Abstract
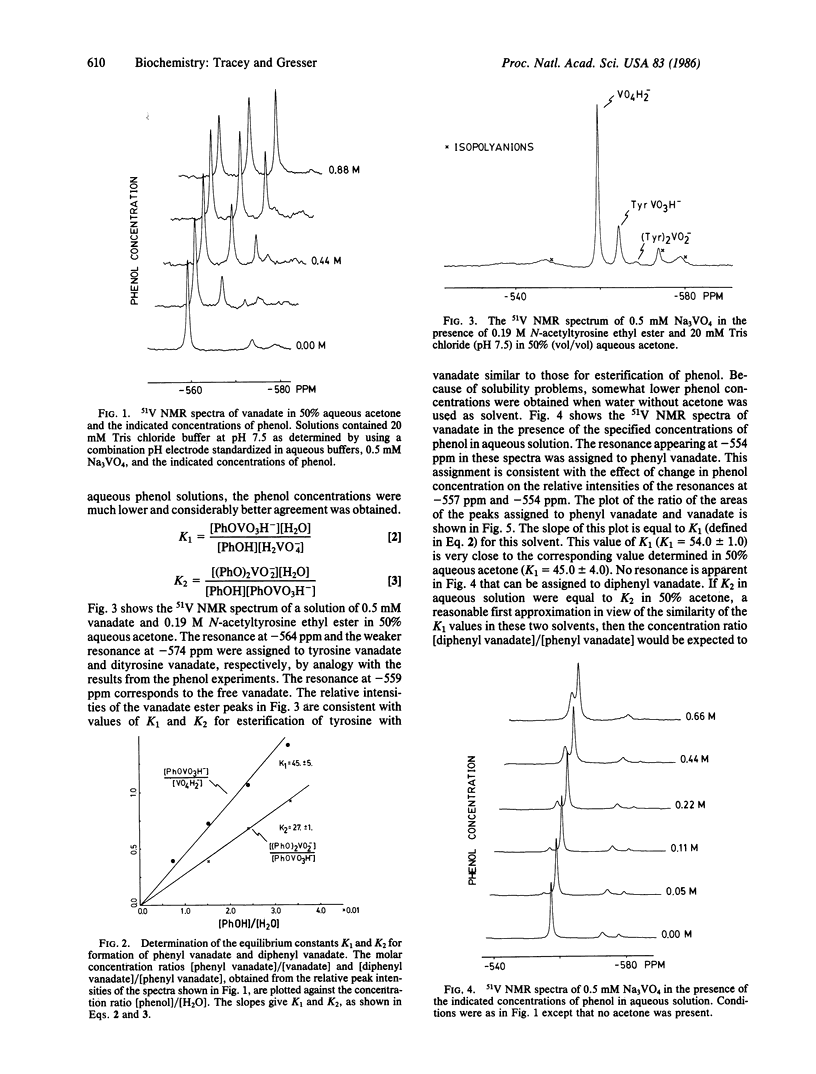
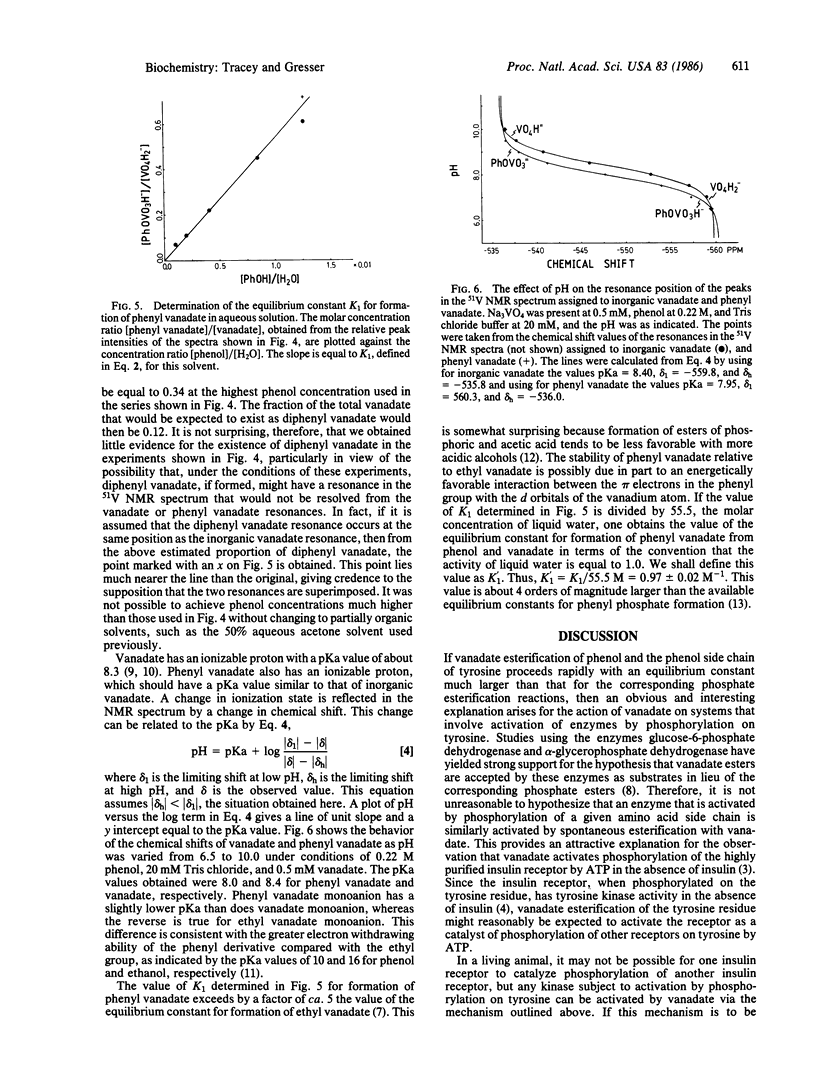
The interaction of vanadate with phenol and N-acetyltyrosine ethyl ester in aqueous solution has been studied by using 51V nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. On the basis of these studies, it has been concluded that vanadate rapidly esterifies the hydroxyl group of the aromatic ring to yield a phenyl vanadate. For phenol, the equilibrium constant for this reaction in terms of the convention that the activity of liquid water is 1.0 is K1 = [phenyl vanadate]/[phenol][vanadate] = 0.97 +/- 0.02. This value is well over 4 orders of magnitude larger than estimates from the literature for the corresponding equilibrium constant for the esterification of phenol by phosphate. The equilibrium constant for esterification of the phenol moiety of N-acetyltyrosine ethyl ester is similar to that for esterification of phenol. The relevance of these observations to processes that are regulated by reversible phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of tyrosine residues is discussed, in particular the insulin-like effect of vanadate.
Full text
PDF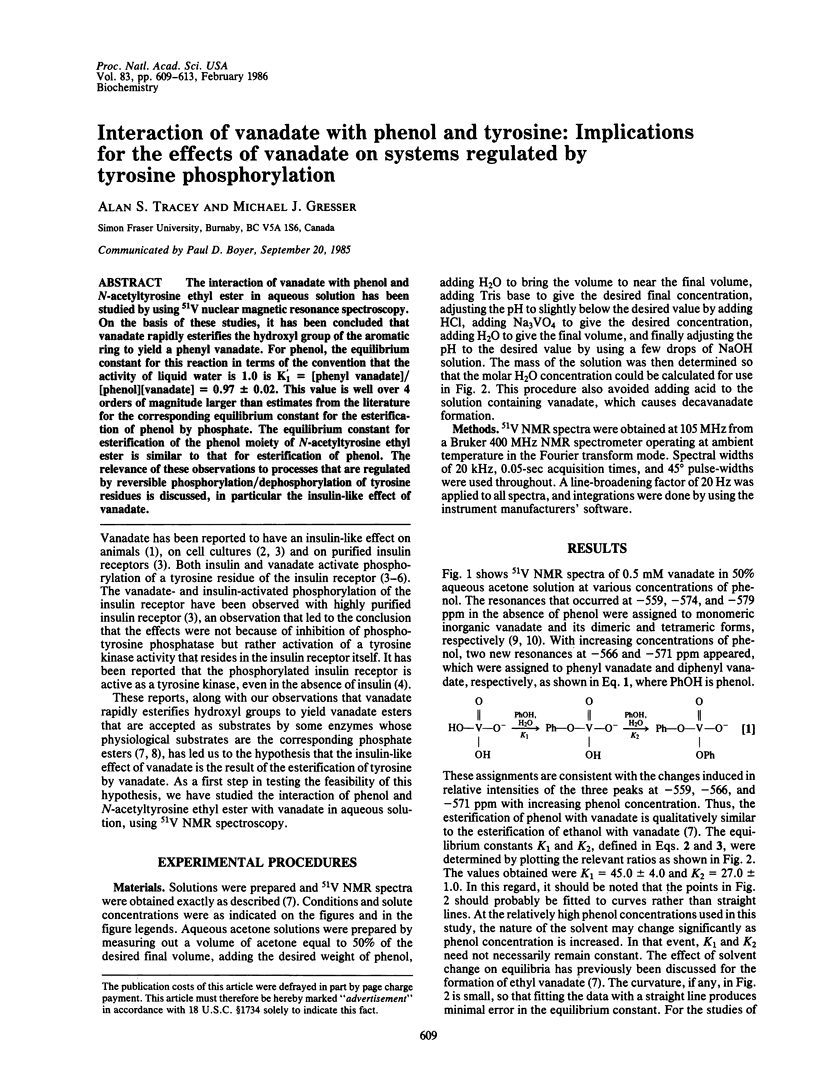


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. J., Gordon J. A. The stimulation of pp60v-src kinase activity by vanadate in intact cells accompanies a new phosphorylation state of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9580–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Aisen P. The fate of cytoplasmic vanadium. Implications on (NA,K)-ATPase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1781–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Vanadate, epidermal growth factor and the stimulation of DNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 30;102(4):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., Kleinzeller A. The insulin-mimetic effects of vanadate in isolated rat adipocytes. Dissociation from effects of vanadate as a (Na+-K+)ATPase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5306–5312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami Y., Lipmann F. Reversal of Rous sarcoma-specific immunoglobulin phosphorylation on tyrosine (ADP as phosphate acceptor) catalyzed by the src gene kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1872–1876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser M. J. Regulation of enzyme activity by cyclic phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cascades. Thermodynamic constraints. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 30;743(3):316–322. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyliger C. E., Tahiliani A. G., McNeill J. H. Effect of vanadate on elevated blood glucose and depressed cardiac performance of diabetic rats. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.3156405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunas R. Sugar-arsenate esters: thermodynamics and biochemical behavior. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Nov;205(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. N., Lynn J. L., Jr, Lienhard G. E. Possible transition-state analogs for ribonuclease. The complexes of uridine with oxovanadium(IV) ion and vanadium(V) ion. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Dec 26;95(26):8762–8768. doi: 10.1021/ja00807a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. W., Ray W. J., Jr Kinetics and thermodynamics of the formation of glucose arsenate. Reaction of glucose arsenate with phosphoglucomutase. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3932–3937. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Yang S. D. Regulation of ATP-Mg-dependent protein phosphatase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:177–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North P., Post R. L. Inhibition of (Na,K)-ATPase by tetravalent vanadium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4971–4978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nour-Eldeen A. F., Craig M. M., Gresser M. J. Interaction of inorganic vanadate with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nonenzymic formation of glucose 6-vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6836–6842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasarma T., Crane F. L. Does vanadium play a role in cellular regulation? Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;20:247–301. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152820-1.50011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees-Jones R. W., Taylor S. I. An endogenous substrate for the insulin receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4461–4467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B. Vanadium ions stimulate DNA synthesis in Swiss mouse 3T3 and 3T6 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Brown T. A., Whipple J. H., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Dubler R. E., Cheng K., Larner J. A novel mechanism for the insulin-like effect of vanadate on glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6650–6658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Vanadate inhibits the ATP-dependent degradation of proteins in reticulocytes without affecting ubiquitin conjugation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2803–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Haring H. U., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Kinetic properties and sites of autophosphorylation of the partially purified insulin receptor from hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



