Abstract
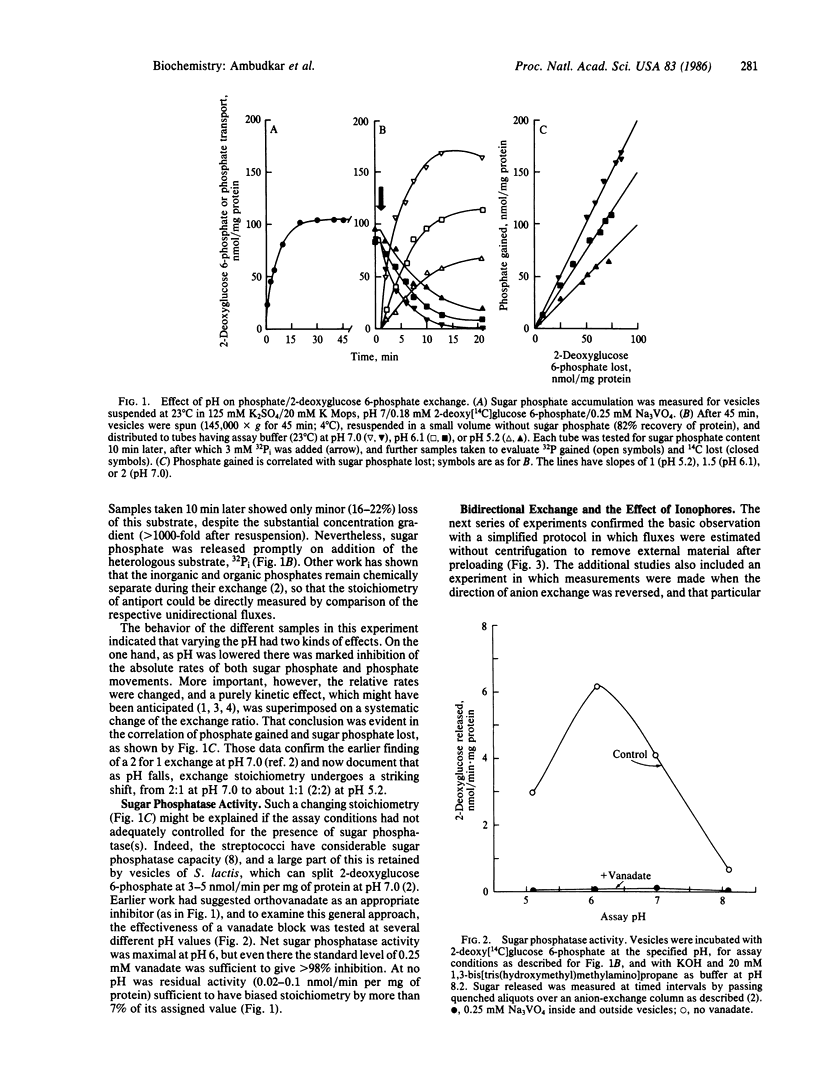
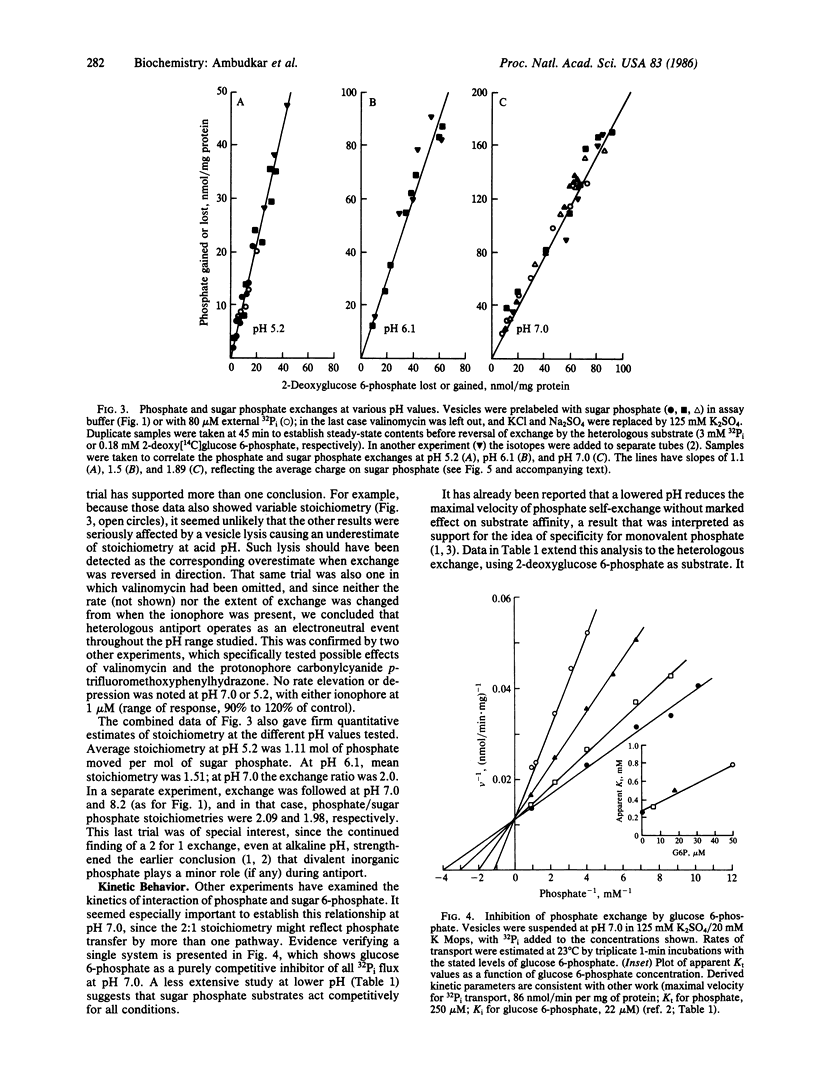
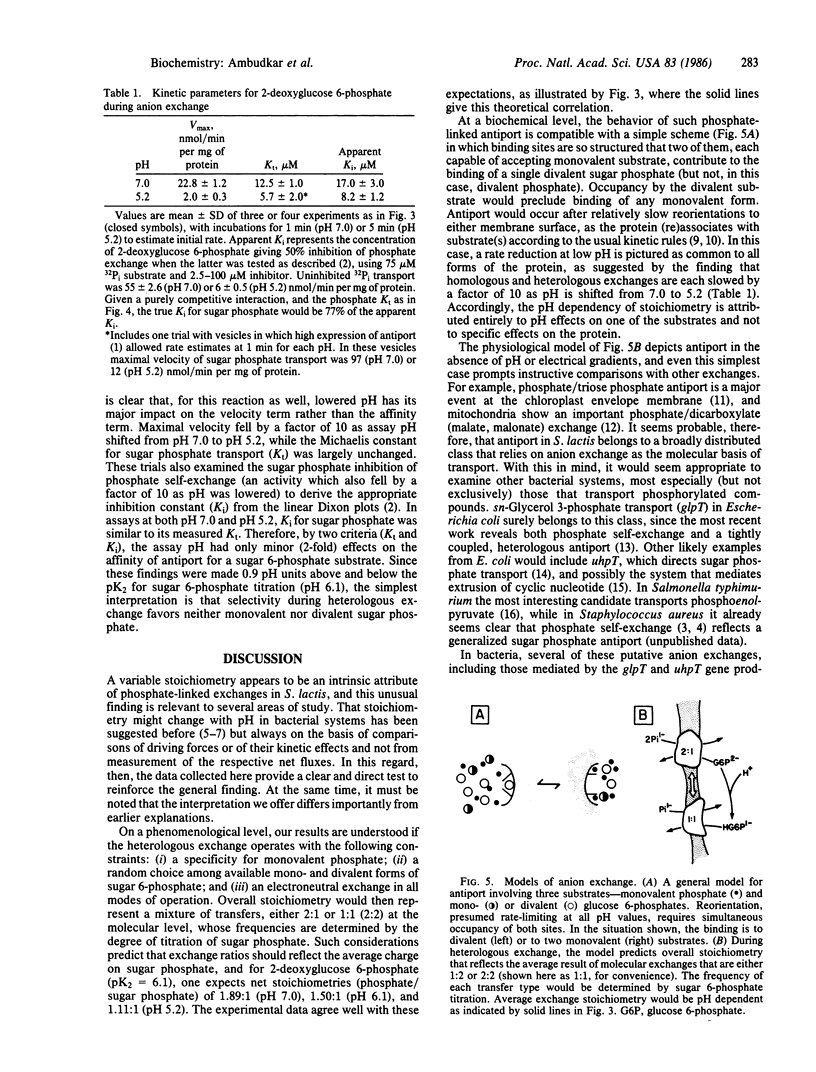
Phosphate/2-deoxyglucose 6-phosphate antiport in Streptococcus lactis showed an exchange stoichiometry that varied over a 2-fold range when assay pH was shifted between pH 8.2 and pH 5.2. At pH 7.0 and above, 2 mol of phosphate moved per mol of sugar phosphate; at pH 6.1 the ratio was 1.5:1, while at pH 5.2 the overall stoichiometry fell to 1.1:1. This pattern was not affected by valinomycin in potassium-based media, nor could variable stoichiometry be attributed to altered hydrolysis of the sugar phosphate substrate. In kinetic studies at pH 7.0 or pH 5.2, sugar 6-phosphate was a competitive inhibitor of phosphate transport, indicating operation of a single system. Parallel tests showed that the affinity of antiport for its sugar 6-phosphate substrate was insensitive to pH in this range. Overall, such results suggest a neutral exchange that has specificity for monovalent phosphate but that selects randomly among the available mono- and divalent sugar 6-phosphates. A simple model that shows this behavior suggests a mechanistic role for anion exchange in bacterial transport of sugar phosphate or other organic anions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambudkar S. V., Maloney P. C. Characterization of phosphate:hexose 6-phosphate antiport in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12576–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz G. W., Jr The hexose phosphate transport system of Escherichia coli. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1976;44:237–259. doi: 10.1002/9780470122891.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvin C. M., Hardy C. M., Rosenberg H. Pi exchange mediated by the GlpT-dependent sn-glycerol-3-phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1054-1058.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliege R., Flügge U. I., Werdan K., Heldt H. W. Specific transport of inorganic phosphate, 3-phosphoglycerate and triosephosphates across the inner membrane of the envelope in spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 10;502(2):232–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI S., KOCH J. P., LIN E. C. ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF L-ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:3098–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M., Hackenberg H., Krämer R., Lin C. S., Aquila H. Two transport proteins from mitochondria: I. Mechanistic aspects of asymmetry of the ADP, ATP translocator, II. The uncoupling protein of brown adipose tissue mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;358:83–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Winkler H. H., Wood D. O. Cloning and expression of the Rickettsia prowazekii ADP/ATP translocator in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaNoue K. F., Schoolwerth A. C. Metabolite transport in mitochondria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:871–922. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. M. Paths of phosphate transfer in Micrococcus pyogenes: phosphate turnover in nucleic acids and other fractions. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):257–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Transport of phosphate across the osmotic barrier of Micrococcus pyogenes; specificity and kinetics. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):73–82. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Ambudkar S. V., Thomas J., Schiller L. Phosphate/hexose 6-phosphate antiport in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.238-245.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Translocations through natural membranes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:33–87. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter K., Chaloner-Larsson G., Yamazaki H. Abnormally high rate of cyclic AMP excretion from an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in cyclic AMP receptor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):379–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90941-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. pH-dependent changes in proton:substrate stoichiometries during active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4270–4275. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The driving force for proton(s) metabolites cotransport in bacterial cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80493-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Wentzel D. L., Feucht B. U., Judice J. J. A transport system for phosphoenolpyruvate, 2-phosphoglycerate, and 3-phosphoglycerate in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5089–5096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Brink B., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient by lactate efflux in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Chassy B. M. Intracellular hexose-6-phosphate:phosphohydrolase from Streptococcus lactis: purification, properties, and function. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):70–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.70-80.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



