Abstract
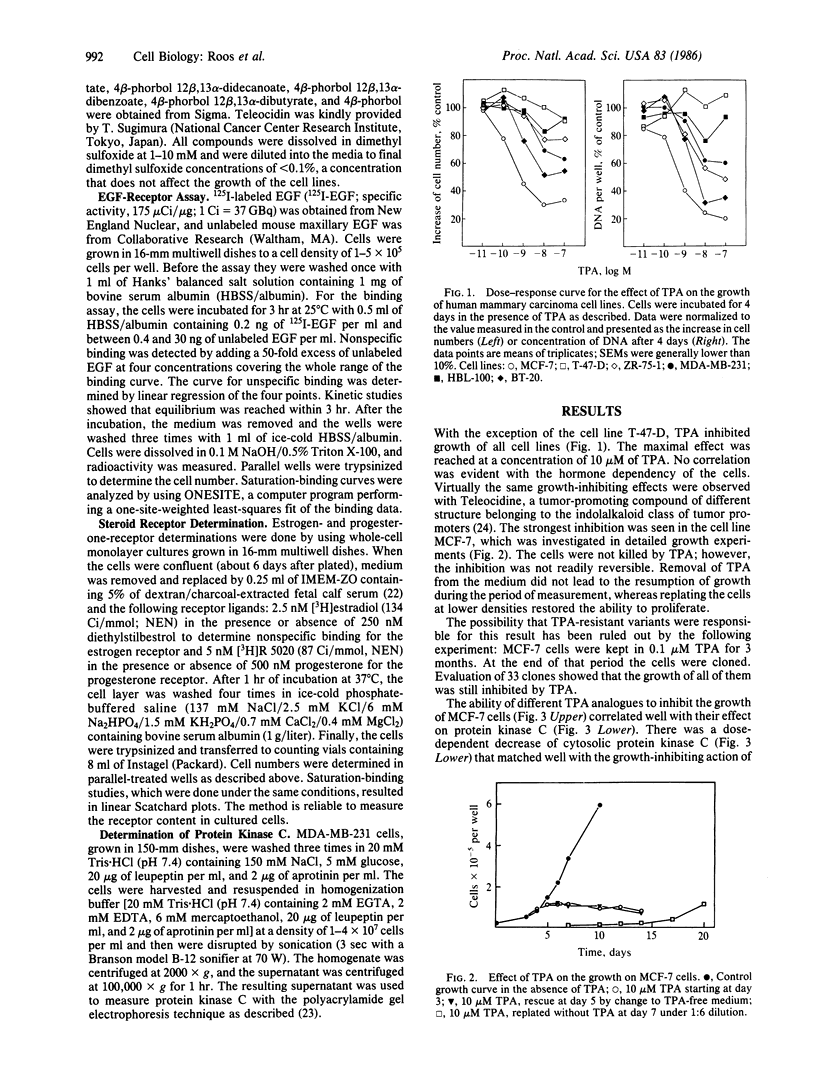
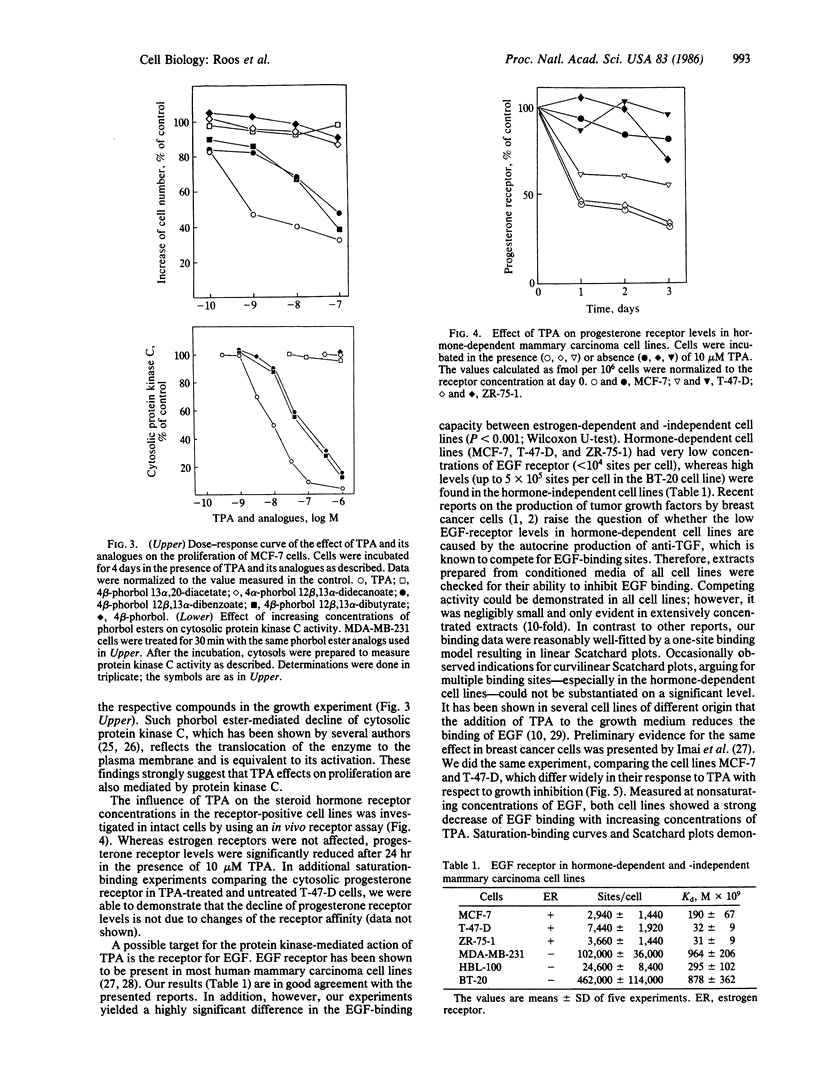
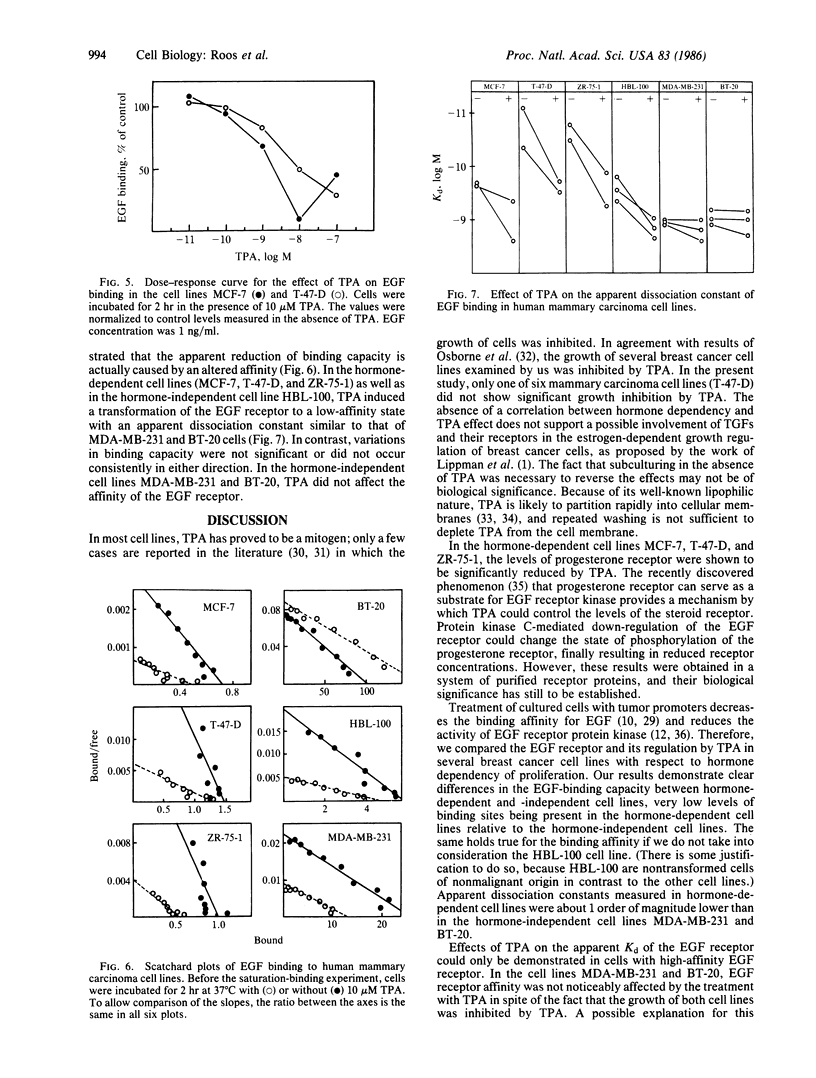
The effects of the tumor promoter phorbol 12-tetradecanoate 13-acetate (TPA) on the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor levels were investigated in hormone-dependent (MCF-7, T-47-D, and ZR-75-1) and hormone-independent (MDA-MB-231, HBL-100, and BT-20) human mammary carcinoma cell lines. In the absence of TPA, hormone-independent cell lines contained high concentrations of low-affinity EGF receptors (apparent Kd = 8 X 10(-10) M), whereas hormone-dependent cell lines exhibited low concentrations of high-affinity receptors (apparent Kd = 1 X 10(-10) M). TPA causes a change of the receptor from a high- to the low-affinity state in hormone-dependent cell lines (MCF-7, T-47-D, and ZR-75-1), as well as in the hormone-independent HBL-100, whereas the affinity remained unchanged in MDA-MB-231 and BT-20 cells. In addition, progesterone receptor levels are decreased after TPA treatment in the hormone-dependent cell lines MCF-7, T-47-D, and ZR-75-1, whereas the estrogen receptor levels remained unchanged. Tumor promoters such as TPA or teleocidin inhibited the proliferation of these cell lines at concentrations above 10 microM with the exception of the T-47-D cells. The most sensitive cell line towards growth inhibition by tumor promoter was the hormone-dependent MCF-7 cell line. Evaluation of different TPA analogs indicated a positive correlation between the growth-inhibitory effects and their ability to stimulate the subcellular redistribution of protein kinase C activity in MCF-7 cells. These data suggest a protein kinase C-mediated down-regulation of the progesterone receptor concentration and of the EGF receptor affinity, which is supposed to mediate the mitogenic response. Furthermore, these results support the hypothesis that the tumor-derived growth factors induced by estradiol act via the EGF receptor in hormone-dependent mammary carcinoma cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M. In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters, part 2. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1981 Jun;8(3):199–234. doi: 10.3109/10408448109109658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blay J., Irvine R. F., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Reduction of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity by heterologous ligands: evidence for a mechanism involving the breakdown of phosphoinositides and the activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):409–410. doi: 10.1038/276409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Rochette-Egly C., Rosenfeld C. Tumour-promoting phorbol diester induces substrate-adhesion and growth inhibition in lymphoblastoid cells. Cancer Lett. 1979 Apr;6(4-5):227–234. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(79)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L. Phorbol ester-induced threonine phosphorylation of the human epidermal growth factor receptor occurs within the EGF binding domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):618–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters mediate phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8545–8549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L., O'Brien T. G., Rovera G. Tumor promoters: effects on proliferation and differentiation of cells in culture. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 13;23(20):1979–1988. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L. W., Young N. A. Human breast carcinoma cells in continuous culture: a review. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4327–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbro D., Jungmann R. A., Eppenberger U. Subcellular distribution of protein kinase C of GH3 cells: quantitation and characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 15;239(1):102–111. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90816-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick S. L., Brightwell J., Wittliff J. L., Barrows G. H., Schultz G. S. Epidermal growth factor binding by breast tumor biopsies and relationship to estrogen receptor and progestin receptor levels. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3448–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick S. L., LaChance M. P., Schultz G. S. Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor and action on human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3442–3447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Connors J. M., Fujiki H., Sugimura T., Rosner M. R. Tumor promoters block tyrosine-specific phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh-Dastidar P., Coty W. A., Griest R. E., Woo D. D., Fox C. F. Progesterone receptor subunits are high-affinity substrates for phosphorylation by epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1654–1658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Zava D. T., Thilagar A. K., Jensen E. M., McGuire W. L. Steroid receptor analyses of nine human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2434–2437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Leung C. K., Friesen H. G., Shiu R. P. Epidermal growth factor receptors and effect of epidermal growth factor on growth of human breast cancer cells in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4394–4398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and potent phorbol tumor promoters induce epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation in a similar but distinctively different manner in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2559–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Sato J. D., Le A., Polikoff J., Sato G. H., Mendelsohn J. Growth stimulation of A431 cells by epidermal growth factor: identification of high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1337–1341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keydar I., Chen L., Karby S., Weiss F. R., Delarea J., Radu M., Chaitcik S., Brenner H. J. Establishment and characterization of a cell line of human breast carcinoma origin. Eur J Cancer. 1979 May;15(5):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(79)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B., Cooper H. L., Sando J. J. Decrease in cytosolic calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity following phorbol ester treatment of EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13193–13196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. C., Tu R. S., Fantone J. C., Varani J. Functional responses of tumor cells to phorbol esters: role for prostaglandins. Oncology. 1984;41(3):210–216. doi: 10.1159/000225825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P. G., Friedman B., Rosner M. R. Diacylglycerol modulates binding and phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12502–12507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Oka T. Evidence for physiological function of epidermal growth factor: pregestational sialoadenectomy of mice decreases milk production and increases offspring mortality during lactation period. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6059–6063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne C. K., Hamilton B., Nover M., Ziegler J. Antagonism between epidermal growth factor and phorbol ester tumor promoters in human breast cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):943–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI110144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne C. K., Hamilton B., Titus G., Livingston R. B. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter A., Sanford K. K., Evans V. J. Influence of oxygen and culture media on plating efficiency of some mammalian tissue cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Dec;49(6):1705–1712. doi: 10.1093/jnci/49.6.1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos W., Oeze L., Löser R., Eppenberger U. Antiestrogenic action of 3-hydroxytamoxifen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Jul;71(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury J. R., Farndon J. R., Sherbet G. V., Harris A. L. Epidermal-growth-factor receptors and oestrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):364–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D. S., Zwiebel J. A., Bano M., Losonczy I., Fehnel P., Kidwell W. R. Presence of transforming growth factors in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):4069–4077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Enhancement of calcium uptake and phosphatidylinositol turnover by epidermal growth factor in A-431 cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6280–6286. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Biologically active phorbol esters specifically alter affinity of epidermal growth factor membrane receptors. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):387–391. doi: 10.1038/279387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketani Y., Oka T. Epidermal growth factor stimulates cell proliferation and inhibits functional differentiation of mouse mammary epithelial cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1983 Sep;113(3):871–877. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-3-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. M., Blanchard B., Zava D. T. A simple method to determine whole cell uptake of radiolabelled oestrogen and progesterone and their subcellular localization in breast cancer cell lines in monolayer culture. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 May;20(5):1083–1088. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Fryling C., Johnson P. A., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factors (TGFs): properties and possible mechanisms of action. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(3):287–301. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



