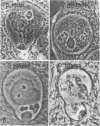
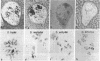
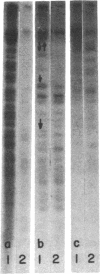
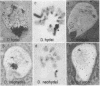
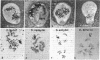
Abstract
The molecular evolution and patterns of conservation of clones from four Y chromosome lampbrush loops of Drosophila hydei were investigated. Each loop contains a discrete family of transcribed repeats that are only slightly conserved even in the hydei subgroup species. Sequencing of clones from the four D. hydei loops indicates that all transcribed repeats evolved from A+T-rich elements of the genome. Evidence is presented that suggests a Y-specific family evolved as a result of the transposition of repeated sequences from an autosomal site to the Y chromosome with the concomitant acquisition of transcriptional activity and loss of non-Y sequences. The results support a structural role for the loops in shaping a spermatocyte-specific nuclear organization. Transcribed heterochomatic sequences could play a similar role in nuclear organization in many cell types.
Keywords: functional repeats, nonconserved sequences, evolutionary implications
Full text
PDF
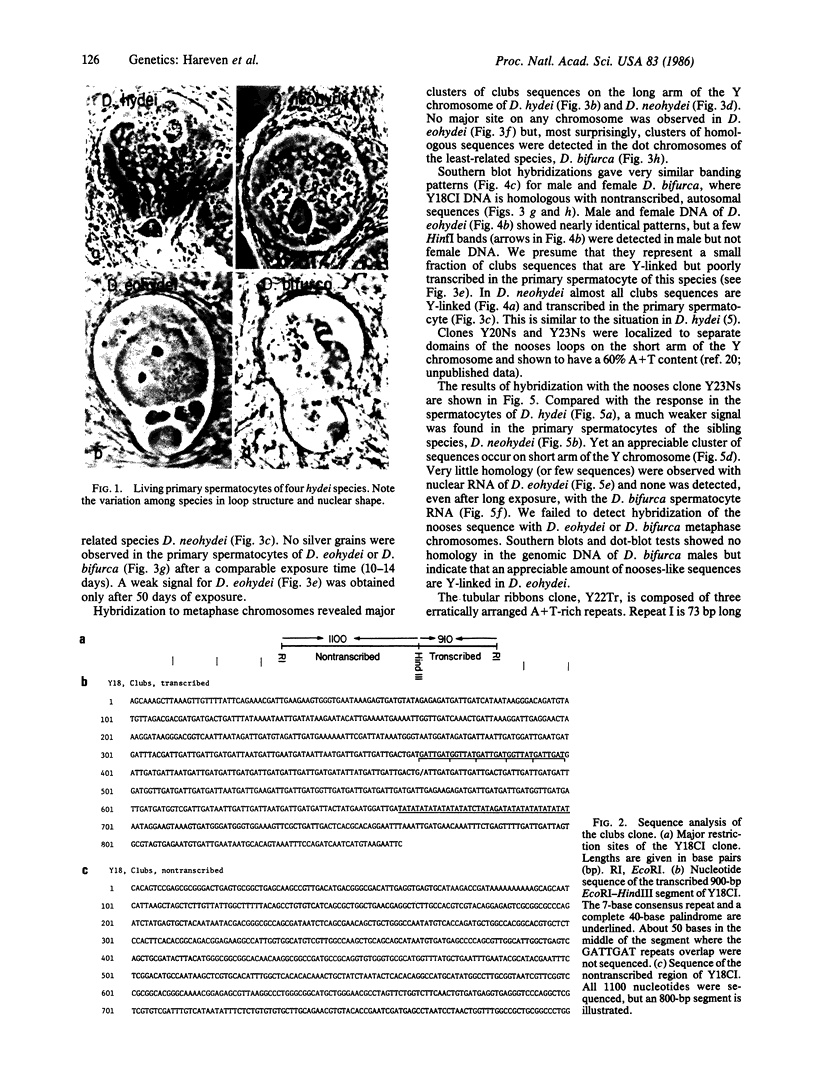
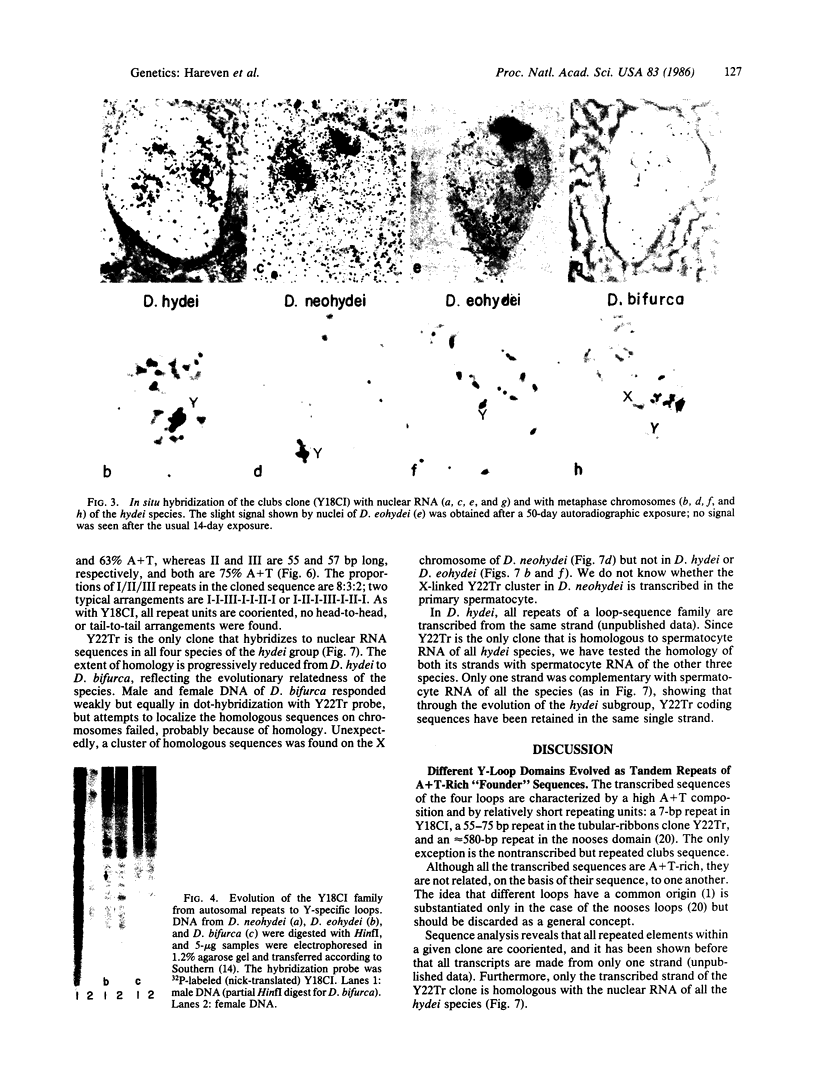
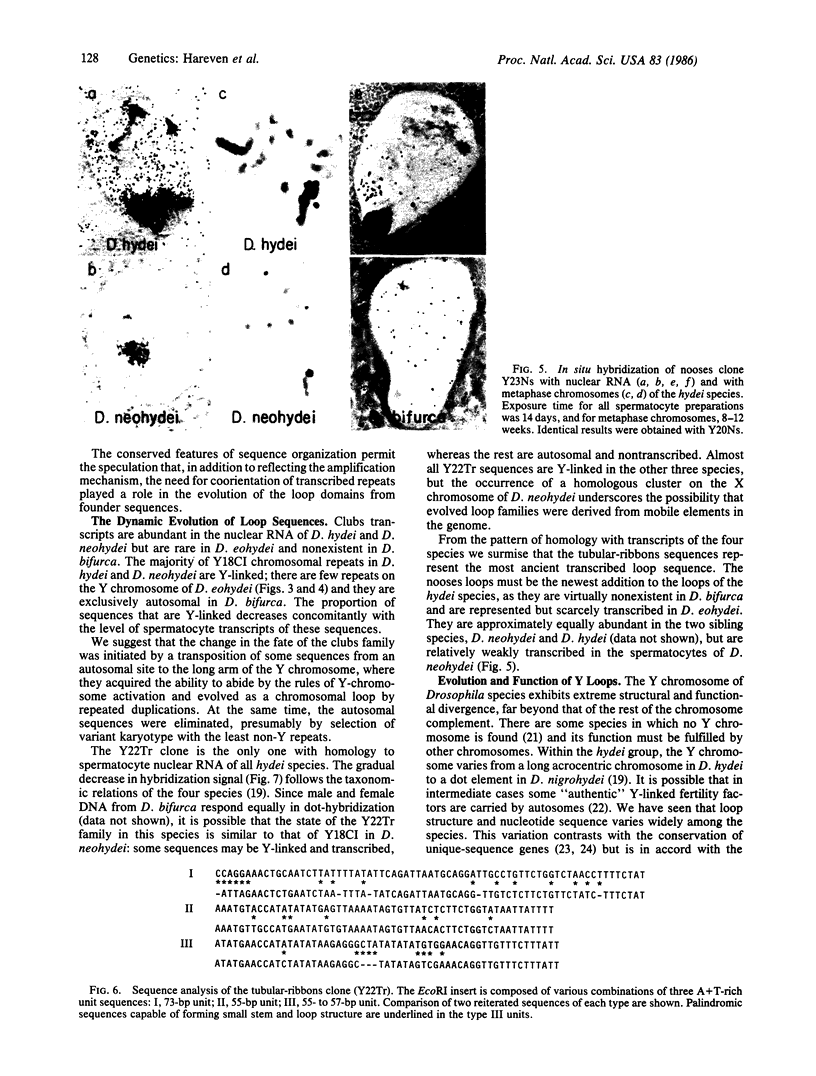
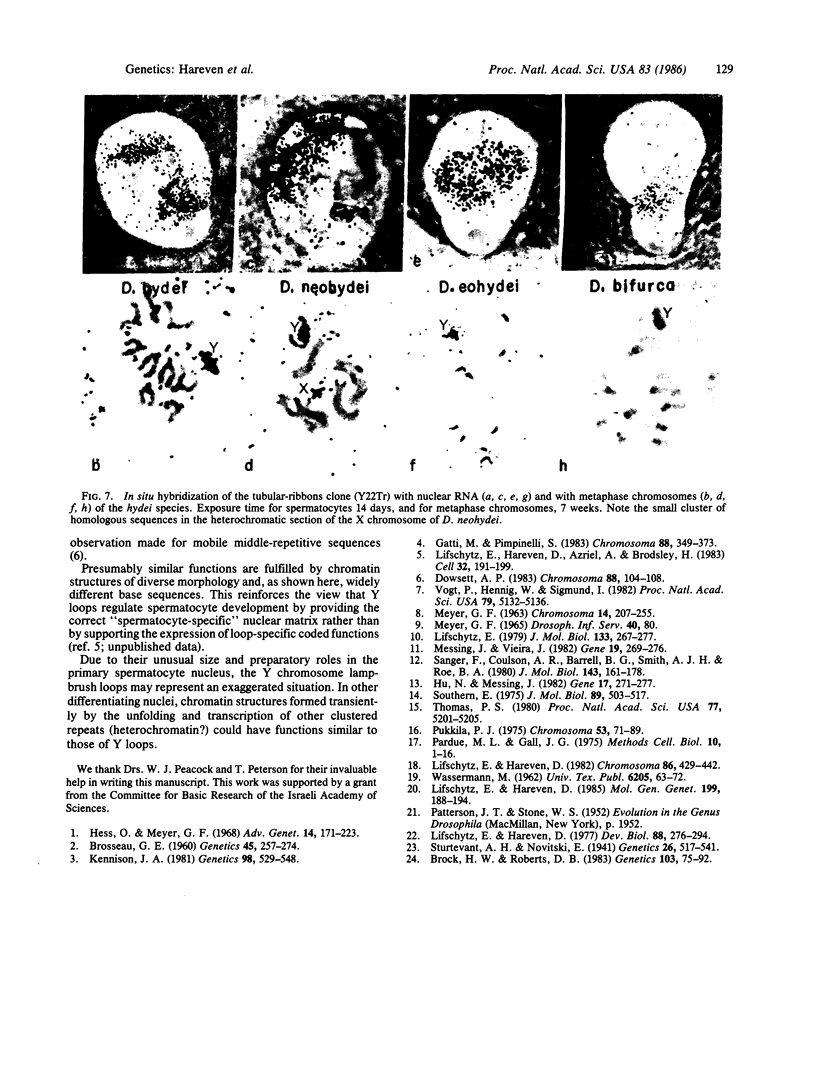
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock H. W., Roberts D. B. Location of the LSP-1 Genes in Drosophila Species by IN SITU Hybridization. Genetics. 1983 Jan;103(1):75–92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosseau G E. Genetic Analysis of the Male Fertility Factors on the Y Chromosome of Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1960 Mar;45(3):257–274. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowsett A. P. Closely related species of Drosophila can contain different libraries of middle repetitive DNA sequences. Chromosoma. 1983;88(2):104–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00327329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess O., Meyer G. F. Genetic activities of the Y chromosome in Drosophila during spermatogenesis. Adv Genet. 1968;14:171–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60427-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennison J. A. The Genetic and Cytological Organization of the Y Chromosome of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):529–548. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E. A procedure for the cloning and identification of Y-specific middle repetitive sequences in Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 15;133(2):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Hareven D., Azriel A., Brodsly H. DNA clones and RNA transcripts of four lampbrush loops from the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Hareven D. Gene expression and the control of spermatid morphogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):276–294. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Hareven D. Heterochromatin markers: a search for heterochromatin specific middle repetitive sequences in Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1982;86(4):429–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00330119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukkila P. J. Identification of the lampbrush chromosome loops which transcribe 5S ribosomal RNA in Notophthalmus (Triturus) viridescens. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 20;53(1):71–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00329391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A H, Novitski E. The Homologies of the Chromosome Elements in the Genus Drosophila. Genetics. 1941 Sep;26(5):517–541. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P., Hennig W., Siegmund I. Identification of cloned Y chromosomal DNA sequences from a lampbrush loop of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5132–5136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]