Abstract
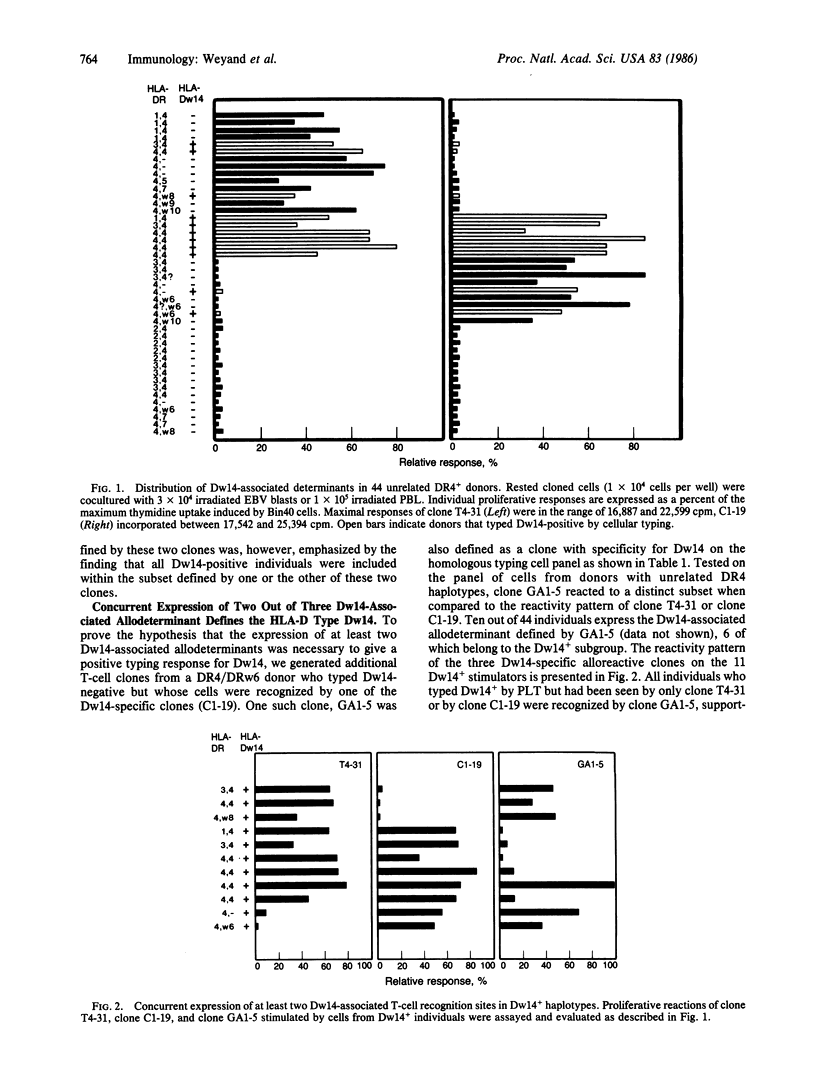
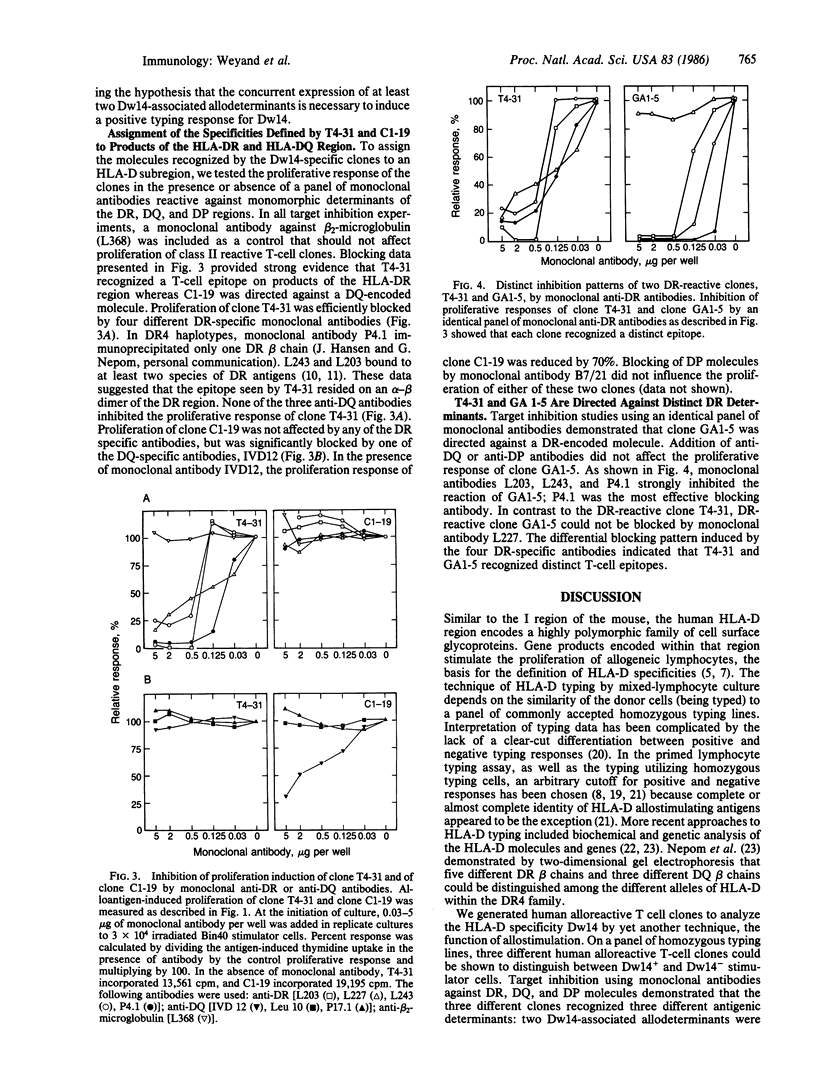
Polyclonal reagents have been used to define HLA class II molecules in conventional serologic and cellular typing. We generated human alloreactive T-cell clones to analyze the functional fine specificities of HLA class II molecules that might be important for the phenomenon of HLA and disease association. We chose to examine HLA-Dw14, an HLA-D specificity that has been associated with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. In this paper we have presented data that suggest that conventional cellular typing does not reflect the distribution of T-cell epitopes on major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. We describe three alloreactive T-cell clones that have defined three separate Dw14-associated T-cell epitopes. Two of these epitopes were on a DR-region molecule; the third was located on a DQ-region product. In a panel of unrelated DR4-positive donors, these three DW14-associated determinants were present in a high frequency but were not linked to each other. Within the tested panel of DR4-positive cells, all possible combinatorial arrangements of these three allodeterminants were seen. The concurrent expression of any two of the three allodeterminants was equivalent to a positive typing response for Dw14. Our finding that HLA-Dw14 is not characterized by a unique allodeterminant but by the combinatorial recognition of independently distributed T-cell interaction sites suggests that analysis of HLA and disease association may be more clearly demonstrated through the use of human T-cell clones.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin P., Trowsdale J., Rudd C., Bodmer W., Feldmann M., Lamb J. Functional expression of HLA-DP genes transfected into mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):61–64. doi: 10.1038/313061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. X., Evans R. L., Pollack M. S., Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H., Rousso C., Warner N. L., Brodsky F. M. Characterization and expression of the HLA-DC antigens defined by anti-Leu 10. Hum Immunol. 1984 Aug;10(4):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Jersild C., Hansen G. S., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A. Typing for MLC determinants by means of LD-homozygous and LD-heterozygous test cells. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1543–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathman C. G., Hengartner H. Crossreactive mixed lymphocyte reaction determinants recognized by cloned alloreactive T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5863–5866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn O. J., Levy R. Multiple HLA-DR antigens: detection with monoclonal antibodies and translation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2658–2662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles R. C., Nunez G., Hurley C. K., Nunez-Roldan A., Winchester R., Stastny P., Capra J. D. Structural analysis of a human I-A homologue using a monoclonal antibody that recognizes an MB3-like specificity. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1461–1470. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner J. P., Watson A. J., Bach F. H. Dw/LD-related molecular polymorphism of DR4 beta-chains. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1687–1691. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. H., Chan M. M., Bias W. B. Genetic control of major histocompatibility complex-linked immune responses to synthetic polypeptides in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):440–444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morling N., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Thomsen M. Data reduction in HLA-D typing with the primed lymphocyte typing (PLT) technique. the normalized median response (NMR). Tissue Antigens. 1980 Feb;15(2):123–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morling N., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Thomsen M. Generation of HLA-D specific primed lymphocyte typing (PLT) cells and cross-reactions of PLT-cells primed with homozygous typing cells. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Feb;15(2):137–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom B. S., Nepom G. T., Mickelson E., Antonelli P., Hansen J. A. Electrophoretic analysis of human HLA-DR antigens from HLA-DR4 homozygous cell lines: correlation between beta-chain diversity and HLA-D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6962–6966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom B. S., Nepom G. T., Mickelson E., Schaller J. G., Antonelli P., Hansen J. A. Specific HLA-DR4-associated histocompatibility molecules characterize patients with seropositive juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):287–291. doi: 10.1172/JCI111413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Nepom B. S., Antonelli P., Mickelson E., Silver J., Goyert S. M., Hansen J. A. The HLA-DR4 family of haplotypes consists of series of distinct DR and DS molecules. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):394–404. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinsmoen N. L., Bach F. H. Five HLA-D clusters associated with HLA-DR4. Hum Immunol. 1982 Jun;4(3):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Kohno Y., Iwamoto I., Tanimura M., Naito S. Association between an HLA haplotype and low responsiveness to tetanus toxoid in man. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):359–361. doi: 10.1038/272359b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., McDevitt H. O., Grumet F. C. The association between genes in the major histocompatibility complex and disease susceptibility,. Annu Rev Med. 1977;28:425–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.28.020177.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Fathman C. G., Sachs D. H. Inhibition of stimulation in murine mixed lymphocyte cultures with an alloantiserum directed against a shared Ia determinant. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):929–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall M., Reinsmoen N. L., Iwaki J., Bach F. H. Determinants not correlated with HLA-Dw, DR, or SB detected by primed lymphocyte typing. Hum Immunol. 1982 Jun;4(3):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P. HLA and disease 1982--a survey. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:193–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., DeMars R., Trowbridge I. S., Bach F. H. Detection of a novel human class II HLA antigen. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):358–361. doi: 10.1038/304358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



