Abstract
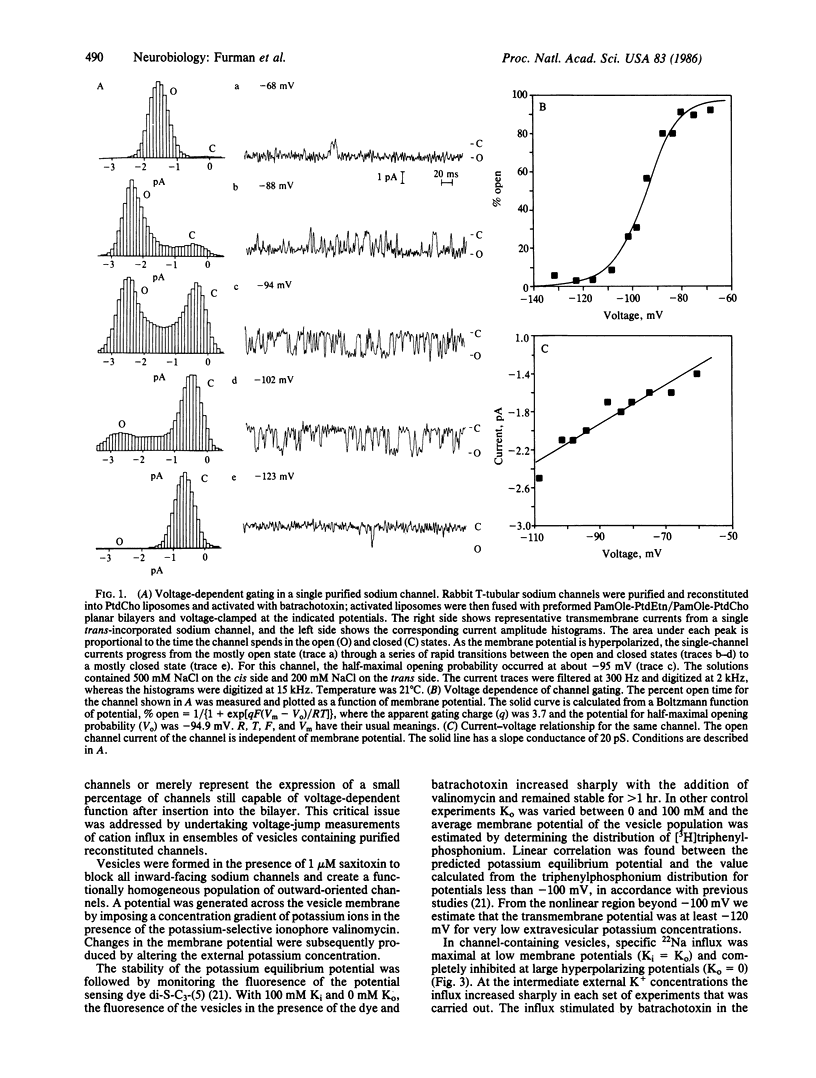
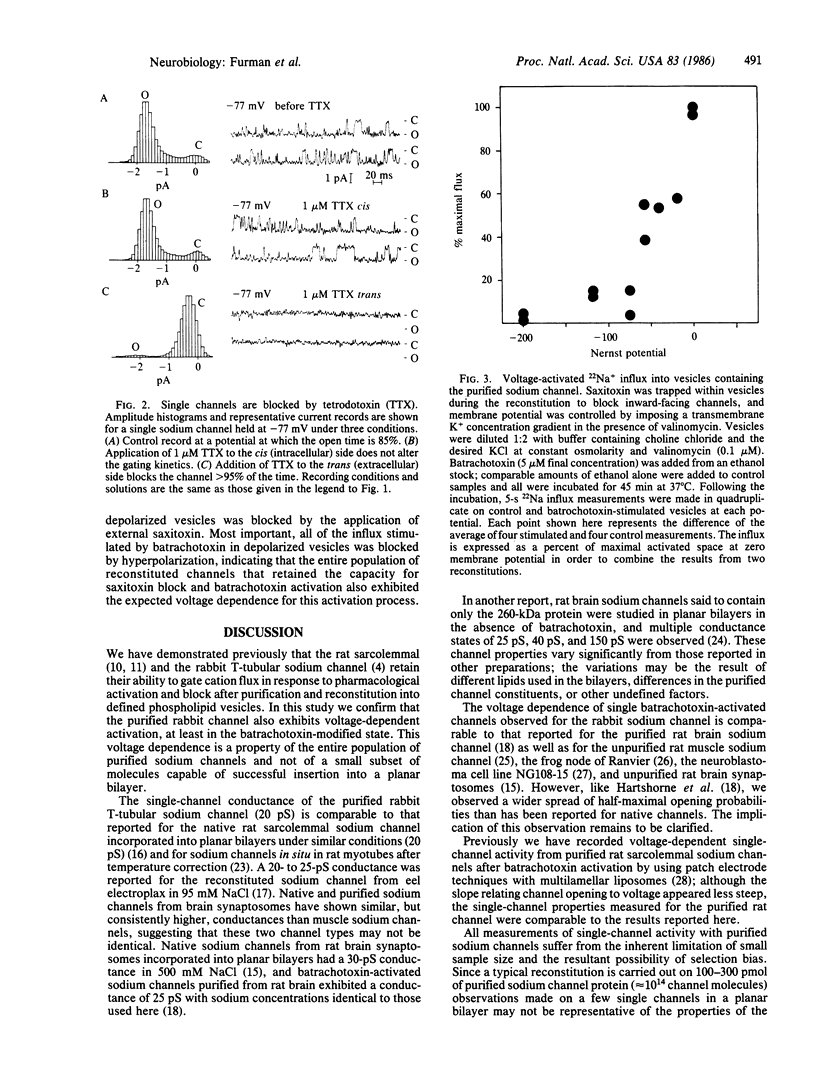
We have examined the voltage-dependent gating of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels purified from rabbit T-tubular membranes in two ways. First, purified channels were reconstituted into planar bilayers and single-channel properties were measured. Batrachotoxin-activated channels showed steep voltage-dependent activation with half-maximal opening probabilities at potentials between -95 and -116 mV. The single-channel conductance (500 mM Na+ cis, 200 mM Na+ trans) averaged 20 pS and was independent of membrane potential. Channels usually inserted with their extracellular faces on the trans side of the bilayer; addition of tetrodotoxin to the cis side had no effect, whereas addition to the trans side blocked greater than 95% of channel openings at -77 mV. A second approach was used to establish that this voltage dependence was a characteristic of the entire population of purified channels and not just those few channels observed in planar bilayers. Channels reconstituted into egg phosphatidylcholine vesicles were functionally oriented by inclusion of internal saxitoxin; vesicle membrane potentials were then generated by K+ gradients in the presence of valinomycin. After batrachotoxin activation, Vm was altered by shifts of K+o. All of the specific 22Na+ influx activated by batrachotoxin and blocked by saxitoxin was found to be voltage sensitive, activating between predicted membrane potentials of -100 and -50 mV. The single-channel properties of the purified T-tubular sodium channel correspond closely to those seen with native sodium channels from rat sarcolemma. The voltage-dependent activation of the batrachotoxin-modified reconstituted channel is the same as that seen with native channels in situ or in bilayers after exposure to this toxin. Most importantly, this voltage-dependent gating is a property of all of the purified channels capable of specific pharmacological activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R., Brabson J. S., Raftery M. A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Cohen S. A., Murphy L. E. Purification from rat sarcolemma of the saxitoxin-binding component of the excitable membrane sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1306–1310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Protein components of the purified sodium channel from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1377–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Tanaka J. C., Furman R. E. Molecular characteristics and functional reconstitution of muscle voltage-sensitive sodium channels. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(3):135–146. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadei J. M., Gordon R. D., Lampson L. A., Schotland D. L., Barchi R. L. Monoclonal antibodies against the voltage-sensitive Na+ channel from mammalian skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6227–6231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C., Erecińska M., Werrlein R., Silver I. A. Cellular energy metabolism, trans-plasma and trans-mitochondrial membrane potentials, and pH gradients in mouse neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Schneider M. F., Khodorov B. I. Voltage dependence of intramembrane charge movement and conductance activation of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jun;81(6):829–844. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Worley J. F., 3rd, Krueger B. K. Voltage-dependent block by saxitoxin of sodium channels incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):301–310. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84156-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Boheim G., Barhanin J., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. Reconstitution of highly purified saxitoxin-sensitive Na+-channels into planar lipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):509–515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. Purification of the saxitoxin receptor of the sodium channel from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Keller B. U., Talvenheimo J. A., Catterall W. A., Montal M. Functional reconstitution of the purified brain sodium channel in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):240–244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Vandenberg C. A., Lange K. Statistical analysis of single sodium channels. Effects of N-bromoacetamide. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):323–335. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84158-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Moran N., Ehrenstein G. Batrachotoxin modifies the gating kinetics of sodium channels in internally perfused neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2082–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraner S. D., Tanaka J. C., Barchi R. L. Purification and functional reconstitution of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from rabbit T-tubular membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6341–6347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J. Single sodium channels from rat brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):172–175. doi: 10.1038/303172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombet A., Lazdunski M. Characterization, solubilization, affinity labeling and purification of the cardiac Na+ channel using Tityus toxin gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):651–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):462–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Garber S. S., Miller C. Batrachotoxin-activated Na+ channels in planar lipid bilayers. Competition of tetrodotoxin block by Na+. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):665–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Hall S., Garber S. S., Strichartz G. S., Miller C. Voltage-dependent blockade of muscle Na+ channels by guanidinium toxins. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):687–704. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J., Horn R. Effect of N-bromoacetamide on single sodium channel currents in excised membrane patches. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Mar;79(3):333–351. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-modulated ion transport by the voltage-regulated sodium channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Single-channel properties of the reconstituted voltage-regulated Na channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5594–5598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Talvenheimo J. A., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-activated ion flux and scorpion toxin binding from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1676–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J. C., Eccleston J. F., Barchi R. L. Cation selectivity characteristics of the reconstituted voltage-dependent sodium channel purified from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7519–7526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S. Dye indicators of membrane potential. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:47–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigele J. B., Barchi R. L. Functional reconstitution of the purified sodium channel protein from rat sarcolemma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


