Abstract
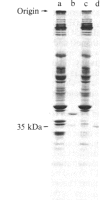
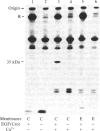
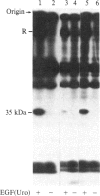
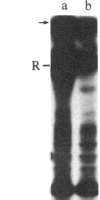
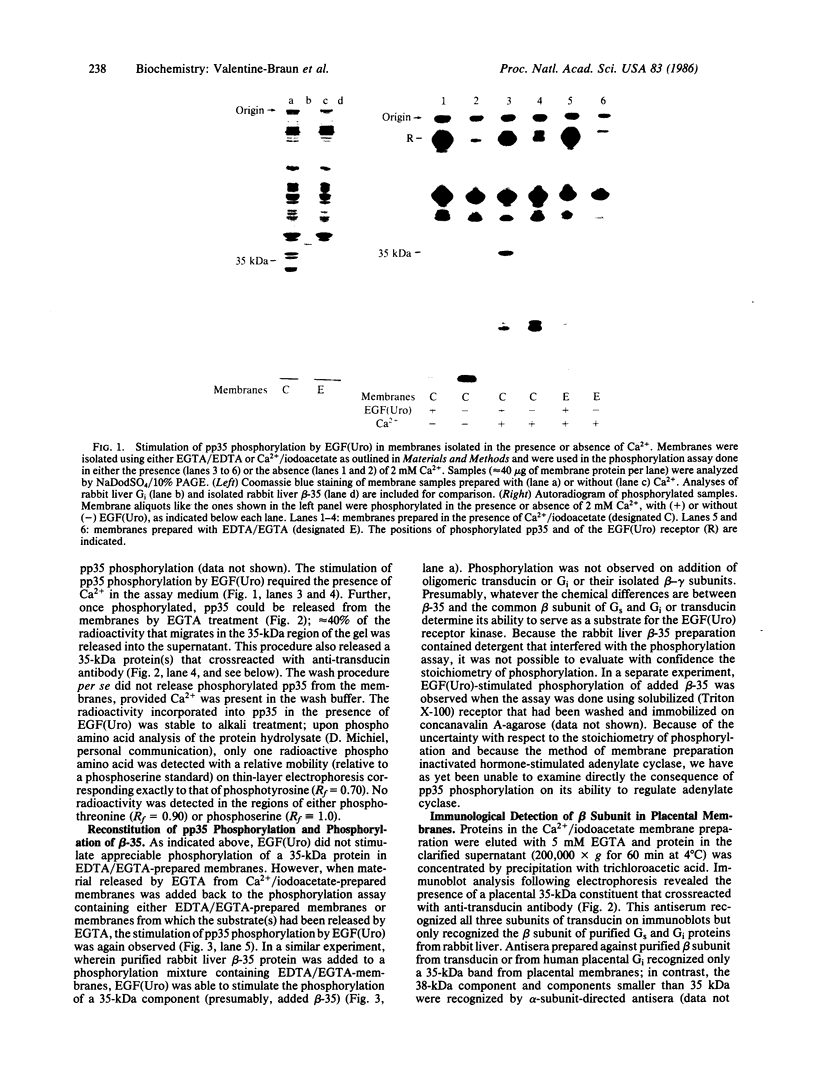
We have identified a component of about 35 kDa (pp35), present in human placental membrane preparations, that is a substrate for epidermal growth factor (urogastrone) [EGF(Uro)]-mediated phosphorylation. The EGF(Uro)-stimulated phosphorylation of pp35 was calcium-dependent and was markedly enhanced in membranes prepared in the presence (but not in the absence) of calcium. The phosphate incorporated into pp35 in the presence of EGF(Uro) was alkali-stable and was present as O4-phosphotyrosine. Under identical conditions, insulin did not stimulate pp35 phosphorylation. Either in its native or in its phosphorylated form, pp35 could be released from the membranes in the presence of calcium-chelating agents (EDTA/EGTA); and EGF(Uro)-stimulated phosphorylation was reconstituted by adding back EDTA/EGTA eluates to EDTA/EGTA-washed membranes in the presence of calcium. The properties of pp35 were similar if not identical to those of beta-35, a 35-kDa polypeptide similar to the beta subunit of the guanine nucleotide-binding oligomers that stimulate (Gs) or inhibit (Gi) the adenylate cyclase system. As with pp35, EGF(Uro)-stimulated phosphorylation of isolated rabbit liver beta-35 was observed in a reconstituted system using either EDTA/EGTA-washed placental membranes or solubilized EGF(Uro) receptor immobilized on concanavalin A-agarose. In contrast, the addition of beta subunits derived from rabbit liver Gi or bovine transducin did not result in phosphorylation of a 35-kDa substrate in the reconstituted system. Further, a 35-kDa protein released from placental membranes crossreacted with an anti-transducin antibody that can recognize the beta subunit isolated from a variety of sources. We conclude that the human placental pp35 substrate likely represents the placental equivalent of the beta-35 protein. Our data point to a possible link between those receptors involved in growth-factor action and the regulatory systems that utilize GTP-binding proteins as transducing elements.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Chen L. B. Detection of phosphotyrosine-containing 34,000-dalton protein in the framework of cells transformed with Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Raines E., Ross R., Hunter T. Similar effects of platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor on the phosphorylation of tyrosine in cellular proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Four different classes of retroviruses induce phosphorylation of tyrosines present in similar cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 May;1(5):394–407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Identification and characterization of cellular targets for tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1108–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Similarities and differences between the effects of epidermal growth factor and Rous sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):878–883. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Reiss N. A., Schwartz R. J., Hunter T. Three glycolytic enzymes are phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):218–223. doi: 10.1038/302218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S., Ralston R., Alitalo K., Bishop J. M. Subcellular location of an abundant substrate (p36) for tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):340–350. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Calcium-dependent conformational changes in the 36-kDa subunit of intestinal protein I related to the cellular 36-kDa target of Rous sarcoma virus tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1688–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Edelman G. M. Comparison of the 34,000-Da pp60src substrate and a 38,000-Da phosphoprotein identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8497–8502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock R. A., Hollenberg M. D. Characterization of the receptor for epidermal growth factor-urogastrone in human placenta membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10731–10736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Northup J. K., Bokoch G. M., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and guanine nucleotide-dependent hormonal inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3578–3585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Tanaka A., Kaji A. In vitro phosphorylation of the 36K protein in extract from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3053–3058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light- and GTP-regulated interaction of GTPase and other proteins with bovine photoreceptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):587–589. doi: 10.1038/283587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution of the activated 45,000-dalton (alpha) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11369–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution, activity, and properties of the 35,000-dalton (beta) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11361–11368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]