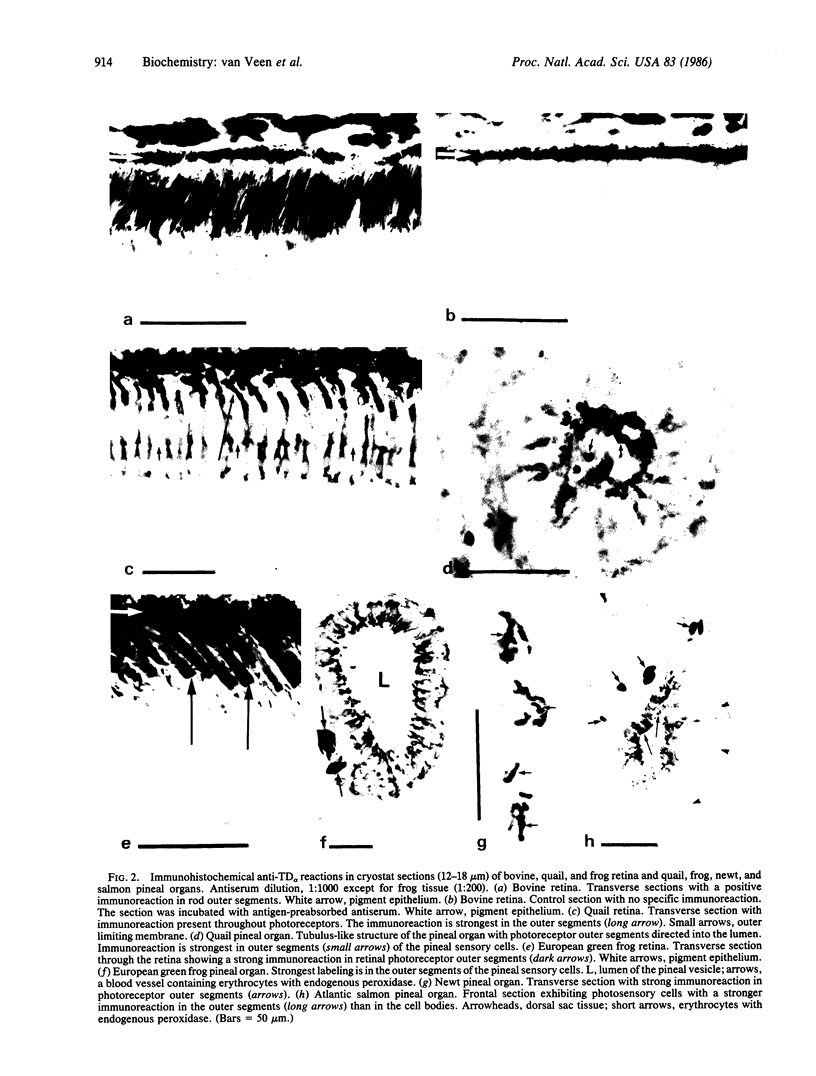
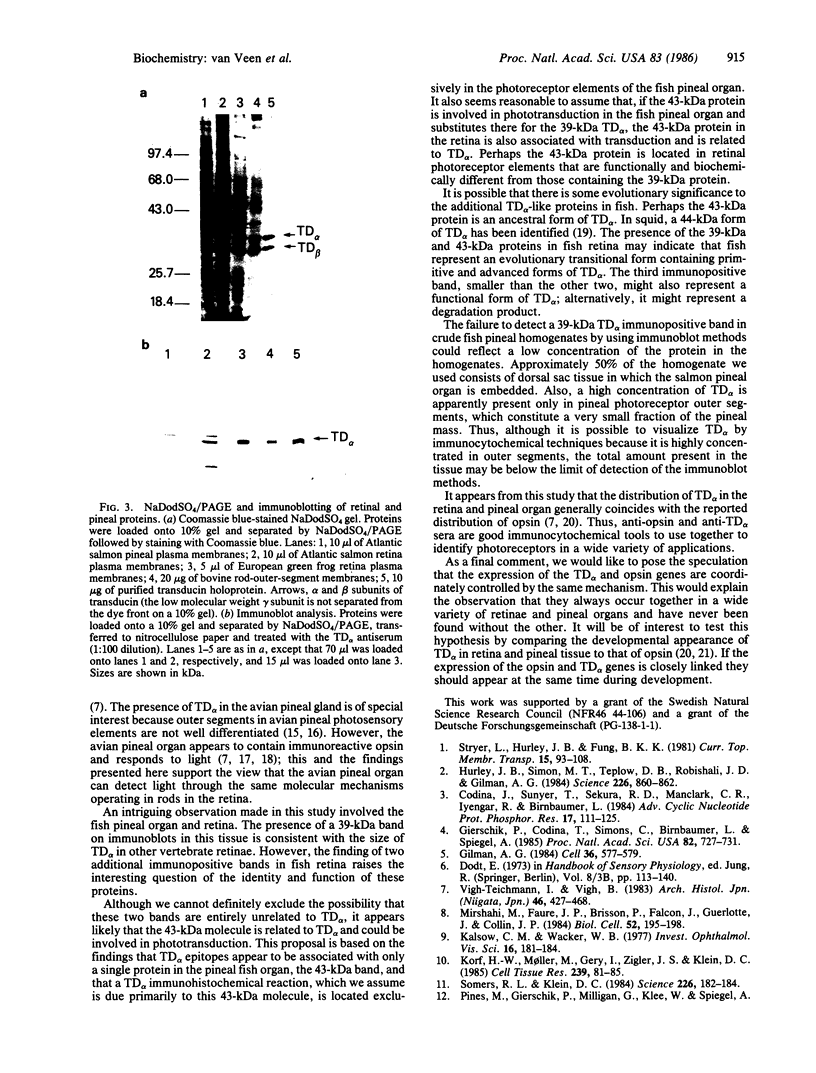
Abstract
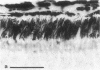
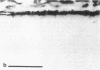
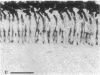
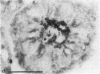
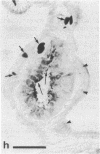
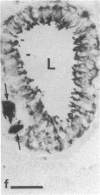
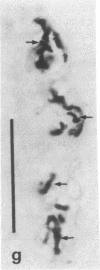
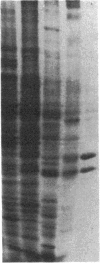
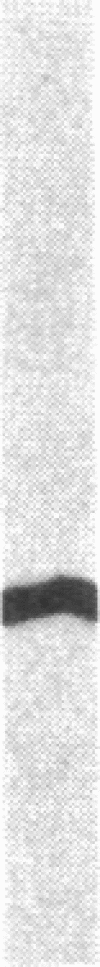
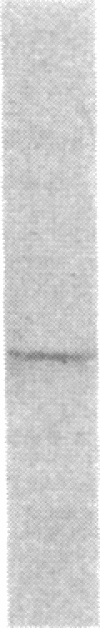
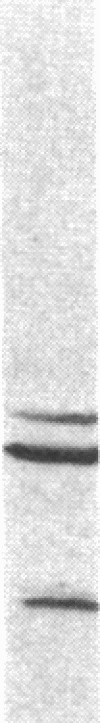
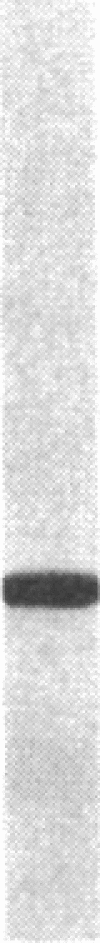
Antiserum against the alpha subunit of bovine rod-outer-segment transducin was used in an immunocytochemical study that identified the protein in retina (human, baboon, owl monkey, cow, rat, quail, newt, frog, salmon, eel, and lamprey), pineal organ (quail, newt, frog, salmon, eel, and lamprey), and parapineal organ (salmon and lamprey). No reaction was observed in the cow or rat pineal organ or the eel parapineal organ. The immunoreaction was very strong in outer segments but weak in perikarya. Immunoblots of crude tissue extracts of bovine rod-outer-segment membranes and frog and fish retina revealed a 39-kDa immunopositive band. The fish retina also contained two additional bands of mass 43 kDa and 25 kDa. Only the 43-kDa band was present in the fish pineal organ, which is photosensitive. This raises the possibility that the 43-kDa alpha transducin-immunopositive molecule present in the fish pineal organ and retina may be involved in phototransduction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Codina J., Hildebrandt J., Sunyer T., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L. Mechanisms in the vectorial receptor-adenylate cyclase signal transduction. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:111–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T. Rhodopsin-like photosensitivity of isolated chicken pineal gland. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):706–707. doi: 10.1038/290706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Codina J., Simons C., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. Antisera against a guanine nucleotide binding protein from retina cross-react with the beta subunit of the adenylyl cyclase-associated guanine nucleotide binding proteins, Ns and Ni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsow C. M., Wacker W. B. Pineal reactivity of anti-retina sera. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Feb;16(2):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf H. W., Møller M., Gery I., Zigler J. S., Klein D. C. Immunocytochemical demonstration of retinal S-antigen in the pineal organ of four mammalian species. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(1):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00214906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirshahi M., Faure J. P., Brisson P., Falcon J., Guerlotte J., Collin J. S-antigen immunoreactivity in retinal rods and cones and pineal photosensitive cells. Biol Cell. 1984;52(2):195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir I., Cohen D., Papermaster D. S. Immunocytochemical localization of opsin in the cell membrane of developing rat retinal photoreceptors. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1788–1795. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saibil H. R., Michel-Villaz M. Squid rhodopsin and GTP-binding protein crossreact with vertebrate photoreceptor enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers R. L., Klein D. C. Rhodopsin kinase activity in the mammalian pineal gland and other tissues. Science. 1984 Oct 12;226(4671):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.6091271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigh-Teichmann I., Vigh B. The system of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons. Arch Histol Jpn. 1983 Sep;46(4):427–468. doi: 10.1679/aohc.46.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Veen T., Ekström P., Nyberg L., Borg B., Vigh-Teichmann I., Vigh B. Serotonin and opsin immunoreactivities in the developing pineal organ of the three-spined stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(3):559–564. doi: 10.1007/BF00228440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]