Abstract
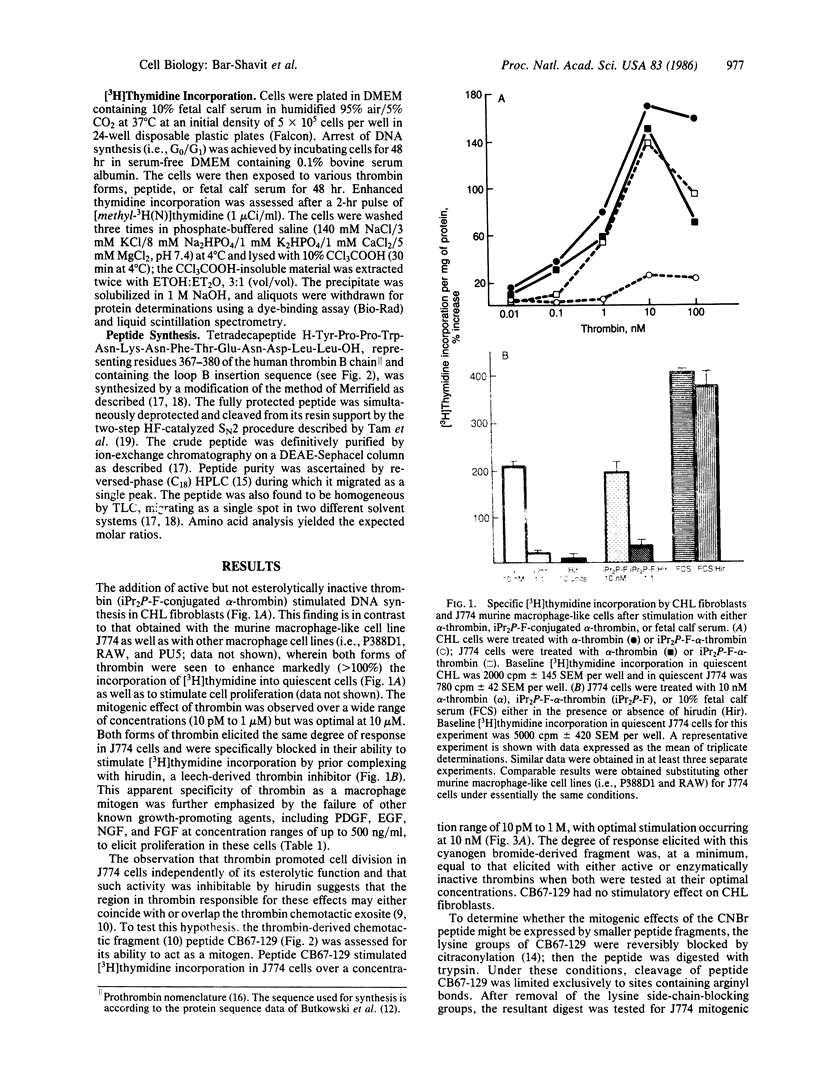
In contrast to fibroblasts, the exposure of G0/G1-arrested J774 cells, a murine macrophage-like tumor cell line, with either active or esterolytically inactive diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate-conjugated alpha-thrombin (the enzymatically active form of thrombin, EC 3.4.21.5) results in a mitogenic response as measured by increased [3H]thymidine incorporation. This response to thrombin is optimal at 10 nM and is specifically blocked by hirudin, a high-affinity thrombin inhibitor. When prethrombin 1 [a single-chain prothrombin derivative lacking fragment 1, resulting from the action of thrombin on prothrombin] is cleaved with cyanogen bromide, a fragment (peptide CB67-129) is produced that, like the parent thrombin molecule, is mitogenic for J774 cells but not for fibroblasts. Limited tryptic digests of this fragment retain the ability to stimulate macrophages--a function that can be mimicked by a synthetic tetradecapeptide homologue of CB67-129 (representing residues 367-380 of the human thrombin B chain sequence) but not by any of a series of well-known growth promoters, including platelet-derived growth factor, epidermal growth factor, nerve growth factor, and fibroblast epidermal growth factor, nerve growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor. The mitogenic effects of this peptide are not limited to J774 cells but can be expressed in other macrophage-like tumor cell lines, including P388D1, RAW, and PU5. In addition to increased [3H]thymidine incorporation, the synthetic B chain peptide stimulates cell proliferation as evidenced by a dose-dependent increase in total protein per culture well and cell number. We conclude that the thrombin molecule contains a macrophage growth factor domain that is separate and distinct from its active center. Thus, thrombin, in addition to its major role in hemostasis and thrombosis, may also have important functions in such basic processes as the inflammatory response and monocytopoiesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Wilner G. D. Chemotactic response of monocytes to thrombin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):282–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Wilner G. D. Receptor-mediated chemotactic response of a macrophage cell line (J774) to thrombin. Lab Invest. 1983 Dec;49(6):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Mudd M. S., Wilner G. D., Mann K. G., Fenton J. W., 2nd Localization of a chemotactic domain in human thrombin. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):397–400. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Wilner G. D., Fenton J. W., 2nd Monocyte chemotaxis: stimulation by specific exosite region in thrombin. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6836310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Jackson C. M., Jörnvall H., Lavine K. K., Nordling K., Salsgiver W. J. The active site of antithrombin. Release of the same proteolytically cleaved form of the inhibitor from complexes with factor IXa, factor Xa, and thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2406–2411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butkowski R. J., Elion J., Downing M. R., Mann K. G. Primary structure of human prethrombin 2 and alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4942–4957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Cunningham D. D. Cell surface action of thrombin is sufficient to initiate division of chick cells. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Glenn K. C., Cunningham D. D. Conditions which affect initiation of animal cell division by trypsin and thrombin. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Apr;95(1):13–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Le Cam A., Pouysségur J. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in G0/G1-arrested fibroblasts. Two distinct classes of growth factors with potentiating effects. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1706–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenic activity of blood components. I. Thrombin and prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. G., Lüscher E. F. Actions of thrombin and other coagulant and proteolytic enzymes on blood platelets. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):857–858. doi: 10.1038/216857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid and gene coding for human prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2087–2097. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. Analytical peptide mapping by high performance liquid chromatography. Application to intestinal calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7208–7212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Bing D. H., Feldmann R. J., Robison D. J., Burnier J. P., Furie B. C. Computer-generated models of blood coagulation factor Xa, factor IXa, and thrombin based upon structural homology with other serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3875–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I., Perham R. N. The reaction of aldolase with 2-methylmaleic anhydride. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj1160843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski M., McDonagh J. Studies on the mechanism of thrombin. Interaction with fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10530–10535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. J., Stanley E. R. Chemical crosslinking of the mononuclear phagocyte specific growth factor CSF-1 to its receptor at the cell surface. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Growth factors activate the Na+/H+ antiporter in quiescent fibroblasts by increasing its affinity for intracellular H+. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10989–10994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue J. F., Lubenskyi W., Kivity E., Sonder S. A., Fenton J. W., 2nd Protease mitogenic response of chick embryo fibroblasts and receptor binding/processing of human alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2767–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohjanpelto P. Proteases stimulate proliferation of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):387–392. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Guilbert L. J., Tushinski R. J., Bartelmez S. H. CSF-1--a mononuclear phagocyte lineage-specific hemopoietic growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1983;21(2):151–159. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240210206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Majerus D. W., Blank M. K. Heparin cofactor II. Purification and properties of a heparin-dependent inhibitor of thrombin in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2162–2169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Eide L. L., Mann K. G. Human prothrombinase complex assembly and function on isolated peripheral blood cell populations. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2119–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Ley C. W., Jaffe E. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):923–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Danitz M. P., Mudd M. S., Hsieh K. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd Selective immobilization of alpha-thrombin by surface-bound fibrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Mar;97(3):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Immunochemical studies of human fibrinopeptide A using synthetic peptide homologues. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1209–1213. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Thomas D. W., Nossel H. L., Robbins P. F., Mudd M. S. Immunochemical analysis of rabbit antihuman fibrinopeptide B antibodies. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5078–5082. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]