Abstract
The D-glucose transporter in the human erythrocyte membranes was photoaffinity-labeled with [3H]cytochalasin B and solubilized with n-octyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (octyl glucoside). [3H]Cytochalasin B-bound proteins were further isolated by using Sephadex G-50 chromatography. The amount of [3H]cytochalasin B associated with the membrane proteins was approximately 10% of the total radioactivity in the octyl glucoside extract. The solubilized photoaffinity-labeled D-glucose transporter was isolated and found to consist of two major peaks by DEAE-Sephacel chromatography. The radioactivity of peak II was considerably greater than that of peak I. The incorporation of [3H]cytochalasin B into both peaks was blocked by the presence of D-glucose during photolysis. With preparative NaDod-SO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the radioactivity of peak I could be released, but that of peak II remained with the D-glucose transporter. These results indicate that [3H]cytochalasin B was covalently bound to the D-glucose transporter only in peak II and that peak II could be generated by the photoaffinity labeling of peak I. However, the D-glucose transport activity was associated only with peak I. These findings suggest that the anionic domain of the D-glucose transporter becomes exposed because of conformational changes of the protein as a result of covalent binding with [3H]cytochalasin B by photoaffinity labeling.
Full text
PDF
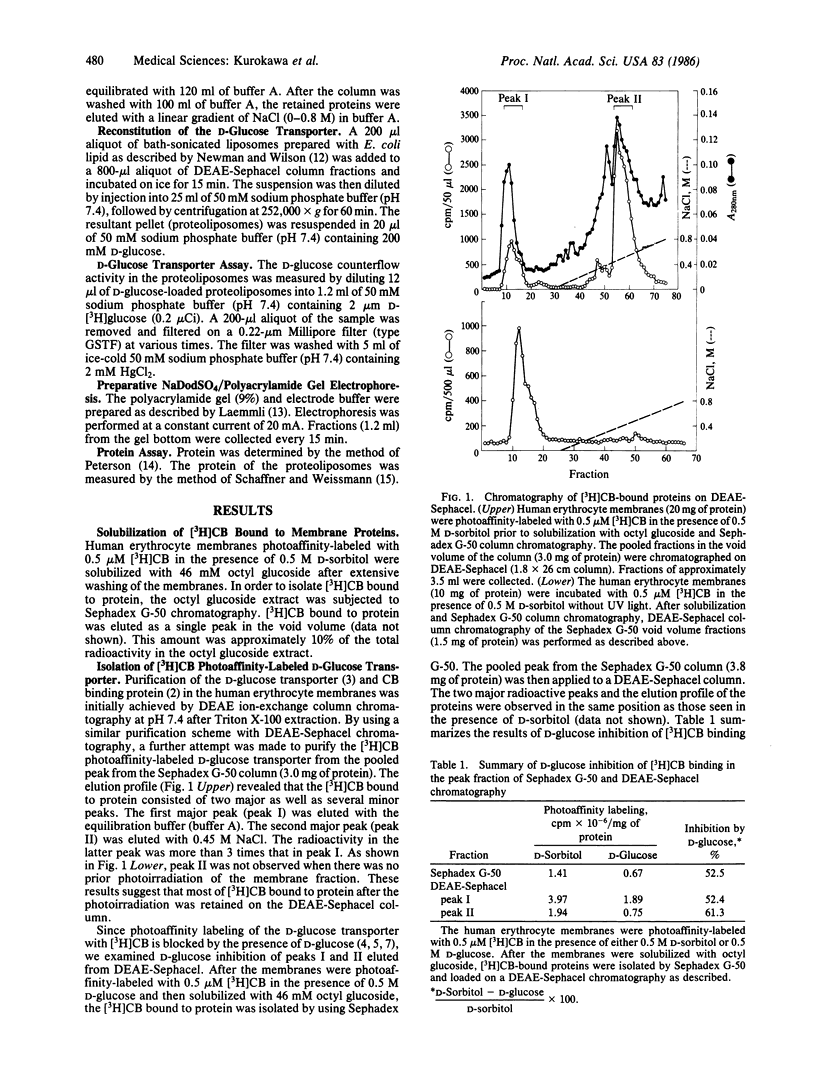

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E. Monoclonal antibodies to the glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. Identification of the transporter as a Mr = 55,000 protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8668–8675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Baldwin J. M., Gorga F. R., Lienhard G. E. Purification of the cytochalasin B binding component of the human erythrocyte monosaccharide transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 23;552(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90257-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Baldwin J. M., Lienhard G. E. Monosaccharide transporter of the human erythrocyte. Characterization of an improved preparation. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3836–3842. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Human erythrocyte ankyrin. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2540–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Su C., Pessin J. E., Mora R., Gitomer W., Czech M. P. Photoaffinity labeling of the human erythrocyte D-glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5419–5425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorga F. R., Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E. The monosaccharide transporter from human erythrocytes is heterogeneously glycosylated. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91972-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Rodbell M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Identification and characterization of the rat adipocyte glucose transporter by photoaffinity crosslinking. FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Walker D., Ransome K. J., Schroer D. W., Lienhard G. E. Identification of the glucose transporter in rat skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Crabb J. H., Ransome K. J. Endoglycosidase f cleaves the oligosaccharides from the glucose transporter of the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Wilson T. H. Solubilization and reconstitution of the lactose transport system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10583–10586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Czech M. P. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin-sensitive hexose transporters in intact rat adipocytes. Direct evidence that latent transporters become exposed to the extracellular space in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8125–8133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Tillotson L. G., Yamada K., Gitomer W., Carter-Su C., Mora R., Isselbacher K. J., Czech M. P. Identification of the stereospecific hexose transporter from starved and fed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2286–2290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F. Characterization of cytochalasin B photoincorporation into human erythrocyte D-glucose transporter and F-actin. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2750–2756. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F. Cytochalasin B. A natural photoaffinity ligand for labeling the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7290–7293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F., D'Artel-Ellis J. Orientation of the glucose transporter in the human erythrocyte membrane. Investigation by in situ proteolytic dissection. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13878–13884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna R. D., Langdon R. G. Reversible association of cytochalasin B with the human erythrocyte membrane. Inhibition of glucose transport and the stoichiometry of cytochalasin binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



