Abstract
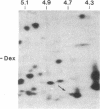
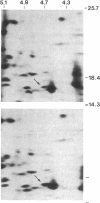
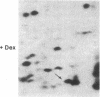
Glucocorticoids are known to rapidly induce four proteins in rat thymus cells in time to account for the earliest known metabolic hormone effects. We report here an additional protein, which we refer to as "glucocortin" (Mr = 17,000, pI = 4.7). It is of special interest since it is the only protein rapidly induced in all of the glucocorticoid target cells we have examined. We have characterized the kinetics of glucocortin mRNA induction in isolated thymus cells. Giant two-dimensional gel electrophoretic analysis of in vitro translation products reveals a 2-fold increase in the level of translatable mRNA within 15 min of dexamethasone addition, with maximal stimulation (approximately equal to 7-fold) by 45 min. Cycloheximide does not reduce the hormone-mediated increase in glucocortin mRNA, suggesting that the induction represents a primary response to glucocorticoids. This protein is induced by dexamethasone in a dose-dependent manner, with maximal induction at 10(-6) M and partial inductions at concentrations as low as 10(-10) M. It is strongly induced by cortisol at 10(-6) M, but it is not induced by estradiol or testosterone or by thyroid hormone, even at concentrations as high as 10(-6) M. Deoxycorticosterone has no effect at 10(-8) M but does generate a half-maximal effect at 10(-6) M, a finding consistent with its status as a partial glucocorticoid agonist. In summary, glucocortin appears to be a primary glucocorticoid-induced protein that represents the most rapid induction so far detected, and it appears to be the only one that may be common to all glucocorticoid target cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Firestone G. L., Burgess T. L., Gross K. W., Yamamoto K. R., Held W. A. Dexamethasone regulation of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and other acute phase reactants in rat liver and hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):563–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert R. A., Amatruda J. M., Young D. A. Changes in the expression of hepatocyte protein gene-products associated with adaptation of cells to primary culture. Clin Chem. 1984 Dec;30(12 Pt 1):2053–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert R. A., Amatruda J. M., Young D. A. The hepatic glucocorticoid domain: evidence for early and late hormone-mediated changes in the synthesis of individual protein gene products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 3;826(1):49–66. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(85)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLap L., Feigelson P. Effect of cycloheximide on the induction of tryptophan oxygenase mRNA by hydrocortisone in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 15;82(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90588-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernest M. J., Chen C. L., Feigelson P. Induction of tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis in isolated liver cell suspensions. Absolute dependence of induction on glucocorticoids and glucagon or cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6783–6791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Young D. A. An in vitro effect of physiological levels of cortisol and related steroids on the structural integrity of the nucleus in rat thymic lymphocytes as measured by resistance to lysis. J Steroid Biochem. 1974 Oct;5(6):587–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(74)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan C., Young D. A., Munck A. Time course of early events in the action of glucocorticoids on rat thymus cells in vitro. Synthesis and turnover of a hypothetical cortisol-induced protein inhibition of glucose metabolism and of a presumed ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2922–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Jacot M. M. Coordinate induction of several mRNA species in rat kidney during glucocorticoid treatment. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7068–7076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Herschman H. R. Dexamethasone stimulation of metallothionein synthesis in HeLa cell cultures. Science. 1979 Apr 13;204(4389):176–177. doi: 10.1126/science.432639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Herschman H. R., Weinstein D. Primary induction of metallothionein by dexamethasone in culture rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):1052–1069. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90808-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson R., Iwata K., Klagsbrun M., Young D. A. Growth factor- and dexamethasone-induced proteins in Swiss 3T3 cells. Relationship to DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8056–8063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. T., Nordeen S. K., Young D. A. Effects of fasting and insulin administration on polyribosome formation in rat epididymal fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6330–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maytin E. V., Colbert R. A., Young D. A. Early heat shock proteins in primary thymocytes. Evidence for transcriptional and translational regulation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2384–2392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maytin E. V., Young D. A. Separate glucocorticoid, heavy metal, and heat shock domains in thymic lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12718–12722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S. The induction of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA by estrogen and progesterone in chick oviduct explant cultures. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher K. M., Young D. A., Munck A. Evidence for irreversible, actinomycin D-sensitive, and temperature-sensitive steps following binding of cortisol to glucocorticoid receptors and preceding effects on glucose metabolism in rat thymus cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):654–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Brinck-Johnsen T. Specific and nonspecific physicochemical interactions of glucocorticoids and related steroids with rat thymus cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5556–5565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A. Metabolic site and time course of cortisol action on glucose uptake, lactic acid output, and glucose 6-phosphate levels of rat thymus cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1039–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols N. R., Khalid B. A., Fuller P. J., Rayson B. M., Funder J. W. A common 43 K protein induced by glucocorticoids in a variety of cells and tissues. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Sep;37(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson M. L., Young D. A. Effect of glucocorticoid hormones in vitro on the structural integrity of nuclei in corticosteroid-sensitive and -resistant lines of lymphosarcoma P1798. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3673–3680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Young D. A. Glucocorticoid action on rat thymic lymphocytes. Experiments utilizing adenosine to support cellular metabolism lead to a reassessment of catabolic hormone actions. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7295–7303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Moore P. B., Mulvihill E. R. A significant lag in the induction of ovalbumin messenger RNA by steroid hormones: a receptor translocation hypothesis. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):557–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Methylmercury hydroxide enhancement of translation and transcription of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA's. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7636–7642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Glucocorticoid-stimulated accumulation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: increased rate of synthesis of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tomkins G. M. Relation of steroid structure to enzyme induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug 28;52(1):57–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmit J. P., Rousseau G. G. Structure-activity relationships for glucocorticoids-II. Theoretical approach of molecular structures based on energy optimisation of a Westheimer model. J Steroid Biochem. 1977 Sep;8(9):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(77)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Taylor J. M., Ringold G. M. Glucocorticoid-mediated induction of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: evidence for hormone-regulated RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voris B. P., Young D. A. Glucocorticoid-induced proteins in rat thymus cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11319–11329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voris B. P., Young D. A. Very-high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of proteins using giant gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 15;104(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A. Advantages of separations on "giant" two-dimensional gels for detection of physiologically relevant changes in the expression of protein gene-products. Clin Chem. 1984 Dec;30(12 Pt 1):2104–2108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Barnard T., Mendelsohn S., Giddings S. An early cordycepin-sensitive event in the action of glucocorticoid hormones on rat thymus cells in vitro: evidence that synthesis of new mRNA initiates the earliest metabolic effects of steroid hormones. Endocr Res Commun. 1974;1(1):63–72. doi: 10.3109/07435807409053816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A. Glucocorticoid action on rat thymus cells. II. Interrelationships between ribonucleic acid and protein metabolism and between cortisol and substrate effects on these metabolic parameters in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2747–2752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A. Glucocorticoid action on rat thymus cells. Interrelationships between carbohydrate, protein, and adenine nucleotide metabolism and cortisol effects on these functions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2210–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Voris B. P., Maytin E. V., Colbert R. A. Very-high-resolution two-dimensional electrophoretic separation of proteins on giant gels. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:190–214. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. A proposed model for the glucocorticoidal regulation of rat hepatic ribosomal RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):754–760. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]