Abstract
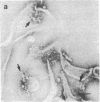
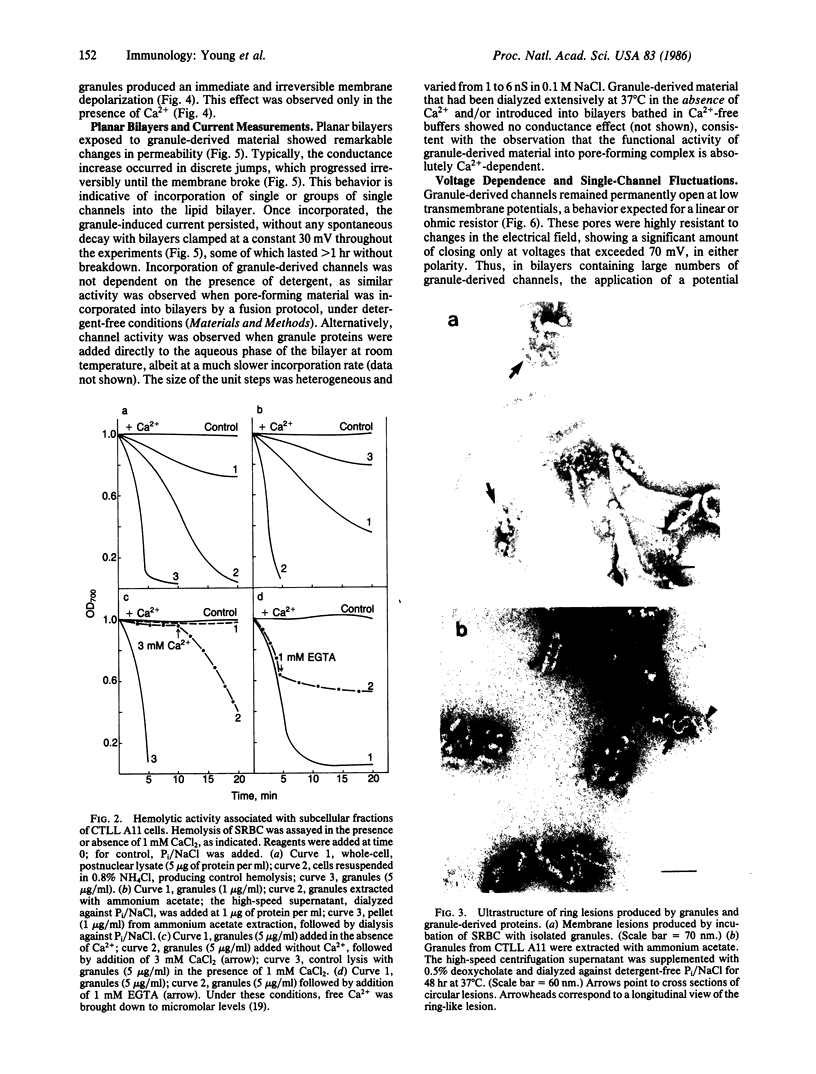
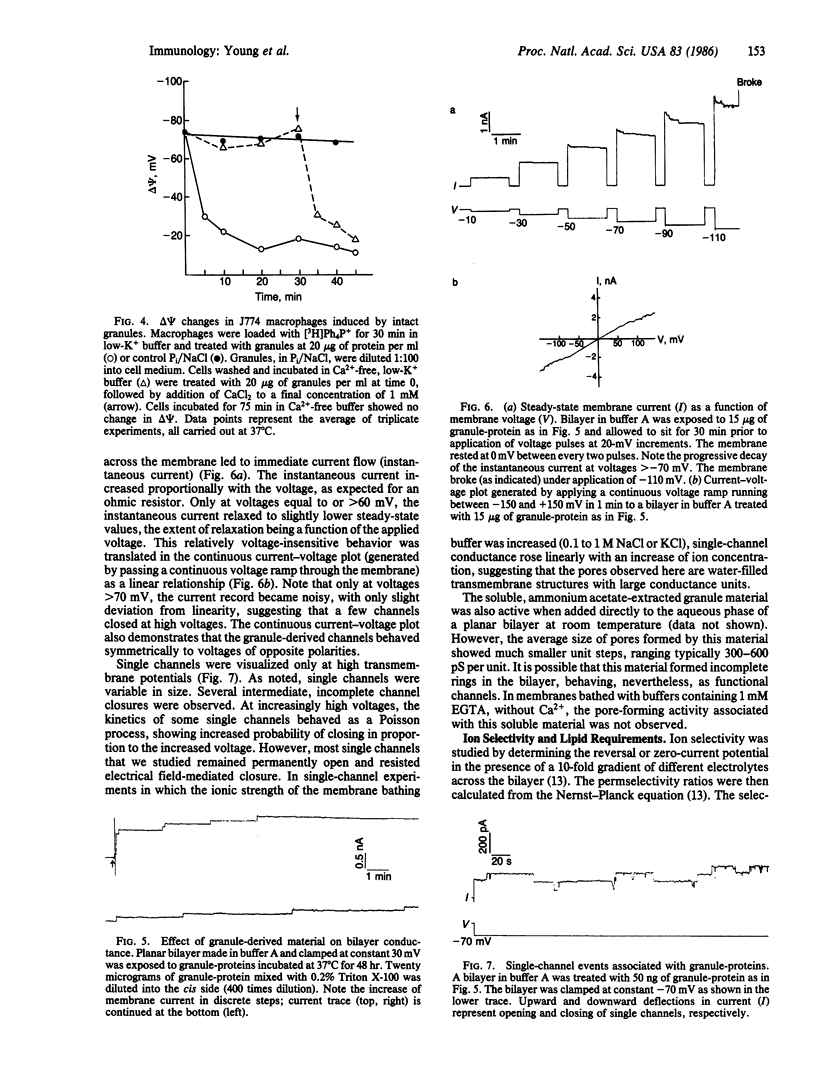
Lymphocyte granules from cytotoxic T-lymphocyte lines A2, A11, and R8 were enriched by subcellular fractionation using a Percoll gradient. Granule-enriched fractions showed potent hemolytic activity in the presence of Ca2+. Isolated granules induced rapid Ca2+-dependent membrane depolarization of J774 macrophage-like cells. When tested in planar bilayers, granules induced the formation of Ca2+-dependent functional ion channels of large conductance steps of 1-6 nS in 0.1 M NaCl. Granule-induced channels were resistant to closing by an increase in transmembrane potential, with few channels shifting to the closed state only at voltages of greater than 70 mV, following a Poisson process. These channels showed poor ion selectivity and were permeable to all monovalent and divalent ions (K+, Na+, Li+, Cl-, Ca2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Ba2+). Ultrastructural examination of soluble granule proteins incubated for 48 hr at 37 degrees C in the presence of Ca2+ revealed ring-like structures of 150-200 A. Structural and functional channel formation may be involved in cytolysis induced by cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borregaard N., Heiple J. M., Simons E. R., Clark R. A. Subcellular localization of the b-cytochrome component of the human neutrophil microbicidal oxidase: translocation during activation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):52–61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Podack E. R. Cytolysis by H-2-specific T killer cells. Assembly of tubular complexes on target membranes. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1483–1495. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R., Deteix P., Simone C. B., Henkart P. Electron microscopic demonstration of lesions in target cell membranes associated with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):554–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Alvarez O. Voltage-dependent channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):77–150. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Henkart M. P., Reynolds C. W., Henkart P. A. Purification and properties of cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat LGL tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino M. A., Obata Y., Stockert E., Oettgen H. F. Characterization of interleukin 2-dependent cytotoxic T-cell clones: specificity, cell surface phenotype, and susceptibility to blocking by Lyt antisera. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):572–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Dennert G. Assembly of two types of tubules with putative cytolytic function by cloned natural killer cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):442–445. doi: 10.1038/302442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschopp J. Circular polymerization of the ninth component of complement. Ring closure of the tubular complex confers resistance to detergent dissociation and to proteolytic degradation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15204–15212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Podack E. R. Formation of transmembrane tubules by spontaneous polymerization of the hydrophilic complement protein C9. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):534–538. doi: 10.1038/298534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young G. P., Young J. D., Deshpande A. K., Goldstein M., Koide S. S., Cohn Z. A. A Ca2+-activated channel from Xenopus laevis oocyte membranes reconstituted into planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5155–5159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Blake M., Mauro A., Cohn Z. A. Properties of the major outer membrane protein from Neisseria gonorrhoeae incorporated into model lipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3831–3835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Kaback H. R., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage membrane potential changes associated with gamma 2b/gamma 1 Fc receptor-ligand binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1357–1361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Young T. M., Mauro A., Cohn Z. A. Role for mouse macrophage IgG Fc receptor as ligand-dependent ion channel. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):186–189. doi: 10.1038/306186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Young T. M., Lu L. P., Unkeless J. C., Cohn Z. A. Characterization of a membrane pore-forming protein from Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1677–1690. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young T. M., Young J. D. Protein-mediated intermembrane contact facilitates fusion of lipid vesicles with planar bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 5;775(3):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]