Abstract
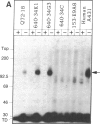
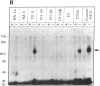
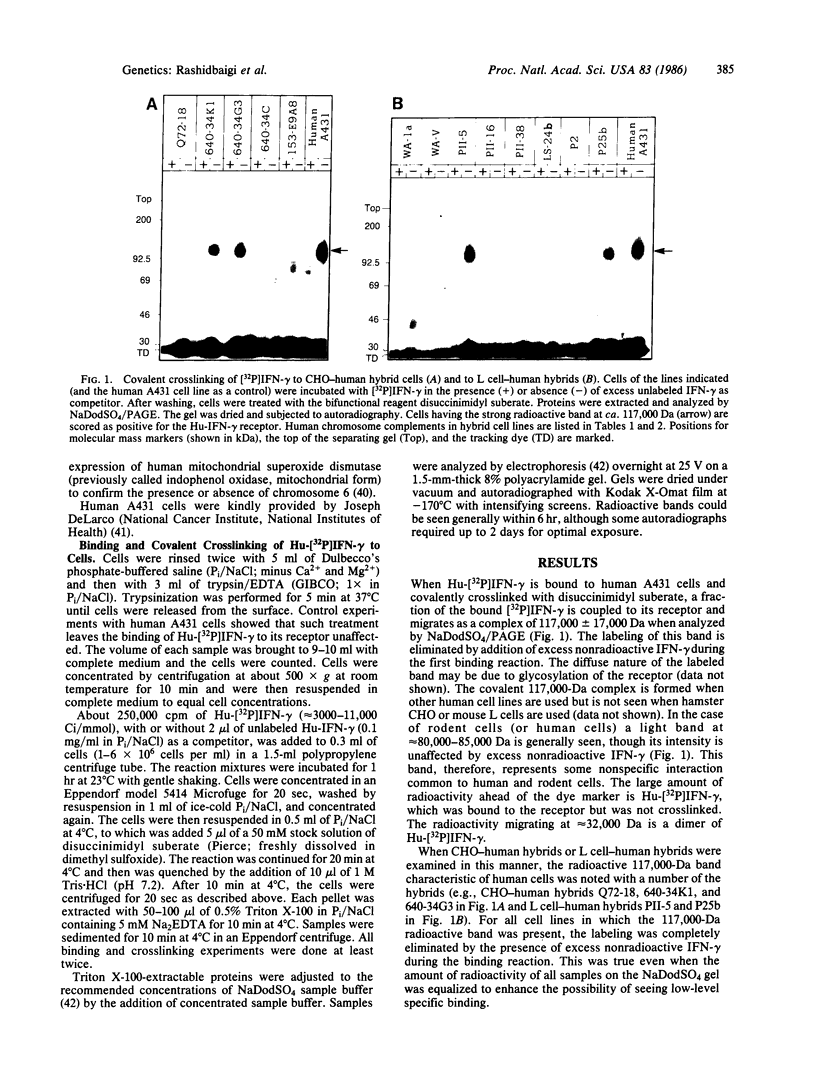
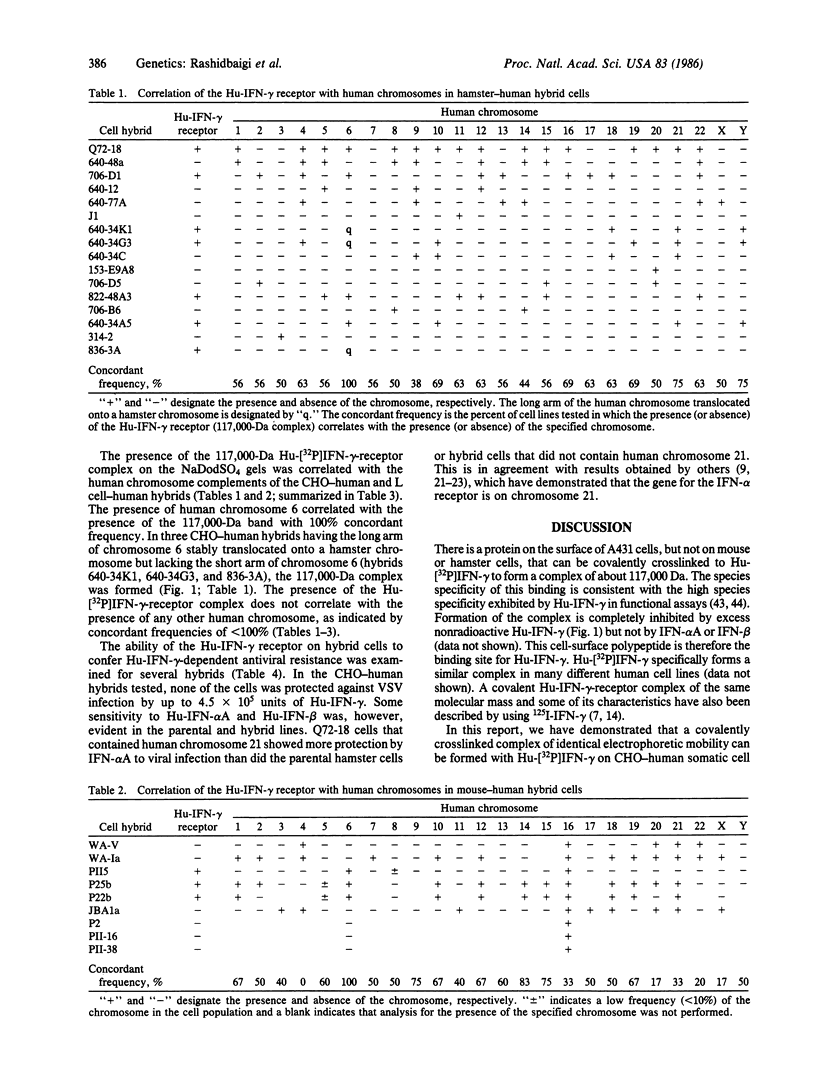
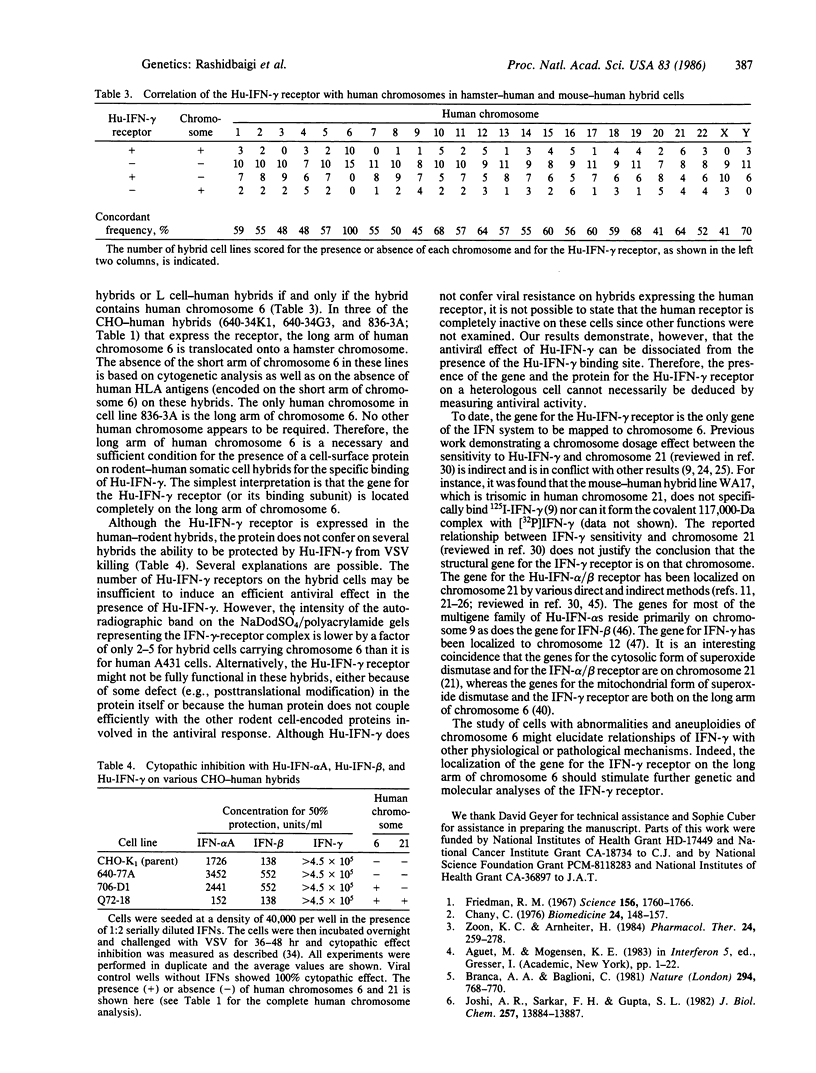
When 32P-labeled human recombinant immune interferon gamma (Hu-[32P]IFN-gamma) is crosslinked to human cells with disuccinimidyl suberate, a complex with a molecular size of approximately equal to 117,000 Da was identified by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The formation of this complex is inhibited when the binding is performed in the presence of excess unlabeled Hu-IFN-gamma. The specific formation of the 117,000-Da complex is not observed in mouse L cells or Chinese hamster ovary cells. This complex shows all of the criteria that identify it as the Hu-IFN-gamma receptor or its binding subunit. The same complex can be formed following binding and covalent crosslinking of Hu-[32P]IFN-gamma to some hamster-human or mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. The presence of human chromosome 6 in the hybrids is necessary and sufficient for the formation of this complex. More specifically, the long arm of chromosome 6 seems sufficient. Therefore, we have localized the gene for the Hu-IFN-gamma receptor (or its binding subunit) to the long arm of human chromosome 6. The presence of this chromosome in the somatic cell hybrids is not adequate, however, to confer antiviral resistance to the hybrids in the presence of Hu-IFN-gamma.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Mogensen K. E. Interferon receptors. Interferon. 1983;5:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Nagler C. Photoaffinity labeling of an interferon-gamma receptor on the surface of cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):828–833. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Specific binding of 125I-human interferon-gamma to high affinity receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11301–11304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Down-regulation of the interferon receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13197–13200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C. Membrane-bound interferon specific cell receptor system: role in the establishment and amplification of the antiviral state. Biomedicine. 1976 Jun;24(3):148–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creagan R., Tischfield J., Ricciuti F., Ruddle F. H. Chromosome assignments of genes in man using mouse-human somatic cell hybrids: mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (indophenol oxidase-B, tetrameric) to chromosome 6. Humangenetik. 1973 Dec 10;20(3):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00385731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley M., Billiau A. Responsiveness of human cells trisomic for chromosome 21 to the antiviral action of human immune interferon. Antiviral Res. 1982 May;2(1-2):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(82)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Cheroutre H., Taya Y., Degrave W., Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human immune interferon cDNA and its expression in eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2487–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid P., Mogensen K. E. Isolated interferon alpha-receptor complexes stabilized in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., McManus N. H., Epstein L. B., Branca A. A., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Direct evidence that the gene product of the human chromosome 21 locus, IFRC, is the interferon-alpha receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1060–1066. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90629-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Branca A. A., McCandless S., Baglioni C. Characterization of an interferon receptor on human lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3269–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familletti P. C., Rubinstein S., Pestka S. A convenient and rapid cytopathic effect inhibition assay for interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Interferon binding: the first step in establishment of antiviral activity. Science. 1967 Jun 30;156(3783):1760–1761. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3783.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Kao F. T., Taylor R. T. Chromosomal assignment of the gene for folylpolyglutamate synthetase to human chromosome 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;28(3):181–194. doi: 10.1159/000131529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Morse H. G., Kao F. T., Carbone A., Palmer E. Human T-cell receptor alpha-chain genes: location on chromosome 14. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.3919444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Patterson D., Kao F. T. Assignment of the gene coding for phosphoribosylglycineamide formyltransferase to human chromosome 14. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Jul;7(4):399–409. doi: 10.1007/BF01542985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. R., Sarkar F. H., Gupta S. L. Interferon receptors. Cross-linking of human leukocyte interferon alpha-2 to its receptor on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13884–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Weide L. G., Tischfield J. A. Suppression of vesicular stomatitis virus defective intefering particle generation by a function(s) associated with human chromosome 16. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):946–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.946-952.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman S. J., Faltynek C. R., Baglioni C. Binding of human recombinant 125I-interferon gamma to receptors on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1191–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Shows T. B., Law M. L., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human immune interferon gene is located on chromosome 12. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke E. C., Drummond R. J., Creasey A. A. Binding of 125I-labeled recombinant beta interferon (IFN-beta Ser17) to human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2745–2749. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchansky P., Novick D., Fischer D. G., Rubinstein M. Type I and Type II interferon receptors. J Interferon Res. 1984 Spring;4(2):275–282. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B., Gray P., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes are located on human chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Kung H. F., Pestka S. Characterization of receptors for immune interferon in U937 cells with 32P-labeled human recombinant immune interferon. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8514–8519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin A., Sarkar F. H., Dutkowski R., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human alpha and beta interferon but not for gamma interferon are specified by human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Bash D., Ruddle F. H. Antibodies to a cell-surface component coded by human chromosome 21 inhibit action of interferon. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):139–141. doi: 10.1038/260139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar F. H., Gupta S. L. Interferon receptor interaction. Internalization of interferon alpha 2 and modulation of its receptor on human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):461–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human gamma interferon: binding and crosslinking of 125I-labeled recombinant human gamma interferon to receptors on WISH cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5160–5164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman L. M., Kamarck M. E., Slate D. L., Ruddle F. H., Branca A. W., Baglioni C., Maxwell B. L., Gutterman J., Anderson P., Nagler C. Antibodies to chromosome 21 coded cell surface components block binding of human alpha interferon but not gamma interferon to human cells. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Hobbs D. S., Kung H., Lai C. Y., Pestka S. Purification and characterization of recombinant human leukocyte interferon (IFLrA) with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9750–9754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H. Chromosome 21 and the cell growth inhibitory effect of human interferon preparations. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):141–143. doi: 10.1038/260141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Tischfield J., Ruddle F. H. The linkage of genes for the human interferon-induced antiviral protein and indophenol oxidase-B traits to chromosome G-21. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):317–330. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Zhang Z., Fournier A., Tan Y. H. Characterization of human beta-interferon-binding sites on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):563–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the gene for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase to human chromosome 16 by mouse-human somatic cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):45–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Feinstein S., Gez M., Lazar A., Mizrahi A. Purification and properties of the alpha-interferon receptor of human lymphoblastoid (Namalva) cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13872–13877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. X., De Clercq E., Heremans H., Verhaegen-Lewalle M., Content J. Antiviral and anticellular activities of human and murine type I and type II interferons in human cells monosomic, disomic, and trisomic for chromosome 21. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 May;170(1):103–111. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Arnheiter H. Studies of the interferon receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(2):259–278. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ley M., van Damme J., Claeys H., Weening H., Heine J. W., Billiau A., Vermylen C., de Somer P. Interferon induced in human leukocytes by mitogens: production, partial purification and characterization. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Nov;10(11):877–883. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]