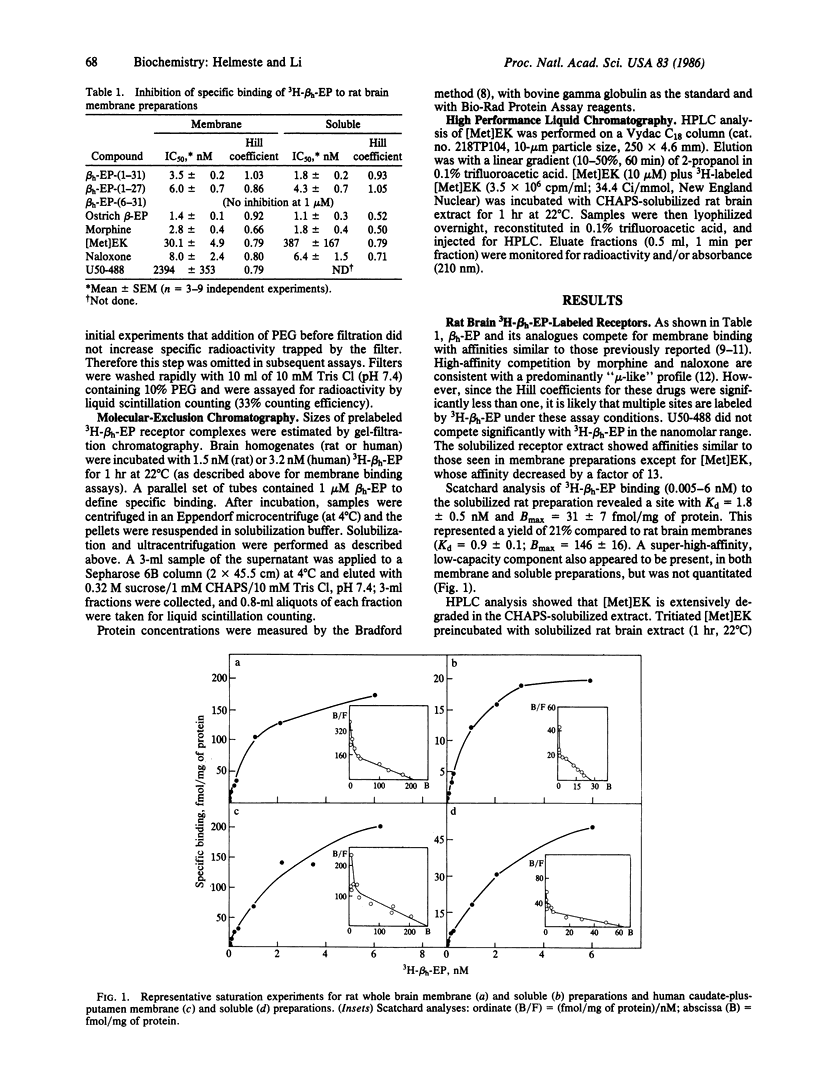
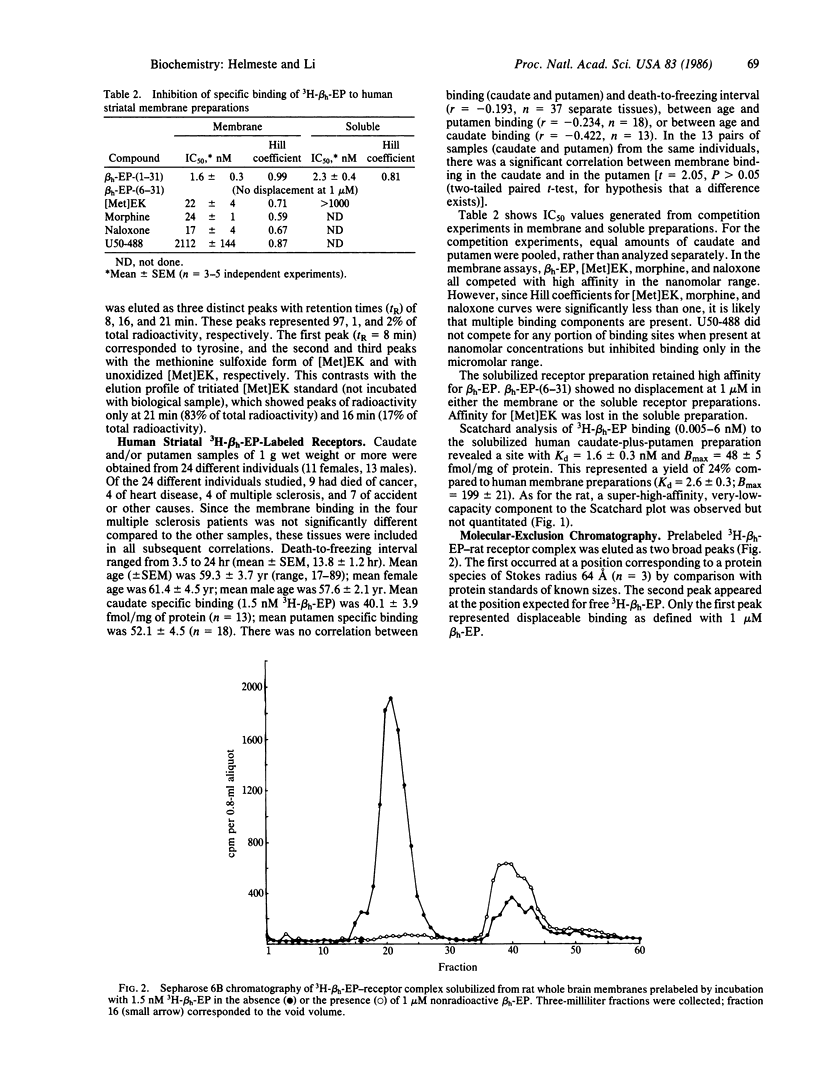
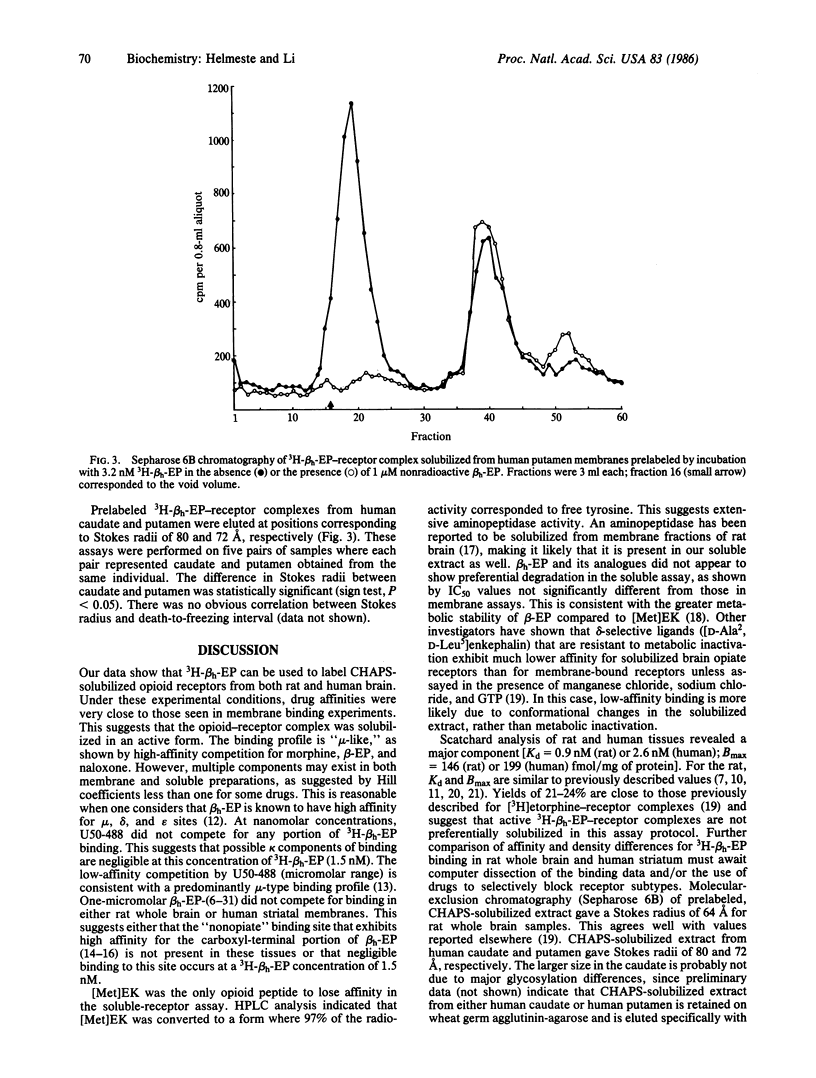
Abstract
Opioid receptors have been solubilized from human striatal and rat whole-brain membranes by use of 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS). Tritiated human beta-endorphin (3H-beta h-EP) binding revealed high-affinity competition by morphine, naloxone, and various beta-EP analogues, suggesting predominantly mu-type binding. Lack of high-affinity competition by (+/-)-3,4-dichloro-N-methyl-N-[2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)cyclohexyl]benzeneaceta mide methanesulfonate (U50-488, Upjohn) indicated that kappa sites were not labeled by 3H-beta h-EP under these conditions. Affinities were similar in both soluble and membrane preparations except for [Met]enkephalin, which appears to be rapidly degraded by the solubilized extract. Size differences between human and rat solubilized 3H-beta h-EP-receptor complexes were revealed by exclusion chromatography.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akil H., Hewlett W. A., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. Binding of 3H-beta-endorphin to rat brain membranes: characterization of opiate properties and interaction with ACTH. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 30;64(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T., Zukin R. S. Solubilization and preliminary characterization of mu and kappa opiate receptor subtypes from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;24(2):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara P., Houghten R., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in the rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):786–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91847-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Snyder S. H. Two distinct enkephalinases: solubilization, partial purification and separation from angiotensin converting enzyme. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 10;25(24-25):2065–2070. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Nicolas P., Li C. H. Characterization of beta-endorphin binding protein (receptor) from rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6494–6496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland L. M. A nondenaturing zwitterionic detergent for membrane biochemistry: design and synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6368–6370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Johnson N., Pasternak G. W. [3H]-beta-endorphin binding in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1984 Oct;4(10):2460–2465. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-10-02460.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Li C. H. Preparation and properties of tritiated human beta-endorphin with high specific radioactivity. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Nov;12(5):325–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Goldstein A. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Properties and localization of beta-endorphin receptor in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. Synthesis and analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin. J Med Chem. 1977 Mar;20(3):325–328. doi: 10.1021/jm00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks N., Grynabaum A., Neidle A. On the degradation of enkephalins and endorphins by rat and mouse brain extracts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1552–1559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90619-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Gomez S., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin: thermodynamics of the binding reaction with rat brain membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Aug;217(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Bhakdi S., Teschemacher H. Specific non-opiate binding sites for human beta-endorphin on the terminal complex of human complement. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):572–574. doi: 10.1038/296572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal M., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin: demonstration of binding sites in three human neuroblastoma cell lines specific for the COOH-terminal segment of the human hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):873–878. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal M., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characterization of binding sites specific for the human hormone in human glioblastoma SF126 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2921–2923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



