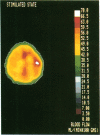
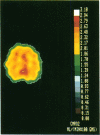
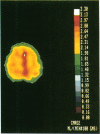
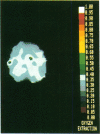
Abstract
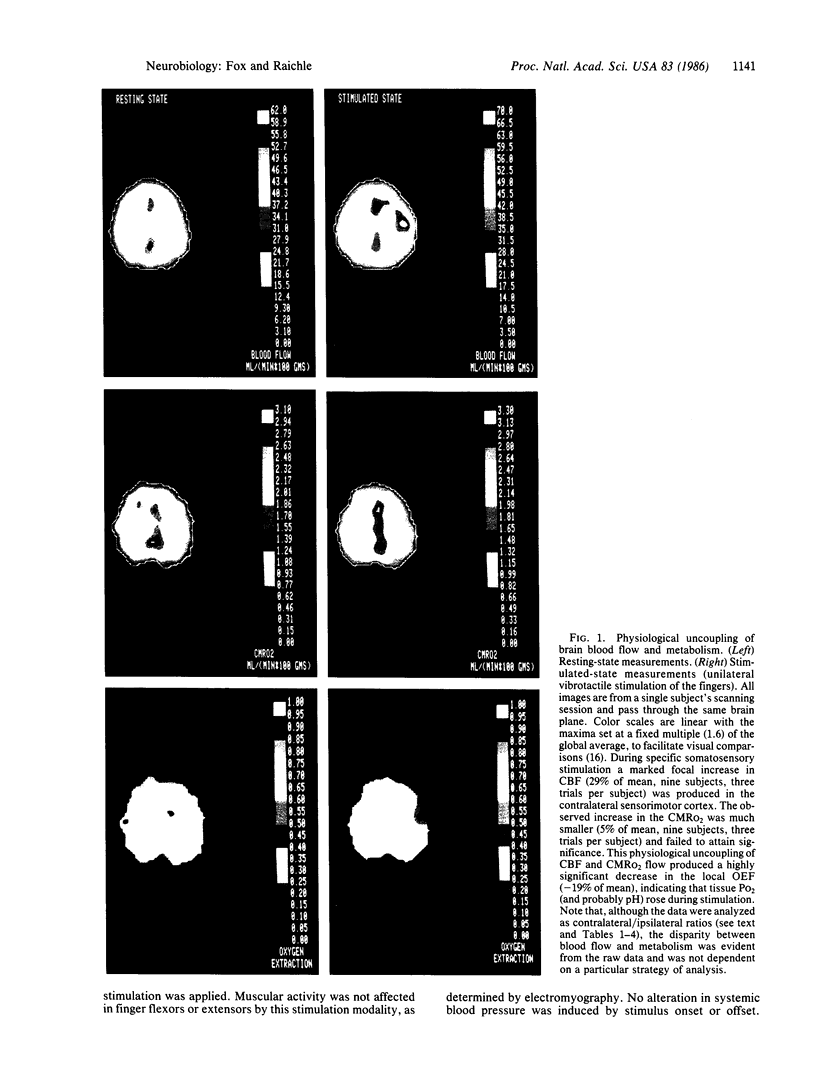
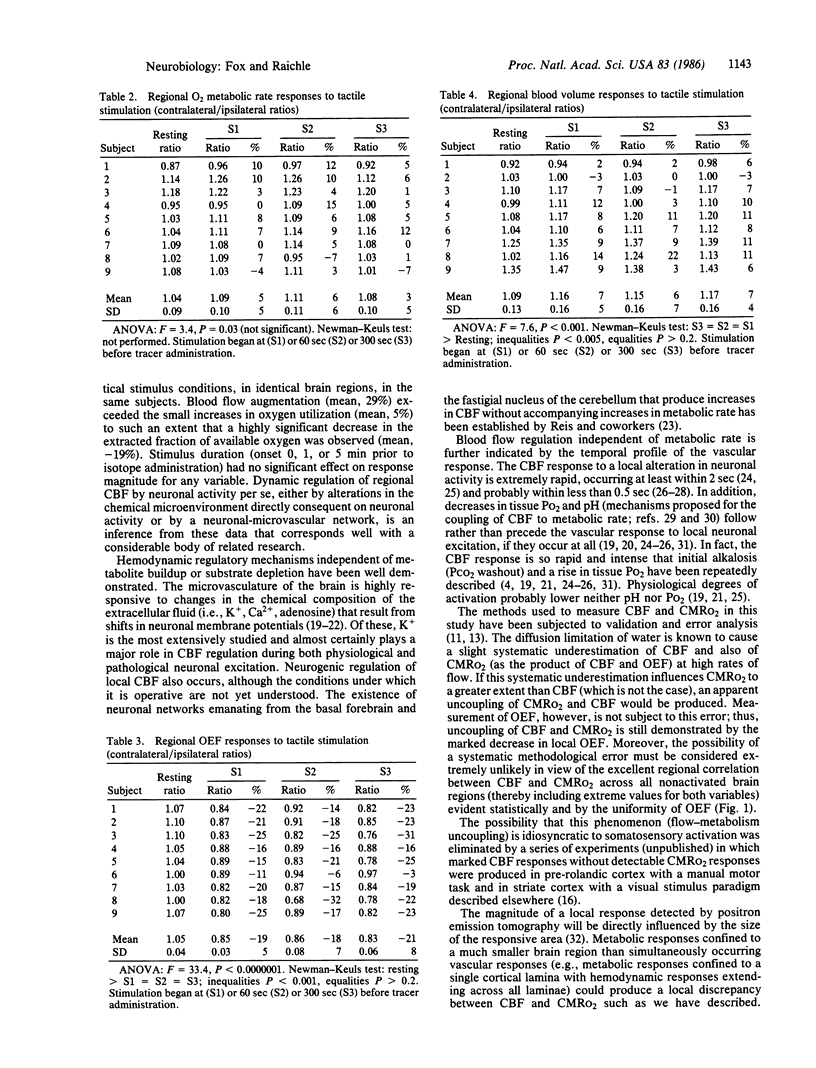
Coupling between cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) was studied using multiple sequential administrations of 15O-labeled radiotracers (half-life, 123 sec) and positron emission tomography. In the resting state an excellent correlation (mean r, 0.87) between CBF and CMRO2 was found when paired measurements of CBF and CMRO2 from multiple (30-48) brain regions were tested in each of 33 normal subjects. Regional uncoupling of CBF and CMRO2 was found, however, during neuronal activation induced by somatosensory stimulation. Stimulus-induced focal augmentation of cerebral blood flow (29% mean) far exceeded the concomitant local increase in tissue metabolic rate (mean, 5%), when resting-state and stimulated-state measurements were obtained in each of 9 subjects. Stimulus duration had no significant effect on response magnitude or on the degree of CBF-CMRO2 uncoupling observed. Dynamic, physiological regulation of CBF by a mechanism (neuronal or biochemical) dependent on neuronal firing per se, but independent of the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen, is hypothesized.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrup J., Heuser D., Lassen N. A., Nilsson B., Norberg K., Siesjö B. K. Evidence against H+ and K+ as main factors for the control of cerebral blood flow: a microelectrode study. Ciba Found Symp. 1978 Mar;(56):313–337. doi: 10.1002/9780470720370.ch16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J. C., Rougemont D., Soussaline F., Bustany P., Crouzel C., Bousser M. G., Comar D. Local interrelationships of cerebral oxygen consumption and glucose utilization in normal subjects and in ischemic stroke patients: a positron tomography study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Jun;4(2):140–149. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples L. A., Heeren T., Schatzkin A., Colton T. Multiple testing of hypotheses in comparing two groups. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jan;100(1):122–129. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-1-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Fox J. M., Raichle M. E., Burde R. M. The role of cerebral cortex in the generation of voluntary saccades: a positron emission tomographic study. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Aug;54(2):348–369. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.2.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Perlmutter J. S., Raichle M. E. A stereotactic method of anatomical localization for positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Jan-Feb;9(1):141–153. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198501000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Stimulus rate dependence of regional cerebral blood flow in human striate cortex, demonstrated by positron emission tomography. J Neurophysiol. 1984 May;51(5):1109–1120. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.5.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb R. L., Jr, Raichle M. E., Higgins C. S., Eichling J. O. Measurement of regional cerebral blood volume by emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1978 Oct;4(4):322–328. doi: 10.1002/ana.410040407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWICZ P., LARRABEE M. G. Oxidation of glucose in a mammalian sympathetic ganglion at rest and in activity. J Neurochem. 1962 Jan-Feb;9:1–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb07488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herscovitch P., Markham J., Raichle M. E. Brain blood flow measured with intravenous H2(15)O. I. Theory and error analysis. J Nucl Med. 1983 Sep;24(9):782–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN N. A. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in man. Physiol Rev. 1959 Apr;39(2):183–238. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leniger-Follert E., Hossmann K. A. Simultaneous measurements of microflow and evoked potentials in the somatomotor cortex of the cat brain during specific sensory activation. Pflugers Arch. 1979 May 15;380(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00582617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leniger-Follert E. Mechanisms of regulation of cerebral microflow during bicuculline-induced seizures in anaesthetized cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Jun;4(2):150–165. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbers D. W., Leniger-Follert E. Capillary flow in the brain cortex during changes in oxygen supply and state of activation. Ciba Found Symp. 1978 Mar;(56):21–47. doi: 10.1002/9780470720370.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintun M. A., Raichle M. E., Martin W. R., Herscovitch P. Brain oxygen utilization measured with O-15 radiotracers and positron emission tomography. J Nucl Med. 1984 Feb;25(2):177–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter J. S., Herscovitch P., Powers W. J., Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Standardized mean regional method for calculating global positron emission tomographic measurements. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Sep;5(3):476–480. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichle M. E., Grubb R. L., Jr, Gado M. H., Eichling J. O., Ter-Pogossian M. M. Correlation between regional cerebral blood flow and oxidative metabolism. In vivo studies in man. Arch Neurol. 1976 Aug;33(8):523–526. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500080001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichle M. E., Martin W. R., Herscovitch P., Mintun M. A., Markham J. Brain blood flow measured with intravenous H2(15)O. II. Implementation and validation. J Nucl Med. 1983 Sep;24(9):790–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandman C. A., O'Halloran J. P., Isenhart R. Is there an evoked vascular response? Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1355–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6729458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago T. V., Guerra E., Neubauer J. A., Edelman N. H. Correlation between ventilation and brain blood flow during sleep. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):497–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI111236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinhoj E. Regulation of cerebral blood flow as a single function of the interstitial pH in the brain. A hypothesis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1966;42(5):604–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L. Relationships among local functional activity, energy metabolism, and blood flow in the central nervous system. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2311–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ter-Pogossian M. M., Ficke D. C., Mintun M. A., Herscovitch P., Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Dynamic cerebral positron emission tomographic studies. Ann Neurol. 1984;15 (Suppl):S46–S47. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanics R., Leniger-Follert E., Lübbers D. W. Time course of changes of extracellular H+ and K+ activities during and after direct electrical stimulation of the brain cortex. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Dec 15;378(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00581957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]