Abstract
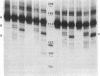
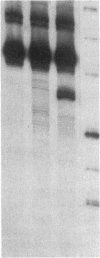
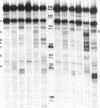
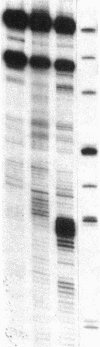
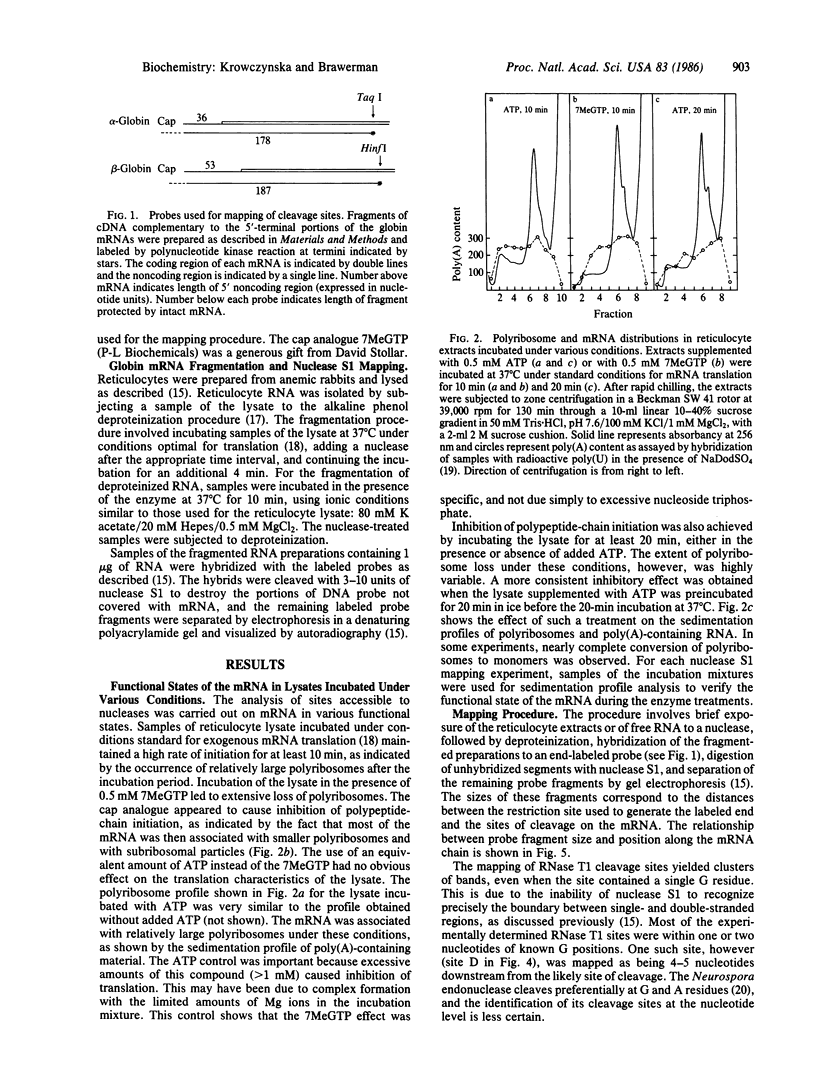
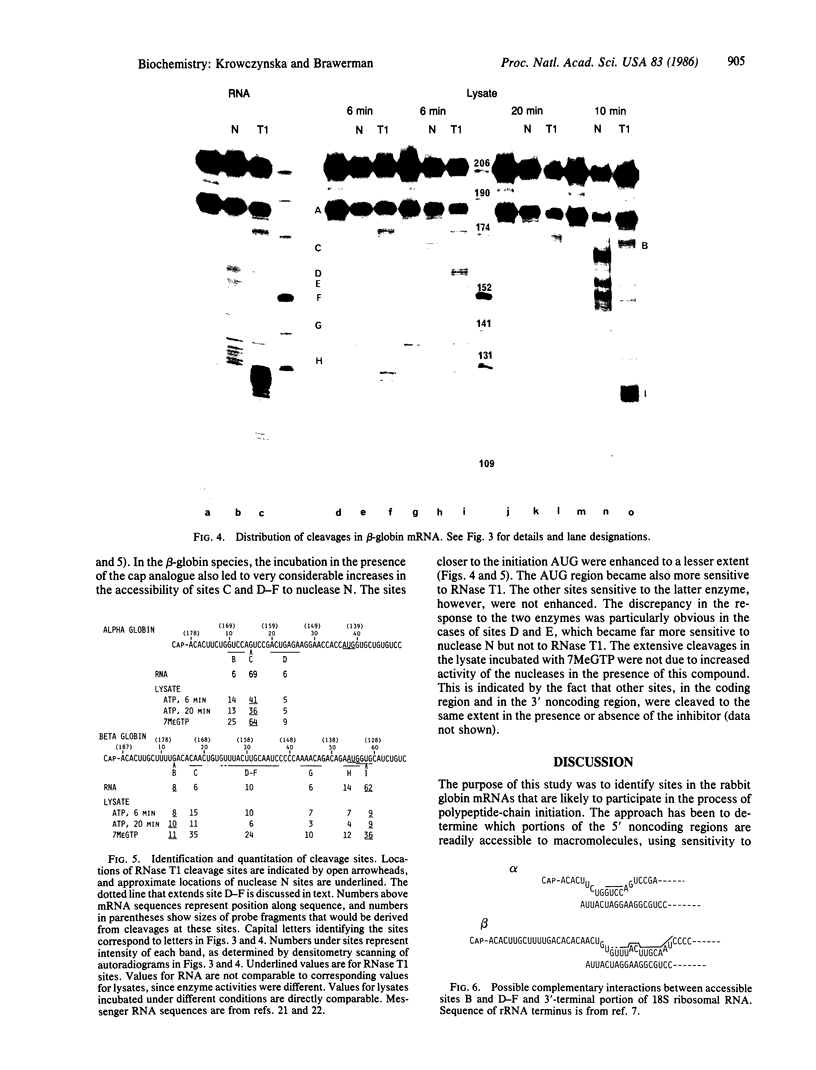
Accessible sites in the 5' noncoding region of the rabbit alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs were identified and compared in deproteinized RNA and in the mRNAs engaged in translation in the reticulocyte lysate. Preparations of RNA and lysate were subjected to limited nuclease digestion by RNase T1 and Neurospora endonuclease, and the cleavage sites were analyzed by a nuclease S1 mapping procedure. The free alpha-globin mRNA contained few nuclease-sensitive sites and its initiation codon AUG was masked. The free beta-globin mRNA contained a larger number of accessible sites and its AUG was highly exposed. The distribution of sensitive sites differed considerably in the lysate. In both mRNA species, a site near the 5' terminus became the one most accessible to Neurospora endonuclease. Also the accessibility of the AUG in beta-globin mRNA decreased considerably. The distribution of accessible sites in the lysate was the same when the mRNAs were undergoing rapid initiation and when initiation became limited after prolonged incubation. Inhibition of initiation by the cap analogue 7-methylguanosine 5'-triphosphate was accompanied by increased sensitivity of some of the sites in both mRNA species. One of the accessible sites in each mRNA species had a sequence complementary to the 3'-terminal portion of the 18S ribosomal RNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht G., Krowczynska A., Brawerman G. Configuration of beta-globin messenger RNA in rabbit reticulocytes. Identification of sites exposed to endogenous and exogenous nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):881–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann I. E., Brawerman G. Loss of the polyadenylate segment from mammalian messenger RNA. Selective cleavage of this sequence from polyribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Geoghegan T., Bergmann I., Brawerman G. Studies on the efficiency of translation and on the stability of actin messenger ribonucleic acid in mouse sarcoma ascites cells. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3153–3159. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser M. J. Purification and properties of Neurospora crassa endo-exonuclease, an enzyme which can be converted to a single-strand specific endonuclease. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):255–263. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan T., Cereghini S., Brawerman G. Inactive mRNA-protein complexes from mouse sarcoma-180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heindell H. C., Liu A., Paddock G. V., Studnicka G. M., Salser W. A. The primary sequence of rabbit alpha-globin mRNA. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Kronenberg M., Hunkapiller T. T cell antigen receptors and the immunoglobulin supergene family. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Evaluation of the "scanning model" for initiation of protein synthesis in eucaryotes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influence of mRNA secondary structure on binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Identification of features in 5' terminal fragments from reovirus mRNA which are important for ribosome binding. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINN S., LEHMAN I. R. AN ENDONUCLEASE FROM NEUROSPORA CRASSA SPECIFIC FOR POLYNUCLEOTIDES LACKING AN ORDERED STRUCTURE. II. STUDIES OF ENZYME SPECIFICITY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1294–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Alpha and beta globin messenger ribonucleic acid. Different amounts and rates of initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7131–7138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Secondary structure of bacteriophage f2 ribonucleic acid and the initiation of in vitro protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):689–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Lockard R. E., Vamvakopoulos N., Rieser L., RajBhandary U. L., Vournakis J. N. Secondary structure of mouse and rabbit alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs: differential accessibility of alpha and beta initiator AUG codons towards nucleases. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Guertin D., Cleveland D., Trachsel H. Probing the function of the eucaryotic 5' cap structure by using a monoclonal antibody directed against cap-binding proteins. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90398-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Rupprecht K. M., Hecht S. M., Shatkin A. J. Eukaryotic mRNA cap binding protein: purification by affinity chromatography on sepharose-coupled m7GDP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4345–4349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Discriminatory ribosome rebinding of isolated regions of protein synthesis initiation from the ribonucleic acid of bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2605–2609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]