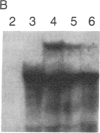
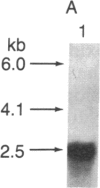
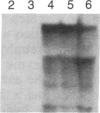
Abstract
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is caused by deficiency of the hepatic enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). A full-length human PAH cDNA sequence has been inserted into pzip-neoSV(X), which is a retroviral vector containing the bacterial neo gene. The recombinant has been transfected into psi 2 cells, which provide synthesis of the retroviral capsid. Recombinant virus was detected in the culture medium of the transfected psi 2 cells, which is capable of transmitting the human PAH gene into mouse NIH 3T3 cells by infection leading to stable incorporation of the recombinant provirus. Infected cells express PAH mRNA, immunoreactive PAH protein, and exhibit pterin-dependent phenylalanine hydroxylase activity. The recombinant virus is also capable of infecting a mouse hepatoma cell line that does not normally synthesize PAH. PAH activity is present in the cellular extracts and the entire hydroxylation system is reconstituted in the hepatoma cells infected with the recombinant viruses. Thus, recombinant viruses containing human PAH cDNA provide a means for introducing functional PAH into mammalian cells of hepatic origin and can potentially be introduced into whole animals as a model for somatic gene therapy for PKU.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Bernhard H. P., Miller R. A., Ruddle F. H. Expression of liver phenotypes in cultured mouse hepatoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Apr;64(4):809–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Papaconstantinou J., Sammons D. W., Brown P. C., Wong E. Y., Esterman A. L., Kang J. Generation and chracterization of variants of mouse hepatoma cells with defects in hepato-specific gene expression. I. Albumin synthesis variants. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Jul;8(4):451–464. doi: 10.1007/BF01538707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Grenett H. E., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Woo S. L. Gene transfer and expression of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.3856322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Prenatal diagnosis of classic phenylketonuria by DNA analysis. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):549–551. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Daiger S. P., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Extensive restriction site polymorphism at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):619–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Eckner R. J., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Expression of a retrovirus encoding human HPRT in mice. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.6377498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. A transmissible retrovirus expressing human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT): gene transfer into cells obtained from humans deficient in HPRT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Ong E. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Infectious and selectable retrovirus containing an inducible rat growth hormone minigene. Science. 1984 Sep 7;225(4666):993–998. doi: 10.1126/science.6089340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson K. J., Beattie W., James R. J., Cotton R. C., Morgan F. J., Woo S. L. Sequence comparison of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase and its cDNA clones. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5671–5675. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson K. J., Chandra T., MacGillivray R. T., Woo S. L. Polysome immunoprecipitation of phenylalanine hydroxylase mRNA from rat liver and cloning of its cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4701–4705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R., Clow C. L. Phenylketonuria: epitome of human biochemical genetics (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 4;303(23):1336–1342. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012043032305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seashore M. R., Friedman E., Novelly R. A., Bapat V. Loss of intellectual function in children with phenylketonuria after relaxation of dietary phenylalanine restriction. Pediatrics. 1985 Feb;75(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Gray D. W., Pater A. A simple purification of phenylalanine hydroxylase by substrate-induced hydrophobic chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11300–11306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis R. C., Jolly D. J., Miller A. D., Plent M. M., Esty A. C., Anderson P. J., Chang H. C., Jones O. W., Seegmiller J. E., Friedmann T. Partial phenotypic correction of human Lesch-Nyhan (hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase-deficient) lymphoblasts with a transmissible retroviral vector. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7842–7849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Chandra T., Robson K. J. Cloned human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene allows prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of classical phenylketonuria. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):151–155. doi: 10.1038/306151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]