Abstract
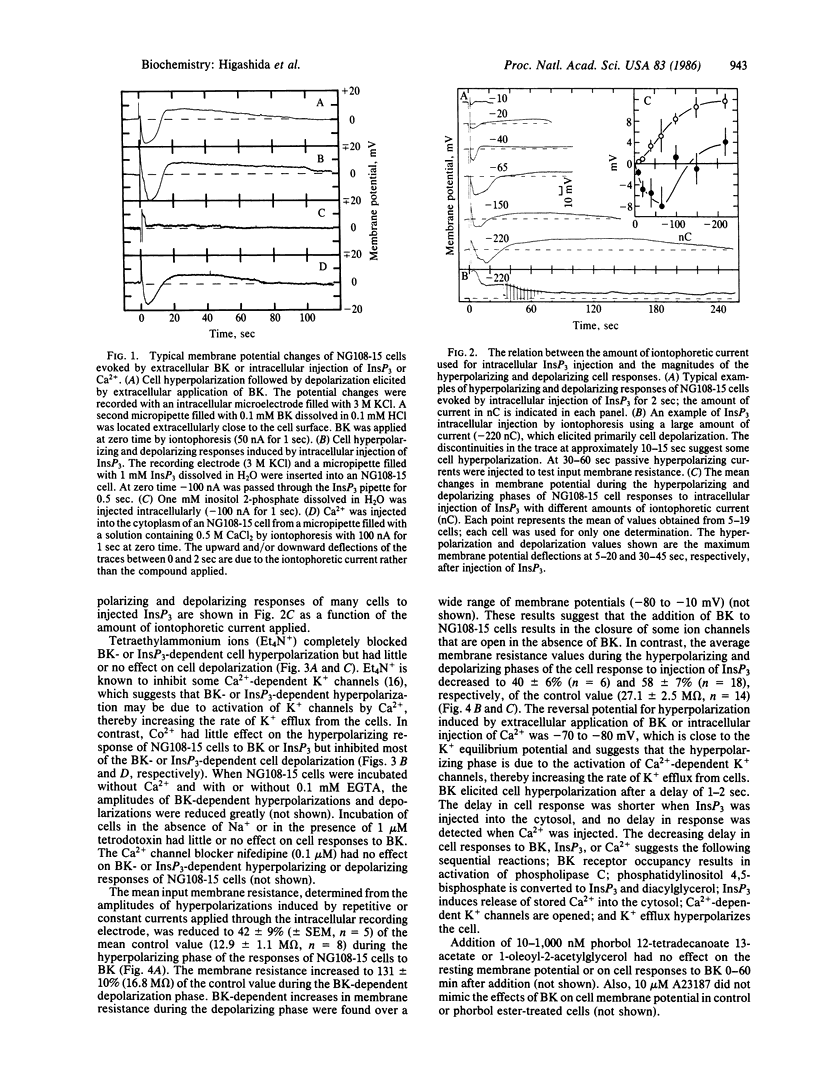
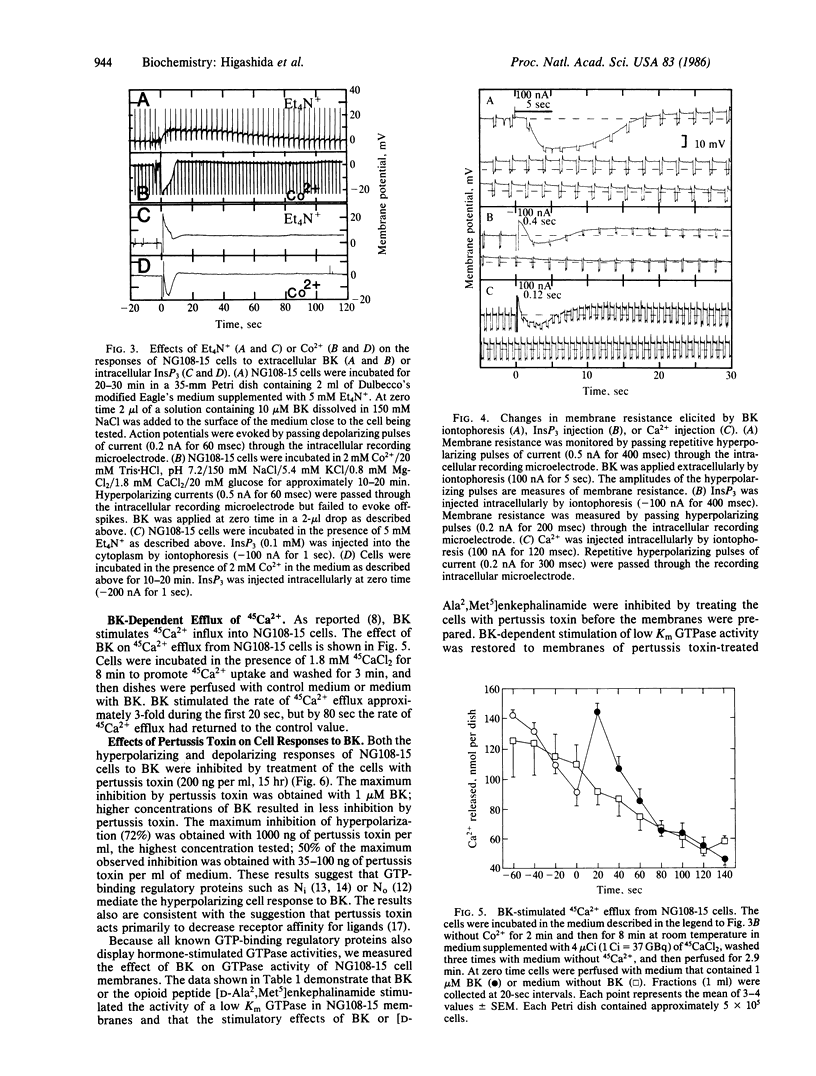
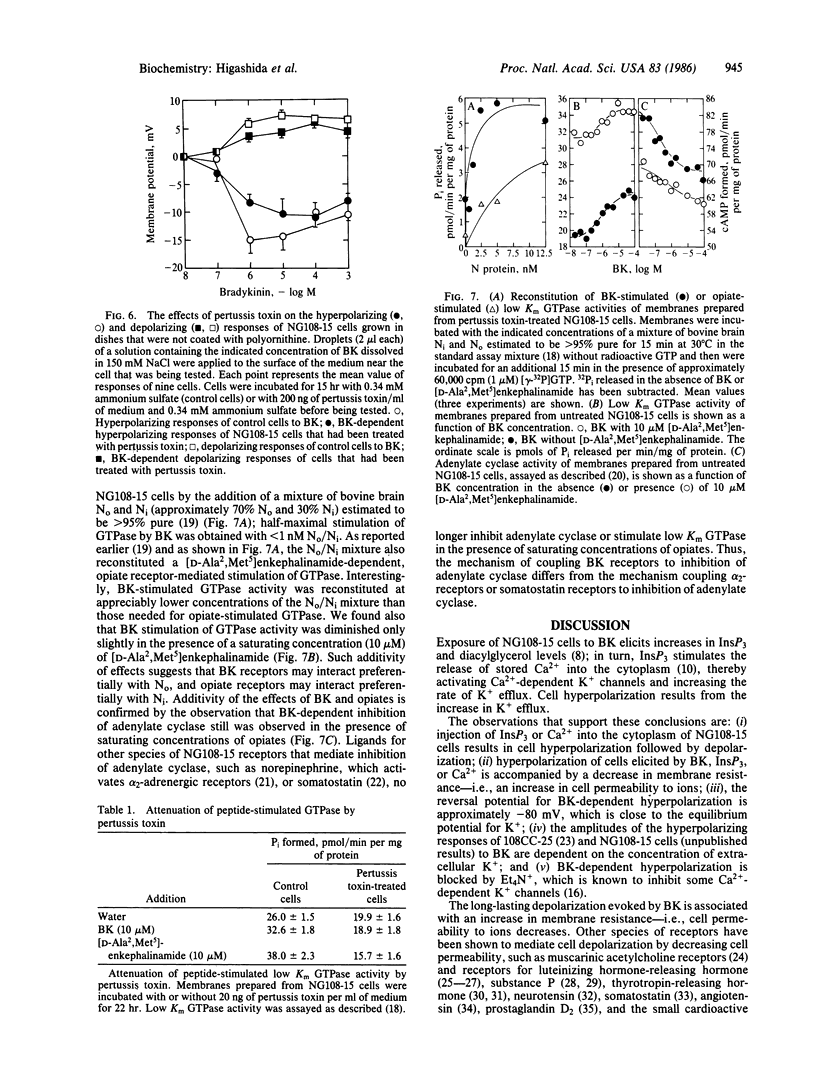
The addition of bradykinin to NG108-15 cells results in a transient hyperpolarization followed by prolonged cell depolarization. Injection of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate or Ca2+ into the cytoplasm of NG108-15 cells also elicits cell hyperpolarization followed by depolarization. Tetraethylammonium ions inhibit the hyperpolarizing response of cells to bradykinin or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Thus, the hyperpolarizing phase of the cell response may be due to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent release of stored Ca2+ into the cytoplasm, which activates Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. The depolarizing phase of the cell response to bradykinin is due largely to inhibition of M channels, thereby decreasing the rate of K+ efflux from cells and, to a lesser extent, to activation of Ca2+-dependent ion channels and Ca2+ channels. In contrast, injection of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate or Ca2+ into the cytosol did not alter M channel activity. Incubation of NG108-15 cells with pertussis toxin inhibits bradykinin-dependent cell hyperpolarization and depolarization. Bradykinin stimulates low Km GTPase activity and inhibits adenylate cyclase in NG108-15 membrane preparations but not in membranes prepared from cells treated with pertussis toxin. Reconstitution of NG108-15 membranes from cells treated with pertussis toxin with nanomolar concentrations of a mixture of highly purified No and Ni [guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that have no known function (No) or inhibit adenylate cyclase (Ni)] restores bradykinin-dependent activation of GTPase and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. These results show that [bradykinin . receptor] complexes interact with No or Ni and suggest that No and/or Ni mediate the transduction of signals from bradykinin receptors to phospholipase C and adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams T. W., Castellucci V. F., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R., Lloyd P. E. Two endogenous neuropeptides modulate the gill and siphon withdrawal reflex in Aplysia by presynaptic facilitation involving cAMP-dependent closure of a serotonin-sensitive potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7956–7960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Marsh S. Angiotensin mimics the action of muscarinic agonists on rat sympathetic neurones. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 14;193(2):614–619. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Hewlett E. L., Moss J., Vaughan M. Pertussis toxin inhibits enkephalin stimulation of GTPase of NG108-15 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1435–1438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa F. M., Graeff F. G. Central site of the hypertensive action of bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):670–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfs J. R., Dichter M. A. Effects of somatostatin on mammalian cortical neurons in culture: physiological actions and unusual dose response characteristics. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1176–1188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01176.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Dual modulation of K channels by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in clonal pituitary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B., Petersen O. H. Quinine inhibits Ca2+-independent K+ channels whereas tetraethylammonium inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):4–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80729-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashida H., Nakagawa Y., Miki N. Facilitation of synaptic transmission by prostaglandin D2 at synapses between NG108-15 hybrid and muscle cells. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 12;295(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90821-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia J. A., Moss J., Hewlett E. L., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase by pertussis toxin. Effects on inhibitory agonist binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1086–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Peptidergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:219–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., Nishi S. Voltage-clamp analysis of peptidergic slow depolarizations in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:305–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Klee W. A. Opiates inhibit adenylate cyclase by stimulating GTP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Sejnowski T. J. Peptidergic and muscarinic excitation at amphibian sympathetic synapses. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:257–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. Specific uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, of negative signal transduction via alpha-adrenergic, cholinergic, and opiate receptors in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4870–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Randić M. Actions of substance P on rat spinal dorsal horn neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:203–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa Y., Higashida H., Miki N. A single class of neurotensin receptors with high affinity in neuroblastoma X glioma NG108-15 hybrid cells that mediate facilitation of synaptic transmission. J Neurosci. 1984 Jun;4(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-06-01653.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nirenberg M., Wilson S., Higashida H., Rotter A., Krueger K., Busis N., Ray R., Kenimer J. G., Adler M. Modulation of synapse formation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):794–799. doi: 10.1126/science.6314503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. ADP-ribosylation of the specific membrane protein by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, associated with inhibition of a chemotactic peptide-induced arachidonate release in neutrophils. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing biosignaling. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13863–13871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S. Biphasic effect of thyrotropin-releasing hormone on membrane K+ permeability in rat clonal pituitary cells. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 23;209(1):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. C., Snyder S. H. Identification of bradykinin in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):1072–1080. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser G., Hamprecht B. Bradykinin induces hyperpolarizations in rat glioma cells and in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90841-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser G., Walter U., Hamprecht B. Bradykinin regulates the level of guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic GMP) in neural cell lines. Brain Res. 1984 Jan 9;290(2):367–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90958-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabol S. L., Nirenberg M. Regulation of adenylate cyclase of neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells by alpha-adrenergic receptors. I. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase mediated by alpha receptors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1913–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Slow excitatory synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:343–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs for human high molecular weight and low molecular weight prekininogens. Primary structures of two human prekininogens. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8601–8609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber J., Glaser T., Brandt M., Klebensberger W., Hamprecht B. Different receptors for somatostatin and opioids in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80552-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., Higashida H., Hattori H., Nozawa Y. Bradykinin-induced transient accumulation of inositol trisphosphate in neuron-like cell line NG108-15 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., Higashida H., Inoue R., Nozawa Y. Bradykinin-induced rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10201–10207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



