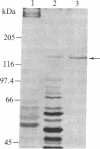
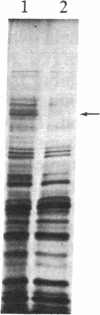
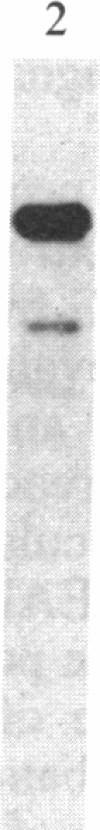
Abstract
The capacity of microtubules to disassemble in vitro is profoundly affected by a protein factor designated STOP (stable tubule only polypeptide). Here we report the isolation of STOP protein and confirm that its activity is, as predicted, highly substoichiometric to the tubulin in microtubules. The isolation of the 145-kDa STOP (STOP145) protein has been effected from isolated cold-stable microtubules by two column steps: DEAE ion-exchange and a calmodulin affinity column. To confirm the protein's activity we have produced an antibody against STOP145 and have used the antibody to specifically remove the protein and the activity using an antibody-linked affinity column. We conclude that the STOP145 protein accounts for the observed in vitro stabilization of microtubules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asnes C. F., Wilson L. Isolation of bovine brain microtubule protein without glycerol: polymerization kinetics change during purification cycles. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):64–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90706-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Tytell M., Lasek R. J. Axonal tubulin and axonal microtubules: biochemical evidence for cold stability. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1716–1724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Bunge M. B. Serial analysis of microtubules in cultured rat sensory axons. J Neurocytol. 1981 Aug;10(4):589–605. doi: 10.1007/BF01262592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Thomson J. N. Organization of neuronal microtubules in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):278–289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. Physical and chemical properties of purified tau factor and the role of tau in microtubule assembly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 25;116(2):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskin F., Cantor C. R., Shelanski M. L. Biochemical studies on the in vitro assembly and disassembly of microtubules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:133–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Rohrschneider L. R., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G. Antibodies to a defined region of pp60src neutralize the tyrosine-specific kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11219–11228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmark P. J., Linn S. Purification and properties of the recBC DNase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1849–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Landers J. M., Hamborg M. A. Polarity orientation of axonal microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):661–665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Rapid disassembly of cold-stable microtubules by calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Rauch C. T., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Recycling of cold-stable microtubules: evidence that cold stability is due to substoichiometric polymer blocks. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):509–515. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Rauch C. T., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Regulation of microtubule cold stability by calmodulin-dependent and -independent phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper M. H. The independent distribution of amino acid near neighbor pairs into polypeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):1018–1024. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Rauch C. T. Characterization of rat brain crude extract microtubule assembly: correlation of cold stability with the phosphorylation state of a microtubule-associated 64K protein. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4451–4458. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Opposite end assembly and disassembly of microtubules at steady state in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. R., Lasek R. J. Stable polymers of the axonal cytoskeleton: the axoplasmic ghost. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):192–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabion M., Job D., Margolis R. L. Sliding of STOP proteins on microtubules. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6642–6648. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirollet F., Job D., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Purification and characterization of sheep brain cold-stable microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1560–1564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, Bronson D., Siegel-Greenstein F., Cuatrecasas P. Cytoskeletal calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Characterization, solubilization, and purification from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1230–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheir-Neiss G., Lai M. H., Morris N. R. Identification of a gene for beta-tubulin in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Capaldi R. A., Muchmore D., Dahlquist F. Cross-linking of ubiquinone cytochrome c reductase (complex III) with periodate-cleavable bifunctional reagents. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3719–3723. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. C., Wilson L. Cold-stable microtubules from brain. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1993–2001. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Calcium-dependent regulator protein: localization in mitotic apparatus of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1867–1871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]