Abstract
Cloned cDNAs have been isolated that encode a variant of hirudin, a potent thrombin inhibitor that is secreted by the salivary glands of the medicinal leech, Hirudo medicinalis. This variant probably corresponds to a form that has been purified from leech heads but differs in amino acid sequence from the hirudin purified from whole leeches. There are at least three hirudin transcripts detectable in leech RNAs that are different in size, site of synthesis, inducibility by starvation, and relationship to hirudin activity. The new hirudin variant predicted by the cDNA and the heterodisperse transcription products suggest a hirudin protein family. The hirudin cDNA was expressed in Escherichia coli under the control of the bacteriophage lambda PL promoter. The recombinant product is biologically active, inhibiting the cleavage by thrombin of fibrinogen and a synthetic tripeptide substrate.
Full text
PDF

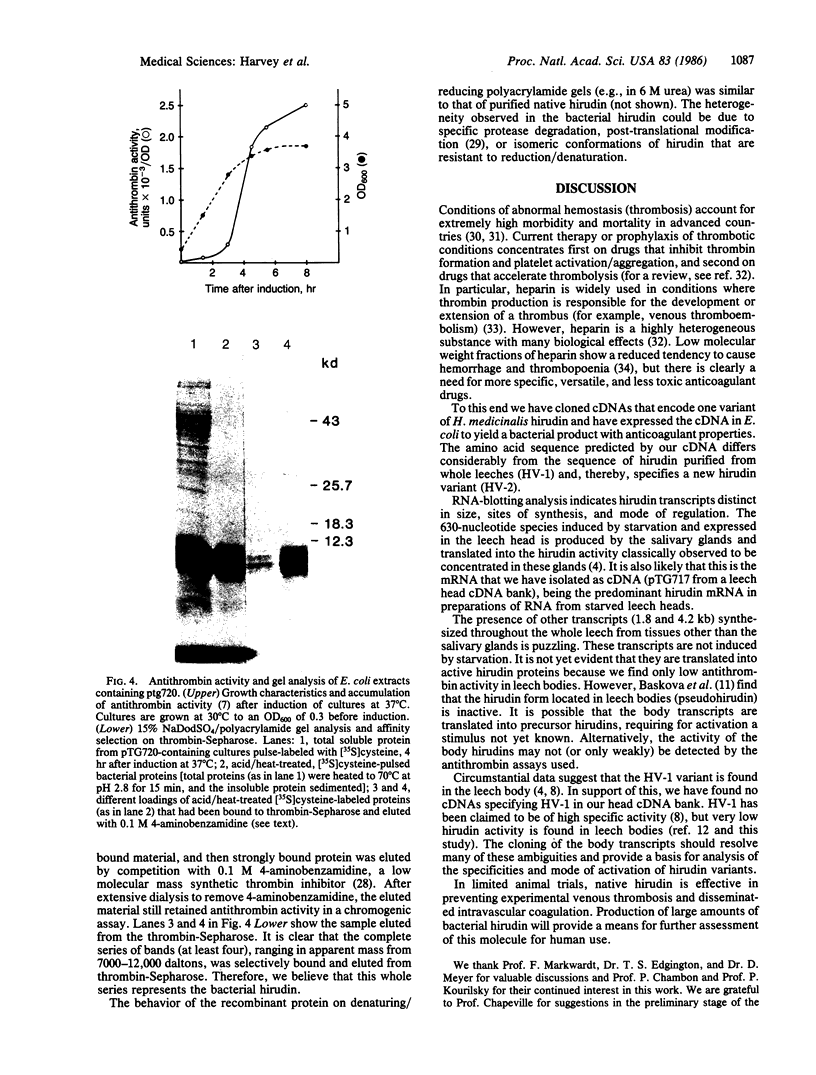

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdy D., Barabas E., Gráf L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Hirudin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:669–678. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskova I. P., Cherkesova D. U., Mosolov V. V. Hirudin from leech heads and whole leeches and "pseudo-hirudin" from leech bodies. Thromb Res. 1983 Jun 1;30(5):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Baugh R. F., Hougie C. The inhibition of the intrinsic generation of activated factor X by heparin and hirudin. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave J. P., Wiesel M. L., Hemmendinger S. Current treatment for thrombotic diseases. Agents Actions Suppl. 1984;15:24–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y. The functional domain of hirudin, a thrombin-specific inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M., Buchwalder A., Tessier L. H., Jaye M., Benavente A., Balland A., Kohli V., Lathe R., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. High-level production of biologically active human alpha 1-antitrypsin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Sloan J. S., Kelly J. D. A Drosophila metabolic gene transcript is alternatively processed. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisse M. G., Guillin M. C., Bezeaud A., Toulemonde F., Kitzis M., Andreassian B. Heparin-associated thrombocytopenia. In vitro effects of different molecular weight heparin fractions. Thromb Res. 1982 Aug 15;27(4):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa A., Hafter R., Seemüller U., Gokel J. M., Graeff H. The effect of hirudin on endotoxin induced disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Thromb Res. 1980 Aug 1;19(3):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., de la Salle H., Schamber F., Balland A., Kohli V., Findeli A., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. Isolation of a human anti-haemophilic factor IX cDNA clone using a unique 52-base synthetic oligonucleotide probe deduced from the amino acid sequence of bovine factor IX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2325–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli V., Balland A., Wintzerith M., Sauerwald R., Staub A., Lecocq J. P. Silica gel: an improved support for the solid-phase phosphotriester synthesis of oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7439–7448. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski T., Blombäck B. The location of tyrosine-O-sulphate in fibrinopeptides. Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(4):1339–1346. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKWARDT F. Die Isolierung und chemische Charakterisierung des Hirudins. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;308(2-4):147–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwardt F., Hauptmann J., Nowak G., Klessen C., Walsmann P. Pharmacological studies on the antithrombotic action of hirudin in experimental animals. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Jun 28;47(3):226–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
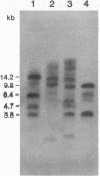
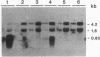
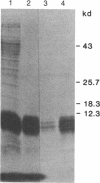
- Markwardt F., Walsmann P. Reindarstellung und Analyse des Thrombininhibitors Hirudin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Nov;348(11):1381–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Packham M. A. Thromboembolism: a manifestation of the response of blood to injury. Circulation. 1970 Jul;42(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.42.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak G., Markwardt F. Influence of hirudin on endotoxin-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) in weaned pigs. Exp Pathol (Jena) 1980;18(7-8):438–443. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4908(80)80045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink H., Liersch M., Sieber P., Meyer F. A large fragment approach to DNA synthesis: total synthesis of a gene for the protease inhibitor eglin c from the leech Hirudo medicinalis and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6369–6387. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Goldberg G. I., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. A mouse alpha-globin-related pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):222–226. doi: 10.1038/286222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]